The Unit of Life TS
Quiz Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
Select the incorrect statement about submetacentric chromosomes
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
The incorrect statement about submetacentric chromosomes is (2) “Chromosomes have equal arms called p arm and q arm” because in submetacentric chromosomes, the arms are not equal, with one arm being slightly shorter than the other, making them heterobrachial; hence, option (2) is the incorrect statement.
-
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
Which of the following represents a typical plant cell?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
In summary, while sieve tube cells and tracheids are essential for plant function, they are specialized cells with structures adapted for specific roles, differing from the generalized structure of a typical plant cell. Therefore, the onion peel cell best represents a typical plant cell
-
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
The number of microtubule doublets and triplets in flagella and centriole are respectively
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
- Flagella: Eukaryotic flagella possess a characteristic microtubule arrangement known as the 9+2 structure. This means there are 9 outer doublet microtubules surrounding 2 central singlet microtubules. This configuration is crucial for the motility of flagella.
-
Centrioles: Centrioles are cylindrical structures composed of 9 sets of microtubule triplets, arranged in a radial symmetry. Each triplet consists of three microtubules: A, B, and C. This 9+0 arrangement is typical for centrioles.
Therefore, the number of microtubule doublets in flagella is 9, and the number of microtubule triplets in centrioles is 9. Thus, the correct pairing is 9 and 9
-
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
Cyanobacteria are not expected to have:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { 1. Chromatophores } & \text { 2. Nitrogenase } \\
\hline \text { 3. Flagella } & \text { 4. Gas vacuoles } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
Mannans, Xylans, Alginic acid and sultonated polysaccharides are seen in the cell walls of:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { 1. Algae } & \text { 2. Archaebacteria } \\
\hline \text { 3. Fungi } & \text { 4. Plants } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
Consider the given two statements:
I. Chloroplasts are considered endosymbiotic Cyanobacteria.
II. Cyanobacteria consist of free-living photosynthetic bacteria.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
Which of the following statements is true for a secretory cell?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Incorrect. The Golgi apparatus is present in secretory cells. It processes and packages proteins synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) for secretion.
2. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) is easily observed in the cell
-
Correct. Secretory cells, such as pancreatic acinar cells, have abundant RER due to their role in synthesizing proteins for secretion. The presence of ribosomes on the RER gives it a rough appearance, making it easily observable under a microscope.
3. Only Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) is present
-
Incorrect. While SER is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification, secretory cells primarily rely on RER for protein synthesis. Therefore, both RER and SER are present, but RER is more prominent in secretory cells.
4. Secretory granules are formed in nucleus
-
Incorrect. Secretory granules are not formed in the nucleus. They are formed in the Golgi apparatus, where proteins synthesized in the RER are packaged into vesicles for secretion
-
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
Consider the following two statements:
I. Secondary constrictions can be used as markers to identify the particular SAT chromosomes.
II. The secondary constrictions are always constant in their positions.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
The largest structures passed through the nuclear pores are:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
In a comparison of a typical bacterial cell and a typical human cell, which of the following would be higher for a bacterial cell?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
In the ultrastructure of cilia/ flagella, the radial spokes connect one of the tubules of each peripheral doublet to:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
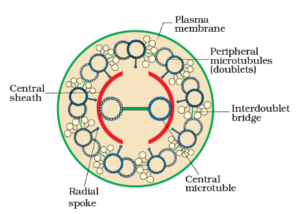
-
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
In a eukaryotic cell, the two organelles that can transform energy are:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
In eukaryotic cells, the two organelles that transform energy are:
-
Mitochondria – involved in cellular respiration (converting glucose into ATP)
-
Chloroplasts – involved in photosynthesis (converting light energy into chemical energy in plants)
These organelles are:
-
Semi-autonomous: They have their own DNA and ribosomes, and they can reproduce independently of the cell.
-
Bound by a double membrane: Not a single membrane.
-
Not part of the endomembrane system: They function independently of it.
-
Chloroplasts are present only in plant cells, but mitochondria are found in both plant and animal cells.
-
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
The space between the two nuclear membranes is called the perinuclear space and is continuous with the:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
The perinuclear space is the space between the inner and outer membranes of the nuclear envelope. This space is:
-
Continuous with the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) because the outer nuclear membrane is physically connected to the RER membrane.
Incorrect Options:
-
1. Nuclear pore complex: These are structures that regulate transport between the nucleus and cytoplasm but are not a space.
-
2. Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm surrounds the nucleus but is not the same as the perinuclear space.
-
4. Golgi lumen: The Golgi apparatus is a separate organelle and not directly continuous with the nuclear envelope.
-
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
Consider the given two statements:
I. Cytoplasmic streaming is more important in plant and algal cells than in animal cells
II. Plant and algae cells are generally larger than animal cellsCorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
In general, the functions of the vacuole include all except:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
Maintaining an alkaline internal pH – False: Vacuoles generally have an acidic pH, not alkaline, to help in degradation processes and maintaining ion balance.
-
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
Identify the correct order of organisation of genetic material from largest to smallest:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Mature sieve tube elements (in phloem tissue of plants) lack a nucleus and most organelles to facilitate efficient transport of sugars. They rely on companion cells for metabolic support.
-
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option :
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Column – I } & & \text { Column – II } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Smooth endoplasmic } \\
\text { reticulum }
\end{array} & \text { (i) } & \text { Protein synthesis } \\
\hline \text { (b) } & \text { Rough endoplasmic reticulum } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Lipid synthesis } \\
\hline \text { (c) } & \text { Golgi complex } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Glycosylation } \\
\hline \text { (d) } & \text { Centriole } & \text { (iv) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Spindle } \\
\text { formation }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { (a) } & \text { (b) } & \text { (c) } & \text { (d) } \\
\hline \text { 1. } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (i) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (iv) } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { (iii) } & \text { (i) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (iv) } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { (iv) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (i) } & \text { (iii) } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { (i) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (iv) } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
An elaborate network of filamentous proteinaceous structures present in the cytoplasm which helps in the maintenance of cell shape is called –
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
Consider the given two statements:
I. Several antibiotics (notably the penicillins and cephalosporins) stop bacterial infections by interfering with cell wall synthesis
II. Such antibiotics have no effects on human cells which have no cell wall, only a cell membraneCorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
The key concept missing is the mechanism of selective toxicity — why the antibiotic targets bacterial cells and why it doesn’t harm human cells. A complete explanation would involve:
-
Biochemical specificity: Penicillins and cephalosporins target specific bacterial enzymes (like transpeptidases, also known as penicillin-binding proteins) involved in the synthesis of peptidoglycan, a component unique to bacterial cell walls.
-
Absence in human cells: Human cells do not have peptidoglycan or those specific enzymes, so these antibiotics have nothing to act on in human cells.
-
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
The given diagram :

I. shows the diagrammatic representation of the ultrastructure of centriole
II. shows the 9+2 arrangement of the axonemal microtubules of cilia/flagellaCorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Its diagramatic structure of cilia and flagella from NCERT
-
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
Consider the two statements:
Statement I: Both the cilium and the flagellum emerge from centriole-like structure called the basal body.
Statement II: Basal body, centrioles, cilia and flagella have identical arrangement of microtubules in their ultrastructure.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
- Basal bodies, centrioles, cilia, and flagella all share a core structural similarity in their microtubule arrangement.
-
This structure is typically referred to as the “9+0” or “9+2” pattern of microtubules:
-
Centrioles and basal bodies have a “9+0” arrangement: 9 triplets of microtubules arranged in a circle, with no central pair.
-
Cilia and flagella have a “9+2” arrangement: 9 doublets in a ring with 2 single microtubules in the center.
-
-
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|c|c|l|}
\hline \text { } & \text { Column I } & \text { } & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { (A) } & \text { Chloroplasts } & \text { (i) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Colourless } \\
\text { plastids }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { (B) } & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Chromoplas } \\
\text { ts }
\end{array} & \text { (ii) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Yellow, orange or } \\
\text { red coloured } \\
\text { plastids }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { (C) } & \text { Leucoplasts } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Green plastids } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
The total length of DNA molecules of 46 chromosomes in a human cell is about ……… whereas a typical cell is 10 m in length
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
Both the nuclear membranes are separated by ________ in perinuclear space.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
CorrectIncorrect