Morphology of Flowering Plants NCERT
Quiz Summary
0 of 45 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 45 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 45
1. Question
1 point(s)What types of leaves are respectively shown in the given picture?
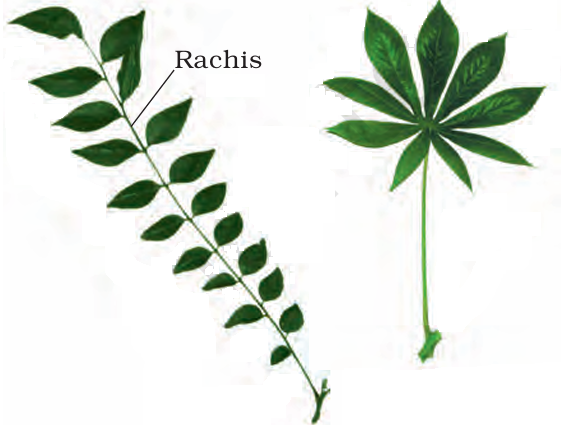 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 2 of 45
2. Question
1 point(s)Roots arising from the parts of a plant other than radical are called as:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 3 of 45
3. Question
1 point(s)At the root tip, the cells that are responsible for the growth of the root in length are located in the region that is:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 4 of 45
4. Question
1 point(s)The phyllotaxy shown in the given picture:-
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 5 of 45
5. Question
1 point(s)A bud is present in the axil of:
I. Petiole in simple leaves
II. Petiole in compound leaves
III. Leaflets of the compound leavesCorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
NCERT: A bud is present
in the axil of petiole in both simple and compound
leaves, but not in the axil of leaflets of the compound
leaf. -
Question 6 of 45
6. Question
1 point(s)The leaves:
I. Develop at the node, bear buds in their axil that later develop into a branches.
II. Originate from shoot apical meristems and are arranged in an acropetal order.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 7 of 45
7. Question
1 point(s)Identify the incorrectly matched pair:
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|l|}
\hline
\text{1.} & \text{Stipules} & \text{Small leaf like structure, generally two in number, that are sometimes present at the leaf base} \\
\hline
\text{2.} & \text{Pulvinus} & \text{Leaf base in monocotyledons expanded into a sheath covering the stem partially or wholly} \\
\hline
\text{3.} & \text{Petiole} & \text{A stalk that connects the blade with the leaf base} \\
\hline
\text{4.} & \text{Leaf blade} & \text{Also called as lamina and is the green expanded part of the leaf with veins and veinlets} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
NCERT: In some leguminous plants the leafbase may become swollen, which is called the pulvinus
-
Question 8 of 45
8. Question
1 point(s)The placentation shown below will be seen in:
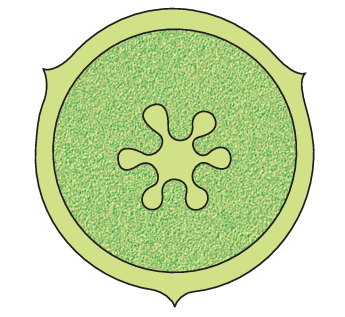 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 9 of 45
9. Question
1 point(s)Match each item in COLUMN I with one in COLUMN II and select the correct match from the codes given:
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|c|l|}
\hline
& \text{COLUMN I} & & \text{COLUMN II} \\
\hline
\text{A} & \text{Simple leaf} & \text{P} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{Lamina is entire or when incised,} \\
\text{the incisions do not touch the midribs}
\end{array} \\
\hline
\text{B} & \text{Pinnately compound leaf} & \text{Q} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{A number of leaflets are present} \\
\text{on a common axis, the rachis}
\end{array} \\
\hline
\text{C} & \text{Palmately compound leaf} & \text{R} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{The leaflets are attached at a} \\
\text{common point, i.e., at the tip of petiole}
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Codes:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \mathrm{A} & \mathrm{~B} & \mathrm{C} \\
\hline 1 . & \mathrm{P} & \mathrm{Q} & \mathrm{R} \\
\hline 2 . & \mathrm{P} & \mathrm{R} & \mathrm{Q} \\
\hline 3 . & \mathrm{R} & \mathrm{Q} & \mathrm{P} \\
\hline 4 . & \mathrm{Q} & \mathrm{P} & \mathrm{R} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 10 of 45
10. Question
1 point(s)Match each item in COLUMN I with one in COLUMN II and select the correct match from the codes given:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { COLUMN I } \\
\text { [Phyllotaxy] }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { COLUMN II } \\
\text { [Example] }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { A. Alternate } & \text { P. Alstonia } \\
\hline \text { B. Opposite } & \text { Q. Calotropis and Guava } \\
\hline \text { C. Whorled } & \text { R. China rose, Mustard and Sunflower } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Codes:
\(
\begin{aligned}
&\text { }\\
&\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { P } & \text { Q } & \text { R } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { P } & \text { R } & \text { Q } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { R } & \text { Q } & \text { P } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { Q } & \text { P } & \text { R } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\end{aligned}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 11 of 45
11. Question
1 point(s)Identify the correct statements amongst the following:
I. When a shoot tip transforms into a flower, it is always solitary
II. In racemose inflorescence, the main axis continues to grow and flowers are borne in basipetal order
III. In cymose inflorescence, the main axis terminates in a flower and flowers are borne in basipetal orderCorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
II. In racemose type
of inflorescences the main axis continues to
grow, the flowers are borne laterally in an
acropetal succession -
Question 12 of 45
12. Question
1 point(s)Consider the two statements:
Statement I: In racemose type of inflorescence, the main axis terminates in a flower, hence is limited in growth and the flowers are borne in a basipetal order.
Statement II: In cymose type of inflorescence, the main axis continues to grow and the flowers are borne laterally in an acropetal succession.CorrectIncorrectHint
(D)
I:- In racemose type
of inflorescences the main axis continues to
grow, the flowers are borne laterally in an
acropetal succession
II:- In cymose type of inflorescence the main
axis terminates in a flower, hence is limited
in growth.The flowers are borne in a basipetal
order -
Question 13 of 45
13. Question
1 point(s)Imbricate aestivation is shown in the diagram part labeled:
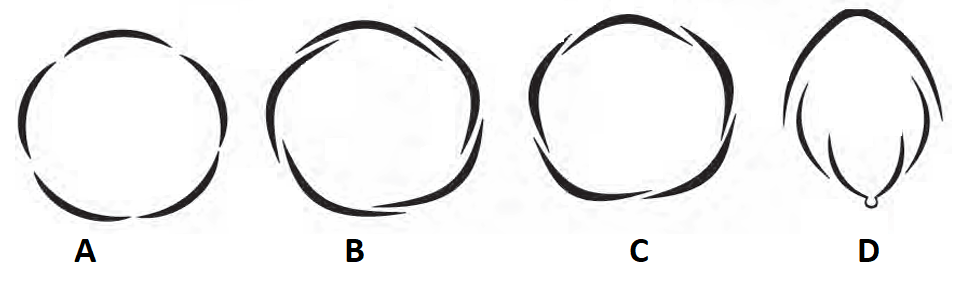 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 14 of 45
14. Question
1 point(s)The flower can be divided into two equal radial halves in any radial plane passing through the centre in all the following except:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
Cassia is zygomorphic having radial Symmetry
-
Question 15 of 45
15. Question
1 point(s)Identify Incorrectly matched pair:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Actinomorphic flower } & \text { Gulmohur } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Zygomorphic flower } & \text { Mustard } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Asymmetric flower } & \text { Cassia } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
Gulmohor and cassia are Zygomorphic
Mustard is Actinomorphic
-
Question 16 of 45
16. Question
1 point(s)Apocarpous Gynoecium is seen in ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 17 of 45
17. Question
1 point(s)The position of the ovary shown in the given diagram would be:
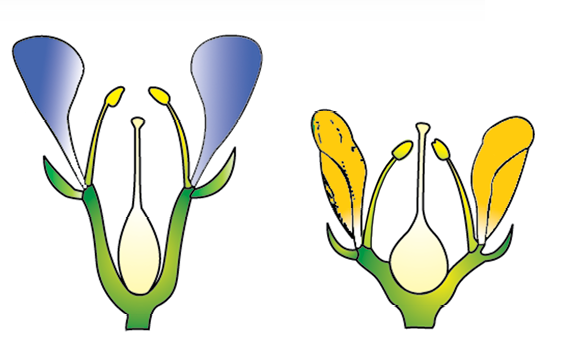 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 18 of 45
18. Question
1 point(s)The term that describes united sepals in a flower is:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 19 of 45
19. Question
1 point(s)In papilionaceous aestivation:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 20 of 45
20. Question
1 point(s)Stamens attached to the perianth as in the flowers of lily are called as:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 21 of 45
21. Question
1 point(s)Identify the incorrect statement/s:
Statement I: Stamens are epipetalous in the flowers of lily.
Statement II: Diadelphous stamen are seen in citrus.
Statement III: A sterile stamen is called as staminate.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
I:
- In lily, the stamens are epiphyllous (attached to perianth), not epipetalous.
- Epipetalous stamens are found in Solanaceae (e.g., brinjal).
II.
- Diadelphous stamens (9 fused + 1 free) are seen in pea (family Fabaceae).
- In Citrus (family Rutaceae), stamens are usually polyadelphous (grouped into more than two bundles).
III.
- A sterile stamen is called a staminode, not staminate.
- The term staminate refers to a flower that has stamens but no carpels (i.e., male flower).
-
Question 22 of 45
22. Question
1 point(s)In the given diagram of structure of a monocotyledonous seed,
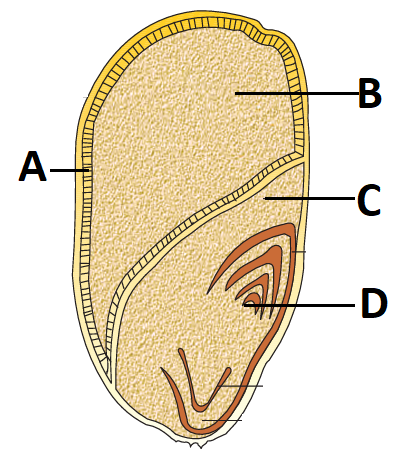 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
Hint:-
- A: Aleurone Layer
- B: Endosperm
- C: Scutellum
- D: Plumule
A:Statement 1 (“A represents the fused testa and tegmen”) is incorrect.
Instead, A is the aleurone layer that secretes enzymes—not a seed coat component.B: The starchy tissue that stores nutrients (starch, proteins, lipids) for the developing embryo .
→ Statement 2 (“B secretes enzymes”) is incorrect.D: Plumule — The embryonic shoot containing the leaf primordia, which gives rise to the first foliage, not part of the radicle/root sheath
→ Statement 4 (“D is the covering of the embryonic root”) is incorrect. That role belongs to the coleorhiza. -
Question 23 of 45
23. Question
1 point(s)When the ovules are borne on central axis and septa are absent, the type of placentation is called as:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 24 of 45
24. Question
1 point(s)The fruit in coconut:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 25 of 45
25. Question
1 point(s)Match each item in Column I regarding structure of a dicotyledonous seed with description in Column II and select the correct option from the codes given below:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline
\begin{array}{l}
\text{COLUMN I}
\end{array} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{COLUMN II}
\end{array} \\
\hline
\text{A. Alternate} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{a. Outer layer} \\
\text{of seed coat}
\end{array} \\
\hline
\text{B. Opposite} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{b. Inner layer} \\
\text{of seed coat}
\end{array} \\
\hline
\text{C. Whorled} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{c. Scar on seed coat through which} \\
\text{the developing seeds were attached} \\
\text{to the fruit}
\end{array} \\
\hline
\text{D. Opposite} &
\begin{array}{l}
\text{d. Small pore through which} \\
\text{pollen tube penetrates}
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Codes:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { a } & \text { b } & \text { c } & \text { d } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { b } & \text { a } & \text { c } & \text { d } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { b } & \text { a } & \text { d } & \text { c } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { a } & \text { b } & \text { d } & \text { c } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 26 of 45
26. Question
1 point(s)Variation in the length of filaments within a flower is seen in:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 27 of 45
27. Question
1 point(s)The figure is related to the root-tip. Identify zones A, B and C:
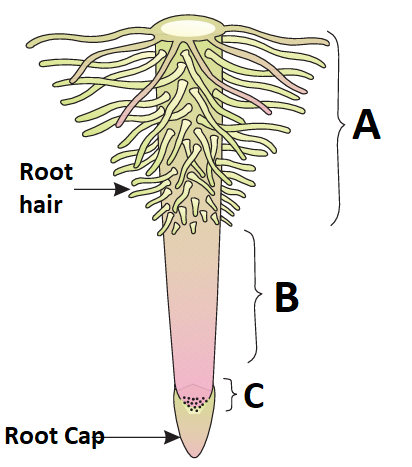 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 28 of 45
28. Question
1 point(s)In mango, the fruit is:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 29 of 45
29. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following is an endospermic seed?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 30 of 45
30. Question
1 point(s)Generally, monocotyledonous seeds are endospermic. An important exception may be:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 31 of 45
31. Question
1 point(s)Scutellum is:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 32 of 45
32. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given two statements:
Statement I: A proteinaceous material, usually in the form of small granules, occurring in the outermost cell layer of the endosperm of wheat and other grains are called as aleurone layer.
Statement II: The radical in a monocot seed is enclosed in a sheath called as coleoptiles.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
NCERT: The plumule and radicle
are enclosed in sheaths which are called coleoptile and
coleorhiza respectively. -
Question 33 of 45
33. Question
1 point(s)Given diagram of a typical leaf. In which of the following all the four parts labelled as A, B, C and D are correctly identified:
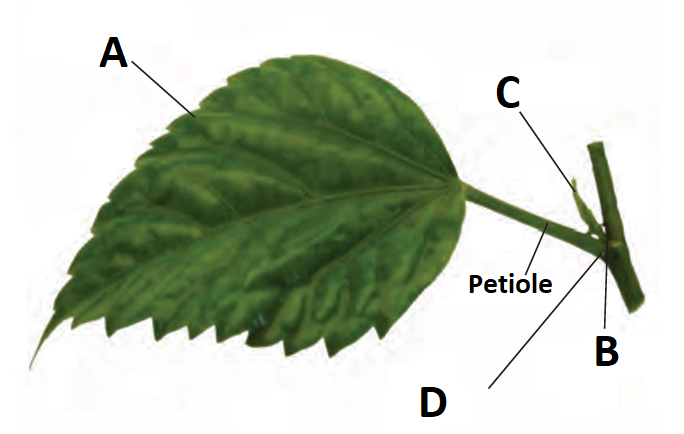
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline
\ & A & B & C & D \\ \hline
1 & \text{Lamina} & \text{Axillary bud} & \text{Stipule} & \text{Leaf base} \\ \hline
2 & \text{Lamina} & \text{Stipule} & \text{Axillary bud} & \text{Leaf base} \\ \hline
3 & \text{Lamina} & \text{Axillary bud} & \text{Stipule} & \text{Pedicel} \\ \hline
4 & \text{Leaflet} & \text{Axillary bud} & \text{Stipule} & \text{Leaf base} \\ \hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 34 of 45
34. Question
1 point(s)In a floral formula, the symbols \( K \) and \(\underline{G} \) represent:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 35 of 45
35. Question
1 point(s)All the following characteristics differentiate stems from the roots except:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d).
4. Endogenous development of branches
❌ Incorrect as a difference.
-
Endogenous branching (branching from deep tissues) is typical of roots, not stems.
-
Stem branches arise exogenously (from axillary buds).
→ So, this statement does not differentiate stem from root, because it’s a root feature.
-
Question 36 of 45
36. Question
1 point(s)Identify the Incorrectly Matched Pair:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Aestivation type } & \text { Example } \\
\hline \text { 1. } & \text { Valvate } & \text { Calotropis } \\
\hline \text { 2. } & \text { Twisted } & \text { Bean } \\
\hline \text { 3. } & \text { Imbricate } & \text { Gulmohur } \\
\hline \text { 4. } & \text { Vexillary } & \text { Pea } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
Bean Having Vexillary aestivation like Pea
-
Question 37 of 45
37. Question
1 point(s)Aestivation is:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 38 of 45
38. Question
1 point(s)Identify Incorrectly Matched Pair:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Placentation } & \text { Example } \\
\hline \text { 1. } & \text { Free central } & \text { Dianthus } \\
\hline \text { 2. } & \text { Basal } & \text { Sunflower } \\
\hline \text { 3. } & \text { Axile } & \text { China rose } \\
\hline \text { 4. } & \text { Marginal } & \text { Mustard } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
Pea Having Marginal aestivation.
NCERT: In parietal
placentation, the ovules develop on the inner wall of the ovary or
on peripheral part. Ovary is one-chambered but it becomes two
chambered due to the formation of the false septum, e.g., mustard
and Argemone -
Question 39 of 45
39. Question
1 point(s)Identify A and B inflorescence:-
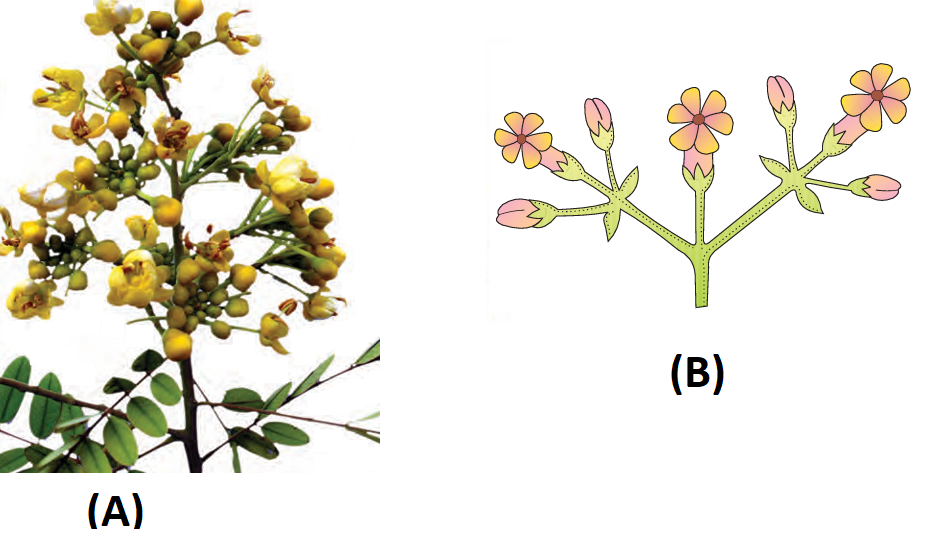 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 40 of 45
40. Question
1 point(s)The mature seed of plants such as gram and peas, possess no endosperm, because
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 41 of 45
41. Question
1 point(s)Match the followings and choose the correct option :
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Group A } & & \text { Group B } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Aleurone layer } & \text { i. } & \text { without fertilization } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Parthenocarpic fruit } & \text { ii. } & \text { Nutrition } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Ovule } & \text { iii. } & \text { Double fertilization } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Endosperm } & \text { iv. } & \text { Seed } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Options:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { i } & \text { ii } & \text { iii } & \text { iv } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { ii } & \text { i } & \text { iv } & \text { iii } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { iv } & \text { ii } & \text { i } & \text { iii } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { ii } & \text { iv } & \text { i } & \text { iii } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 42 of 45
42. Question
1 point(s)Given below is the diagram of a typical structure of monocotyledonous seeds. In which one of the options all the five parts A, B, C, D and E are correct?
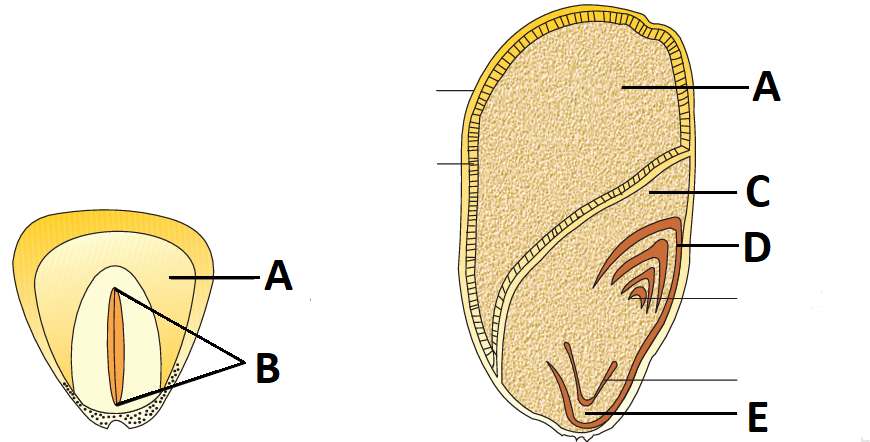 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 43 of 45
43. Question
1 point(s)Rearrange the following zones as seen in the root in vertical section and choose the correct option.
A. Root hair zone
B. Zone of meristems
C. Root-cap zone
D. Zone of maturation
E. Zone of elongationCorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 44 of 45
44. Question
1 point(s)Parts of the fruit: Figure – I – Mango, Figure – II – Coconut are shown in the following diagram. A, B, C and D are respectively
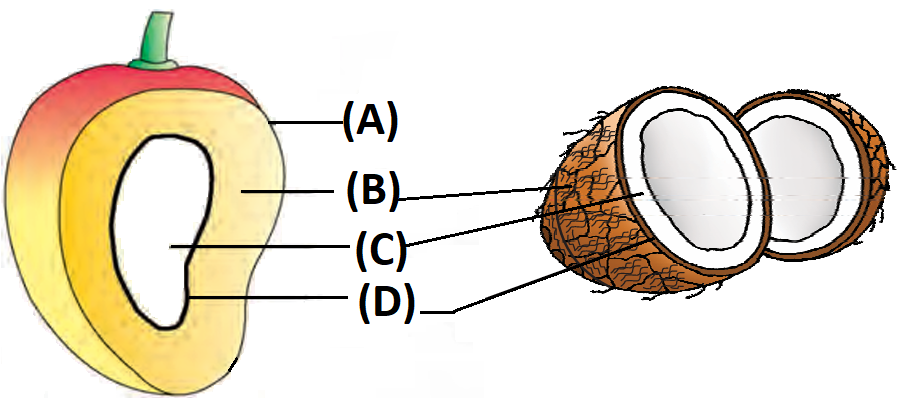 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 45 of 45
45. Question
1 point(s)Identify the correct features of Mango and Coconut fruits.
(i) In both, fruit is a drupe
(ii) Endocarp is edible in both
(iii) Mesocarp in Coconut is fibrous, and in Mango, it is fleshy
(iv) In both, the fruit develops from the monocarpellary ovary
Select the correct option from below :CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
(ii) Endocarp is edible in both
❌ Incorrect
- In mango, the edible part is the mesocarp (fleshy).
- In coconut, the edible part is the endosperm, not endocarp.
→ False