Plant Growth and Development TS
Quiz Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
1 point(s)All the following contribute to an increase in girth of dicots and gymnosperms except:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { 1. Apical meristem } & \text { 2. Lateral meristems } \\
\hline \text { 3. Vascular cambium } & \text { 4. Cork-cambium } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
1 point(s)The shape of the growth curve characteristic of a living organism growing in natural environment is:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
1 point(s)Plants follow different pathways in response to environment or phases of life to form different kinds of structures. This ability is called:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
1 point(s)Identify the plant growth regulator that, though is largely an inhibitor but, can be placed in both plant growth promoter and plant growth inhibitor groups?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
1 point(s)Callus from internodal segments of tobacco stem gets proliferated only if in addition to one of the following – extracts of vascular tissues, yeast extract, coconut milk or DNA, the nutrient medium also contains:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
1 point(s)\(
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Auxin was first isolated from: }\\
&\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { 1. Coconut milk } & \text { 2. Barley endosperm } \\
\hline \text { 3. Oat coleoptiles } & \text { 4. Human urine } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{aligned}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
1 point(s)Auxin does not:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
Ethylene is the hormone that promotes the formation of female flowers in cucumbers.
-
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
1 point(s)To extend their market period, fruits can be left on trees longer by the application of:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
1 point(s)\(
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Kinetin was first discovered from: }\\
&\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { 1. Herring sperm DNA } & \text { 2. Coconut milk } \\
\hline \text { 3. Yeast extract } & \text { 4. Corn kernels } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{aligned}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
1 point(s)Cytokinins do not help in:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
1 point(s)Cytokinins help in delay of leaf senescence because they:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
1 point(s)Normally, when the seeds are mature, ethylene production increases and builds-up within the fruit, resulting in a climactic event that means:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
1 point(s)Which PGR is used to initiate flowering and for synchronizing fruit set in pineapple?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
1 point(s)How does pruning help in making the hedge dense?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following is not an inhibitory substance governing seed dormancy?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
1 point(s)Which PGR stimulates the closure of stomata in the epidermis and increases the tolerance of plants to various kinds of stress?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
1 point(s)Cell elongation in internodal regions of the green plants takes place due to :-
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
1 point(s)Cytokinins
a. Stimulate lateral shoot growth
b. Help in mobilization of nutrients
c. Inhibit cell division
d. Delay senescenceCorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
Inhibit cell division ❌
(This is incorrect — cytokinins actually promote cell division.) -
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
1 point(s)In most situations, which PGR acts as an antagonist to GAs?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
1 point(s)To promote stem elongation, gibberellins act in concert with:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
1 point(s)The given figure shows the effects of increasing concentration of a certain PGR on the growth of seven-day-old dark-grown pea seedlings. The effects include a decrease in epicotyl elongation, a thickening of the shoot and a change in orientation of growth from vertical to horizontal. Which PGR would be responsible for these effects?
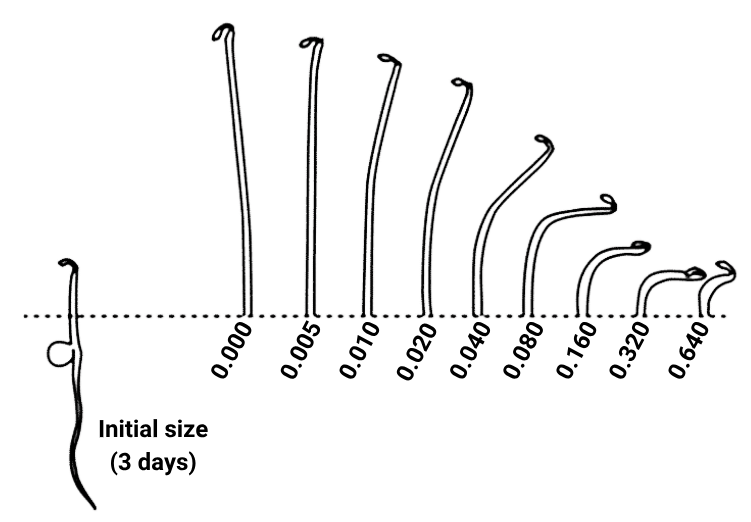 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
1 point(s)All the following statements regarding cytokinins are true except:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Statement 3: Kinetin occurs widely in almost all plants.
❌ Incorrect. While kinetin was initially considered a synthetic compound, subsequent studies have detected its presence in various organisms, including plants. However, its occurrence is not widespread across all plant species, and it is not as prevalent as other natural cytokinins like zeatin.
-
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
1 point(s)Which gaseous PGR is synthesised in large amounts by tissues undergoing senescence and ripening fruits?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following is not a function of the PGR ethylene?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
Horizontal growth of seedlings not vertical
-
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
1 point(s)Ethylene does not:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Ethylene actually promotes abscission (the shedding) of flowers and fruits in cotton, cherry, and walnut
-
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
1 point(s)PGR causing the closure of stomata in response to water stress is:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
1 point(s)When compared to their normal sized counterparts, the dwarf mutant varieties of a plant generally produce less:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
Explanation:
-
Dwarf mutant varieties of plants often have a genetic defect that results in:
-
Reduced synthesis of gibberellins or
-
Impaired response to gibberellins.
-
-
Gibberellins (GAs) are essential plant hormones that promote:
-
Stem elongation,
-
Seed germination,
-
Flowering, and
-
Fruit development.
-
-
When gibberellins are deficient or not perceived properly, the plant exhibits dwarfism due to inhibited cell elongation and division
-
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
1 point(s)Plant growth is generally indeterminate because of:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
1 point(s)One of the synthetic auxin is:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
1 point(s)Parthenocarpy in tomato plants can be induced by:
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
1 point(s)Select the odd one out w.r.t. developmental heterophylly.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
1 point(s)The ‘bakanae’ (foolish seedling) disease of rice
seedlings led to the discovery of which of the following
plant growth regulators?CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
1 point(s)In the equation of arithmetic growth \(
L_t=L_0+r t,{ }^{\prime} r \text { ‘ }
\)
representsCorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
1 point(s)Abscisic acid is also called:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
1 point(s)Hormones which are essential in tissue culture for promoting root and shoot development respectively in callus are:-
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following statements is incorrect ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Abscisic acid (ABA) is often called a “stress hormone” because it plays a role in responses to adverse conditions like drought, cold, and high salt. It slows down or inhibits growth, promotes stomatal closure to conserve water, and initiates bud dormancy. While some growth may be slowed down under stressful conditions, ABA’s primary function is not to promote overall growth.
-
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
1 point(s)By the application of which plant hormone, stem elongation can be induced in “rossette plants”?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
1 point(s)Who has discovered and confirmed that release of a volatile substance from ripened oranges hastened the ripening of unripe banana kept with it ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
1 point(s)Read the given statements and choose the correct option regarding plant growth.
A. Increased vacuolation, cell enlargement and new cell wall deposition are characteristics of cells
in elongation phase.
B. Cells of maturation zone attain maximal size in terms of wall thickening and protoplasmic
modifications.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following PGRs is known as fruit ripening hormone ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following is correct w.r.t. auxins?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
1 point(s)Auxins and cytokinins act antagonistically w.r.t.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following plant growth regulators is mainly involved in growth inhibiting activities ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
1 point(s)Which among the following is not the characteristic of cells in meristematic phase of growth ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
Explanation: Meristematic cells are actively dividing cells with dense cytoplasm, large nuclei, and abundant plasmodesmatal connections, but they lack significant vacuolation as they are primarily focused on producing new cells rather than storing materials in vacuoles. -
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
1 point(s)Ethylene can be used in all, except
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
1 point(s)Precursor of auxins is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
1 point(s)Identify the following statements and state true (T)
or false (F) and choose the correct option.
A. Single maize root apical meristem can give rise
to more than 17,500 new cells per hour.
B. Cells in a watermelon may increase in size of
the cell by upto 3,50,000 times.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following pair of hormones promote flowering in pineapple
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
1 point(s)Hormone responsible for Climacteric effect is —
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
1 point(s)Which phytohormone is synthesized by the tissues of senescing organs?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
The correct answer is: (B) Ethylene
Explanation:
Ethylene is a gaseous phytohormone that is synthesized in large amounts by senescing tissues and ripening fruits. It plays a crucial role in:
-
Promoting senescence (aging) of leaves and flowers
-
Accelerating fruit ripening
-
Inducing abscission (shedding of leaves, flowers, and fruits)