Ecosystem NCERT
Quiz Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
1 point(s)The given figure shows pyramid of numbers in a grassland ecosystem. What will be be true for pyramid of numbers ?
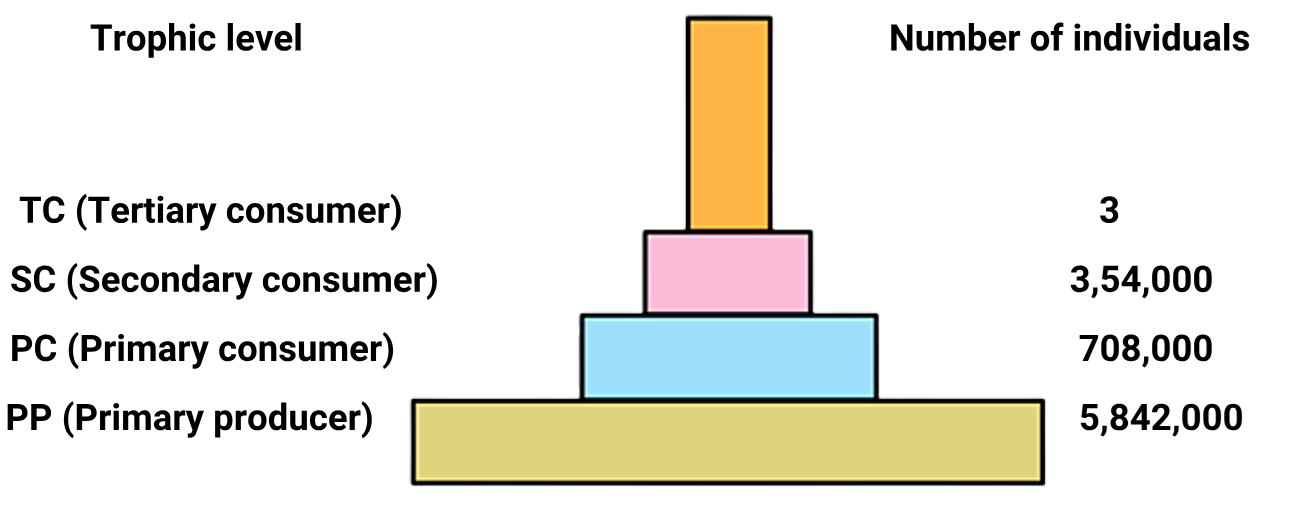
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { A pyramid of numbers shows graphically the } \\
\text { population, or abundance, in terms of the number of } \\
\text { individual organisms involved at each level in a food } \\
\text { chain. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { The pyramid shows the number of organisms in each } \\
\text { trophic level and it does not consider individual sizes } \\
\text { or biomass. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { III: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { It is not necessary that the pyramid is always } \\
\text { upright. For example, it will be inverted if beetles are } \\
\text { feeding from the output of forest trees, or parasites } \\
\text { are feeding on large host animals. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
1 point(s)Energy flow and nutrient cycling are two important components of an ecosystem. What will be true comparison of the two ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
1 point(s)Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels in an ecosystem is called :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
1 point(s)Productivity is the rate of production of biomass expressed in terms of :
i. \( \left(\mathrm{kcal} \mathrm{m}^{-3}\right) \mathrm{yr}^{-1} \)
ii. \( \mathrm{g} \mathrm{m}^{-2} \mathrm{yr}^{-1} \)
iii. \( \mathrm{g} \mathrm{m}^{-1} \mathrm{yr}^{-1} \)
iv. \( \left(\mathrm{kcal} \mathrm{m}^{-2}\right) \mathrm{yr}^{-1} \)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Perfect! ✅ That matches the conceptual reasoning:
-
Correct units for productivity are:
-
g m⁻² yr⁻¹ → mass of biomass produced per unit area per year (common in plants/ecosystem studies).
-
kcal m⁻² yr⁻¹ → energy equivalent per unit area per year.
-
-
So ii and iv are correct → Option 3 (c).
-
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
1 point(s)In an ecosystem, the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis is called as its :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
1 point(s)Net primary productivity is the gross primary productivity minus :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
1 point(s)Secondary productivity in an ecosystem can be defined as :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
1 point(s)The annual net primary productivity of whole biosphere is approximately:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
1 point(s)Humus:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
1 point(s)The given pyramid of biomass shows a sharp decrease in biomass at higher trophic levels. What can be the reason for this sharp decrease ?
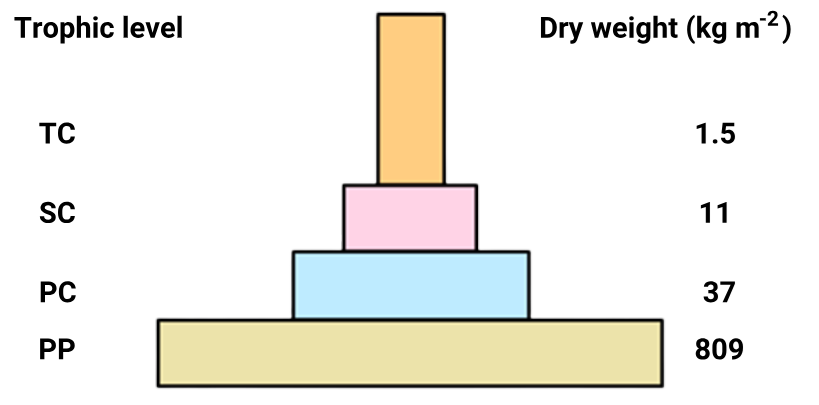
I: The respiration cost increases sharply along successive higher trophic levels.
II: There can be lower amounts of biomass at the bottom of the pyramid if the rate of primary production per unit biomass is high.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
1 point(s)By process of leaching during decomposition of detritus, water soluble :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
1 point(s)During decomposition of detritus, the step that is performed by bacteria and fungi includes :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
1 point(s)The process of mineralization by micro-organisms helps in the release of :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
1 point(s)Decomposition of detritus is rapid when :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
1 point(s)Among the following, where do you think the process of decomposition would be the fastest ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
1 point(s)What percentage of photosynthetic active radiation is captured by plants ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
1 point(s)Suppose in an area, the energy present in total incident sunlight falling on primary producers is \( 10,00,000 \mathrm{~J} \) and about \( 10,000 \mathrm{~J} \) is converted by them into biomass. What percent of PAR have the primary producers been able to convert?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
1 point(s)Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Assertion (A): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Some aquatic ecosystems have inverted } \\
\text { biomass pyramids. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Reason (R): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { The pyramid of energy is also inverted } \\
\text { in such ecosystems. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Reason (R): “The pyramid of energy is also inverted in such ecosystems.” ❌ False — pyramid of energy is always upright, even in aquatic ecosystems, because energy flow decreases at higher trophic levels.
-
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
1 point(s)The ecological pyramids that can never be inverted in a natural ecosystem include :
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I: } & \text { pyramid of numbers } \\
\hline \text { II: } & \text { pyramid of energy in any ecosystem } \\
\hline \text { III: } & \text { pyramid of biomass in the sea } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
I: Pyramid of numbers ❌ Can be inverted in some cases, e.g., a tree with many herbivores.
-
II: Pyramid of energy in any ecosystem ✅ Never inverted — energy decreases at each trophic level in all ecosystems.
-
III: Pyramid of biomass in the sea ❌ Can be inverted in aquatic ecosystems where small phytoplankton biomass supports large zooplankton biomass.
-
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
1 point(s)The figure shows an inverted pyramid of biomass. What will be true for such a pyramid ?
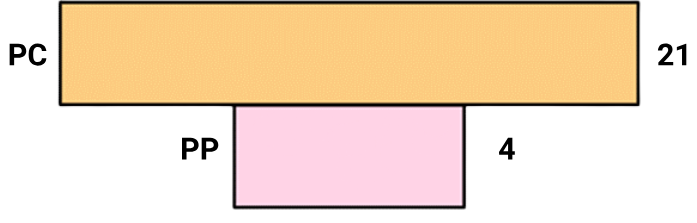
I: An example of such a pyramid will be the pyramid of biomass in a pond ecosystem, where the standing crop of phytoplankton, the major producers, at any given point will be lower than the mass of the heterotrophs.
II: The phytoplankton reproduce very quickly, but have much shorter individual lives.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
1 point(s)The three steps of decomposition occur :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
1 point(s)On the land, almost all primary production is performed by :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
1 point(s)Consider the two statements :
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Statement I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { No energy that is trapped into an organism } \\
\text { remains in it forever. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Statement II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { All animals depend on plants [directly or } \\
\text { indirectly] for their food requirements. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
1 point(s)Of the total solar radiation that falls on the leaves of the plants, about what percent is captured by them ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
1 point(s)Primary carnivores are, most aptly, characterized as:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
1 point(s)The detritus food chain :
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I: } & \text { begins with dead organic matter } \\
\hline \text { II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { is the major conduit of energy flow in aquatic } \\
\text { ecosystem. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
Statement II: “Is the major conduit of energy flow in aquatic ecosystems” ❌ Not entirely correct — in aquatic ecosystems, grazing (green) food chains often dominate energy flow; the detritus chain is important but not the major conduit.
-
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
1 point(s)In a terrestrial ecosystem, a much larger fraction of energy flows through the :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
1 point(s)Consider the following statements:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { In an aquatic ecosystem, GFC is the major conduit } \\
\text { for energy flow. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { In a terrestrial ecosystem, DFC is the major conduit } \\
\text { for energy flow. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { III: } & \text { GFC and DFC are not interconnected at any level. } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Which of the above statements are true ?CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
III: “GFC and DFC are not interconnected at any level.” ❌ Incorrect — GFC and DFC are interconnected, e.g., when organisms die or produce waste, energy flows into the DFC.
-
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
1 point(s)Each trophic level has a certain mass of living material at a particular time, best called as :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given two statements :
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { In most ecosystems, all the ecological pyramids are } \\
\text { largely upright. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Pyramid of energy can be a notable exception to the } \\
\text { above rule. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
II: “Pyramid of energy can be a notable exception to the above rule.” ❌ Incorrect — Pyramid of energy is always upright because energy flow decreases at higher trophic levels. Exceptions usually occur in pyramid of biomass, not energy.
-
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
1 point(s)Pyramid of numbers is :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
1 point(s)Secondary productivity refers to :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
1 point(s)Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Assertion (A): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Saprophytes play a vital role in the } \\
\text { ecosystem. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Reason (R): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Saprophytes are accorded the highest } \\
\text { trophic level in a food chain or a food } \\
\text { web. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Reason (R): “Saprophytes are accorded the highest trophic level in a food chain or a food web.” ❌ False — Saprophytes are not at the highest trophic level; they are decomposers and function outside the classic trophic levels, recycling matter.
-
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
1 point(s)Net primary productivity (NPP) is the biomass available to herbivores and decomposers. Which of the following is correct ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
1 point(s)Consider the two statements :
I: Food chains rarely extend for more than 4 or 5 levels. Consumers at each level convert, on an average, only
II: about \( 10 \% \) of the chemical energy in their food to their own organic tissue.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
1 point(s)Approximately, what percent of energy is transferred to each trophic level from the lower trophic level in an ecosystem ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
1 point(s)Standing crop is :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
1 point(s)Standing state refers to :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following is correct about primary productivity ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
1 point(s)Primary productivity of an ecosystem depends on :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
1 point(s)Q10. Match the following:
1. GPP – A. Biomass available to consumers
2. NPP – B. Total photosynthate including respiration
3. Secondary productivity – C. Rate of organic matter formation by consumers
4. Standing crop – D. Living biomass per unit area at a given timeCorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following is the correct sequence of decomposition ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
1 point(s)Humification leads to formation of :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
1 point(s)Which step of decomposition is correctly matched ?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
1 point(s)Decomposition is favoured under:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
1 point(s)Which is incorrect regarding humus ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
1 point(s)Mineralisation is :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
1 point(s)Which process during decomposition converts detritus into smaller particles ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
1 point(s)The rate of decomposition is slower when :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
1 point(s)Which is true for grazing food chain ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)