-
(4) ❌ Incorrect — removing nucleotides from 3′ or 5′ ends is the function of exonucleases, not restriction endonucleases (which cut within the DNA at specific sequences)
UNIT-2 GENETICS AND EVOLUTION
CH5 – Molecular basis of Inheritance
2 Quizzes
CH6 – Evolution
2 Quizzes
UNIT-3 BIOLOGY IN HUMAN WELFARE
CH8 – Microbes in Human Welfare
2 Quizzes
UNIT-4 BIOTECHNOLOGY
Unit-5 ECOLOGY
CH11 – Organisms and Populations
2 Quizzes
CH12 – Ecosystem
2 Quizzes
CH13 – Biodiversity and Conservation
2 Quizzes
Biotechnology : Principles and Processes NCERT
Time limit: 0
Quiz Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Quiz complete. Results are being recorded.
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
1 point(s)Two core techniques that enabled birth of modern biotechnology are:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { A. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Techniques to alter the chemistry of genetic material, } \\
\text { to introduce these into host organisms and thus } \\
\text { change the phenotype of the host organism. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { B. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Maintenance of sterile ambience in chemical } \\
\text { engineering process to enable growth of only the } \\
\text { desired microbes/eukaryotic cell in large quantities } \\
\text { for the manufacture of biotechnological products. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
1 point(s)What is true regarding A, B and C in the given diagrammatic representation of rDNA technology ?
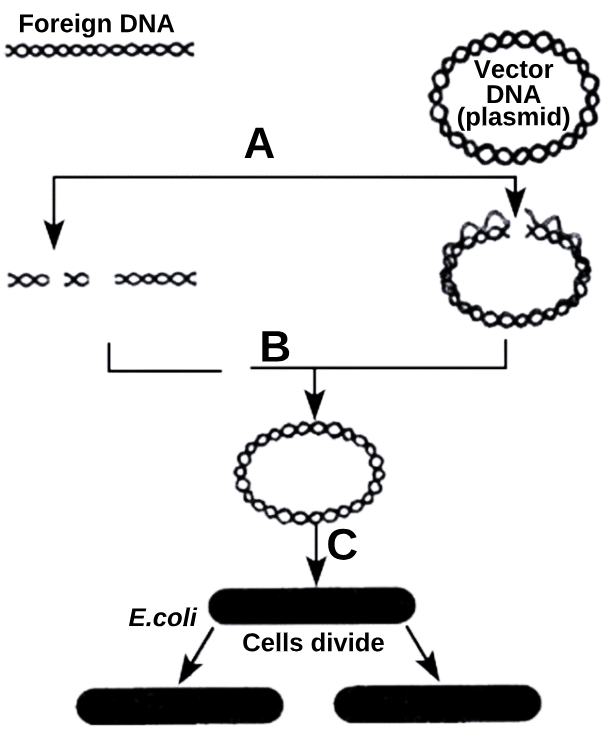
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I: } & \text { At A, same restriction enzyme is used to cut both foreign and vector DNA } \\
\hline \text { II: } & \text { The enzyme used at B is DNA ligase } \\
\hline \text { III: } & \text { Step C can be called as transformation } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
1 point(s)The European Federation of Biotechnology [EFB] defines biotechnology as :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
1 point(s)The construction of first rDNA emerged from the possibility of linking a gene encoding antibiotic resistance with a native plasmid of:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
1 point(s)The term ‘molecular scissors’ is used for :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
1 point(s)Identify the correct statements :
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { In the Cohen and Boyer experiment, the linking of } \\
\text { antibiotic resistance gene with a plasmid vector } \\
\text { became possible with the enzyme DNA ligase. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Recombinant DNA molecules are DNA molecules } \\
\text { formed by laboratory methods of genetic } \\
\text { recombination that bring together genetic material } \\
\text { from multiple sources, creating sequences that would } \\
\text { not otherwise be found in the genome. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
1 point(s)\(
A \text { and } B \text { in pBR322, shown in the diagram given below, respectively represent recognition sequences of: }
\)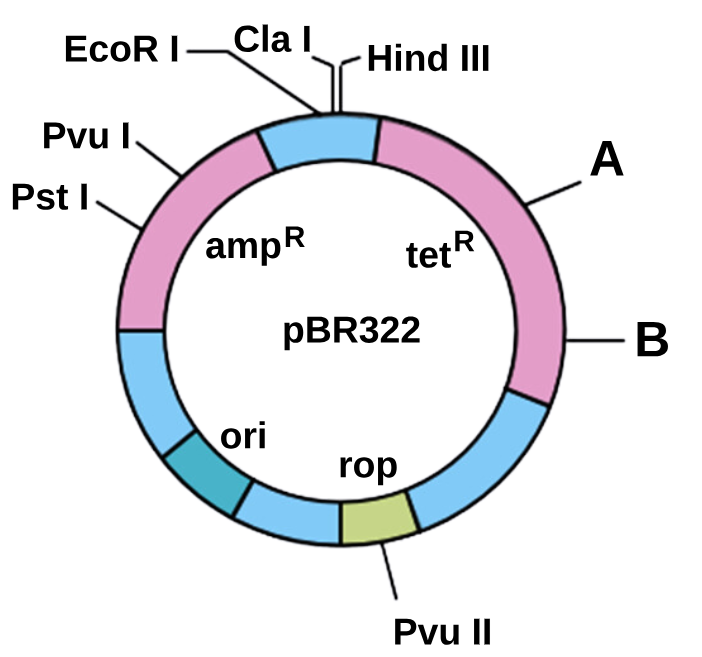 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
1 point(s)In recombinant DNA experiments, a vector :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
1 point(s)Identify the correct statements :
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Statement I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { In 1963, two enzymes responsible for } \\
\text { restricting the growth of bacteriophage in } \\
\text { E.coli were isolated. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Statement II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { In 1968, the first restriction endonuclease, } \\
\text { that always cut DNA molecules by } \\
\text { recognising a specific sequence six base } \\
\text { pairs, was isolated and characterised. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
1 point(s)The palindrome in DNA is a sequence of base pairs:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
1 point(s)Identify the incorrect statement regarding restriction endonucleases :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
They digest DNA by removing nucleotides from a free 3′ end.” ❌ Incorrect — that’s the function of exonucleases, not restriction endonucleases (which are endonucleases and cut within the DNA sequence).
-
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
1 point(s)The first type II restriction endonuclease whose functioning depended on a specific DNA nucleotide sequence was:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
1 point(s)DNA fragments digested by restriction endonucleases separate on agar gel electrophoresis according to their size because :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
1 point(s)Elution is :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
1 point(s)The ability of plasmids and bacteriophage DNA to replicate within bacterial cells :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
1 point(s)A cloning vector must :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
1 point(s)What is true about the steps of PCR shown in the diagram given below ?
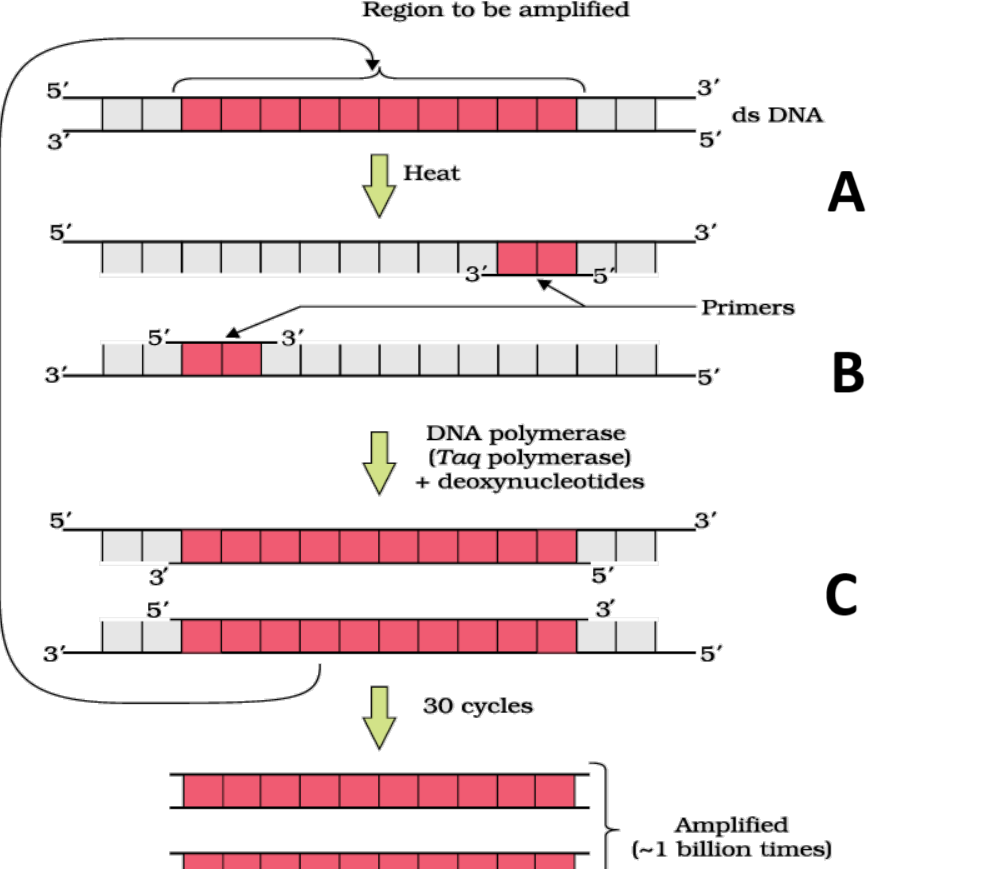
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I: } & \text { Step A occurs at the temperature of } 95-98^{\circ} \mathrm{C} \\
\hline \text { II: } & \text { Step B occurs at the temperature of } 55^{\circ} \mathrm{C} \\
\hline \text { III: } & \text { Step C occurs at the temperature of } 72^{\circ} \mathrm{C} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
1 point(s)The most important feature in a plasmid to serve as a vector in gene cloning experiment is :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
1 point(s)Some bacteria are resistant to antibiotics. This trait is normally due to :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
1 point(s)Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Assertion (A): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { In order to link the alien DNA, the } \\
\text { vector needs to have very few, preferably } \\
\text { single, recognition sites for the } \\
\text { commonly used restriction enzymes: }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Reason: (R): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Presence of more than one recognition } \\
\text { sites within the vector will generate } \\
\text { several fragments, which will complicate } \\
\text { the gene cloning. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
1 point(s)A cloning vector has two antibiotic resistance genes for tetracycline and ampicillin. A foreign DNA was inserted into the tetracycline gene. Non-recombinants transformants would survive on the medium containing:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
1 point(s)In agarose gel electrophoresis, the DNA fragments produced by restriction enzyme digestion
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
1 point(s)What is true for the plasmids used as cloning vectors in recombinant procedures ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
1 point(s)A donor DNA and plasmid vector DNA of E. coli are cut by EcoR I. The plasmid contains genes for resistance to ampicillin and tetracycline. The ECoR I recognition sequence lies within the gene for tetracycline resistance. Ligase is used and the recombinant DNA is produced. The plasmids are transferred to E.coli with the help of electroporation. Samples of the bacterial colonies are then grown in four different media: nutrient medium plus ampicillin, nutrient medium plus tetracycline, nutrient medium plus ampicillin and tetracycline, and nutrient medium without antibiotics. Non recombinant transformants will grow on:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
Let’s break it down carefully:
Plasmid: \(
\mathrm{Amp}^R
\) + \(
\operatorname{Tet}^R
\).EcoRI cuts inside \(
\operatorname{Tet}^R
\) gene.Recombinant → \(
\operatorname{Tet}^R
\) disrupted → \(
\mathrm{Amp}^R
\) intact.Non-recombinant → \(
\operatorname{Tet}^R
\) intact + \(
\mathrm{Amp}^R
\) intact.
Growth patterns:
Non-recombinant: resistant to both ampicillin and tetracycline → grows on:Nutrient + ampicillin ✅
Nutrient + tetracycline ✅
Nutrient + ampicillin + tetracycline ✅
Nutrient without antibiotics ✅
That means they grow on all four types of medium.
Correct answer: 4. on all four types of medium ✅ -
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
1 point(s)The bioreactor shown in the diagram is :
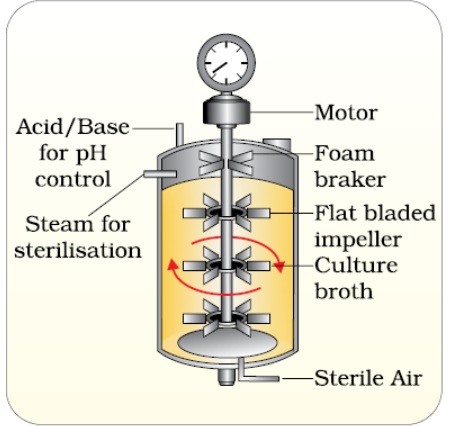 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
1 point(s)A host cell normally does not take up a foreign DNA until it has been made competent to do so. This is because :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
1 point(s)The number of correct statements regarding cloning vectors amongst the given statements is:
I. Bacteriophages because of their high number per cell, have very high copy numbers of their genome within the bacterial cells.
II. If one wants to recover many copies of the target DNA, it should be cloned in a vector whose origin supports high copy number.
III. A selectable marker helps in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and selectively permits the growth of the transformants.
IV. Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens has now been modified into a cloning vector which is no more pathogenic to the plants but is still able to use mechanisms to deliver genes of our interest into a variety of plants.
V. Retroviruses in animals have the ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells and hence can never be used as a cloning vector in rDNA procedures.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Retroviruses in animals have the ability to transform normal cells into cancerous cells and hence can never be used as a cloning vector in rDNA procedures.
❌ Incorrect — retroviruses can be modified to be non-oncogenic and are used in gene therapy. -
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
1 point(s)In microinjection, the rDNA :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
1 point(s)Primers used in PCR are :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
1 point(s)Consider the following statements :-
I: Asexual reproduction preserves genetic information while sexual reproduction permits variations.
II: Traditional hybridization often leads to the inclusion and multiplication of undesirable genes along with the desired genes.
III: rDNA technology allows us to isolate and introduce only one or a set of desirable genes without introducing undesirable genes in the target organism.Which of the above statements are true ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
1 point(s)The following palindrome is recognized by the restriction enzyme :
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
1 point(s)If we are able to link an alien piece of DNA with bacteriophage or plasmid DNA, we can multiply its number :
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following statements is incorrect with respect to gene transfer ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
❌ Incorrect — after heat shock at 42∘42^\circ42∘C, bacterial cells are placed on ice (not in chilled ethanol). Chilled ethanol is used in DNA precipitation, not transformation.
-
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
1 point(s)Which of the given statements is correct in the context of visualizing DNA molecules separated by agarose gel electrophoresis ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
1 point(s)The trait ‘resistance to certain antibiotics’ is seen in some bacteria due to the presence in them of :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
1 point(s)DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis are shown. Mark the correct statement :
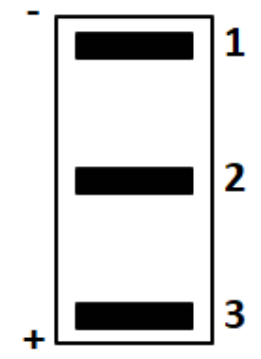 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Let’s break this down step-by-step.
-
In gel electrophoresis for DNA, the negatively charged DNA migrates toward the positive (+) electrode.
-
Smaller DNA fragments move faster and travel farther down the gel, so the bottom bands correspond to shorter fragments.
-
Larger DNA fragments move more slowly and remain near the top.
From the image:
-
Band 1 (top) → longest DNA fragment
-
Band 2 (middle) → intermediate length
-
Band 3 (bottom) → shortest fragment
-
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
1 point(s)How does the bacterium protects its own DNA from the action of restriction endonucleases present in its cytoplasm ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
The correct answer is 3 ✅
Bacteria protect their own DNA from their restriction endonucleases by methylating specific bases within the recognition sequences.
-
This is done by DNA methyltransferases.
-
Methylation prevents the restriction enzyme from binding and cutting the bacterial DNA, while any unmethylated foreign DNA (like phage DNA) gets cleaved.
-
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following is incorrect with respect to isolation of genetic material ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
(2) ❌ Incorrect — Alkaline phosphatase removes phosphate groups from DNA/RNA ends (used in cloning), not for removing RNA or proteins. For RNA removal, RNase is used; for protein removal, proteases are used.
-
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following is incorrect for the techniques of gel electrophoresis ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
(3) ❌ Incorrect — ethidium bromide bound to DNA fluoresces orange (not blue) under UV light.
-
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following statement is incorrect with respect to restriction enzyme ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
1 point(s)In agarose gel electrophoresis, DNA molecules are separated on the basis of their :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
1 point(s)In the above diagram showing a typical agaro gel electrophoresis :
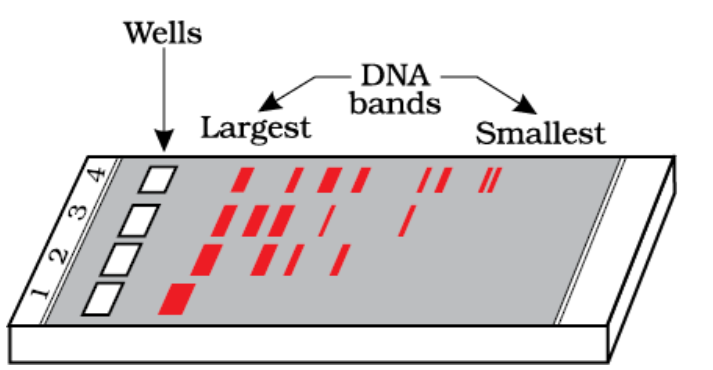 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
1 point(s)To isolate DNA in pure form from a bacterial cell, it should initially be treated with :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
1 point(s)Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Assertion (A): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { It is possible to select a bacterial cell } \\
\text { transformed with a recombinant DNA } \\
\text { bearing gene for an antibiotic resistance } \\
\text { if the transformed cells are spread on } \\
\text { agar plates containing the antibiotic. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Reason (R): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Due to insertional inactivation of the } \\
\text { gene for antibiotic resistance gene, only } \\
\text { the untransformed bacterial cells will } \\
\text { grow and the transformed bacterial cells } \\
\text { will die. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Assertion (A): True — Plating on an antibiotic selects transformants that carry an intact antibiotic-resistance gene (they survive; non-transformants die).
-
Reason (R): False — Insertional inactivation disrupts the resistance gene; such recombinants would not grow on that antibiotic. Hence R contradicts A and doesn’t explain it.
-
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
1 point(s)The underlying basis of the Polymerase Chain Rxn is:-
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
1 point(s)Following are the steps in the formation of recombinant DNA by action of a restriction endonuclease. Which one of the given option incorrectly identifies the steps, components labelled as A, B, C and D ?
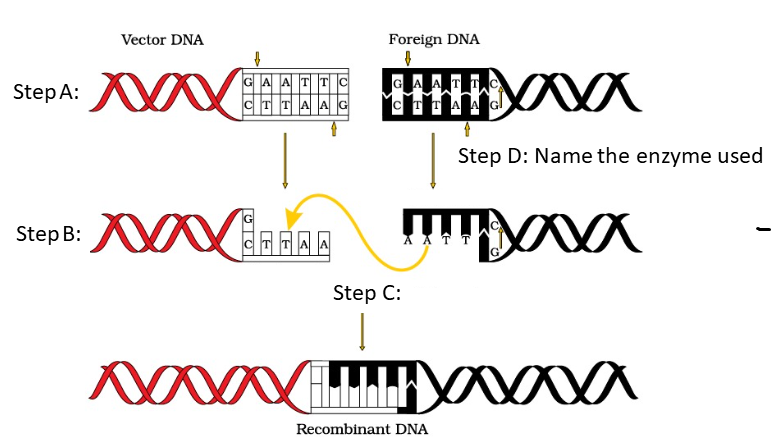 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
1 point(s)Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Assertion (A): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Bioreactors are important in } \\
\text { biotechnology procedures to obtain } \\
\text { desired products. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Reason (R): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Bioreactor provides the optimal } \\
\text { conditions for achieving the desired } \\
\text { product by providing optimum growth } \\
\text { conditions }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
1 point(s)The significance of the ‘heat shock‘ method in bacterial transformation is to facilitate:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following statements does not hold true for restriction enzyme ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
“It is isolated from viruses” ❌ Incorrect — they are isolated from bacteria, not viruses.
-
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
1 point(s)Identify (a) and (b) bioreactors respectively in the given diagram :
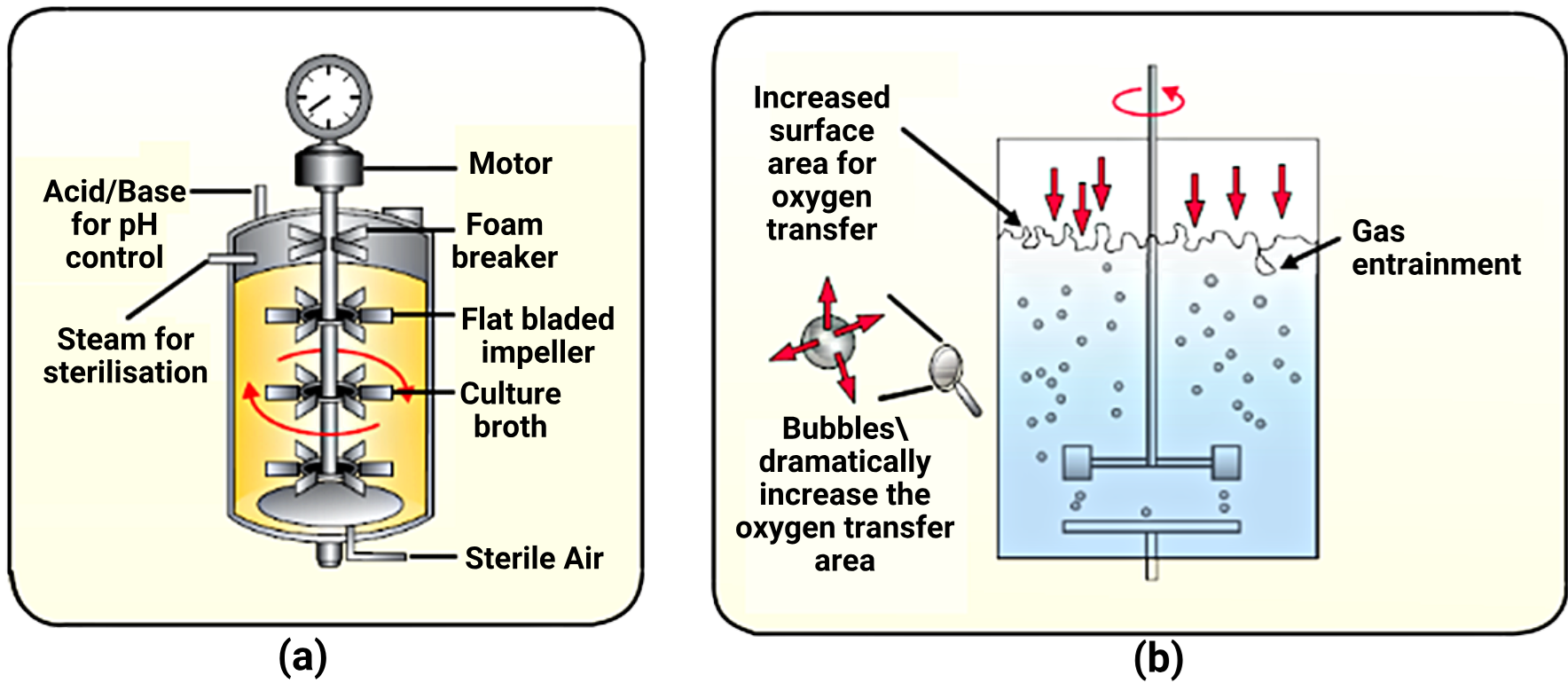 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)