Neural Control and Coordination NCERT
Quiz Summary
0 of 45 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 45 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 45
1. Question
1 point(s)A nerve-net, a network of neurons, makes up the neural organization in:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 2 of 45
2. Question
1 point(s)Match each item in Column I with one in Column II and select the correct match from the codes given:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { A. Peripheral } \\
\text { neural system }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { P. Comprises of all nerves associated } \\
\text { with brain and spinal cord }
\end{array} \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { B. Somatic } \\
\text { neural system }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Q. Relays impulses from CNS to } \\
\text { skeletal muscles }
\end{array} \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { C. Visceral } \\
\text { neural system }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { R. Transmits impulse from CNS to } \\
\text { involuntary organs and smooth muscles }
\end{array} \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { D. Autonomic } \\
\text { neural system }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { S. Part of PNS where impulses travel } \\
\text { from CNS to the viscera and from the } \\
\text { viscera to the CNS }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Codes:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { P } & \text { Q } & \text { R } & \text { S } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { Q } & \text { R } & \text { S } & \text { P } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { R } & \text { S } & \text { P } & \text { Q } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { S } & \text { P } & \text { Q } & \text { R } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 3 of 45
3. Question
1 point(s)In a neuron, Nissl’s granules are seen in:
I. Cell body
II. Dendrites
III. Axon\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { 1. I and II only } & \text { 2. I and III only } \\
\hline \text { 3. II and III only } & \text { 4. I, II and III } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 4 of 45
4. Question
1 point(s)Match each item in Column I with one in Column II and select the correct match from the codes given:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { COLUMN I } & & \text { COLUMN II } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { Multipolar neuron } & \text { P } & \text { Embryonic stage } \\
\hline \text { B } & \text { Bipolar neuron } & \text { Q } & \text { Retina } \\
\hline \text { C } & \text { Unipolar neuron } & \text { R } & \text { Cerebral cortex } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Code:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { P } & \text { Q } & \text { R } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { Q } & \text { R } & \text { P } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { R } & \text { Q } & \text { P } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { R } & \text { P } & \text { Q } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 5 of 45
5. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given statements:
I: Myelinated nerve fibres are enveloped with Schwann cells, which form a myelin sheath around the axon.
II: Unmyelinated nerve fibre is not enclosed by a Schwann cell or a myelin sheath.
III: Myelinated nerve fibres are found in spinal and cranial nerves.
IV: Unmyelinated nerve fibres are commonly found in autonomous and somatic neural systems.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
Unmyelinated nerve fibre enclosed by a Schwann cell or a myelin sheath.
-
Question 6 of 45
6. Question
1 point(s)Assertion: Neurons are excitable cells.
Reason: Their membranes are in a polarised state.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 7 of 45
7. Question
1 point(s)When the neuron is not conducting any impulse, i.e., resting, the axonal membrane:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 8 of 45
8. Question
1 point(s)The resting axonal membrane is impermeable to:
I. Sodium ions
II. Potassium ions
III. Negatively charges proteins present in the axoplasmCorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 9 of 45
9. Question
1 point(s)Each time the sodium-potassium pump functions, it actively transports:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 10 of 45
10. Question
1 point(s)In a resting axonal membrane:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 11 of 45
11. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given statements:
I. When a stimulus is applied at a site on the polarised axonal membrane, the membrane at that site becomes freely permeable to sodium ions.
II. A rapid influx of sodium at this point leads to reversal of polarity and the membrane at the site is said to be depolarised.
III. The electric potential difference at the site is called the action potential which is in fact termed as nerve impulse.CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 12 of 45
12. Question
1 point(s)Identify the correct statements regarding the sequence of events taking place during transmission of impulse across a chemical synapse as shown in the given figure:
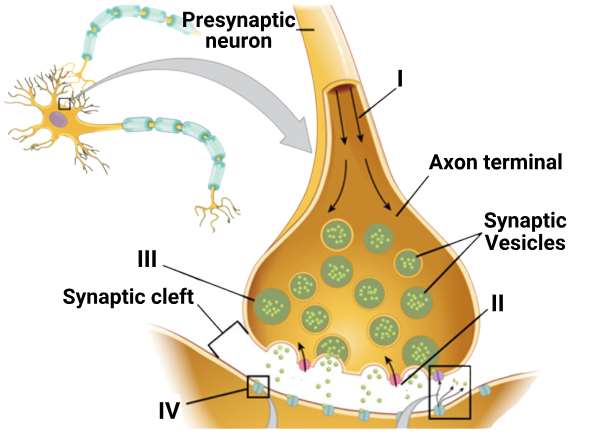
I: The action potential, generated due to the depolarization of the axonal membrane, arrives at the axon terminal.
II. Potassium ions enter the synaptic knob.
III. Synaptic vesicles are activated and release neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft.
IV. Neurotransmitter binds to the receptor on the postsynaptic membrane.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
II. “Potassium ions enter the synaptic knob.”
❌ Incorrect
- This is the trap statement.
- It is calcium ions (Ca²⁺) that enter the synaptic knob after depolarization.
- The influx of Ca²⁺ causes the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane and release neurotransmitters.
- Potassium (K⁺) typically moves out of neurons during repolarization, not into the synaptic knob during transmission.
-
Question 13 of 45
13. Question
1 point(s)Match each item in COLUMN I [part of the brain] with one in COLUMN II [function] and select the answer from the codes given below:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline
& \text{COLUMN I} & & \text{COLUMN II} \\
\hline
\text{A.} & \text{Amygdala} & \text{a.} & \text{Relays motor and sensory signals to} \\
& & & \text{the cerebral cortex} \\
\hline
\text{B.} & \text{Hippocampus} & \text{b.} & \text{Reflex centers involving vision and} \\
& & & \text{hearing} \\
\hline
\text{C.} & \text{Thalamus} & \text{c.} & \text{Plays a key role in the processing of} \\
& & & \text{emotions} \\
\hline
\text{D.} & \text{Corpora quadrigemina} & \text{d.} & \text{Formation of new memories and is} \\
& & & \text{also associated with learning and emotions} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Codes:-
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { c } & \text { d } & \text { b } & \text { a } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { d } & \text { c } & \text { a } & \text { b } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { c } & \text { d } & \text { a } & \text { b } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { d } & \text { c } & \text { b } & \text { a } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 14 of 45
14. Question
1 point(s)Match each item in COLUMN I [part of the brain] with one in COLUMN II [function] and select the answer from the codes given below:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { COLUMN I } & & \text { COLUMN II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Medulla } \\
\text { oblongata }
\end{array} & \text { a. } & \text { Motor control } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Pons varoli } & \text { b. } & \text { Hunger center } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Cerebellum } & \text { c. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Bridge between cerebellum and rest } \\
\text { of brain }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Hypothalamus } & \text { d. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Gastric secretions, respiratory } \\
\text { rhythm center }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Codes:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { c } & \text { d } & \text { b } & \text { a } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { d } & \text { c } & \text { a } & \text { b } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { c } & \text { d } & \text { a } & \text { b } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { d } & \text { c } & \text { b } & \text { a } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 15 of 45
15. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given two statements:
I: The cerebral cortex, referred to as the grey matter, is thrown into prominent folds.
II: The cerebral white mater contains motor areas, and association area.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Statement II:
“The cerebral white matter contains motor areas, and association area.”
❌ Incorrect- The motor and association areas are located in the cerebral cortex (grey matter) — not in white matter.
- White matter lies beneath the cortex and consists of myelinated nerve fibres (axons) that connect different brain regions.
-
Question 16 of 45
16. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given two statements:
I. The association areas of the cerebral cortex are neither clearly sensory nor motor in function.
II: The association areas are responsible for complex functions like intersensory associations, memory and communication.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 17 of 45
17. Question
1 point(s)What would be true regarding the structure shown in the given figure?
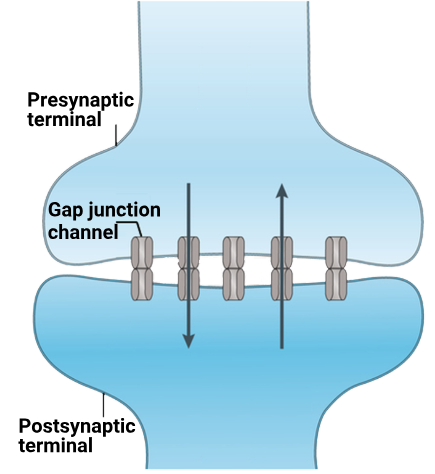 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 18 of 45
18. Question
1 point(s)The structure highlighted in orange colour in the figure is:
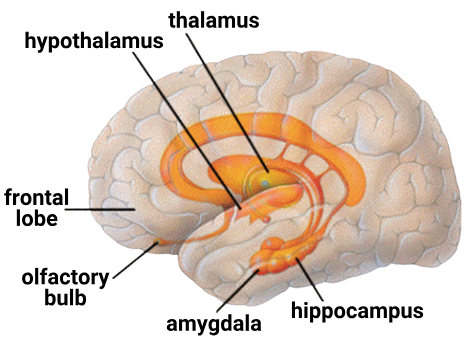 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 19 of 45
19. Question
1 point(s)All the following statements with respect to the propagation of action potentials are correct except:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
The speed of action potential propagation is determined by the properties of the axon, not the strength of the stimulus. Once an action potential is triggered, its propagation along the axon is relatively constant. A stronger stimulus might initially generate a larger action potential, but the propagation speed remains the same. The important factor is the presence of myelin (for faster saltatory conduction) and the characteristics of the axon membrane.
-
Question 20 of 45
20. Question
1 point(s)The change in membrane potential that returns it to a negative value just after an action potential has changed the membrane potential to a positive value is called as:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 21 of 45
21. Question
1 point(s)During the propagation of a nerve impulse, the action potential results from the movement of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 22 of 45
22. Question
1 point(s)Most of the neurons in the cerebral cortex are:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 23 of 45
23. Question
1 point(s)Consider the two statements:
I. Electrical synapses are rare in our system.
II. Electrical synapses conduct impulse faster than the chemical synapse.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 24 of 45
24. Question
1 point(s)Read the following statements [A-D]
A. Neural system coordinates and integrates functions as well as metabolic and homeostatic activities
of all organs.
B. Cerebrum is transversely divided into 2 halves.
C. Pons consist of fiber tracts that interconnect different regions of brain
D. Limbic system is concerned with olfaction
How many above statements are correct ?CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
B. False – The cerebrum is divided into two halves by a longitudinal fissure (running front to back), not transversely
-
Question 25 of 45
25. Question
1 point(s)Arrange the following statements in correct sequence w.r.t nerve impulse generation
a. Rise in stimulus induced Na+ influx
b. Stimulus application
c. Membrane is said to be polarized
d. K+ channel activationCorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 26 of 45
26. Question
1 point(s)Identify A, B and C in the sagittal section of the human brain:
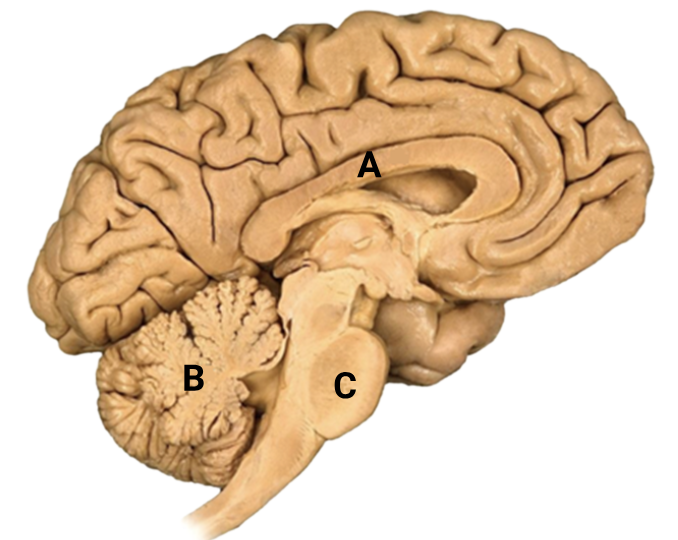
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } \\
\hline \text { 1. } & \text { Corpus callosum } & \text { Cerebellum } & \text { Pons } \\
\hline \text { 2. } & \text { Cerebellar peduncle } & \text { Cerebrum } & \text { Medulla } \\
\hline \text { 3. } & \text { Corpus callosum } & \text { Cerebrum } & \text { Pons } \\
\hline \text { 4. } & \text { Corpus luteum } & \text { Cerebellum } & \text { Medulla } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 27 of 45
27. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following statements is false?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
The neural organisation is very simple in lower invertebrates
-
Question 28 of 45
28. Question
1 point(s)Pick out the correct combihation:-
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { A. Unipolar neuron } & \text { I. In cerebral cortex } \\
\text { B. Bipolar neuron } & \text { II. In embryonic stage } \\
\text { C. Multipolar neuron } & \text { III. In retina of eye }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 29 of 45
29. Question
1 point(s)\(
\mathrm{Na}^{+}-\mathrm{K}^{+} \text {pump }
\)I. Needs energy (ATP) to work
II. Expels \( 3 \mathrm{Na}^{+} \) for every \( 2 \mathrm{K}^{+} \) ions imported
III. Works against a concentration gradient
IV. Maintains resting potentialCorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 30 of 45
30. Question
1 point(s)Neurons are excitable cells due to
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 31 of 45
31. Question
1 point(s)In the resting state, the axon membrane is ________ with more ___________ charged ions outside than inside.
This unequal distribution of ions is due to (1) the selective permeability of the membrane, which forms an almost
impenetrable barrier to ________ and (2) the action of the ____________, which pumps__________ \( \mathrm{Na}^{+} \)
out of neuron for every ________\( \mathrm{K}^{+} \) brought in.CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 32 of 45
32. Question
1 point(s)Identify the correct statements regarding the events A and B in the given diagram:
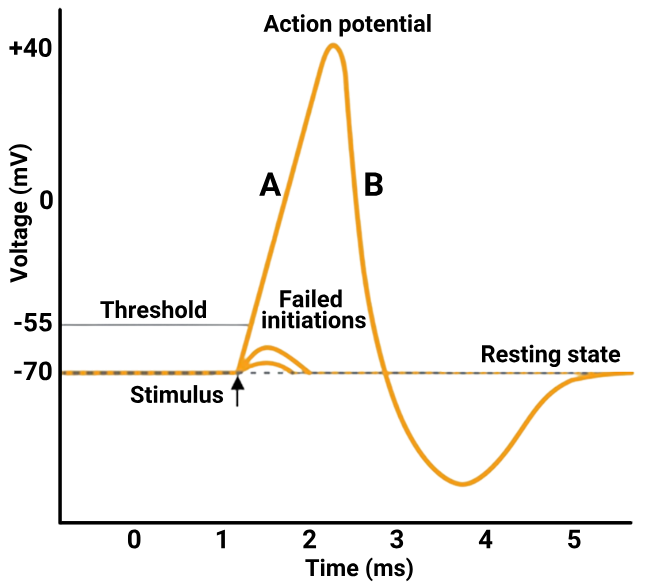
I: A is depolarization and is caused by the influx of sodium ions.
II: B is repolarization and is caused by the efflux of potassium ions.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 33 of 45
33. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following statements is false about the electrical synapse?
I. At electrical synapses, the membranes of pre and post synaptic neurons are in very close proximity
II. Electrical current can flow directly from one neuron into the other across the synapses
III. Transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is very similar to impulse conduction along single axon.
IV. Electrical synapses pass electrical signal between cells with the use of Ach
V. Electrical synapses are fast
VI. Electrical synapses are rare in our systemCorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
The false statement about electrical synapses is:
-
IV. Electrical synapses pass electrical signal between cells with the use of Ach
This is incorrect because electrical synapses do not use neurotransmitters like acetylcholine (ACh). Instead, they rely on gap junctions — direct cytoplasmic connections that allow ionic currents to flow straight between cells
-
Question 34 of 45
34. Question
1 point(s)Choose the incorrect statement
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
(4) Hypothalamus lies laterally to thalamus
❌ Incorrect. The hypothalamus is located below (ventral to) the thalamus, forming the floor and part of the lateral walls of the third ventricle. It does not lie laterally to the thalamus.
-
Question 35 of 45
35. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following statements is correct?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 36 of 45
36. Question
1 point(s)
The above diagram can be used to show the functional organization of the human nervous system. Identify 1 to 5
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline \mathbf{1} & \mathbf{2} & \mathbf{3} & \mathbf{4} & \mathbf{5} \\
\hline \text { PNS } & \text { CNS } & \text { ANS } & \text { Sympathetic N.S} & \text { Parasympathetic N.S } \\
\hline \text { ANS } & \text { CNS } & \text { PNS } & \text { Sympathetic N.S} & \text { Parasympathetic N.S } \\
\hline \text { CNS } & \text { PNS } & \text { ANS } & \text { Sympathetic N.S} & \text { Parasympathetic N.S } \\
\hline \text { ANS } & \text { PNS } & \text { CNS } & \text { Sympathetic N.S} & \text { Parasympathetic N.S} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 37 of 45
37. Question
1 point(s)Identify the statements as true (T) or false (F)
I. Cerebral cortex has sensory and motor areas
II. Cerebrum wraps around thalamus
III. Occipital lobe interprets the sensation of light.
IV. Thalamus is for sensory and motor signalling\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \mathrm{I} & \mathrm{II} & \mathrm{III} & \mathrm{IV} \\
\hline(1) & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~T} \\
\hline(2) & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} \\
\hline(3) & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} \\
\hline(4) & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~T} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 38 of 45
38. Question
1 point(s)The accompanying diagram show the structure of neuron. Identify A to E.
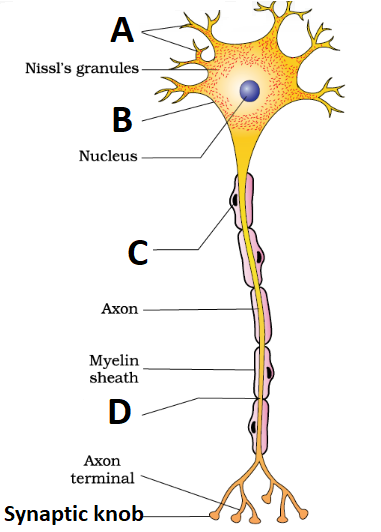
\(
\begin{array}{lccc}
\textbf{A} & \textbf{B} & \textbf{C} & \textbf{D} \\
\text{(1) Nerve fibre} & \text{Cyton or cell body} & \text{Schwann cell} & \text{Node of Ranvier} \\
\text{(2) Dendrites} & \text{Cyton or cell body} & \text{Schwann cell} & \text{Node of Ranvier} \\
\text{(3) Dendrites} & \text{Nerve cell} & \text{Schwann cell} & \text{Node of Ranvier} \\
\text{(4) Dendrites} & \text{Cyton or cell body} & \text{Nerve cell} & \text{Node of Ranvier}
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 39 of 45
39. Question
1 point(s)A : Cerebral cortex is referred to as gray matter due to its grayish appearance
R : Myelinated nerve fibers are concentrated in the cerebral cortex.
In light of the above statements select the correct optionCorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 40 of 45
40. Question
1 point(s)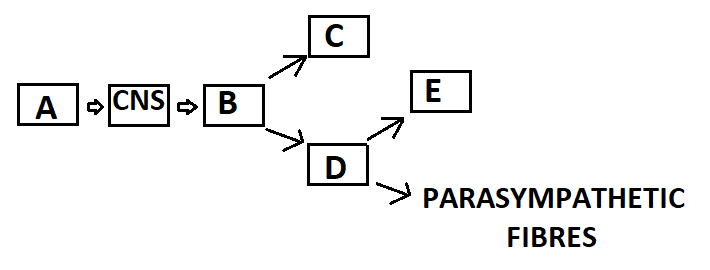
Which of the following shows the correct arrangement of fibres in above diagram –
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline \mathbf{A} & \mathbf{B} & \mathbf{C} & \mathbf{D} & \mathbf{E} \\
\hline \text { Afferent } & \text { Efferent } & \text { Somatic motor } & \text { Autonomic } & \text { Sympathetic } \\
\hline \text { Efferent } & \text { Afferent } & \text { Somatic motor } & \text { Autonomic } & \text { Sympathetic } \\
\hline \text { Afferent } & \text { Efferent } & \text { Autonomic } & \text { Somatic Motor } & \text { Sympathetic } \\
\hline \text { Efferent } & \text { Afferent } & \text { Autonomic } & \text { Somatic Motor } & \text { Sympathetic } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 41 of 45
41. Question
1 point(s)I. Cerebellum has very convoluted surface in order to provide the additional space for more neurons
II. The medulla is connected to the spinal cord
III. Medulla contains controlling centres for respiration, cardiovascular reflexes and gastric secretionCorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 42 of 45
42. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following statement is incorrect with respect to medulla ?
I. It contains “vomiting centre”
II. It contains respiratory rhythm centre.
III. It contain centres to control personality
IV. It controls gastric secretions and cardiovascular reflexesCorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 43 of 45
43. Question
1 point(s)The correct sequence meninges from inner to outerside is :-
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 44 of 45
44. Question
1 point(s)Five events in the transmission of nerve impulse across the synapse
A. Opening of specific ion channels allows the entry of ions, a new action potential is generated in the post-synaptic
neuron.
B. Neurotransmitter binds to the receptor on post synaptic membrane
C. Synaptic vesicle fuses with pre-synaptic membrane, neurotransmitter releases into synaptic cleft.
D. Depolarization of pre-synaptic membrane
E. Arrival of action potential at axon terminal.
In which sequence do these events occur?CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 45 of 45
45. Question
1 point(s)Study the diagram of synapse:-
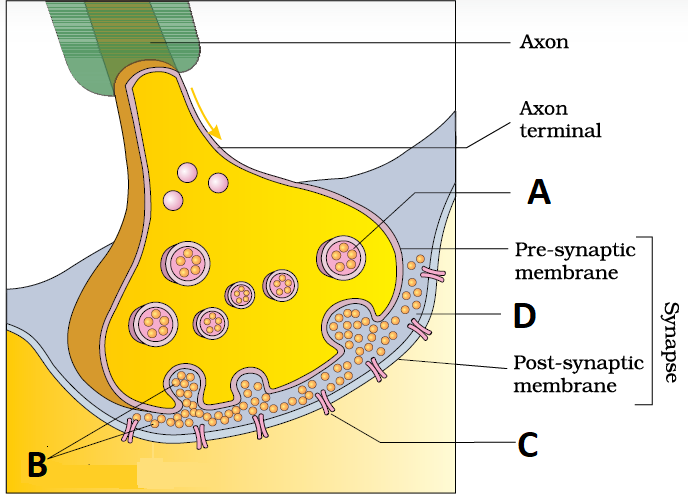
I. Which numbered label indicate the location of the receptor molecules.
II. Which number points to a synaptic vesicles.
III. Which number points to neurotransmitter.
IV. Which number points to synaptic cleft.\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { I } & \text { II } & \text { III } & \text { IV } \\
\hline \text { C } & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { D } \\
\hline \text { B } & \text { A } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline \text { C } & \text { A } & \text { D } & \text { B } \\
\hline \text { C } & \text { D } & \text { A } & \text { B } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)