CH7- Structural Organisation in Animals
Q1. Mark the statement as true or false
(a) In unicellular organisms all the functions are performed by single cell.
(b) In the complex body of multicellular animals different functions are carried out by different group of cells.
(c) In multicellular animals, a group of similar cells along with intercellular substances perform a specific function. Such an organisation is called tissue.
(d) The functions of cells vary according to their structure.
Answer: (a) – True, (b) – True, (c) – True, (d) – False
Q2. This tissue has a free surface, which faces either a body fluid or the outside environment and thus provides a covering or a lining for some part of the body. The cells are compactly packed with little intercellular matrix. This tissue is __________.
Answer: Epithelial tissue
Q3. ______________ epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells and functions as a lining for body cavities, ducts and tubes.
Answer: Simple
Q4. ____________ epithelium consists of two or more cell layers and has protective function as it does in our skin.
Answer: Compound
Q5. This epithelium is found in (marked by the line)
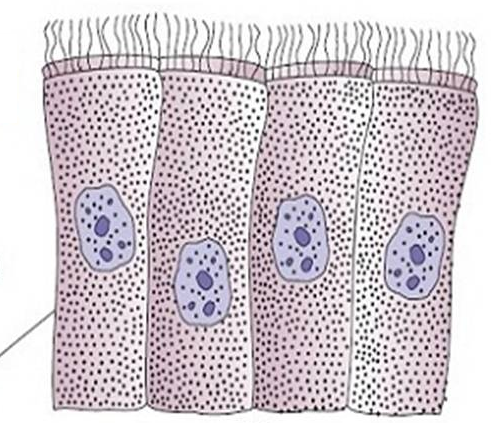
Answer: Fallopian tubes, Brain ventricles
Q6.
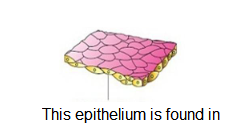
Answer: Air sacs and blood vessels
Q7. The __________ epithelium is made of a single thin layer of flattened cells with irregular boundaries.
Answer: simple squamous
Q8. The __________ epithelium is composed of a single layer of cube-like cells. This is commonly found in __________ and tubular parts of nephrons in kidneys and its main functions are _________ and __________.
Answer: Cuboidal, Ducts of glands, Secretion, Absorption
Q9. The epithelium of ________ of nephron in the kidney has microvilli.
Answer: Proximal convoluted tubule
Q10. Columnar epithelium is found in the walls of _______ and _________.
Answer: Stomach, intestine
Q11. What is the function of Cilia?
Answer: Cilia are microscopic hairs that line cells in various organs and help with fluid movement, sensory perception, and disease prevention.
Q12. Bronchioles and fallopian tubes are lined by _______.
Answer: Ciliated epithelium
Q13. Some of the columnar or cuboidal cells get specialised for secretion and are called __________ epithelium.
Answer: glandular
Q14. ___________ glands secrete mucus, saliva, earwax, oil, milk, digestive enzymes and other cell products.
Answer: Exocrine
Q15. ___________ epithelium is made of more than one layer (multi-layered) of cells and thus has a limited role in __________.
Answer: Compound, Secretion and absorption
Q16. Write the functions of compound epithelium.
Answer: To provide protection against chemical and mechanical stress
Q17. __________ junctions help to stop substances from leaking across a tissue.
Answer: To provide protection against chemical and mechanical stress
Q18. __________ junctions perform cementing to keep neighbouring cells together.
Answer: Adhering
Q19. __________ junctions facilitate the cells to communicate with each other by connecting the cytoplasm of adjoining cells, for rapid transfer of ions, small molecules and sometimes big molecules.
Answer: Gap
Q20. _________ tissues are most abundant and widely distributed in the body of complex animals.
Answer: Connective
Q21. Connective tissues are named as connective tissues. Why?
Answer: Because of their special function of linking and supporting other tissues /organs of the body.
Q22. In all connective tissues except _________ the cells secrete fibres of structural proteins called collagen or elastin.
Answer: Blood
Q23. Connective tissue’s are classified into three types :
(i). ________ connective tissue, (ii) _________ connective tissue and (iii) ___________ connective tissue.
Answer: (i) loose, (ii) dense, (iii) specialised
Q24. __________ connective tissue has cells and fibres loosely arranged in a semi-fluid ground substance, for example, areolar tissue present bencath the skin.
Answer: Loose
Q25. Loose connective tissue which store fat is
Answer: adipose
Q26. In the _________ connective tissues, the collage fibres are present in rows between many parallel bundles of fibres ________which attach skeletal muscles to bones and _________ which attach ono hone to another are examples of this tissue.
Answer: Dense regular, tendons, ligaments
Q27. The intercellular material of cartilage is __________ and ___________ and resists compression.
Answer: solid, pliable
Q28. Most of the cartilages in vertebrate embryos are replaced by _________ in adults.
Answer: bones
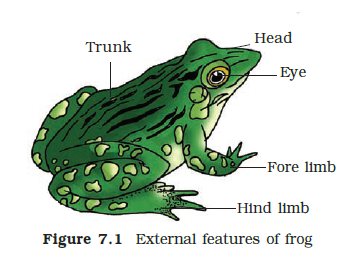
Q29. Show external features of frog in a diagram.
Answer:
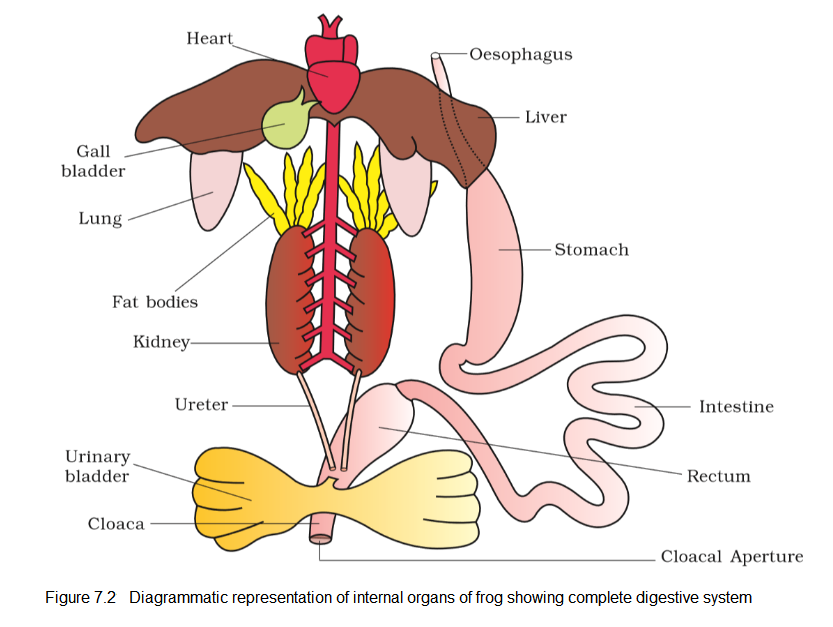
Q30. Draw the Diagrammatic representation of internal organs of frog showing complete digestive system.
Answer:
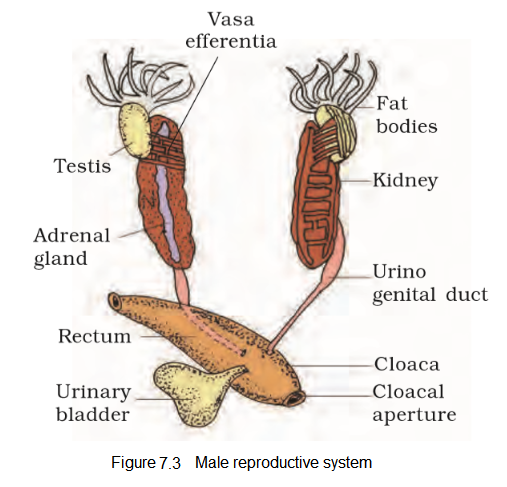
Q31. Draw the mail Male reproductive system.
Answer:
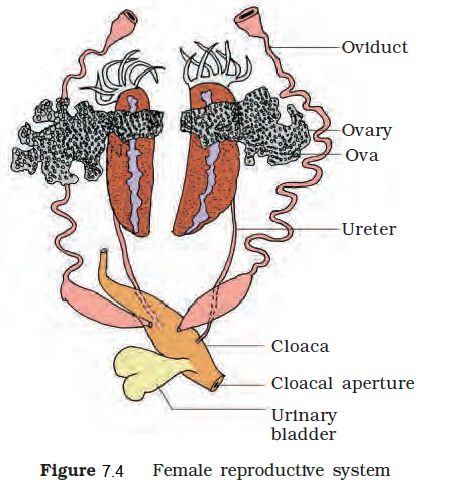
Q32. Draw the female reproductive system
Answer:
Q33.
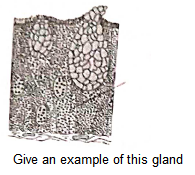
Answer: Goblet cells
Q34. Identify A, B, C, D, E and F in the given diagram
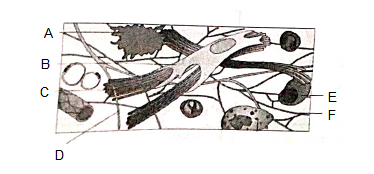
Answer: (A) MACROPHAGE, (B) FIBROBLASTS, (C) COLLAGEN FIBERS, (D) ELASTIN FIBRES, (E) LYMPHOCYTE, (F) RETICULAR FIBRES