Animal Kingdom TS
Quiz Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
Match the following columns:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { (Parts/organs) } & \text { (Functions) } \\
\text { (A) Statocysts } & \text { (1) } \text { Radiating plates } \\
\text { (B) Radula } & \text { (2) } \text { Respiratory function } \\
\text { (C) Gills } & \text { (3) } \text { Organs of balance } \\
\text { (D) Tentacles } & \text { (4) } \text { Sensory organs } \\
\text { } & \text { (5) } \text { Organs of feeding }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(2)
[NCERT-I-44]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { (Parts/organs) } & \text { (Functions) } \\
\text { Statocysts } & – \text { Organs of balance } \\
\text { Radula } & – \text { Organs of feeding } \\
\text { Gills } & – \text { Respiratory function } \\
\text { Tentacles } & – \text { Sensory organs }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
Here two basic body forms of cniderians are given :
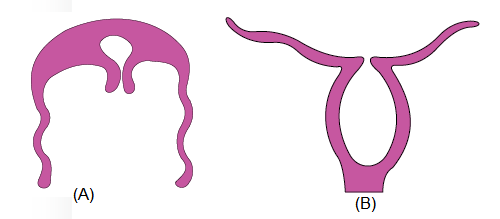 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-I-41]
B produce A asexually and A form the ‘B’ sexually -
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
Match the following columns:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } \text { (Specialised cell or part) } & \text { Column II } \text { (Animal phylum) } \\
\text { A. Choanocytes } & \text { 1. Platyhelminthes } \\
\text { B. Cnidoblasts } & \text { 2. Ctenophora } \\
\text { C. Flame cells } & \text { 3. Porifera } \\
\text { D. Nephridia } & \text { 4. Coelenterata } \\
\text { E. Comb Plates } & \text { 5. Annelida } \\
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-I-40,43]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { (Specialised cell } & \text { (Animal phylum) } \\
\text { Choanocytes } & – \text { Porifera } \\
\text { Cnidoblasts } & – \text { Coelenterata } \\
\text { Flame cells } & – \text { Platyhelminthes } \\
\text { Nephridia } & – \text { Annelida } \\
\text { Comb Plates } & – \text { Ctenophora }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: In Echinodermata water vascular system present which help in locomotion, capture and transport of food and respiration.
Statement II : In Scoliodon notochord is persistent through out life.
Choose the correct answer from the options given belowCorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-I-54] In Echinodermata water vascular system present which help in locomotion, capture and transport of food and respiration.
In Scoliodon notochord is persistent through out life. -
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
The space between hump and mantle is called mantle cavity in which A are present:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(2)
[NCERT-XI-53]
The space between the hump and the mantle is called the mantle cavity in which feather like gills are present. -
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
Read the following statement and choose correct option:
(i) Cyclostomes are marine but migrate for spawning to fresh water.
(ii) Cyclostomes have 6-15 pairs of gill slits for respiration.
(iii) In aves oil gland present at the base of tail
(iv) In aves hind limbs are modified into wings.CorrectIncorrectHint
(3)
[NCERT-I-56]
– Cyclostomes are marine but migrate for spawning to fresh water.
– Cyclostomes have 6-15 pairs of gill slits for respiration.
– In aves oil gland present at the base of tail
– In aves forelimbs are modified into wings. -
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
Which one of the following matching are correct :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-I-50]
Polyp – Hydra
Examples: Physalia (Portuguese man-of-war), Adamsia (Sea anemone), Pennatula (Sea-pen), Gorgonia (Sea-fan) and Meandrina (Brain coral). -
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
Match the following columns:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { a. Ascaris } & \text { i. King crab } \\
\text { b. Gorgonia } & \text { ii. Sea lily } \\
\text { c. Limulus } & \text { iii. Round worm } \\
\text { d. Antedon } & \text { iv. Sea fan }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
\(
\begin{aligned}
&\text { (4) }\\
&\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Ascaris } & – \text { Round worm } \\
\text { Gorgonia } & – \text { Sea fan } \\
\text { Limulus } & – \text { King crab } \\
\text { Antedon } & – \text { Sea lily }
\end{array}
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
Match the following columns:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { a. Pristis } & \text { i. Electric organ } \\
\text { b. Trygon } & \text { ii. Flying fish } \\
\text { c. Carcharodon } & \text { iii. Saw fish } \\
\text { d. Torpedo } & \text { iv. Great white shark } \\
\text { e. Exocoetus } & \text { v. sting ray }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(2) [NCERT-I-57]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Pristis } & – \text { Saw fish } \\
\text { Trygon } & – \text { sting ray } \\
\text { Carcharodon } & – \text { Great white shark } \\
\text { Torpedo } & – \text { Electric organ } \\
\text { Exocoetus } & – \text { Flying fish }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
Which is a correct matching set:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { a. Metamerism } & \text { i. Canal system constituent } \\
\text { b. Spongocoel } & \text { ii. Leech } \\
\text { c. Acoelomate } & \text { iii. Apis } \\
\text { d. Honey bee } & \text { iv. Platyhelminthes }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
Metamerism – Leech
Spongocoel – Canal system constituent
Acoelomate – Platyhelminthes
Honey bee – Apis -
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
Which is a correct matching set:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { a. Compound eye } & \text { i. Arthropoda } \\
\text { b. Stomochord } & \text { ii. Mollusca } \\
\text { c. Gills } & \text { iii. Saccoglossus } \\
\text { d. Mantle cavity } & \text { iv. Pisces }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(2) [NCERT-I-53,54]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Compound eye } & – \text { Arthropoda } \\
\text { Stomochord } & – \text { Saccoglossus } \\
\text { Gills } & – \text { Pisces } \\
\text { Mantle cavity } & – \text { Mollusca }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
How many animals among following have jointed appendages :
Bombyx, Apis, Limulus, Sepia, Octopus, EarthwormCorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NCERT-I-53]
All arthropods have jointed appendages. -
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
Given below are two statements :
Statement I: Platyhelminthes are hermaphrodite and fertilisation is internal occur.
Statement II : Sponges are exclusively marine and mostly are asymetrical.
Choose the correct answer from the options given belowCorrectIncorrectHint
(2)
[NCERT-I-49]
Platyhelminthes are hermaphrodite and fertilisation is internally occur.
Sponges are generally marine and some fresh water sponges and mostly are asymetrical. -
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
Notochord is derived from:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(2)
[NCERT-I-48]
Notochord is a mesodermally derived rod-like structure formed on the dorsal side during embryonic development in some animals. -
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
Match the following columns:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } \text { (Cnidarian) } & \text { Column II } \text { (Common names) } \\
\text { A. Pennatula } & \text { 1. Brain coral } \\
\text { B. Meandrina } & \text { 2. Sea fan } \\
\text { C. Gorgonia } & \text { 3. Sea pen } \\
\text { D. Adamsia } & \text { 4. Sea anemone }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(1) [NCERT-I-41]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { (Cnidarian) } & \text { (Common names) } \\
\text { Pennatula } & – \text { Sea pen } \\
\text { Meandrina } & – \text { Brain coral } \\
\text { Gorgonia } & – \text { Sea fan } \\
\text { Adamsia } & – \text { Sea anemone }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
Match the following columns:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } \text { (Common name arthropdoes) } & \text { Column II } \text { (Scientific names) } \\
\text { A. Honeybee } & \text { 1. Aedes } \\
\text { B. Mosquito } & \text { 2. Apis } \\
\text { C. Lac insect } & \text { 3. Laccifer } \\
\text { D. Silkworm } & \text { 4. Bombyx }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(3) [NCERT-I-44]
\(
\begin{array}{cl}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { (Common name anthropdoes} & \text { (Scientific names) } \\
\text { Honeybee } & – \text { Apis } \\
\text { Mosquito } & – \text { Aedes } \\
\text { Lac insect } & – \text { Laccifer } \\
\text { Silkworm } & – \text { Bombyx }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
Given below are two statements :
Statement I: In chondrichthyes Notochord persistant throught life.
Statement II : In Aves respiration occur by lungs and airsacs connected to lungs suppliment respiration.
Choose the correct answer from the options given belowCorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-II-56,58,59]
In chondrichthyes Notochord persistant throught life.In Aves respiration occur by lungs and Airsacs connected to lungs suppliment respiration.
-
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
Match the column I with column II and choose correct option:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { A. Viviparous Vertebrate } & \text { i. Scoliodon } \\
\text { B. Oviparous Vertibrate } & \text { ii. Labeo } \\
\text { C. Flying vertebrate } & \text { iii. Pteropus } \\
\text { } & \text { iv. Macropus } \\
\text { } & \text { v. Neophron }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(2)
[NCERT-XI-55,56,57]
\(
\begin{array}{lll}
\text { Viviparous Vertebrate } & – & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Scoliodon } \\
\text { Pteropus, } \\
\text { Macropus, }
\end{array} \\
\text { Oviparous Vertibrate – } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Labeo, } \\
\text { Neophron }
\end{array} \\
\text { Flying vertebrate } & – & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Pteropus, } \\
\text { Neophron }
\end{array}
\end{array}
\) -
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
How many of the following organism is not hermaphrodite
sponge, cockroach, leech, earthworm, tape wormCorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NC-II-11]
Earthworms, sponge, tapeworm and leech, typical examples of bisexual animals that possess both male and female reproductive organs, are hermaphrodites. Cockroach is an example of a unisexual species. -
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
Given below are two statements :
Statement I: In Cephalochordates notochord is present only in larval tail.
Statement II : In urochordates notochord extends from head to tail and persist throughout life.
Choose the correct answer from the options given belowCorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NCERT-I-55]
In Urochordates notochord is present only in larval tail.In Cephalochordates notochord extends from head to tail and persist throughout life.
-
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
In phylum porifera, water transport is helpful in
CorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-I-49]
This pathway of water transport is helpful in food gathering, respiratory exchange and removal of waste porifera phylum. -
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
Match the column A with column B:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column A } & \text { Column B } \\
\text { a. Columba } & \text { i. Vulture } \\
\text { b. Psittacula } & \text { ii. Penguin } \\
\text { c. Aptenodytes } & \text { iii. Parrot } \\
\text { d. Neophron } & \text { iv. Pigeon }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(3)
[NCERT-I-59]
Columba-Pigeon
Psittacula – Parrot
Aptenodytes-Penguin
Neophron-Vulture -
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
Match the column I with column II:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { A. Bufo } & \text { i. Frog } \\
\text { B. Hyla } & \text { ii. Tree frog } \\
\text { C. Ichthyophis } & \text { iii. Toad } \\
\text { D. Rana } & \text { iv. Limbless amphibia }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(3)
[NC-I-57]
Bufo-Toad
Rana-Frog
Hyla-Tree frog
Ichthyophis-Limbless amphibia -
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
Choose the correct statement about the phylum chordata:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(2)
[NC-I-55]
vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates. -
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
Which one of the following is not a characteristics of phylum annelida :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(2)
[NCERT-I-52]
They are triploblastic, metamerically segmented and coelomate animals. -
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
Which one of the following kinds of animals are triploblastic:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NCERT-I-52]
They are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and pseudocoelomate animals. -
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
Select the correct statements for amphibia :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-I-57]
The eyes have eyelids. Atympanum represents the ear. -
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
Choose the economically important insects :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-I-53]
Economically important insects – Apis (Honey bee), Bombyx (Silkworm), Laccifer (Lac insect) -
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
Match the column I with column II:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { A. Hippocampus } & \text { i. Fighting fish } \\
\text { B. Beta } & \text { ii. Sea horse } \\
\text { C. Clarias } & \text { iii. Rohu } \\
\text { D. Labeo } & \text { iv. Magur }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NCERT-I-57]
Hippocampus-Sea horse
Beta – Fighting fish
Clarias – Magur
Labeo – Rohu -
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
Malpighian tubules are :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NCERT-I-53]
Excretion takes place through malpighian tubules -
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
Select the correct statements with reference to sponge:
a. These are primitive multicellular animals and have cellular level of organization
b. Sponges have a water canal system
c. Sponges reproduce sexually by fragmentation and asexually by formation of gametes
d. Choanocytes or collar cells line the spongocoel and the canalsCorrectIncorrectHint
(3)
[NCERT-I-49]
These are primitive multicellular animals and have cellular level of organisation.
Sponges have a water transport or canal system.
Choanocytes or collar cells line the spongocoel and the canals -
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
Match the column I with column II and select the correct option:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { A. Wings } & \text { i. Reptiles } \\
\text { B. Operculum } & \text { ii. Chondrichthyes } \\
\text { C. Scutes } & \text { iii. Birds } \\
\text { D. Cartilaginous endoskeleton } & \text { iv. Osteichthyes }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NCERT-I-56,58,59]
Wings – Birds
Operculum – Osteichthyes
Scutes – Reptiles
Cartilaginous endoskeleton – Chondrichthyes -
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
How many statements are incorrect with respect to class reptilia
(A) Creeping or crawling mode of locomotion
(B) They are mostly terrestrial animal
(C) They have external ear opening
(D) Snakes and lizard shed their scales as skin cast
(E) Limbs when present are two pairs
(F) Heart is usually four chambered but three chambered in crocodile
(G) They are HomoiothermsCorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-I-58]
The class name refers to their creeping or crawling mode of locomotion (Latin, repere or reptum, to creep or crawl). They are mostly terrestrial animals and their body is covered by dry and cornified skin, epidermal scales or scutes. They do not have external ear openings. Tympanum represents ear. Limbs, when present, are two pairs. Heart is usually three-chambered, but four-chambered in crocodiles. Reptiles are poikilotherms. Snakes and lizards shed their scales as skin cast. Sexes are separate. Fertilisation is internal. They are oviparous and development is direct. -
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
Given below are two statements :
Statement I: Bioluminescence is well marked in ctenophores
Statement II : Feather like gills are present in molluscs which help in respiration and excreation.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given belowCorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-I-51,55]
Bioluminescence is well marked in ctenophores Feather like gills are present in molluses which help in respiration and excreation. -
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
Which is the matching correct set:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { a. Pinctada } & \text { i. Tusk shell } \\
\text { b. Sepia } & \text { ii. Devil fish } \\
\text { c. Dentalium } & \text { iii. Pearl oyster } \\
\text { d. Octopus } & \text { iv. Cuttle fish }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NCERT-56, 57]
Pinctada – Pearl oyster
Sepia – Cuttle fish
Dentalium – Tusk shell
Octopus – Devil fish -
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
Which one of the following pair of animals are jawless
CorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-I-56]
Members of cyclostomata are jawless vertebrate animals.Petromyzon (Lamprey) and myxine (Hag fish) are members of cyclostomata.
-
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
In the given below example, How many animals in which two chambered heart occurs :
Dog fish, Saw fish, Flying fish, Hyla, Bufo, Salamandra, ClariasCorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NCERT-I-57]
In pisces two chambered heart occurs. In amphibia three chambered heart i.e., 2 auricle and one ventricle. -
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
The radial symmetry occurs in which phylum
a. Coelenterata
b. Ctenophora
c. Adult antedon
d. ChordataCorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NCERT-I-47]
Radial symmetry are occurs in which phylum Coelentrata, Ctenophora, Echinodermata . -
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
Which is the matching columns:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I (Scientific names) } & \text { Column II (Common names) } \\
\text { A. Ancylostoma } & \text { 1. Hook worm } \\
\text { B. Wuchereria } & \text { 2. Filaria worm } \\
\text { C. Ascaris } & \text { 3. Roundworm } \\
\text { D. Fasciola } & \text { 4. Liver fluke } \\
\text { } & \text { 5. Flatworms } \\
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(4) [NCERT-I-42,43]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { (Scientific names) } & \text { (Common names) } \\
\hline \text { Ancylostoma } & \text { – } & \text { Hook worm } \\
\hline \text { Wucheria } & \text { – } & \text { Filaria worm } \\
\hline \text { Ascaris } & \text { – } & \text { Roundworm } \\
\hline \text { Fasciola } & \text { – } & \text { Liver fluke } \\
\end{array}
\) -
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
Which is the matching columns:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I (Scientific names) } & \text { Column II (Common names) } \\
\text { A. Branchiostoma } & \text { 1. Hagfish } \\
\text { B. Petromyzon } & \text { 2. Lamprey } \\
\text { C. Trygon } & \text { 3. Sting ray } \\
\text { D. Myxine } & \text { 4. Ascidia } \\
\text { } & \text { 5. Amphioxus } \\
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(4) [NCERT-I-47,48]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { (Scientific names) } & \text { (Common names) } \\
\text { Branchiostoma } & – \text { Amphioxus } \\
\text { Petromyzon } & – \text { Lamprey } \\
\text { Trygon } & – \text { Sting ray } \\
\text { Myxine } & – \text { Hagfish }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
Funaria plant body is attached to the substratum by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NCERT-I-36]
They are attached to the soil through multicellular and branched rhizoids. -
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
In cycas
CorrectIncorrectHint
(2)
[NCERT-I-39]
In cycas male cones and magasporophylls are borne on different trees -
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
Which of the following is not a member of phylum porifera
CorrectIncorrectHint
(2)
[NCERT-I-41]
Sea anemon are member of phylum coelenterata. -
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
In how many groups Aristotle divided animals on the basis of presence/absence of RBC?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(2)
[NCERT-I-16]
Aristotle was the earliest to attempt a more scientific basis for classification. He used simple morphological characters to classify plants into trees, shrubs and herbs. He also divided animals into two groups, those which had red blood and those that did not. -
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
Examine the figures A, B and C. In which one of the four options about the animals (poriferans) are correct?
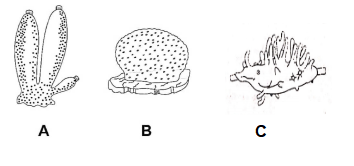 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(1)
[NCERT-I-40]
A – Sycon, B – Euspongia, C – Spongilla -
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
An undifferentiated layer Mesoglea is present in :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(3)
[NCERT-I-47]
Undifferentiated layer mesogloea is present in coelenterata. -
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
In the given below example how many are dioecious animals :
Leech, Earthworm, Hookworm, Fasciola, Tapeworm, NereisCorrectIncorrectHint
(3)
[NCERT-I-52]
Leach, Earthworm, Flatworm Tapewrom = Monoecious
Hook worm, Nereis = Dioecious -
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
Following features belong to
A. Complete lacking of cell wall
B. Anaerobic
C. Smallest living cell
D. Many of them are pathogenic to plants and animalsCorrectIncorrectHint
(4)
[NCERT-I-20]
The Mycoplasma are organisms that completely lack a cell wall. They are the smallest living cells known and can survive without oxygen. Many mycoplasma are pathogenic in animals and plants. -
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
Order Carnivora includes family:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(3)
[NCERT-XI-10]
The animal order, Carnivora, includes families like Felidae and Canidae. -
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
Which of the following organism form water bloom in polluted water body:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(3)
[NCERT-XI-19]
Cynobacteria often form blooms in polluted water bodies.