Biomolecules TS
Quiz Summary
0 of 20 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 20 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 20
1. Question
The given figure show as:-
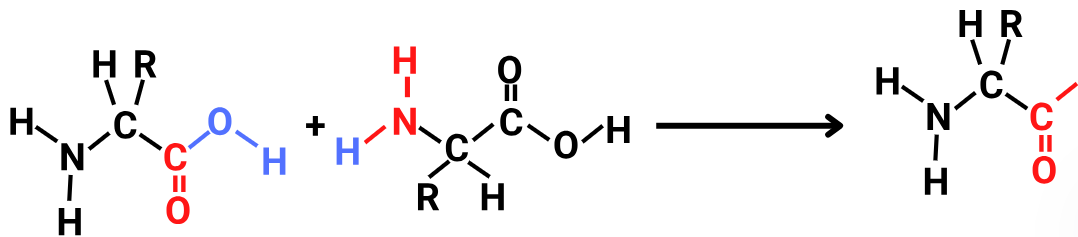 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 2 of 20
2. Question
An example of a metabolic conversion not catalyzed by an enzyme in a living system will be:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
1. Formation of a peptide bond – ✅ This is enzyme-catalyzed in living cells by ribosomes, which act as ribozymes (RNA enzymes).
- 2. Carbonic anhydrase enzyme envolved
-
3. Crossing over in meiosis – ✅ This process is mediated by proteins and enzymes like recombinases
-
Question 3 of 20
3. Question
Statement-I: Co-enzyme nicotinamide adenine
dinucleotide (NAD) and NADP contain a vitamin
niacin.
Statement-II: The association of co-enzyme
with apoenzyme is enduring.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
“The association of coenzyme with apoenzyme is transient or reversible, not enduring.”
-
Question 4 of 20
4. Question
Statement-I: Enzyme substrate complex is
short-lived.
Statement-II: Cofactors are bound to the
enzyme to make the enzyme catalytically
active.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 5 of 20
5. Question
An organic substance bound to an enzyme and
essential for its activity is;CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 6 of 20
6. Question
Triglyceride consists of:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 7 of 20
7. Question
Which of the following statements is incorrect
regarding proteins?CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
The first amino acid in the polypeptide chain
is called as N-terminal amino acid and the
last amino acid is called as C-terminal
amino acid -
Question 8 of 20
8. Question
Choose the incorrect statement w.r.t. enzyme
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
Incorrect: Most antibacterial drugs are non-competitive inhibitors or function by irreversibly inhibiting enzymes essential for bacterial survival (e.g., penicillin inhibiting transpeptidase). Competitive inhibitors are less commonly used in clinical settings due to issues like needing high concentrations to outcompete the natural substrate.
-
Question 9 of 20
9. Question
Identify the correct statement from those given
belowCorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
(A) Incorrect: Lipids, even with molecular weight <800 Da, are largely insoluble in acid due to their hydrophobic nature. They typically do not fall into the acid-soluble fraction.
-
(B) Incorrect: The acid-soluble fraction primarily contains small molecules (metabolites), not macromolecules like proteins, nucleic acids, polysaccharides, or lipids.
-
(C) Correct: Macromolecules such as proteins, DNA, RNA, and polysaccharides from cytoplasm and organelles are not soluble in acid and therefore become part of the acid-insoluble fraction.
-
(D) Incorrect: The acid-insoluble pool doesn’t exactly represent the cytoplasmic composition, as it excludes acid-soluble small molecules and includes macromolecules from organelles too.
-
Question 10 of 20
10. Question
Assertion (A): Exoskeleton of arthropods have a
complex polysaccharide ca led chitin.
Reason (R): Chitin is a polymer of sugar
derivative N-acetyl glucosamine.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 11 of 20
11. Question
Assertion (A): When the inhibitor closely
resembles the substrate in its molecular
structure and inhibits the activity of the enzyme,
it is known as competitive inhibitor.
Reason (R): In the presence of a competitive
inhibitor, the formation of the ES complex
increases.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
❌ Evaluation of Reason (R)
This statement is false. In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor competes with the substrate for the active site of the enzyme. This competition reduces the formation of the ES complex because the inhibitor occupies the active site, preventing substrate binding. Therefore, the presence of a competitive inhibitor decreases the formation of the ES complex, not increases it
-
Question 12 of 20
12. Question
Enzyme required for joining of C–O, C–S, C–N,
and P–O bonds is;CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
Ligases are a class of enzymes that facilitate the joining (ligation) of two molecules by forming new covalent bonds, often accompanied by the hydrolysis of ATP. Specifically, they catalyze the formation of bonds such as:
-
C–O (carbon–oxygen)
-
C–S (carbon–sulfur)
-
C–N (carbon–nitrogen)
-
P–O (phosphorus–oxygen)
-
Question 13 of 20
13. Question
Study the given statements.
I. In peroxidase and catalase, haem is the
prosthetic group and it is a part of the active
site of the enzyme.
II. The four main categories of macromolecules
present in living systems are proteins, nucleic
acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
III. Hydrolysis of starch into glucose is an organic
chemical reaction.
IV. The building blocks or monomers of nucleic
acid molecules are ca led nucleosides.
How many statements are correct?CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Total Three Statements are correct
Statement IV: The building blocks or monomers of nucleic acid molecules are called nucleosides.
❌ Incorrect. The monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides, not nucleosides. A nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar, and one or more phosphate groups. In contrast, a nucleoside comprises only the nitrogenous base and the sugar, lacking the phosphate group.
-
Question 14 of 20
14. Question
Assertion (A): Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA
consist of nucleotides only.
Reason (R): The heterocyclic compounds in
nucleic acids are the nitrogenous bases named
adenine, guanine, uracil, cytosine, and thymine.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
❌ Why Reason (R) is not a correct explanation of Assertion (A):
While both statements are individually true, Reason (R) does not directly explain why nucleic acids consist solely of nucleotides. The composition of nucleic acids as chains of nucleotides is due to the polymerization of these monomer units, involving the sugar and phosphate groups forming the backbone, with nitrogenous bases as side groups. The fact that nitrogenous bases are heterocyclic compounds is a structural detail of the bases themselves and does not explain the overall composition of nucleic acids.
-
Question 15 of 20
15. Question
Assertion (A): The primary structure of protein is
the positional information of amino acids in
protein.
Reason (R): An enzyme like any protein has a
primary structure only, i.e., amino acid sequence
of the protein.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
❌ Evaluating Reason (R):
While it’s accurate that enzymes, being proteins, possess a primary structure (their amino acid sequence), it’s incorrect to state that they have only a primary structure. Proteins, including enzymes, typically exhibit multiple levels of structure:
-
Secondary structure: Local folding patterns like α-helices and β-sheets.
-
Tertiary structure: The overall 3D shape of a single polypeptide chain.
-
Quaternary structure: The assembly of multiple polypeptide subunits.
These higher-order structures are crucial for the protein’s functionality
-
Question 16 of 20
16. Question
Statement I: Primary metabolites have
identifiable functions and play known roles in
normal physiological processes.
Statement II: Some secondary metabolites
have ecological importanceCorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 17 of 20
17. Question
Assertion: Metals ions are important for
functioning of cells.
Reason: Metal ions may act as co-factor for
several enzymes.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 18 of 20
18. Question
The three chemically distinct components of a
nucleotide are;CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
The three chemically distinct components of a nucleotide are:
-
Nitrogenous base (a heterocyclic compound)
-
Pentose sugar (a monosaccharide)
-
Phosphate group (derived from phosphoric acid)
-
Question 19 of 20
19. Question
What does the term ‘ash’ refer to in the analysis
of living tissue?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 20 of 20
20. Question
Even in the presence of malonate, the velocity of the reaction catalyzed by the enzyme succinic dehydrogenase can be increased by:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Malonate is a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase. It closely resembles the substrate succinate in structure and competes for binding at the enzyme’s active site. In competitive inhibition, increasing the concentration of the substrate (succinate) can overcome the inhibitor’s effect by outcompeting it for the active site, thereby increasing the reaction velocity. Doubtnut+1ScienceDirect+1Chemguide
Analysis of Other Options:
-
Increasing the temperature beyond 40°C: Enzymes have an optimal temperature range. Exceeding this range can lead to enzyme denaturation, reducing activity.
-
Decreasing the pH: Enzymes also have an optimal pH range. Altering the pH can affect enzyme structure and function, potentially decreasing activity. Decreasing the production of ATP by chemiosmosis: This process is downstream of the succinate dehydrogenase reaction in cellular respiration. Altering ATP production doesn’t directly influence the enzyme’s activity in the presence of malonate.