Morphology of Flowering Plants TS
Quiz Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
Given below are two statements one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R)
Assertion (A) : In mustard, chinarose and brinjal superior ovary present
Reason (R) : In Epigynous flower gynoecium occupies the lowest position while other part of flower arises above the ovary In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-73]
In mustard, chinarose and brinjal superior ovary present
In Epigynous flower gynoecium occupies the lowest position while other part of flower arises above the ovary -
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
Match the following column I and column II :
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline \text { Column-I } & \text { Column-II } \\
\hline \text { a. Valvate } & \text { i. Pea } \\
\hline \text { b. Twisted } & \text { ii. Cotton } \\
\hline \text { c. Imbricate } & \text { iii. Gulmohar } \\
\hline \text { d. Vaxillary } & \text { iv. Calotropis } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) NCERT-74
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Valvate } & – \text { Calotropis } \\
\text { Twisted } & – \text { Cotton } \\
\text { Imbricate } & – \text { Gulmohur } \\
\text { Vaxillary } & – \text { Pea }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
Match the following column I and column II :
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline \text { Column-I } & \text { Column-II } \\
\hline \text { a. Marginal } & \text { i. Lemon } \\
\hline \text { b. Axil } & \text { ii. Pea } \\
\hline \text { c. Parietal } & \text { iii. Primrose } \\
\hline \text { d. Free – central } & \text { iv. Argemone } \\
\hline \text { d. Basal } & \text { iv. Marigold } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-75]
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { Marginal } & \text { – } & \text { Pea } \\
\hline \text { Axil } & \text { – } & \text { Lemon } \\
\hline \text { Parietal } & \text { – } & \text { Argemon } \\
\hline \text { Free-central } & \text { – } & \text { Primrose } \\
\hline \text { Basal } & \text { – } & \text { Marigold } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\) -
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
Stem modified into flattened and fleshy structures are known as :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-68]
They protect plants from browsing animals. Some plants of arid regions modify their stems into flattened (Opuntia), or fleshy cylindrical (Euphorbia) structures. -
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
Match the following columns
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { Column-I } & & \text { Column-II } \\
\hline \text { a. Tap root } & \text { i. } & \text { Monstera } \\
\hline \text { b. Fibrous root } & \text { ii. } & \text { Guava } \\
\hline \text { c. Adventitious root } & \text { iii. } & \text { Banyan } \\
\hline \text { d. Prop root } & \text { iv. } & \text { Wheat } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-66,67]
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { Tap root } & \text { – } & \text { Guava } \\
\hline \text { Fibrous root } & \text { – } & \text { Wheat } \\
\hline \text { Adventitious root } & \text { – } & \text { Monstera } \\
\hline \text { Prop root } & \text { – } & \text { Banyan } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\) -
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
In the given following statements, select the correct statements
(a) A number of leaflets are present on a common axis, the rachis, which represent the midrib of the leaf in pinnately compound leaf
(b) The leaf base may become swollen is pulvinus in some leguminous plants
(c) Supporting roots coming out of the lower nodes of the stem called stilt roots in Banyan and Rhizophora
(d) Axillary buds of stems may also get modified into woody, straight pointed thorns as in Citrus and BougainvilleaCorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I- 67, 68, 70]
In sugarcane and maize, the supporting roots coming out of the lower nodes of the stems called stilt roots. In Rhizophora, Pneumatophores are present where as in Banyan tree prop roots are arises. -
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
Match the following columns
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { Column-I } & & \text { Column-II } \\
\hline \text { a. Stem tendril } & \text { i. } & \text { Maize } \\
\hline \text { b. Thorns } & \text { ii. } & \text { Bougainvillea } \\
\hline \text { c. Underground stem } & \text { iii. } & \text { Watermelon } \\
\hline \text { d. Stilt root } & \text { iv. } & \text { Colocasia } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-67-68,69]
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { Stem tendril } & \text { – } & \text { Watermelon } \\
\hline \text { Thorns } & \text { – } & \text { Bougainvillea } \\
\hline \text { Underground stem } & \text { – } & \text { Colocasia } \\
\hline \text { Stilt root } & \text { – } & \text { Maize } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\) -
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
Select the correct match:
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline \text { Family } & \text { Fruit } \\
\hline \text { Brassicaceae } & \text { Siliques } \\
\hline \text { Fabaceae } & \text { Legume } \\
\hline \text { Malvaceae } & \text { capsule or schizocarps } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-79-81]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Brassicaceae } & \text { Siliques } \\
\text { Fabaceae } & \text { Legume } \\
\text { Malvaceae } & \text { capsule or schizocarps }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
Which of these belong to the family Malvaceae
(i) Lady Finger
(ii) Cotton
(iii) Petunia
(iv) Colchicum autumnale
(v) Asparagus
(vi) ChilliCorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NC-I-80, 81]
Lady finger and cotton belong to the family Malvaceae. -
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
Phyllode (petiole modified) is present in :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-71]
In some plants such as Australian acacia, the leaves are small and short-lived. The petioles in these plants expand, become green and synthesise food. -
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
The following diagrams represent the types of aestivation in corolla. Identify the correct combination of labelling.
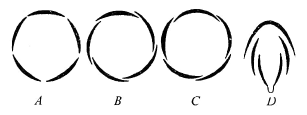 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-74]
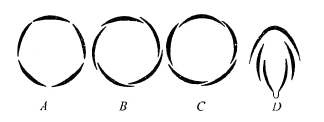
-
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
Pneumatophores show which of the following type of growth:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-67]
Pneumatophores show negative geotropic. -
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
Given below are two statements :
Statement I : In parietal placentation, the ovule develop on the inner wall of ovary.
Statement II : When stamens are attached to parianth they are epipitalous as in lily.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given belowCorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-75]
In parietal placentation, the ovule develop on the inner wall of ovary.
When stamens are attached to parianth they are epiphilous as in lily. -
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
Given below are two statements :
Statement I: In pinnately compound leaf, leaflet are present on a common axis, the rachis and it found in silk cotton.
Statement-II: In compound leaf, lamina is divided into number of leaflet.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-70,71]
In compound leaf, lamina is divided into number of leaflet. In pinnately compound leaf, leaflet are present on a common axis, the rachis and it found in neem. -
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
Find the correct matching of the following
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline \text { (A) Marginal placentation } & \text { (i) Sunflower } \\
\hline \text { (B) Parietal placentation } & \text { (ii) Gram } \\
\hline \text { (C) Axile placentation } & \text { (iii) Mustard } \\
\hline \text { (D) Basal placentation } & \text { (iv) Chinarose } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-75]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Marginal placentation } & \text { Gram } \\
\text { Parietal placentation } & \text { Mustard } \\
\text { Axile placentation } & \text { Chinarose } \\
\text { Basal placentation } & \text { Sunflower }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
Find the correct matching of the following
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline \text { Column-I } & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { a. Epipetalous } & \text { (i. Brinjal } \\
\hline \text { b. Epiphyllous } & \text { (ii. Lilly } \\
\hline \text { c. Monodelphous } & \text { iii. China rose } \\
\hline \text { d. Diadelphous } & \text { iv. Pea } \\
\hline \text { e. Polyadelphous } & \text { v. Citrus } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-75]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Epipetalous } & \text { Brinjal } \\
\text { Epiphyllous } & \text { Lilly } \\
\text { Monodelphous } & \text { China rose } \\
\text { Diadelphous } & \text { Pea } \\
\text { Polyadelphous } & \text { Citrus }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
Find out the correct statements
a. The roots which store food in Turnip are modified tap roots
b. Stems of maize \& sugarcane have stilt roots coming out from upper nodes
c. In Monstera, roots arise from parts other than radicle
d. Colocasia has organ of perennationCorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
[NCERT-I-66, 67]
The roots which store food in Turnip are tap roots
Stems of maize & sugarcane have stilt roots coming out from lower nodesIn Monstera, roots arise from parts other than radicle
Colocasia has organ of perennation
-
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
In following diagram placentation represent
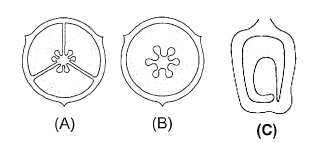 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT – I – 75]
A-Axile, B-Free central, C – in marigold -
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
Which of the following is/are correct :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT- I-64]
Anatomy of seed plant by Katherine Esau was published in 1960
Dr. esau’s plant anatomy published in 1954
Katherine Esau reported that the Curly top virus spreads through a plant via the food conducting tissue -
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
Which among the following statement regarding ‘Leaf’ is incorrect :
(a) These are lateral generally flattened structure borne on stem
(b) It orginates from shoot axillary parenchyma
(c) These are arranged basipetally
(d) The leaf is attached to stem by laminaCorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NC-I-69]
The leaf is a lateral, generally flattened structure borne on the stem. It develops at the node and bears a bud in its axil. The axillary bud later develops into a branch. Leaves originate from shoot apical meristems and are arranged in an acropetal order. They are the most important vegetative organs for photosynthesis. The leaf is attached to the stem by the leaf base. -
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
A typical flower has four different kind of whorl, arranged successively on the swollen end of the stalk called :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NC-I-72]
A typical flower has four different kind of whorl, arranged successively on the swollen end of the stalk called Receptacle. Single stalk of flower is called Pedicel. -
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
Which among the following statement is false with respect to drupe :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NC-I-76]
In mango and coconut, the fruit is known as a drupe. They develop from monocarpellary superior ovaries and are one seeded. In mango the pericarp is well differentiated into an outer thin epicarp, a middle fleshy edible mesocarp and an inner stony hard endocarp. In coconut which is also a drupe, the mesocarp is fibrous. -
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
What is correct about ovary of Dianthus :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-75]
When the ovules are borne on central axis and septa are absent, as in Dianthus and Primrose the placentation is called free central. In basal placentation, the placenta develops at the base of ovary and a single ovule is attached to it, as in sunflower, marigold. -
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
Apocarpous condition is found in
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NC-I-75]
When more than one carpel is present, they may be free (as in lotus and rose) and are called apocarpous. -
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
Which among the following is described as reduced leaf found at the base of the pedicel :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NC-I-72]
Flowers with bracts, reduced leaf found at the base of the pedicel, are called bracteate and those without bracts, ebracteate. -
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
Match the following Column I and II
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline \text { Column-I } & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { a. Hypogynous } & \text { (i. Mustard } \\
\hline \text { b. Perigynous } & \text { (ii. Peach } \\
\hline \text { c. Epigynous } & \text { iii. Guava } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-73]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Hypogynous } & \text { Mustard } \\
\text { Perigynous } & \text { Peach } \\
\text { Epigynous } & \text { Guava }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
The covering of radicle in monocot seed is known as :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NC-I-77]
The covering of radicle in monocot seed is known as Coleorhiza. The covering of plumule in monocot seed is known as Coleoptile. -
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
Alstonia is known for :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NC-I-71]
If more than two leaves arise at a node and form a whorl, it is called whorled, as in Alstonia -
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
Select the correct match
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { (i) Chilli } & – \text { Actinomorphic flower } \\
\text { (ii) Canna } & – \text { Asymmetric flower } \\
\text { (iii) Trifolium } & – \text { Zygomorphic flower } \\
\text { (iv) Cassia } & – \text { Asymmetric flower }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-72]
Chilli – Actinomorphic flower
Canna – Asymmetric flower
Trifolium – Zygomorphic flower
Cassia & – Zygomorphic flower -
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
Androecium is composed of stamens, which have pollen sacs, producing pollen grains. However, some stamens do not produce pollen grains are :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-75]
Some stamens do not produce pollen grains are called staminode. -
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
In a cereal grain the single cotyledon of embryo is represented by :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NC-I-77]
It consists of one large and shield shaped cotyledon known as scutellum and a short axis with a plumule and a radicle. The plumule and radicle are enclosed in sheaths which are called coleoptile and coleorhiza respectively. -
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
In dicots, radicle elongates to form :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [N CERT-1-65]
In majority of the dicotyledonous plants, the direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of primary root which grows inside the soil. -
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
Axillary buds which develop into tendrils are found in:
CorrectIncorrectHint
[NCERT-I-68]
Underground stems of potato, ginger, turmeric, zaminkand, Colocasia are modified to store food in them. They also act as organs of perenation to tide over conditions unfavourable for growth. -
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
In which leaf base expands into a sheath covering the stem partially or wholly :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-70]
In monocotyledons, the leaf base expands into a sheath covering the stem partially or wholly. In some leguminous plants the leafbase may become swollen, which is called the pulvinus. -
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
Given below are two statements :
Statement I : Actinomorphic flower can be divided in to two equal halves by any radial plane passing through the centre.
Statement-II: Asymmetric flower cannot be divided in to two similar half by any vertical plane passing through the centre.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-72]
Actinomorphic flower can be divided in to two equal halves by any radial plane passing through the centre. Asymmetric flower cannot be divided in to two similar half by any vertical plane passing through the centre. -
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
How many matchings are correct:
(a) Fucus – Oogamous
(b) Eudorina – Isogamous
(c) Ulothrix – Anisogamous
(d) Spirogyra – IsogamousCorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-24]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Fucus } & – \text { Oogamous } \\
\text { Eudorina } & – \text { Anisogamous } \\
\text { Ulothrix } & – \text { Isogamous } \\
\text { Spirogyra } & – \text { Isogamous }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
How many matchings are correct:
a. Pinus – Male cone
b. Cycas – Female cone
c. Pinus – Female cone
d. Cycas – Male coneCorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-33]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Pinus } & – \text { Male cone } \\
\text { Cycas } & – \text { megasporophyll } \\
\text { Pinus } & – \text { Female cone } \\
\text { Cycas } & – \text { Male cone }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
Accoding to circulatory system how many matching are incorrect
(a) Open type – In Anopheles
(b) Close type – In Pheretima
(c) Open type – In Nereis
(d) Close type – In NeophronCorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-38]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Open type } & – \text { In anopheles } \\
\text { Close type } & – \text { In Pheretima } \\
\text { Close type } & – \text { In Nereis } \\
\text { Close type } & – \text { In Neophron }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
How many matching is/are correct
a. Acoelomates – Platyhelminthes
b. Pseudocoelomates – Aschelminthes
c. Coelomate – Coelenterata
d. Coelomate – PoriferaCorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
[NCERT-I-39]
Acoelomates – Platyhelminthes
Pseudocoelomates – Aschelminthes -
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : In twisted aestivation, one margin of sepals or petals overlaps that of the next one and soon.
Statement-II: In imbricate aestivation, margins of sepals or petals overlap on another but not in any perticular direction.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-74]
In twisted aestivation, one margin of sepals or pet als overlaps that of the next one and soon. In imbricate aestivation, margins of sepals or petals overlap on another but not in any particular direction as. -
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
Identify the figure and choose correct option
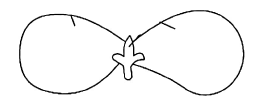
(a) Dicotyledonous seed, example – gram
(b) Monocotyledonous seed, example – maize
(c) Generally non- albuminous
(d) Generally endospermicCorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-77]
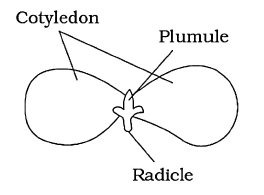
Dicotyledonous seed, example – gram
Generally non- albuminous -
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
Which is floral formula of family brassicaceae :
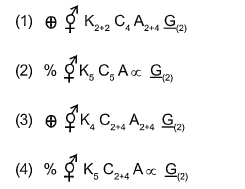 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT – I – 78]
Floral formula of family brassicaceae is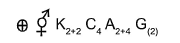
-
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
Keel is characteristic of the flowers of :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-74]
In pea and bean flowers, there are five petals, the largest (standard) overlaps the two lateral petals (wings) which in turn overlap the two smallest anterior petals (keel); this type of aestivation is known as vexillary or papilionaceous. -
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
Which statement is true among the following:
(a) When the stamens are united into more than two bundles this condition is seen in Citrus.
(b) When more than one carpel is present it can be free as in tomato.
(c) Petiole in Australian acacia expands become green and synthesised food.
(d) Irregular symmetry present in cannaCorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-75]
When more than one carpel is present, they may be free as in lotus and rose and are called apocarpous. -
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
Select the correct statement about mustard :
i. Alternate phyllotaxy
ii. Superior ovary
iii. Tetradynamous stamen
iv. Variation in length of filament
v. Apocarpous ovaryCorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
[NCERT-I-71, 73,78]
Mustard shows :
– Alternate phyllotaxy
– Hypogynous superior ovary
– Tetradynamous anther
– Variation in length of filament
– Syncarpous ovary -
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A) : Both apical and intercalary meristems are primary meristems.
Reason (R) : They appear early in life of plant and contributes to the formation of primary plant body.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given belowCorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-85]
They appear early in life of plant and contributes to the formation of primary plant body. Both apical and intercalary meristems are primary meristems. -
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
Simple tissue that don’t contain chloroplasts :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT – I – 86]
Simple tissue that don’t contain chloroplasts is Sclerenchyma. -
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
Which of the following is not an element of xylem in gymnosperms
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT – I- 88]
Vessels is not an element of xylem in gymnosperms. -
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
Suberin layer is found in :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT – I – 91]
Suberin layer is found in Innermost layer of cortex of root (endodermis). -
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
Intercalary meristems are :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT – I – 85]
Intercalary meristems are Primary meristems and are in present in grasses.