Excretory Products and their Elimination NCERT
Quiz Summary
0 of 45 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 45 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 45
1. Question
1 point(s)Urea in humans is synthesized in:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 2 of 45
2. Question
1 point(s)The most toxic nitrogenous metabolic waste product is:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 3 of 45
3. Question
1 point(s)All the following animals are uricotelic except:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 4 of 45
4. Question
1 point(s)Protonephridia are the excretory structures in all the following except:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 5 of 45
5. Question
1 point(s)Match each item in Column I with one in Column II and select the correct match from the codes given:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline
\textbf{Column I (Organism)} & \textbf{Column II (Osmoregulatory and excretory structure)} \\
\hline
\text{A. Flatworms, rotifers, Amphioxus} & \text{P. Protonephridia} \\
\text{B. Earthworm} & \text{Q. Nephridia} \\
\text{C. Insects} & \text{R. Malpighian tubule} \\
\text{D. Prawn} & \text{S. Green gland or antennal gland} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Codes:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { P } & \text { Q } & \text { R } & \text { S } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { Q } & \text { R } & \text { S } & \text { P } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { R } & \text { S } & \text { P } & \text { Q } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { S } & \text { P } & \text { Q } & \text { R } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 6 of 45
6. Question
1 point(s)In majority of the nephrons, the loop of Henle:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 7 of 45
7. Question
1 point(s)Juxtamedullary nephrons:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 8 of 45
8. Question
1 point(s)The location of kidneys in humans can be best described as:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 9 of 45
9. Question
1 point(s)Extension of renal cortex between the medullary pyramids is called as:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 10 of 45
10. Question
1 point(s)Figure shows human urinary system with structures labelled A to D. Select option which correctly identifies them and gives their characteristics and / or functions.
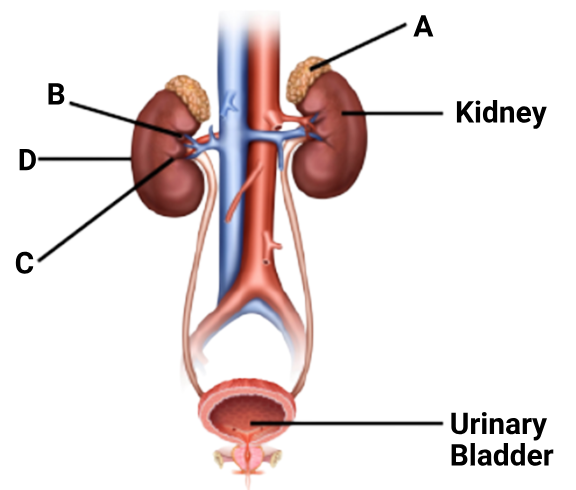 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
- A → Adrenal gland (sits on top of the kidney
- B → Renal pelvis (central collecting region inside the kidney)
- C → Medulla (inner region of the kidney)
- D → Cortex (outer region of the kidney)
- B – Pelvis
❌ “Broad funnel-shaped space inner to hilum, directly connected to loops of Henle.”-
✅ The pelvis is funnel-shaped and located inside the hilum.
-
❌ But it is not directly connected to loops of Henle.
➤ Loops of Henle connect to collecting ducts, which drain into the pelvis.
✅✅ This incorrect connection invalidates the statement.2.C – Medulla
❌ “Inner zone of kidney and contains complex nephrons.”
-
-
✅ Medulla is the inner zone.
-
⚠️ However, saying it contains “complex nephrons” is vague and imprecise.
➤ Nephrons span both cortex and medulla.
➤ Parts like loops of Henle and collecting ducts extend into the medulla, but the nephron as a whole is not confined to medulla.
-
-
D – Cortex
❌ “Outer part of kidney and does not contain any part of nephrons.”-
❌ This is factually incorrect.
➤ The cortex contains Bowman’s capsule, PCT, DCT — all are parts of nephrons.
-
4.A – Adrenal gland
✅ “Located at the anterior part of kidney; secretes catecholamines which stimulate glycogen breakdown.”
-
-
⚠️ Though technically the adrenal gland is located on the superior (top) part of the kidney (not anterior),
-
✅ Functionally: adrenal gland secretes catecholamines (adrenaline & noradrenaline) → cause glycogenolysis (glycogen breakdown).
-
-
Question 11 of 45
11. Question
1 point(s)All of the following regarding juxtamedullary nephrons in human kidneys are correct except:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
1. “The entire nephron is located in the superficial cortex of the kidney”
❌ Incorrect – This is the false statement.
-
Juxtamedullary nephrons are located near the medulla (not superficial cortex).
-
Their loops of Henle extend deep into the medulla, which allows them to concentrate urine efficiently.
-
Question 12 of 45
12. Question
1 point(s)Given figure shows a sagittal section of human kidney. Identify A, B, C and D :
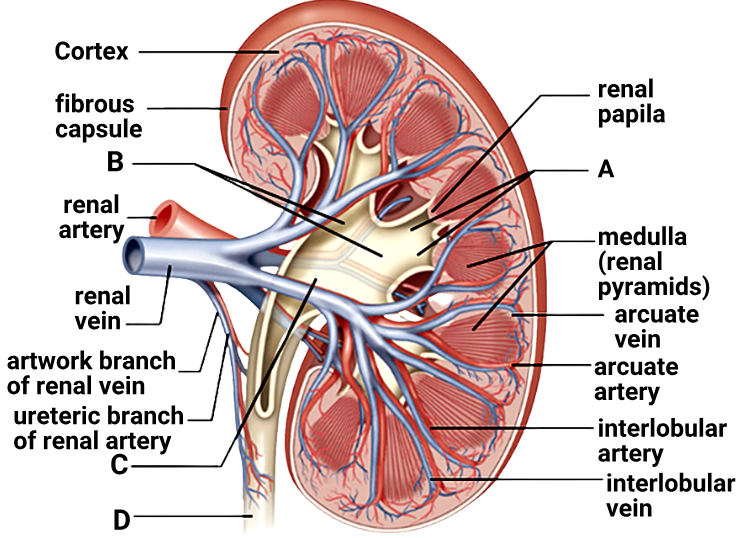
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline \text { 1. } & \text { Minor calyx } & \text { Major calyx } & \text { Renal pelvis } & \text { Urethra } \\
\hline \text { 2. } & \text { Major calyx } & \text { Minor calyx } & \text { Renal pelvis } & \text { Ureter } \\
\hline \text { 3. } & \text { Minor calyx } & \text { Major calyx } & \text { Renal pelvis } & \text { Ureter } \\
\hline \text { 4. } & \text { Minor calyx } & \text { Major calyx } & \text { Renal pectoral } & \text { Urethra } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 13 of 45
13. Question
1 point(s)Identify the correct statements:
I: Each kidney of an adult human measures \( 10-12 \mathrm{~cm}\) in length, \(5-7 \mathrm{~cm}\) in width and \(2-3 \mathrm{~cm}\) in thickness.
II. The DCTs of many nephrons open into a straight tube called collecting duct.
III. Each nephron has two parts – the glomerulus and the renal tubule.
IV. The renal tubule begins with the proximal convoluted tubule.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
Statement IV:
“The renal tubule begins with the proximal convoluted tubule.”
❌ Incorrect — The renal tubule actually begins with Bowman’s capsule, which encloses the glomerulus. The PCT follows after that. -
Question 14 of 45
14. Question
1 point(s)The functions of human kidneys include:
I: Formation of urine
II: Regulation of erythropoiesis
III: Regulation of calcium levels in body fluidsCorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 15 of 45
15. Question
1 point(s)Consider the two statements:
I. The process of filtration at Malpighian body is regarded as ultrafiltration.
II. Blood is filtered so finely that all constituents of plasma pass into the lumen of Bowman’s capsule.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Statement II:
“Blood is filtered so finely that all constituents of plasma pass into the lumen of Bowman’s capsule.”
❌ Incorrect — While most components of plasma (like water, glucose, amino acids, urea, salts, etc.) do filter into Bowman’s capsule, plasma proteins and blood cells do not, due to their large size. So not all plasma constituents are filtered. -
Question 16 of 45
16. Question
1 point(s)Where do you expect to find podocytes?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 17 of 45
17. Question
1 point(s)The reabsorption, from the filtrate, of sodium, glucose and amino acids:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 18 of 45
18. Question
1 point(s)Filtration slits in the glomerular membrane are formed by:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 19 of 45
19. Question
1 point(s)Identify the correctly matched rows regarding A-F in the given figure:
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 20 of 45
20. Question
1 point(s)About what percent of the glomerular ultrafiltrate is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 21 of 45
21. Question
1 point(s)JGA is a special sensitive region formed by cellular modifications in the:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 22 of 45
22. Question
1 point(s)Identify the incorrectly matched pair [assume normal physiological conditions]:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
Amount of urea produced – 25 to \( 30 \mathrm{gm} /\) day
-
Question 23 of 45
23. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given two statements:
I: Vasa recta is absent or highly reduced in cortical nephrons.
II: Efferent arteriole forms a peritubular capillary network around renal tubules.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 24 of 45
24. Question
1 point(s)Identify the incorrect statement regarding proximal convoluted tubule:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
In juxtamedullary nephrons, it extends deep into the renal medulla
❌ Incorrect. As previously mentioned, the PCT remains within the renal cortex in all nephrons. It is the loop of Henle that extends into the medulla, especially in juxtamedullary nephrons -
Question 25 of 45
25. Question
1 point(s)The proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron is lined by:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 26 of 45
26. Question
1 point(s)As the filtrate passes upward in the ascending limb of loop of Henle:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 27 of 45
27. Question
1 point(s)Collecting duct does not:
I: allow reabsorption of large amount of water during concentration of urine.
II. allow passage of small amounts of urea into medullary interstitium to keep up the osmolarity.
III. play a role in the maintenance of pH and ionic balance of blood by the selective secretion of \( \mathrm{H}^{+} and \mathrm{\,K}^{+} \) ions.CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
Given all statements are correct with respect to collecting duct
-
Question 28 of 45
28. Question
1 point(s)Refer the given figure of nephron.
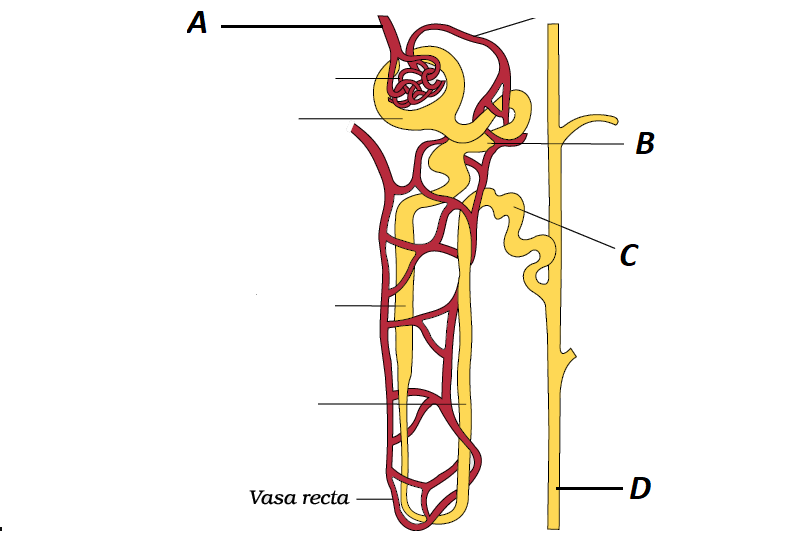
Identify \( \mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}, \mathrm{C}\) and D and select the correct option regarding them
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
Based on the information provided, the correct answer is:
1. A – A tuft of capillaries formed by afferent arteriole.
Explanation:
-
A – Glomerulus: This is a network of capillaries formed by the afferent arteriole. It is responsible for the filtration of blood in the nephron.
-
B – Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT): The PCT plays a significant role in the reabsorption of bicarbonate ions and the selective secretion of hydrogen and potassium ions, contributing to the maintenance of pH and electrolyte balance in the body.
-
C – Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT): While the DCT is involved in the selective reabsorption and secretion of ions, the statement that “almost all glucose, amino acids, water, Na⁺, K⁺, and uric acid are absorbed here” is inaccurate. The majority of these substances are reabsorbed in the PCT.
-
D – Collecting Duct: The collecting duct extends from the cortex of the kidney to the inner parts of the medulla. It is primarily involved in the reabsorption of water, especially under the influence of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), rather than the secretion of large amounts of water.
Therefore, option 1 correctly identifies the glomerulus as a tuft of capillaries formed by the afferent arteriole.
-
Question 29 of 45
29. Question
1 point(s)During concentration of urine, NaCl is returned to medullary interstitium by:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 30 of 45
30. Question
1 point(s)During the counter current mechanism, small amount of urea from interstitium enters:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 31 of 45
31. Question
1 point(s)The increasing gradient of osmolarity in medullary interstitium, during concentration of urine, is mainly caused by reabsortion of:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 32 of 45
32. Question
1 point(s)The osmolarity of interstitial fluid in renal cortex of vertebrates is about ______ mOsm per litre, which can be increased to about ______ mOsm per litre in the inner medulla during concentration of urine by the kidneys.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 33 of 45
33. Question
1 point(s)An excessive loss of body fluid can:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 34 of 45
34. Question
1 point(s)The figure shows a diagrammatic representation of a nephron and vasa recta showing counter current mechanisms. Identify the correct statements:
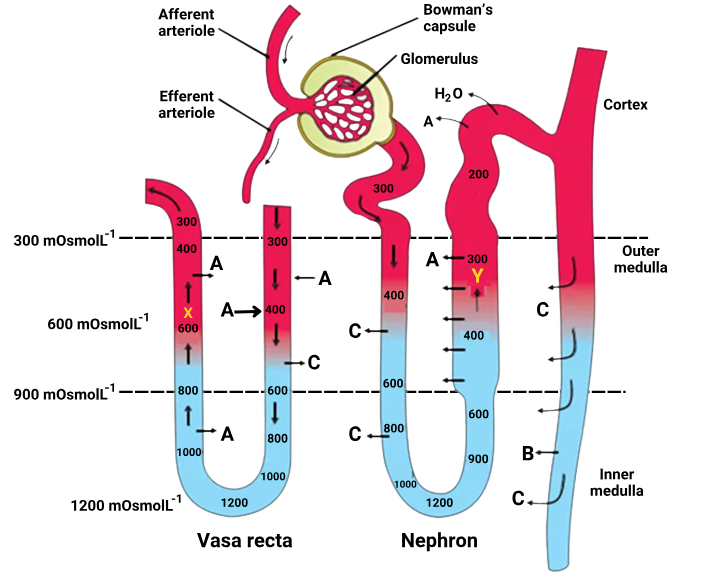
I: A is NaCl which is transported by the ascending limb of Henle’s loop, exchanged with the ascending limb of vasa recta and returned to the interstitium by the descending portion of vasa recta.
II: B is urea which enters the thin segment of the ascending limb of Henle’s loop and is transported back to the interstitium by the collecting tubule.
III:C is water.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
In the Diagram:
-
A (Marked in both nephron & vasa recta): This corresponds to NaCl (salt) movement.
-
B: Located in the collecting duct in the inner medulla, represents urea.
-
C: Corresponds to water, moving in and out due to osmotic gradients.
Statement I is also incorrect
-
-
NaCl is actively transported out of the ascending limb of Henle’s loop (which is impermeable to water).
-
In the vasa recta, NaCl enters the descending limb and leaves from the ascending limb, helping maintain medullary osmolarity.
-
-
However, the statement says NaCl is returned to the interstitium by the descending portion of vasa recta, which is incorrect. It’s the ascending limb of vasa recta that returns NaCl to the interstitium.
-
Question 35 of 45
35. Question
1 point(s)JG cells can be activated to release renin by all the following except:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 36 of 45
36. Question
1 point(s)Identify the incorrect statement regarding GFR:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
2. The GFR increases during sympathetic stimulation due to the vasodilation of afferent arterioles.
❌ Incorrect.
Sympathetic stimulation causes vasoconstriction of the afferent arterioles, reducing GFR — not increasing it.
This is a protective mechanism during stress, shock, or blood loss to conserve fluid. -
Question 37 of 45
37. Question
1 point(s)The given diagram shows the schematic functioning of the Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System in the regulation of kidney function. Identify A, B, C and D:
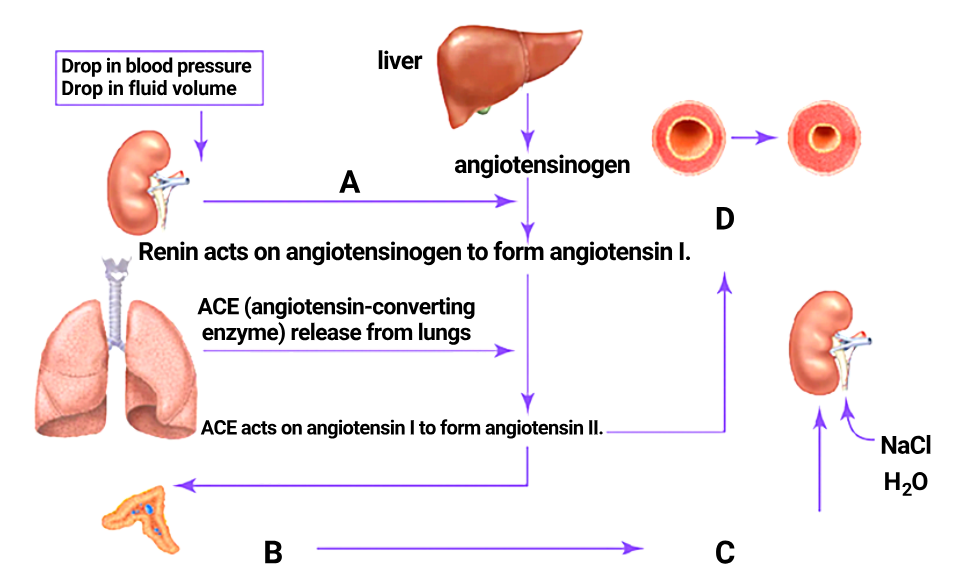
\[
\begin{array}{|c|l|l|l|l|}
\hline
\textbf{} & \textbf{A} & \textbf{B} & \textbf{C} & \textbf{D} \\
\hline
1. & \text{Renin released from kidney} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Angiotensin II stimulates adrenal} \\
\text{medulla to secrete aldosterone}
\end{array} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Reabsorption of sodium} \\
\text{and water}
\end{array} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Vaso-} \\
\text{dilation}
\end{array} \\
\hline
2. & \text{Renin released from kidney} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Angiotensin II stimulates adrenal} \\
\text{cortex to secrete aldosterone}
\end{array} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Reabsorption of sodium} \\
\text{and water}
\end{array} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Vaso-} \\
\text{constriction}
\end{array} \\
\hline
3. & \text{ADH released from kidney} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Angiotensin II stimulates adrenal} \\
\text{cortex to secrete aldosterone}
\end{array} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Diuresis}
\end{array} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Vaso-} \\
\text{constriction}
\end{array} \\
\hline
4. & \text{Angiotensin I released from kidney} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Angiotensin II stimulates adrenal} \\
\text{cortex to secrete aldosterone}
\end{array} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Reabsorption of sodium} \\
\text{and water}
\end{array} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Vaso-} \\
\text{dilation}
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 38 of 45
38. Question
1 point(s)Urination will be caused by simultaneous:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 39 of 45
39. Question
1 point(s)Accessory excretory organs and their waste materials are given below. Find out the incorrect pair
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 40 of 45
40. Question
1 point(s)Given below is a diagram showing the functioning of the micturition reflex in humans. Identify the correct statements:
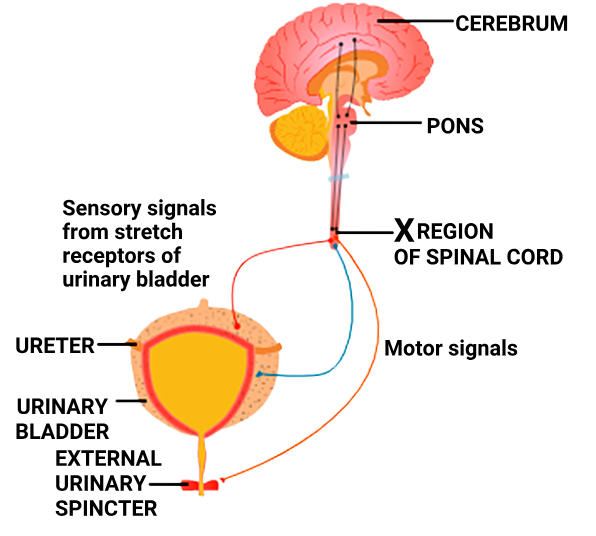
I: The region designated as ‘ \( X \) ‘ in the diagram is the sacral region of the spinal cord.
II: Motor signals from the spinal cord lead to relaxation of the muscle in the wall of the urinary bladder and constriction of the urinary sphincter.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
Statement I:
“The region designated as ‘X’ in the diagram is the sacral region of the spinal cord.”
✅ Correct.-
The sacral spinal cord (S2–S4) is responsible for the micturition reflex.
-
Sensory signals from bladder stretch receptors go to this region.
-
It sends parasympathetic motor output to contract the detrusor muscle (bladder wall) and relax the internal sphincter.
Statement II:
“Motor signals from the spinal cord lead to relaxation of the muscle in the wall of the urinary bladder and constriction of the urinary sphincter.”
❌ Incorrect.-
This reverses the actual physiological response.
-
Motor signals from the sacral region cause:
-
Contraction of the detrusor (bladder wall) muscle, and
-
Relaxation of the internal urinary sphincter
➝ These actions promote urination, not inhibit it.
-
-
Question 41 of 45
41. Question
1 point(s)Statement A : Dialysis fluid contains all the constituents as in plasma except nitrogenous wastes
Statement B : In dialysis all the steps of urine formation i.e. ultrafiltration, reabsorption and secretion
are performed simultaneouslyCorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Statement A is correct: Dialysis fluid mimics plasma but excludes nitrogenous wastes to allow diffusion out of the blood.
-
Statement B is incorrect: Dialysis does not replicate all three steps of urine formation — it mainly works by diffusion and ultrafiltration, but no active secretion or reabsorption as in nephrons.
-
Question 42 of 45
42. Question
1 point(s)During hemodialysis:
I: Cellophane tube in a dialysing unit acts as artificial
II: Heparin is added to the blood before it is passed on to kidney. the dialysing unit.
III: The cleared blood is pumped back to the body through a vein after adding anti-heparin to it.CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
All are correct
-
Question 43 of 45
43. Question
1 point(s)Most renal calculi are:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 44 of 45
44. Question
1 point(s)Uremia patients can have all the following except:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 45 of 45
45. Question
1 point(s)Identify the statements as true (T) or false (F)
I. Excess of urea in urine is called uremia
II. Inflammation of glomeruli of kidney is called glomerulonephritis
III. Counter current mechanism in mammals is essential to concentrate urine
IV. Reabsorption of \( \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \) at PCT is under the influence of ADH\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { I } & \text { II } & \text { III } & \text { IV } \\
\hline(1) & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~T} \\
\hline(2) & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~F} \\
\hline(3) & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} \\
\hline(4) & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~F} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)