Cell Cycle and Cell Division NCERT
Quiz Summary
0 of 45 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 45 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 45
1. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given statements:
Statement I: If the initial number of chromosomes in a cell at \(
G_1
\) phase is 2 N and DNA content is 2 C , the number of chromosomes and the content of DNA at the end of the S-phase will be 4 N and 4 C .
Statement II: The cell replicates its DNA and doubles its number of chromosomes during the S-phase of the cell cycle.CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
Statement I:
If the initial number of chromosomes in a cell at G1G_1G1 phase is 2N2N2N and DNA content is 2C2C2C, the number of chromosomes and the content of DNA at the end of the S-phase will be 4N4N4N and 4C4C4C.
???? Incorrect:
-
In S-phase, the DNA replicates, so DNA content doubles, but the chromosome number does not double.
-
After S-phase:
-
DNA content becomes 4C
-
Chromosome number remains 2N (each chromosome has two sister chromatids, but it’s still counted as one chromosome)
-
Therefore, Statement I is incorrect.
Statement II:
The cell replicates its DNA and doubles its number of chromosomes during the S-phase of the cell cycle.
???? Incorrect:
-
DNA is replicated ✅ (correct)
-
But the number of chromosomes does not double ❌.
-
Chromosomes are duplicated in the sense that they now have sister chromatids, but they are still considered one chromosome until they separate during anaphase.
Hence, Statement II is also incorrect.
-
Question 2 of 45
2. Question
1 point(s)Identify the incorrect statement regarding the cell cycle of a typical eukaryotic cell:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Interphase is the resting stage in the cell cycle where the cell is metabolically active.
-
Question 3 of 45
3. Question
1 point(s)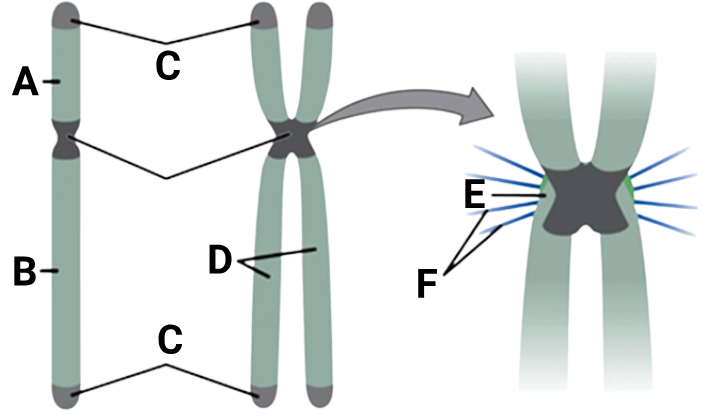
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline
\text{} & \text{A} & \text{B} & \text{C} & \text{D} & \text{E} & \text{F} \\
\hline
\text{1.} & \text{P arm} & \text{Q arm} & \text{Telomere} & \text{Non-sister chromatids} & \text{Centrosome} & \text{Spindle microtubules} \\
\hline
\text{2.} & \text{Q arm} & \text{P} & \text{Secondary constriction} & \text{Sister chromatids} & \text{Kinetochore} & \text{Polar microtubules} \\
\hline
\text{3.} & \text{P arm} & \text{Q arm} & \text{Telomere} & \text{Sister chromatids} & \text{Kinetochore} & \text{Spindle microtubules} \\
\hline
\text{4.} & \text{Q arm} & \text{P arm} & \text{Primary constriction} & \text{Non-sister chromatids} & \text{Centromere} & \text{Spindle microfilaments} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 4 of 45
4. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given two statements:
Statement I: In animals, mitotic cell division is only seen in the diploid somatic cells.
Statement II: Plants can show mitotic divisions in both haploid and diploid cells.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 5 of 45
5. Question
1 point(s)The correct chronology of stages of karyokinesis in mitosis is:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 6 of 45
6. Question
1 point(s)Mitosis is also called ‘equational division’ because:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 7 of 45
7. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given two statements:
I. Morphology of chromosomes is best studied at metaphase
II. At this stage, a chromosome is made up of two sister chromatids, held together at the centromereCorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
Both Statements are correct but actual reason for this assertion should be ” condensation of chromosomes is completed
and they can be observed clearly under the microscope”Reference NCERT
-
Question 8 of 45
8. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given two statements:I. Most adult neuronal cells in humans reside in a terminal \(
\mathrm{G}_0
\) phaseII. The adult neuronal cells are not very active metabolically and are not differentiated to a higher degree.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Statement II:
The adult neuronal cells are not very active metabolically and are not differentiated to a higher degree.
❌ Incorrect-
Neuronal cells are highly differentiated and metabolically very active, especially in terms of:
-
Neurotransmitter synthesis and signaling
-
Ionic balance maintenance
-
Energy consumption
-
-
Question 9 of 45
9. Question
1 point(s)At the metaphase plate:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 10 of 45
10. Question
1 point(s)Identify the correct statement amongst the following.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
Option 1:
Crossing over occurs in prophase I of meiosis and metaphase of mitosis.
❌ Incorrect-
Crossing over occurs only during prophase I of meiosis (specifically in pachytene stage).
-
It does not occur during mitosis at all.
Option 2:
DNA replication occurs once prior to mitosis and twice prior to meiosis.
❌ Incorrect-
DNA replication occurs once before both mitosis and meiosis (during S-phase of interphase).
-
Meiosis has two divisions, but only one round of DNA replication.
Option 3:
Both mitosis and meiosis result in daughter cells identical to the parent cells.
❌ Incorrect-
In mitosis, daughter cells are genetically identical to the parent cell.
-
In meiosis, daughter cells are not identical (due to crossing over and independent assortment), and they are haploid, not diploid.
-
Question 11 of 45
11. Question
1 point(s)Consider the following two statements:
I. Plant cells undergo cytokinesis in a different manner than the animal cells.
II. Plant cells are enclosed by a relatively inextensible cell wall.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 12 of 45
12. Question
1 point(s)Identify the incorrect statement regarding cytokinesis:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c0
Option 3:
The cell wall formation in plant cells starts near the existing lateral walls and grows inwards
❌ Incorrect-
Incorrect direction described.
-
In plant cells, the cell plate forms in the center of the cell and grows outward toward the lateral walls to separate the daughter cells.
-
Question 13 of 45
13. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given two statements:
Statement I: In animal cells, cytokinesis is achieved by the appearance of a furrow in the plasma membrane.
Statement II: During cytokinesis in plant cells, the formation of the new cell wall begins with the formation of a simple precursor called the cell plate that represents the middle lamella between the walls of the two adjacent cells.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 14 of 45
14. Question
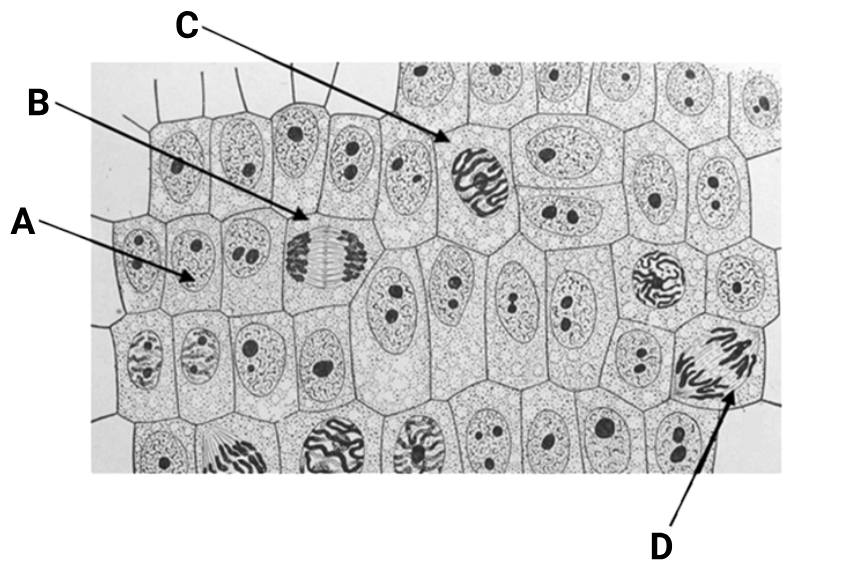
1 point(s)The given diagram shows a slide with cells labeled as A , B , C and D at different stages of cell division. Identify the correct match:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline
\text{} & \text{A} & \text{B} & \text{C} & \text{D} \\
\hline
\text{1.} & \text{Interphase} & \text{Telophase} & \text{Prophase} & \text{Anaphase} \\
\hline
\text{2.} & \text{Interkinesis} & \text{Anaphase} & \text{Prophase} & \text{Metaphase} \\
\hline
\text{3.} & \text{Interkinesis} & \text{Telophase} & \text{Metaphase} & \text{Anaphase} \\
\hline
\text{4.} & \text{Interphase} & \text{Prophase} & \text{Metaphase} & \text{Anaphase} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 15 of 45
15. Question
1 point(s)In meiosis:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Meiosis Overview:
-
DNA replication: Occurs once, during interphase before meiosis I.
-
Two divisions follow:
-
Meiosis I:
-
Homologous chromosomes separate
-
Chromosome number is reduced (diploid → haploid)
-
DNA content is also halved
-
-
Meiosis II:
-
Sister chromatids separate
-
DNA content is halved again, but chromosome number remains the same
-
-
What gets reduced when?
-
Chromosome number: Reduced once → during meiosis I
-
DNA content: Reduced twice → during meiosis I and meiosis II
-
Question 16 of 45
16. Question
1 point(s)\(
\text { Match each item in Column I with one in Column II and select the correct answer from the codes given below: }
\)\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline
\text{} & \text{Column I} & \text{} & \text{Column II} \\
\hline
\text{A} & \text{Zygotene} & \text{a} & \text{Pairing of homologous chromosomes} \\
\hline
\text{B} & \text{Pachytene} & \text{b} & \text{Appearance of chiasma} \\
\hline
\text{C} & \text{Diplotene} & \text{c} & \text{Terminalization of chiasma} \\
\hline
\text{D} & \text{Diakinesis} & \text{d} & \text{Crossing over} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Codes:
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { a } & \text { c } & \text { b } & \text { d } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { a } & \text { d } & \text { b } & \text { c } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { a } & \text { b } & \text { c } & \text { d } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { b } & \text { c } & \text { d } & \text { a } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 17 of 45
17. Question
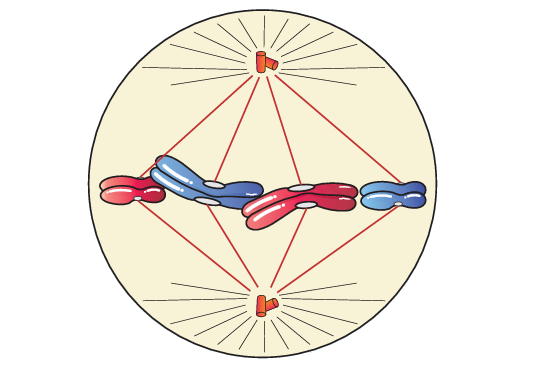
1 point(s)The cell shown in the given diagram is in which phase?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
NCERT Diagram
-
Question 18 of 45
18. Question
1 point(s)The correct chronology of stages of Prophase I is:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 19 of 45
19. Question
1 point(s)Which of the following is not a feature of diakinesis stage of prophase I of meiosis I?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Decondensation of chromatin – ❌ incorrect, because chromatin remains highly condensed in diakinesis.
-
Question 20 of 45
20. Question
1 point(s)Crossing over or recombination can be defined as:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 21 of 45
21. Question
1 point(s)The beginning of diplotene is recognized by:
I. dissolution of the synaptonemal complex
II. the tendency of recombined homologues of bivalents to separate
III. tetrads becoming clearly visibleCorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
Tetrads becoming clearly visible – ❌ Not exclusive to diplotene. Tetrads (bivalents) are already clearly visible by the pachytene stage when homologues are fully synapsed.
-
Question 22 of 45
22. Question
1 point(s)Consider the following statements regarding meiosis:
I. At metaphase I, the microtubules from the opposite poles of the spindle attach to the pair of homologous chromosomes.
II. At anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes separate, while sister chromatids remain associated with each other.
Of the two statements:CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Both are correct
-
Question 23 of 45
23. Question
1 point(s)Match the following with respect to meiosis:0
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline \text { (a) } & \text { Zygotene } & \text { (i) } & \text { Terminalization } \\
\hline \text { (b) } & \text { Pachytene } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Chiasmata } \\
\hline \text { (c) } & \text { Diplotene } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Crossing over } \\
\hline \text { (d) } & \text { Diakinesis } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Synapsis } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { (a) } & \text { (b) } & \text { (c) } & \text { (d) } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { (iv) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (i) } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { (i) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (iv) } & \text { (iii) } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { (ii) } & \text { (iv) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (i) } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { (iii) } & \text { (iv) } & \text { (i) } & \text { (ii) } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 24 of 45
24. Question
1 point(s)Consider the following two statements:
I. The growth of multi-cellular organisms is due to mitosis.
II. Mitosis results in the production of diploid daughter cells with identical genetic complement usually.Of the two statements:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
A better explanatory statement for growth would be something like:
“Mitosis increases the number of cells, allowing tissue and organ enlargement.”
-
Question 25 of 45
25. Question
1 point(s)The cell shown in the given diagram is in which phase:-
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 26 of 45
26. Question
1 point(s)Consider the following key events:
I. Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles and their identity is lost as discrete elements.
II. Nucleolus, Golgi complex and ER reform.
The stage of mitosis characterized by these key events is:CorrectIncorrect -
Question 27 of 45
27. Question
1 point(s)During diakinesis of prophase I:
I. Terminalisation of chiasmata takes place.
II. Meiotic spindle is assembled.
III. Nucleolus disappears and the nuclear membrane breaks down.
The correct statements are:CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
All are correct
-
Question 28 of 45
28. Question
1 point(s)The mechanisms that contribute to the genetic variation arising from sexual reproduction include:
I. Independent assortment of chromosomes
II. Crossing over
III. Random fertilizationCorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
All are correct
-
Question 29 of 45
29. Question
1 point(s)Consider the given two statements:
I. The kinetochore is essential for the chromosome segregation that is classically associated with mitosis and meiosis.
II. The kinetochore assembles on the centromere and links the chromosome to microtubule polymers from the mitotic spindle during mitosis and meiosis.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 30 of 45
30. Question
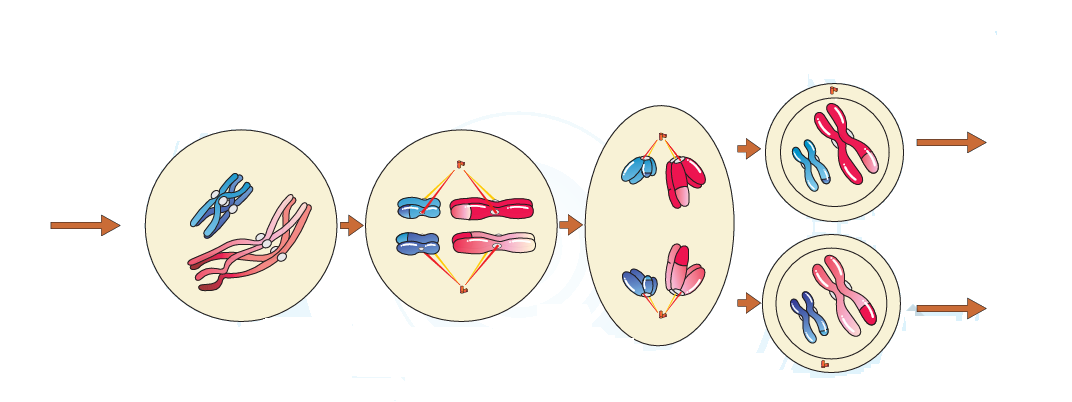
1 point(s)The cell shown in the given diagram is in which phase:-
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
NCERT diagram
-
Question 31 of 45
31. Question
1 point(s)Organisms prefer sexual mode of reproduction in adverse conditions because:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 32 of 45
32. Question
1 point(s)The most important significance of meiosis is that:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Increases variations – ✅ Important, but not the most fundamental.
-
Growth in multicellular organisms – ❌ That’s the role of mitosis, not meiosis.
-
Conserves specific number of chromosomes – ✅ Most essential function.
-
Repair and regeneration – ❌ Again, a function of mitosis.
Therefore, the correct answer is:
3. It conserves specific number of chromosomes in each species across generations.
-
Question 33 of 45
33. Question
1 point(s)Identify the correct statement regarding meiosis amongst the following:
I. Meiosis involves two sequential cycles of nuclear and cell divisions but only a single cycle of DNA replication.
II. Meiosis II is initiated after the parental chromosomes have replicated to produce identical sister chromatids at the S phase.
III. Meiosis involves pairing of bivalents and recombinations between them.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Statement II is incorrect
Reason:-
-
❌ Incorrect.
-
S phase DNA replication happens before meiosis I, not between meiosis I and II.
-
No DNA replication occurs before meiosis II.
-
Meiosis II begins with the chromosomes already replicated (as sister chromatids), but these were formed before meiosis I.
-
Question 34 of 45
34. Question
1 point(s)Cells at the end of prophase of mitosis, when viewed under the microscope, do not show:
I. Golgi complexes
II. Endoplasmic reticulum
III. Nucleolus
IV. Nuclear envelopeCorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
All are correct
-
Question 35 of 45
35. Question
1 point(s)How many of the following statements with respect to this phase are not incorrect ?
- Cell division proper lasts for only about an hour.
- This Phase represents the phase when the
actual cell division - In this phase Cell remains Metabolically inactive
- This phase is divided into three further phases
- This phase is also Known as Resting phase
- In this phase the time during which the cell is preparing for division
by undergoing only cell growth in an orderly manner.
CorrectIncorrectHint
1 and 2 statements are for M Phase not for interphase
3- Remains metabolically active
4. not only cell growth
Right statement the time during which the cell is preparing for division
by undergoing both cell growth and DNA replication in an orderly manner. -
Question 36 of 45
36. Question
1 point(s)Arrange the following events of meiosis in correct
sequence
(a) Crossing over
(b) Synapsis
(c) Terminalisation of chiasmata
(d) Disappearance of nucleolusCorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 37 of 45
37. Question
1 point(s)Match the following events that occur in their respective phases of cell cycle and select the correct option
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline \text { (a) } & \text { G }_1 \text { phase } & \text { (i) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Cell grows and organelle } \\
\text { duplication }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { (b) } & \text { S phase } & \text { (ii) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { DNA replication and } \\
\text { chromosome duplication }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { (c) } & \text { G }_2 \text { phase } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Cytoplasmic growth } \\
\hline \text { (d) } & \text { Metaphase } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Alignment of chromosomes } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { (a) } & \text { (b) } & \text { (c) } & \text { (d) } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { (ii) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (iv) } & \text { (i) } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { (iii) } & \text { (iv) } & \text { (i) } & \text { (ii) } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { (iv) } & \text { (i) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (iii) } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { (i) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (iv) } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 38 of 45
38. Question
1 point(s)Consider the following events:
I. Centromere split and chromatids separate
II. Chromatids move to opposite poles
The stage of mitosis characterized by these two events is:CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 39 of 45
39. Question
1 point(s)In meiosis, DNA replication occurs:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
In meiosis, DNA replication occurs:
-
Once — during the S phase before meiosis I.
-
After this, the cell undergoes two sequential divisions:
-
Meiosis I – homologous chromosomes separate.
-
Meiosis II – sister chromatids separate.
-
❌ No DNA replication occurs:
-
Before Meiosis II (interkinesis is a resting stage without DNA replication)
-
During Anaphase or any stage of division — because DNA is being segregated, not replicated.
-
Question 40 of 45
40. Question
1 point(s)Match the stage of meiotic cell division in column I with corresponding event in Column II and select the correct option from the codes given:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline
& \text{COLUMN I} & & \text{COLUMN II} \\
\hline
\text{A} & \text{Metaphase I} & \text{P} & \text{Homologous chromosomes separate, sister chromatids remain associated} \\
\hline
\text{B} & \text{Anaphase I} & \text{Q} & \text{Centromere splits} \\
\hline
\text{C} & \text{Metaphase II} & \text{R} & \text{Bivalents align at the equatorial plate} \\
\hline
\text{D} & \text{Anaphase II} & \text{S} & \text{Microtubules from the opposite poles get attached to kinetochores of sister chromatids} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Codes:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \mathrm{A} & \mathrm{~B} & \mathrm{C} & \mathrm{D} \\
\hline \text { 1. } & \mathrm{P} & \mathrm{R} & \mathrm{~S} & \mathrm{Q} \\
\hline \text { 2. } & \mathrm{P} & \mathrm{R} & \mathrm{Q} & \mathrm{~S} \\
\hline \text { 3. } & \mathrm{R} & \mathrm{P} & \mathrm{Q} & \mathrm{~S} \\
\hline \text { 4. } & \mathrm{R} & \mathrm{P} & \mathrm{~S} & \mathrm{Q} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 41 of 45
41. Question
1 point(s)Read the following statements and identify them as
true (T) or false (F) and accordingly choose the
correct option.
A. The compaction of chromosomal material
continues throughout leptotene
B. Bivalent clearly appear as tetrad in zygotene.
C. Cells are haploid with double DNA content after
meiosis-I as compared to \(
G_2
\)
phase.
D. Daughter cell produced after equational division
differ from one another but identical to the parent
cell
\(
\begin{array}{lllll}
&\text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\text { (1) } &\mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} \\
\text { (2) } &\mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~F} \\
\text { (3) } &\mathrm{F} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} \\
\text { (4) } &\mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~F}
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
B:- tetrads are clearly seen in pachytene, not zygotene
C:-DNA content is half that of G₂, not double
D:-daughter cells are not identical to parent due to recombination
-
Question 42 of 45
42. Question
1 point(s)If there are \(
30
\) chromosomes in \(
G_1
\)
phase then the
number of chromosomes in prophase-I of meiosis
will beCorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
n G₁ phase, chromosomes are single chromatid structures:
→ Diploid cell has 30 chromosomes -
After S phase, DNA is replicated → each chromosome becomes 2 chromatids, but chromosome number doesn’t change
-
In prophase I of meiosis, the chromosome number remains the same as G₁, though DNA content is doubled.
-
Question 43 of 45
43. Question
1 point(s)A diploid organism has \(
24
\) chromosomes in each
cell. If the number of chromosomes at G1
phase is \(
24
\), then what would be the number of chromosomes
just after S phase?CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
A diploid organism has 24 chromosomes in each cell. If the number of chromosomes at G₁ phase is 24, then what would be the number of chromosomes just after S phase?
-
After S phase, DNA replicates, but chromosome number remains 24
-
Each chromosome now has two sister chromatids, but still counted as one chromosome
-
Question 44 of 45
44. Question
1 point(s)How many homologous pairs of chromosomes will
be found in metaphase I of a diploid cell of an
angiospermic plant having \(
40
\) chromosomes in its
root meristematic cell?CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
If the root meristematic cell has \(
40
\)
chromosomes, it is diploid (2n = \(
40
\)
) -
In metaphase I, homologous chromosomes pair up as bivalents (tetrads)
-
\(
\text { So number of homologous pairs }=\frac{40}{2}=20
\)
-
Question 45 of 45
45. Question
1 point(s)Prophase is marked by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)