CH4- Animal Kingdom
Q1. Members of which phylum are commonly known as sponges?
Answer: Porifera
Q2. Which type of symmetry is mostly found in sponges?
Answer: Asymmetry
Q3. Presence of water transport system is characteristic of which phylum?
Answer: Porifera(Sponges)
Q4. What is the name of pores through which water enters into the body of sponges?
Answer: Ostia
Q5. What is the name of pore through which water comes out from body of sponges?
Answer: Osculum
Q6. What is the name of central cavity found in the body of members of phylum porifera?
Answer: Spongocoel (Para gastric cavity)
Q7. What is the function of water canal system in sponges?
Answer: Food gathering, respiratory exchange and removal of waste.
Q8. What is the name of cells those line the spongocoel?
Answer: Choanocytes or collar cells.
Q9. Name the structures which support the body of sponges as a skeleton:
Answer: Spicules and spongin fibres.
Q10. The animals which don’t have separate sexes are called as :
Answer: Hermaphrodite (Bisexual)
Q11. When development of an organism occurs through larval stage, then this type of development is called as :
Answer: Indirect development
Q12. Which type of symmetry is found in coelenterates?
Answer: Radial symmetry
Q13. Name the cell that is used for defense purposes in coelenterates.
Answer: Cnidoblast
Q14. Which cnidarians possess a skeleton made up of calcium carbonate?
Answer: Corals
Q15. The alternation of Polyp and Medusa forms in coelenterates is called as :
Answer: Metagenesis
Q16. Which organism is also known as Portuguese man of war?
Answer: Physalia
Q17. Members of which phylum are commonly known as sea walnuts or comb jellies?
Answer: Ctenophora
Q18. Which structure helps in locomotion in ctenophores?
Answer: Comb plates
Q19. The property of a living organism to emit light is called as :
Answer: Bioluminescence
Q20. Members of which phylum are known as flatworms?
Answer: Platyhelminthes
Q21. Which type of symmetry is found in the members of phylum platyhelminthes?
Answer: Bilateral symmetry
Q22. Structures which help in osmoregulation and excretion in flatworms are called.
Answer: Flame cells
Q23. Members of which phylum are also known as roundworms?
Answer: Aschelminthes (Nematoda)
Q24. Name the phylum in which organ system level of body organisation appeared for the first time :
Answer: Aschelminthes (Nematoda)
Q25. Which phylum of animals possess pseudocoelomic type of body cavity?
Answer: Aschelminthes (Nematoda)
Q26. Which structures help in osmoregulation and excretion in Annelids ?
Answer: Nephridia
Q27. The body of annelids is distinctly marked out into segments. These segments are called as :
Answer: Metameres
Q28. Name the largest phylum of animal kingdom.
Answer: Arthropoda
Q29. The exoskeleton of arthropods is made up of
Answer: Chitin
Q30. The name of the balancing organ in arthropods.
Answer: Statocyst
Q31. What is the main function of malpighian tubules?
Answer: Excretion
Q32. Name the organism which produces silk.
Answer: Bombyx (Silk worm)
Q33. Name the organism which produces lac.
Answer: Laccifer (Lac insecta)
Q34. Name the second largest phylum of animal kingdom :
Answer: Mollusca
Q35. The soft and spongy layer of skin over the visceral hump of molluscs is known as :
Answer: Mantle
Q36. In which phylum the mantle cavity is found?
Answer: Mollusca
Q37. What is the name of file like rasping organ found in molluscs?
Answer: Radula
Q38. Animals of which phylum are reared for the production of pearls?
Answer: Mollusca
Q39. In which phylum the spiny bodied organisms are included?
Answer: Echinodermata
Q40. In which phylum organisms alter their symmetry from bilateral to radial during the development?
Answer: Echinodermata
Q41. Members of which phylum have ventral mouth and dorsal anus?
Answer: Echinodermata
Q42. Water vascular system is a characteristic of which phylum?
Answer: Echinodermata
Q43. Name the excretory organ of balanoglossus:
Answer: Proboscis gland
Q44. Which subphylums are classified under protochordates?
Answer: Urochordata and Cephalochordata
Q45. In which subphylum notochord is present only in larval tail?
Answer: Urochordata
Q46. In which subphylum notochord extends from head to tail and is persistent throughout the life?
Answer: Cephalochordata
Q47. In which subphylum notochord is replaced by vertebral column?
Answer: Vertebrata
Q48. Animals of which class possess a sucking and circular mouth without jaws?
Answer: Cyclostomata
Q49. In which class of fishes mouth is located ventrally?
Answer: Chondrichthyes
Q50. Which types of scales are found on the body of cartilaginous fishes?
Answer: Placoid scales
Q51. In which class of fishes notochord is persistent throughout the life?
Answer: Chondrichthyes
Q52. The teeth of cartilaginous fishes are formed due to modification of which type of scales?
Answer: Placoid scales
Q53. What is the name of structure which prevents the bony fishes from sinking?
Answer: Air bladder
Q54. Why cartilaginous fishes have to swim constantly?
Answer: Because they lack air bladder
Q55. Name a fish which has electric organ.
Answer: Torpedo
Q56. Name a fish which possess poisonous sting.
Answer: Trygon
Q57. The animals which don’t have the capacity to regulate their body temperature are called as __________ .
Answer: Poikilothermous
Q58. The animals which have the capacity to regulate their body temperature are called as __________.
Answer: Homoiothermous
Q59. How many pairs of gills are present in bony fishes?
Answer: 4-pairs
Q60. Name the cap which covers the gills in osteichthyes fishes :
Answer: Operculum
Q61. Which structure represents ear in amphibians and reptiles ?
Answer: Tympanum
Q62. In which class of vertebrates 3-chambered heart is found?
Answer: Amphibia and Reptilia
Q63. The common chamber for alimentary canal, urinary bladder and reproductive tracts is called as :
Answer: Cloaca
Q64. Which class of vertebrates possesses dry and cornified skin with epidermal scales or scutes?
Answer: Reptilia
Q65. In which reptiles 4-chambered heart is present?
Answer: Crocodiles
Q66. Snakes and lizards shed off their scales. This phenomenon is called as :
Answer: Skin cast
Q67. The presence of feathers is characteristic of which class?
Answer: Aves
Q68. The long bones of birds are hollow with air cavities. These types of bones are called as :
Answer: Pneumatic bones
Q69. Name of the additional chambers found in the digestive tract of birds:
Answer: Crop and Gizzard
Q70. Name the respiratory organs in birds and mammals :
Answer: Lungs
Q71. Presence of mammary gland is the unique character of which class?
Answer: Mammalia
Q72. Name an oviparous animal with presence of mammary glands:
Answer: Ornithorhynchus(Platypus)
Q73. Name the phyla which have radial symmetry:
Answer: Coelenterata, Ctenophora,Echinodermata (adult)
Q74. The undifferentiated layer present between ectoderm and endoderm in diploblastic animals is known as :
Answer: Mesoglea
Q75. A body cavity in which mesoderm is found in scattered form is called as :
Answer: Pseudocoelom
Q76. Match the columns:
(A) Sycon (i) Bath sponge
(B) Spongilla (ii) Scypha
(C) Euspongia (iii) Fresh water sponge
Answer:
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \text { (A)-(ii) } \\
& \text { (B)-(iii) } \\
& \text { (C)-(i) }
\end{aligned}
\)
Q77. Match the columns :
(A) Adamsia (i) Sea fan
(B) Pennatula (ii) Brain coral
(C) Gorgonia (iii) Sea pen
(D) Meandrina (iv) Sea anemone
Answer:
(A)-(iv)
(B)-(iii)
(C)-(i)
(D)-(ii)
Q78. Match the columns:
(A) Taenia (i) Filaria worm
(B) Fasciola (ii) Round worm
(C) Ascaris (iii) Tapeworm
(D) Wuchereria (iv) Hook worm
(E) Ancylostoma (v) Liver fluke
Answer:
(A)-(iii)
(B) (v)
(C)-(ii)
(D)-(i)
(E)-(iv)
Q79. Match the columns :
(A) Pheretima (i) King crab
(B) Hirudinaria (ii) Honey bee
(C) Apis (iii) Earthworm
(D) Limulus (iv) Blood sucking leech
Answer:
(A)-(iii)
(B)-(iv)
(C)-(ii)
(D)-(i)
Q80. Match the columns:
(A) Pila (i) Devil fish
(B) Pinctada (ii) Chiton
(C) Sepia (iii) Apple snail
(D) Loligo (iv) Tusk shell
(E) Octopus (v) Pearl oyster
(F) Aplysia (vi) Cuttlefish
(G) Dentalium (vii) Squid
(H) Chaetopleura (viii) Sea hare
Answer:
(A)-(iii)
(B) (v)
(C)-(vi)
(D)-(vii)
(E)-(i)
(F)-(viii)
(G)-(iv)
(H)-(ii)
Q81. Match the columns:
(A) Asterias (i) Brittle star
(B) Echinus (ii) Sea lily
(C) Antedon (iii) Star fish
(D) Cucumaria (iv) Sea urchin
(E) Ophiura (v) Sea cucumber
Answer:
(A)(iii)
(B)-iv)
(C)-(ii)
(D)-(v)
(E)-(i)
Q82. Match the columns :
(A) Branchiostoma (i) Saw fish
(B) Petromyzon (ii) Dog fish
(C) Myxine (iii) Lancelet
(D) Scoliodon (iv) Sting ray
(E) Pristis (v) Lamprey
(F) Carcharodon (vi) Hag fish
(G) Trygon (vii) Great white shark
Answer:
(A)-(iii)
(B)(v)
(C)-(vi)
(D)-(ii)
(E)-(i)
(F)-(vii)
(G)-(iv)
Q83. Match the columns :
(A) Exocoetus (i) Angel fish
(B) Hippocampus (ii) Rohu
(C) Labeo (iii) Fighting fish
(D) Clarias (iv) Magur
(E) Betta (v) Flying fish
(F) Pterophyllum (vi) Sea horse
Answer:
(A)-(V)
(B)-(vi)
(C)-(ii)
(D)-(iv)
(E)-(iii)
(F)-(i)
Q84. Match the columns :
(A) Bufo (i) Limbless amphibian
(B) Rana (ii) Indian bull frog
(C) Hyla (iii) Commontoad
(D) Ichthyophis (iv) Tree frog
Answer:
(A)-(iii)
(B)-(ii)
(C)-(iv)
(D)-(i)
Q85. Match the columns:
(A) Chelone (i) Krait
(B) Testudo (ii) Wall lizard
(C) Chameleon (iii) Garden lizard
(D) Calotes (iv) Turtle
(E) Naja (v) Tortoise
(F) Bangarus (vi) Tree lizard
(G) Hemidactylus (vii) Cobra
Answer:
(A)-(iv)
(B) (v)
(C)-(vi)
(D)-(iii)
(E)-(vii)
(F)-(i)
(G)-(ii)
Q86. Match the columns :
(A) Corvus (i) Vulture
(B) Columba (ii) Crow
(C) Psittacula (iii) Penguin
(D) Struthio (iv) Peacock
(E) Pavo (v) Ostrich
(F) Aptenodytes (vi) Pigeon
(G) Neophron (vii) Parrot
Answer:
(A)-(ii)
(B)-(vi)
(C)-(vii)
(D)-(v)
(E)-(iv)
(F)-(iii)
(G)-(i)
Q87. Match the columns:
(A) Omithorhynchus (i) Flying fox
(B) Macropus (ii) Blue whale
(C) Pteropus (iii) Monkey
(D) Balaenoptera (iv) Dog
(E) Canis (v) Platypus
(F) Macaca (vi) Cat
(G) Felis (vii) Kangaroo
(H) Equus (viii) Horse
Answer:
(A)-(v)
(B) (vii)
(C)-(i)
(D)-(ii)
(E)-(iv)
(F)-(iii)
(G) (vi)
(H)-(viii)
Q88. Match the columns :
(A) Operculum (i) Ctenophora
(B) Parapodia (ii) Mollusca
(C) Scales/Scutes (iii) Porifera
(D) Comb plates (iv) Reptilia
(E) Radula (v) Annelida
(F) Hairs (vi) Cyclostomata
(G) Choanocytes (vii) Mammalia
(H) Gill slits (viii) Osteichthyes
Answer:
(A)-(viii)
(B)-(v)
(C)-(iv)
(D)-(i)
(E)-(ii)
(F)-(vii)
(G)-(iii)
(H)-(vi)
Q89. Match the columns :
(A) Water canal system (i) Coelenterata
(B) Metagenesis (ii) Platyhelminthes
(C) Comb plates (iii) Mollusca
(D) Flame cells (iv) Arthropoda
(E) Pseudocoelom (v) Echinodermata
(F) Jointed appendages (vi) Aschelminthes
(G) Soft bodied animals (vii) Porifera
(H) Water vascular system (vili) Ctenophora
Answer:
(A)-(vii)
(B)-(i)
(C)-(viii)
(D)-(ii)
(E)-(vi)
(F)-(iv)
(G)-(iii)
(H)-(v)
Q90. Match the Columns:
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline \text {(A) Urochordata } & \text {(i) Camelus } \\
\hline \text {(B) Hemichordata } & \text {(ii) Ascidia } \\
\hline \text {(C) Arthropoda } & \text {(iii) Crocodihus } \\
\hline \text {(D) Reptilia } & \text {(iv) Elephas } \\
\hline \text {(E) Mammalia } & \text {(v) Balanoglossus } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(vi) Rattus } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(vii) Culex } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(viii) Salpa } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(ix) Doliolum } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(x) Delphinus } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xi) Saccoglossus } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xii) Panthera } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xiii) Aedes } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xiv) Vipera } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xv) Anopheles } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xvi) Alligator } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
(A)-(ii), (viii), (ix)
(B)-(v), (xi)
(C)-(vii), (xiii), (xv)
(D)-(iii), (xiv), (xvi)
(E)-(i), (iv), (vi), (x), (xii)
Q91. Mark the given statements True (T) or False (F) :
(i) All members of Animalia are multicellular.
(ii) Sponges exhibit tissue grade level of body organization.
(iii) A complete digestive system has two openings, mouth and anus.
(iv) Annelids are pseudocoelomate animals.
(v) Notochord is an endodermally derived structure.
(vi) All vertebrates are chordates.
(vii) All chordates are vertebrates.
(viii) Polyps produce medusae asexually and medusae form the polyps sexually.
(ix) Hooks and suckers are present in non parasitic flatworms.
(x) Lamprey dies after few days of spawning.
Answer: (i)-T, (ii)-F, (iii)-T, (iv)-F, (v)-F, (vi)-T, (vii)-F, (viii)-T, (ix)-F, (x)-T
Q92. Fill in the blanks:
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { Character } & \text { Non Chordates } & \text { Chordates } \\
\hline \text { Notochord } & \text { Absent } & \text { (a) } \\
\hline \text { Central nervous system } & \text { Ventral } & \text { (b) } \\
\hline \text { Central nervous system } & \text { (c) } & \text { (Hollow) } \\
\hline \text { Central nervous system } & \text { (Double) } & \text { (d) } \\
\hline \text { Gills slits } & \text { (Absent) } & \text { (e) } \\
\hline \text { Heart } & \text { (f) } & \text { (Ventral) } \\
\hline \text { Post anal tail } & \text { (g) } & \text { (Present) } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
(a) – Present
(b) – Dorsal
(c) – Solid
(d) – Single
(e) – Present
(f) – Dorsal
(g) – Absent
Q93. Identify the following \(A, B, C\) and \(D\) in given figure :
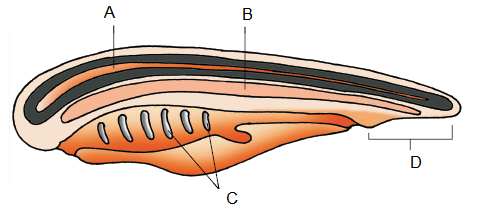
Answer: (A) – Nerve cord, (B) – Notochord, (C) – Gill slits, (D) – Post anal tail
Q94. Identify the following symmetries shown in the figures A and B :
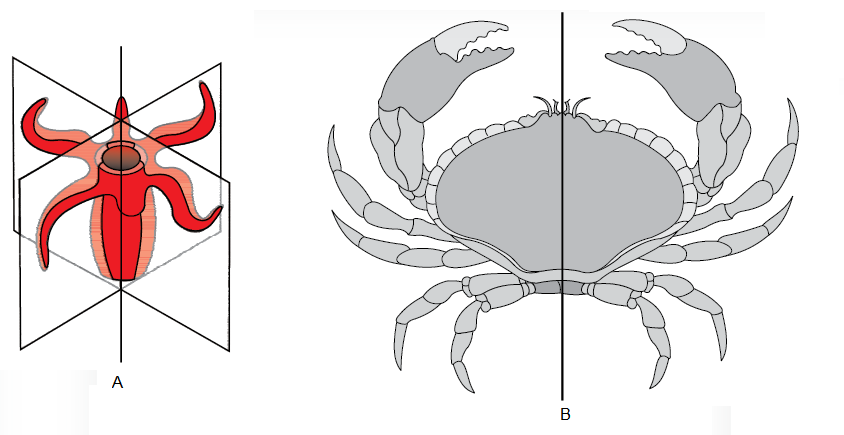
Answer: (A)-Radial Symmetry, (B)- Bilateral symmetry
Q95. Identify the following coelom shown in the diagrams \(A , B\) and C :
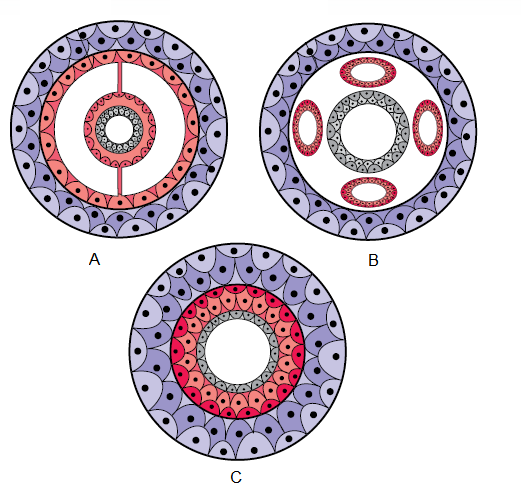
Answer: (A) Eucoelom, (B) Pseudocoelom, (C) Acoelom
Q96. Identify the following body organisations on the basis of germinal layers :
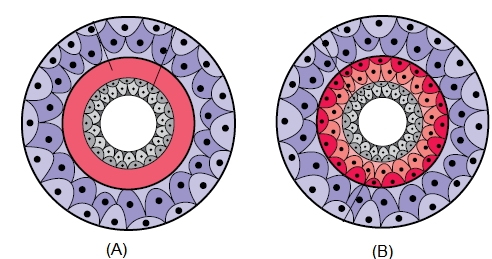
Answer: (A)-Diploblastic, (B)-Triploblastic
Q97. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :
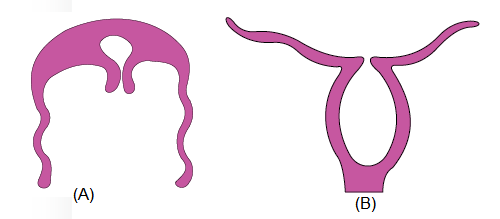
Answer: (A)- Aurelia (Medusa), (B)- Adamsia (Polyp)
Q98. The given structure is found in phylum (a) and helps in (b).
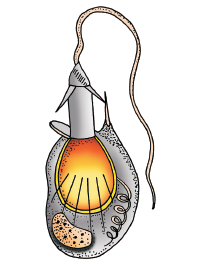
Answer: (a)- Coelenterata, (b)- Anchorage, defense and capturing prey.
Q99. Give the answer of following questions by observations from given figures :
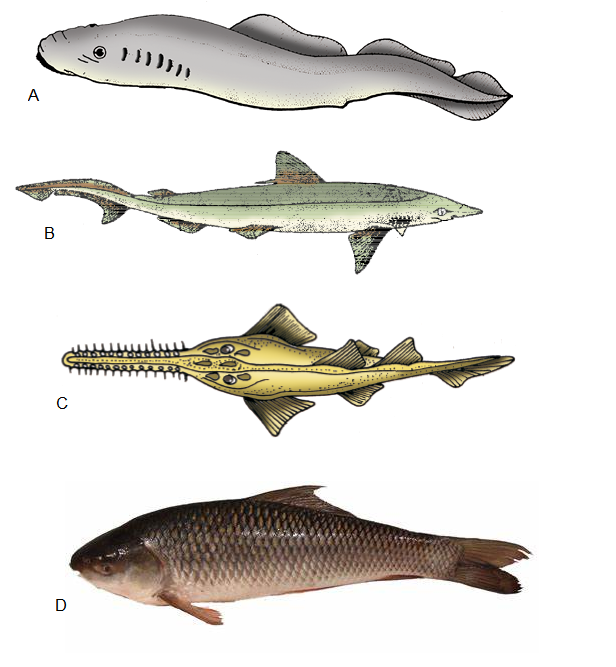
(i) Which fish has air bladder?
(ii) Which fish is known as saw fish ?
(iii) Which fish is cartilaginous fish ?
(iv) Which animal is ectoparasite on true fishes ?
(v) Which fish has paired fins?
(vi) Which fish has bony skeleton?
(vii) Which fish has 4 – pairs of gills?
(viii) Which fish has operculum ?
(ix) Which fishes are viviparous?
(x) Which fish lives in fresh water?
Answer: (i) – D, (ii) – C, (iii) – B, C, (iv) – A, (v) – B, C, D, (vi) – D, (vii) – D, (viii) – D, (ix) – B, C, ( x )- D
Q100. Select the correct options for given animal :
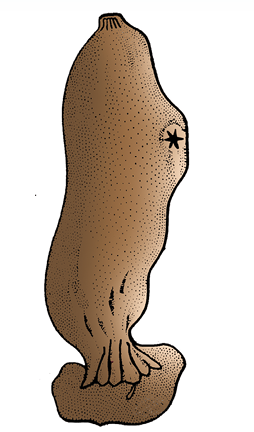
(i) Diploblastic / Triploblastic
(ii) Acoelomate / Pseudocoelomate / Eucoelomate
(iii) Chordate / Non Chordate
(iv) Urochordate / Cephalochordate
Answer: (i) – Triploblastic, (ii) – Eucoelomate, (iii) – Chordate, (iv) – Urochordate
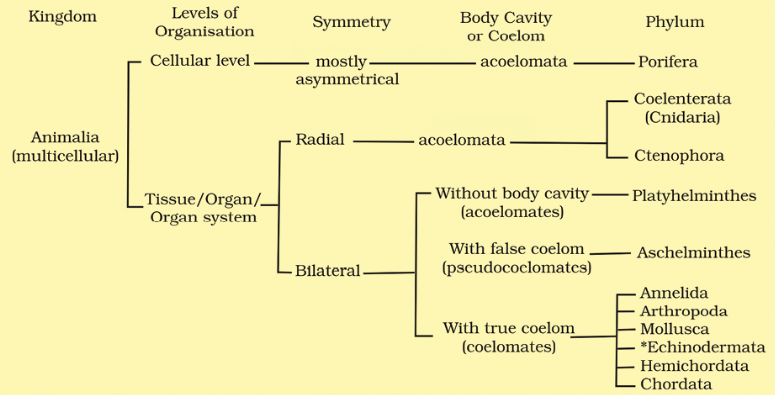
Q101. Draw broad classification of animals.
Answer:
Q102. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :
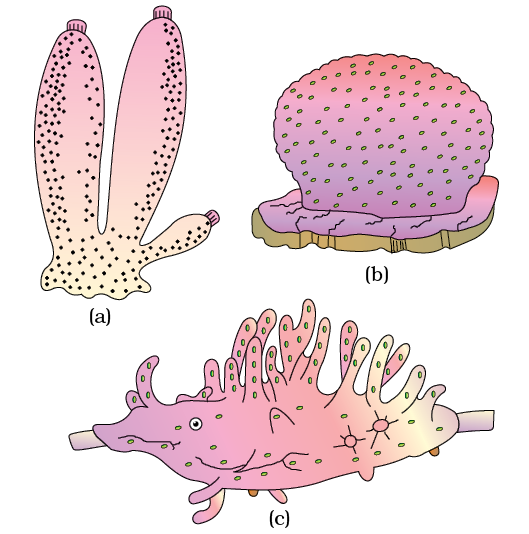
Answer: Examples of Porifera : (a) Sycon (b) Euspongia (c) Spongilla
Q103. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :
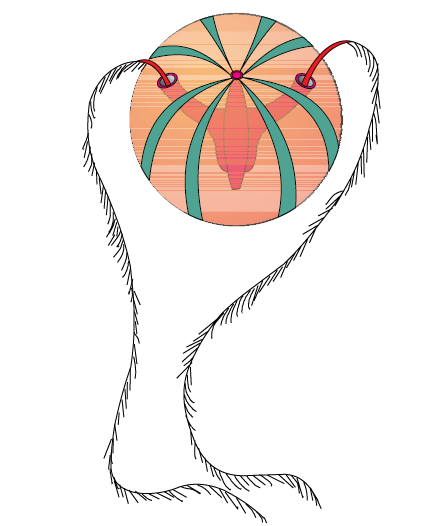

Answer:
Q1. Members of which phylum are commonly known as sponges?
Answer: Porifera
Q2. Which type of symmetry is mostly found in sponges?
Answer: Asymmetry
Q3. Presence of water transport system is characteristic of which phylum?
Answer: Porifera(Sponges)
Q4. What is the name of pores through which water enters into the body of sponges?
Answer: Ostia
Q5. What is the name of pore through which water comes out from body of sponges?
Answer: Osculum
Q6. What is the name of central cavity found in the body of members of phylum porifera?
Answer: Spongocoel (Para gastric cavity)
Q7. What is the function of water canal system in sponges?
Answer: Food gathering, respiratory exchange and removal of waste.
Q8. What is the name of cells those line the spongocoel?
Answer: Choanocytes or collar cells.
Q9. Name the structures which support the body of sponges as a skeleton:
Answer: Spicules and spongin fibres.
Q10. The animals which don’t have separate sexes are called as :
Answer: Hermaphrodite (Bisexual)
Q11. When development of an organism occurs through larval stage, then this type of development is called as :
Answer: Indirect development
Q12. Which type of symmetry is found in coelenterates?
Answer: Radial symmetry
Q13. Name the cell that is used for defense purposes in coelenterates.
Answer: Cnidoblast
Q14. Which cnidarians possess a skeleton made up of calcium carbonate?
Answer: Corals
Q15. The alternation of Polyp and Medusa forms in coelenterates is called as :
Answer: Metagenesis
Q16. Which organism is also known as Portuguese man of war?
Answer: Physalia
Q17. Members of which phylum are commonly known as sea walnuts or comb jellies?
Answer: Ctenophora
Q18. Which structure helps in locomotion in ctenophores?
Answer: Comb plates
Q19. The property of a living organism to emit light is called as :
Answer: Bioluminescence
Q20. Members of which phylum are known as flatworms?
Answer: Platyhelminthes
Q21. Which type of symmetry is found in the members of phylum platyhelminthes?
Answer: Bilateral symmetry
Q22. Structures which help in osmoregulation and excretion in flatworms are called.
Answer: Flame cells
Q23. Members of which phylum are also known as roundworms?
Answer: Aschelminthes (Nematoda)
Q24. Name the phylum in which organ system level of body organisation appeared for the first time :
Answer: Aschelminthes (Nematoda)
Q25. Which phylum of animals possess pseudocoelomic type of body cavity?
Answer: Aschelminthes (Nematoda)
Q26. Which structures help in osmoregulation and excretion in Annelids ?
Answer: Nephridia
Q27. The body of annelids is distinctly marked out into segments. These segments are called as :
Answer: Metameres
Q28. Name the largest phylum of animal kingdom.
Answer: Arthropoda
Q29. The exoskeleton of arthropods is made up of
Answer: Chitin
Q30. The name of the balancing organ in arthropods.
Answer: Statocyst
Q31. What is the main function of malpighian tubules?
Answer: Excretion
Q32. Name the organism which produces silk.
Answer: Bombyx (Silk worm)
Q33. Name the organism which produces lac.
Answer: Laccifer (Lac insecta)
Q34. Name the second largest phylum of animal kingdom :
Answer: Mollusca
Q35. The soft and spongy layer of skin over the visceral hump of molluscs is known as :
Answer: Mantle
Q36. In which phylum the mantle cavity is found?
Answer: Mollusca
Q37. What is the name of file like rasping organ found in molluscs?
Answer: Radula
Q38. Animals of which phylum are reared for the production of pearls?
Answer: Mollusca
Q39. In which phylum the spiny bodied organisms are included?
Answer: Echinodermata
Q40. In which phylum organisms alter their symmetry from bilateral to radial during the development?
Answer: Echinodermata
Q41. Members of which phylum have ventral mouth and dorsal anus?
Answer: Echinodermata
Q42. Water vascular system is a characteristic of which phylum?
Answer: Echinodermata
Q43. Name the excretory organ of balanoglossus:
Answer: Proboscis gland
Q44. Which subphylums are classified under protochordates?
Answer: Urochordata and Cephalochordata
Q45. In which subphylum notochord is present only in larval tail?
Answer: Urochordata
Q46. In which subphylum notochord extends from head to tail and is persistent throughout the life?
Answer: Cephalochordata
Q47. In which subphylum notochord is replaced by vertebral column?
Answer: Vertebrata
Q48. Animals of which class possess a sucking and circular mouth without jaws?
Answer: Cyclostomata
Q49. In which class of fishes mouth is located ventrally?
Answer: Chondrichthyes
Q50. Which types of scales are found on the body of cartilaginous fishes?
Answer: Placoid scales
Q51. In which class of fishes notochord is persistent throughout the life?
Answer: Chondrichthyes
Q52. The teeth of cartilaginous fishes are formed due to modification of which type of scales?
Answer: Placoid scales
Q53. What is the name of structure which prevents the bony fishes from sinking?
Answer: Air bladder
Q54. Why cartilaginous fishes have to swim constantly?
Answer: Because they lack air bladder
Q55. Name a fish which has electric organ.
Answer: Torpedo
Q56. Name a fish which possess poisonous sting.
Answer: Trygon
Q57. The animals which don’t have the capacity to regulate their body temperature are called as __________ .
Answer: Poikilothermous
Q58. The animals which have the capacity to regulate their body temperature are called as __________.
Answer: Homoiothermous
Q59. How many pairs of gills are present in bony fishes?
Answer: 4-pairs
Q60. Name the cap which covers the gills in osteichthyes fishes :
Answer: Operculum
Q61. Which structure represents ear in amphibians and reptiles ?
Answer: Tympanum
Q62. In which class of vertebrates 3-chambered heart is found?
Answer: Amphibia and Reptilia
Q63. The common chamber for alimentary canal, urinary bladder and reproductive tracts is called as :
Answer: Cloaca
Q64. Which class of vertebrates possesses dry and cornified skin with epidermal scales or scutes?
Answer: Reptilia
Q65. In which reptiles 4-chambered heart is present?
Answer: Crocodiles
Q66. Snakes and lizards shed off their scales. This phenomenon is called as :
Answer: Skin cast
Q67. The presence of feathers is characteristic of which class?
Answer: Aves
Q68. The long bones of birds are hollow with air cavities. These types of bones are called as :
Answer: Pneumatic bones
Q69. Name of the additional chambers found in the digestive tract of birds:
Answer: Crop and Gizzard
Q70. Name the respiratory organs in birds and mammals :
Answer: Lungs
Q71. Presence of mammary gland is the unique character of which class?
Answer: Mammalia
Q72. Name an oviparous animal with presence of mammary glands:
Answer: Ornithorhynchus(Platypus)
Q73. Name the phyla which have radial symmetry:
Answer: Coelenterata, Ctenophora,Echinodermata (adult)
Q74. The undifferentiated layer present between ectoderm and endoderm in diploblastic animals is known as :
Answer: Mesoglea
Q75. A body cavity in which mesoderm is found in scattered form is called as :
Answer: Pseudocoelom
Q76. Match the columns:
(A) Sycon (i) Bath sponge
(B) Spongilla (ii) Scypha
(C) Euspongia (iii) Fresh water sponge
Answer:
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \text { (A)-(ii) } \\
& \text { (B)-(iii) } \\
& \text { (C)-(i) }
\end{aligned}
\)
Q77. Match the columns :
(A) Adamsia (i) Sea fan
(B) Pennatula (ii) Brain coral
(C) Gorgonia (iii) Sea pen
(D) Meandrina (iv) Sea anemone
Answer:
(A)-(iv)
(B)-(iii)
(C)-(i)
(D)-(ii)
Q78. Match the columns:
(A) Taenia (i) Filaria worm
(B) Fasciola (ii) Round worm
(C) Ascaris (iii) Tapeworm
(D) Wuchereria (iv) Hook worm
(E) Ancylostoma (v) Liver fluke
Answer:
(A)-(iii)
(B) (v)
(C)-(ii)
(D)-(i)
(E)-(iv)
Q79. Match the columns :
(A) Pheretima (i) King crab
(B) Hirudinaria (ii) Honey bee
(C) Apis (iii) Earthworm
(D) Limulus (iv) Blood sucking leech
Answer:
(A)-(iii)
(B)-(iv)
(C)-(ii)
(D)-(i)
Q80. Match the columns:
(A) Pila (i) Devil fish
(B) Pinctada (ii) Chiton
(C) Sepia (iii) Apple snail
(D) Loligo (iv) Tusk shell
(E) Octopus (v) Pearl oyster
(F) Aplysia (vi) Cuttlefish
(G) Dentalium (vii) Squid
(H) Chaetopleura (viii) Sea hare
Answer:
(A)-(iii)
(B) (v)
(C)-(vi)
(D)-(vii)
(E)-(i)
(F)-(viii)
(G)-(iv)
(H)-(ii)
Q81. Match the columns:
(A) Asterias (i) Brittle star
(B) Echinus (ii) Sea lily
(C) Antedon (iii) Star fish
(D) Cucumaria (iv) Sea urchin
(E) Ophiura (v) Sea cucumber
Answer:
(A)(iii)
(B)-iv)
(C)-(ii)
(D)-(v)
(E)-(i)
Q82. Match the columns :
(A) Branchiostoma (i) Saw fish
(B) Petromyzon (ii) Dog fish
(C) Myxine (iii) Lancelet
(D) Scoliodon (iv) Sting ray
(E) Pristis (v) Lamprey
(F) Carcharodon (vi) Hag fish
(G) Trygon (vii) Great white shark
Answer:
(A)-(iii)
(B)(v)
(C)-(vi)
(D)-(ii)
(E)-(i)
(F)-(vii)
(G)-(iv)
Q83. Match the columns :
(A) Exocoetus (i) Angel fish
(B) Hippocampus (ii) Rohu
(C) Labeo (iii) Fighting fish
(D) Clarias (iv) Magur
(E) Betta (v) Flying fish
(F) Pterophyllum (vi) Sea horse
Answer:
(A)-(V)
(B)-(vi)
(C)-(ii)
(D)-(iv)
(E)-(iii)
(F)-(i)
Q84. Match the columns :
(A) Bufo (i) Limbless amphibian
(B) Rana (ii) Indian bull frog
(C) Hyla (iii) Commontoad
(D) Ichthyophis (iv) Tree frog
Answer:
(A)-(iii)
(B)-(ii)
(C)-(iv)
(D)-(i)
Q85. Match the columns:
(A) Chelone (i) Krait
(B) Testudo (ii) Wall lizard
(C) Chameleon (iii) Garden lizard
(D) Calotes (iv) Turtle
(E) Naja (v) Tortoise
(F) Bangarus (vi) Tree lizard
(G) Hemidactylus (vii) Cobra
Answer:
(A)-(iv)
(B) (v)
(C)-(vi)
(D)-(iii)
(E)-(vii)
(F)-(i)
(G)-(ii)
Q86. Match the columns :
(A) Corvus (i) Vulture
(B) Columba (ii) Crow
(C) Psittacula (iii) Penguin
(D) Struthio (iv) Peacock
(E) Pavo (v) Ostrich
(F) Aptenodytes (vi) Pigeon
(G) Neophron (vii) Parrot
Answer:
(A)-(ii)
(B)-(vi)
(C)-(vii)
(D)-(v)
(E)-(iv)
(F)-(iii)
(G)-(i)
Q87. Match the columns:
(A) Omithorhynchus (i) Flying fox
(B) Macropus (ii) Blue whale
(C) Pteropus (iii) Monkey
(D) Balaenoptera (iv) Dog
(E) Canis (v) Platypus
(F) Macaca (vi) Cat
(G) Felis (vii) Kangaroo
(H) Equus (viii) Horse
Answer:
(A)-(v)
(B) (vii)
(C)-(i)
(D)-(ii)
(E)-(iv)
(F)-(iii)
(G) (vi)
(H)-(viii)
Q88. Match the columns :
(A) Operculum (i) Ctenophora
(B) Parapodia (ii) Mollusca
(C) Scales/Scutes (iii) Porifera
(D) Comb plates (iv) Reptilia
(E) Radula (v) Annelida
(F) Hairs (vi) Cyclostomata
(G) Choanocytes (vii) Mammalia
(H) Gill slits (viii) Osteichthyes
Answer:
(A)-(viii)
(B)-(v)
(C)-(iv)
(D)-(i)
(E)-(ii)
(F)-(vii)
(G)-(iii)
(H)-(vi)
Q89. Match the columns :
(A) Water canal system (i) Coelenterata
(B) Metagenesis (ii) Platyhelminthes
(C) Comb plates (iii) Mollusca
(D) Flame cells (iv) Arthropoda
(E) Pseudocoelom (v) Echinodermata
(F) Jointed appendages (vi) Aschelminthes
(G) Soft bodied animals (vii) Porifera
(H) Water vascular system (vili) Ctenophora
Answer:
(A)-(vii)
(B)-(i)
(C)-(viii)
(D)-(ii)
(E)-(vi)
(F)-(iv)
(G)-(iii)
(H)-(v)
Q90. Match the Columns:
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline \text {(A) Urochordata } & \text {(i) Camelus } \\
\hline \text {(B) Hemichordata } & \text {(ii) Ascidia } \\
\hline \text {(C) Arthropoda } & \text {(iii) Crocodihus } \\
\hline \text {(D) Reptilia } & \text {(iv) Elephas } \\
\hline \text {(E) Mammalia } & \text {(v) Balanoglossus } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(vi) Rattus } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(vii) Culex } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(viii) Salpa } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(ix) Doliolum } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(x) Delphinus } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xi) Saccoglossus } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xii) Panthera } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xiii) Aedes } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xiv) Vipera } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xv) Anopheles } \\
\hline \text { } & \text {(xvi) Alligator } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
(A)-(ii), (viii), (ix)
(B)-(v), (xi)
(C)-(vii), (xiii), (xv)
(D)-(iii), (xiv), (xvi)
(E)-(i), (iv), (vi), (x), (xii)
Q91. Mark the given statements True (T) or False (F) :
(i) All members of Animalia are multicellular.
(ii) Sponges exhibit tissue grade level of body organization.
(iii) A complete digestive system has two openings, mouth and anus.
(iv) Annelids are pseudocoelomate animals.
(v) Notochord is an endodermally derived structure.
(vi) All vertebrates are chordates.
(vii) All chordates are vertebrates.
(viii) Polyps produce medusae asexually and medusae form the polyps sexually.
(ix) Hooks and suckers are present in non parasitic flatworms.
(x) Lamprey dies after few days of spawning.
Answer: (i)-T, (ii)-F, (iii)-T, (iv)-F, (v)-F, (vi)-T, (vii)-F, (viii)-T, (ix)-F, (x)-T
Q92. Fill in the blanks:
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { Character } & \text { Non Chordates } & \text { Chordates } \\
\hline \text { Notochord } & \text { Absent } & \text { (a) } \\
\hline \text { Central nervous system } & \text { Ventral } & \text { (b) } \\
\hline \text { Central nervous system } & \text { (c) } & \text { (Hollow) } \\
\hline \text { Central nervous system } & \text { (Double) } & \text { (d) } \\
\hline \text { Gills slits } & \text { (Absent) } & \text { (e) } \\
\hline \text { Heart } & \text { (f) } & \text { (Ventral) } \\
\hline \text { Post anal tail } & \text { (g) } & \text { (Present) } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
(a) – Present
(b) – Dorsal
(c) – Solid
(d) – Single
(e) – Present
(f) – Dorsal
(g) – Absent
Q93. Identify the following \(A, B, C\) and \(D\) in given figure :

Answer: (A) – Nerve cord, (B) – Notochord, (C) – Gill slits, (D) – Post anal tail
Q94. Identify the following symmetries shown in the figures A and B :

Answer: (A)-Radial Symmetry, (B)- Bilateral symmetry
Q95. Identify the following coelom shown in the diagrams \(A , B\) and C :

Answer: (A) Eucoelom, (B) Pseudocoelom, (C) Acoelom
Q96. Identify the following body organisations on the basis of germinal layers :

Answer: (A)-Diploblastic, (B)-Triploblastic
Q97. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :

Answer: (A)- Aurelia (Medusa), (B)- Adamsia (Polyp)
Q98. The given structure is found in phylum (a) and helps in (b).

Answer: (a)- Coelenterata, (b)- Anchorage, defense and capturing prey.
Q99. Give the answer of following questions by observations from given figures :

(i) Which fish has air bladder?
(ii) Which fish is known as saw fish ?
(iii) Which fish is cartilaginous fish ?
(iv) Which animal is ectoparasite on true fishes ?
(v) Which fish has paired fins?
(vi) Which fish has bony skeleton?
(vii) Which fish has 4 – pairs of gills?
(viii) Which fish has operculum ?
(ix) Which fishes are viviparous?
(x) Which fish lives in fresh water?
Answer: (i) – D, (ii) – C, (iii) – B, C, (iv) – A, (v) – B, C, D, (vi) – D, (vii) – D, (viii) – D, (ix) – B, C, ( x )- D
Q100. Select the correct options for given animal :

(i) Diploblastic / Triploblastic
(ii) Acoelomate / Pseudocoelomate / Eucoelomate
(iii) Chordate / Non Chordate
(iv) Urochordate / Cephalochordate
Answer: (i) – Triploblastic, (ii) – Eucoelomate, (iii) – Chordate, (iv) – Urochordate
Q101. Draw broad classification of animals.
Answer:

Q102. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :

Answer: Examples of Porifera : (a) Sycon (b) Euspongia (c) Spongilla
Q103. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :

Answer: Example of Ctenophora (Pleurobrachia)
Q104. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :
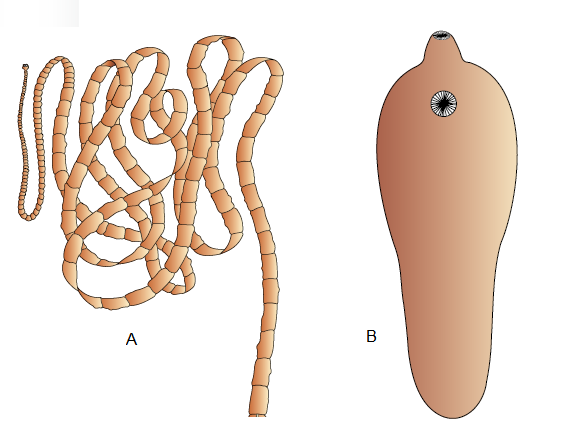
Answer: Examples of Platyhelminthes : (A) Tape worm (B) Liver fluke
Q105. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :
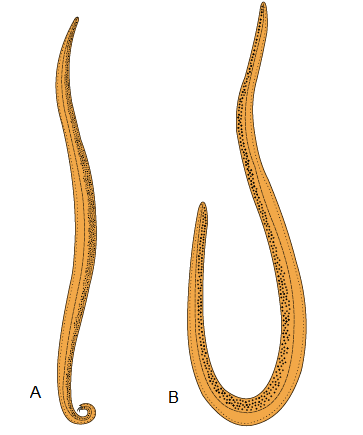
Answer: Example of Aschelminthes: Roundworm
Q106. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :
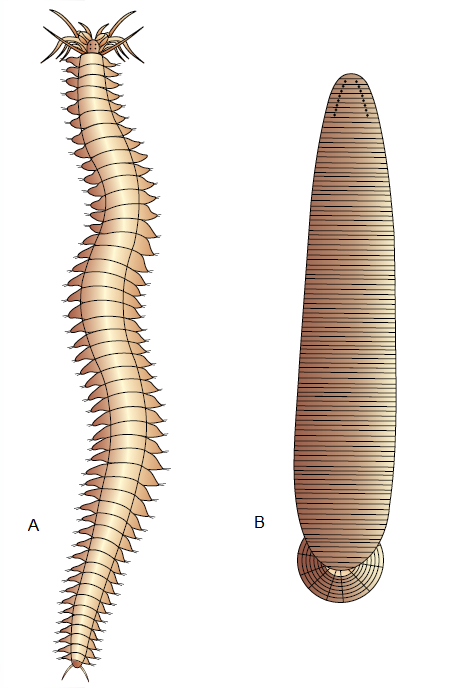
Answer: Examples of Annelida : (A) Nereis (B) Hirudinaria
Q107. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :
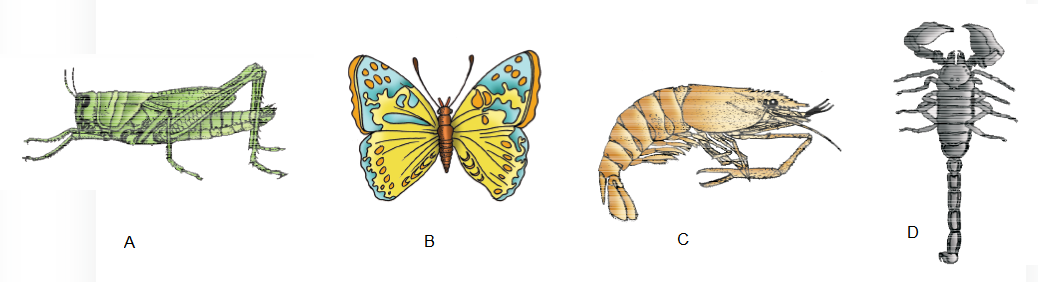
Answer: Examples of Arthropoda : (A) Locust (B) Butterfly (C) Scorpion (D) Prawn
Q108. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :
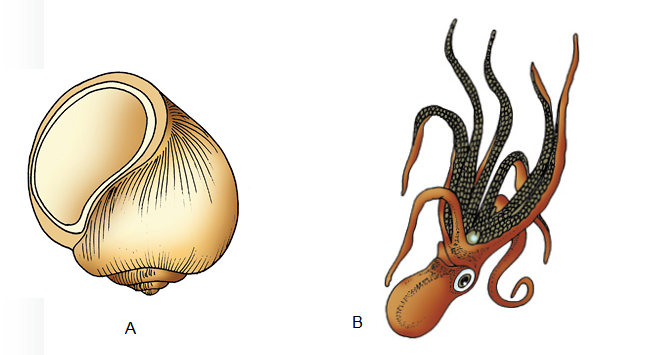
Answer: Examples of Mollusca :(A) Pila (B) Octopus
Q109. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :
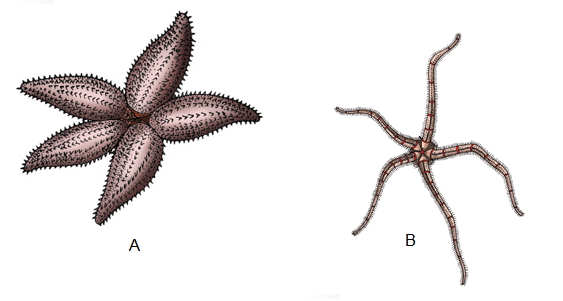
Answer: Examples of Echinodermata : (A) Asterias (B) Ophiura
Q110. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure A, B & C:
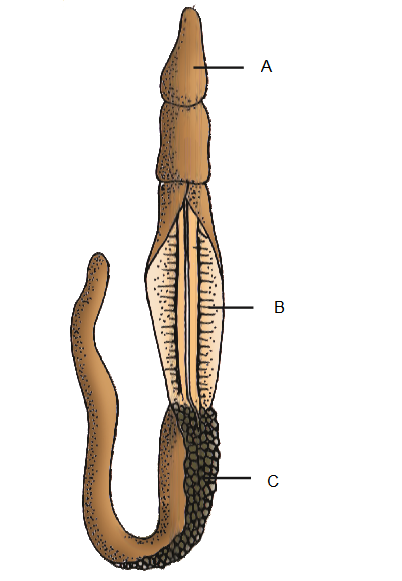
Answer: A- Proboscis, B- Collar, C-Trunk
Q111. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure :

Answer: Examples of Bony fishes : (a) Hippocampus
Q112. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure A & B:
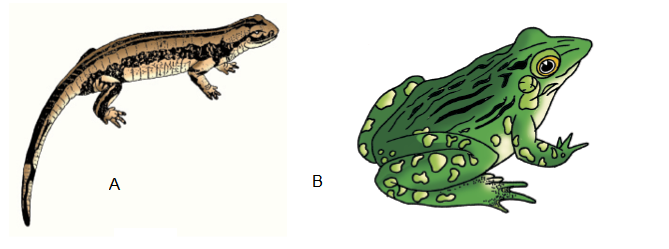
Answer: Examples of Amphibia :(A) Salamandra (B) Rana
Q113. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure A, B, C & D:
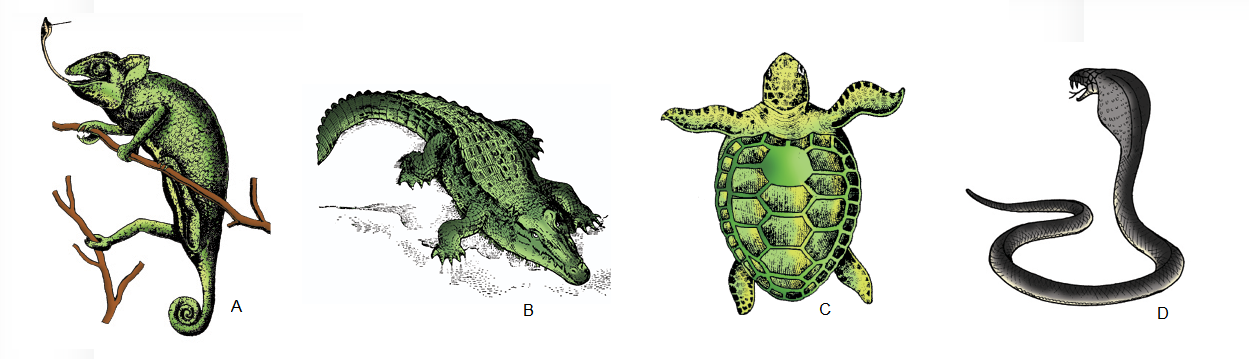
Answer: Reptiles: (A) Chameleon (B) Crocodilus (C) Chelone (D) Naja
Q114. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure A, B, C & D:
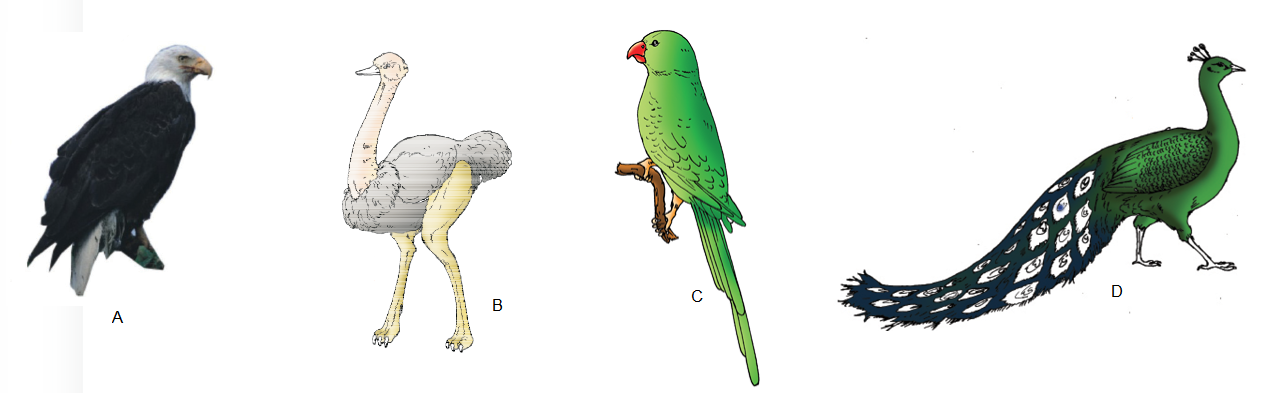
Answer: Some birds : (A) Neophron (B) Struthio (C) Psittacula (D) Pavo
Q115. Identify the following body forms shown in the figure A, B, C & D:
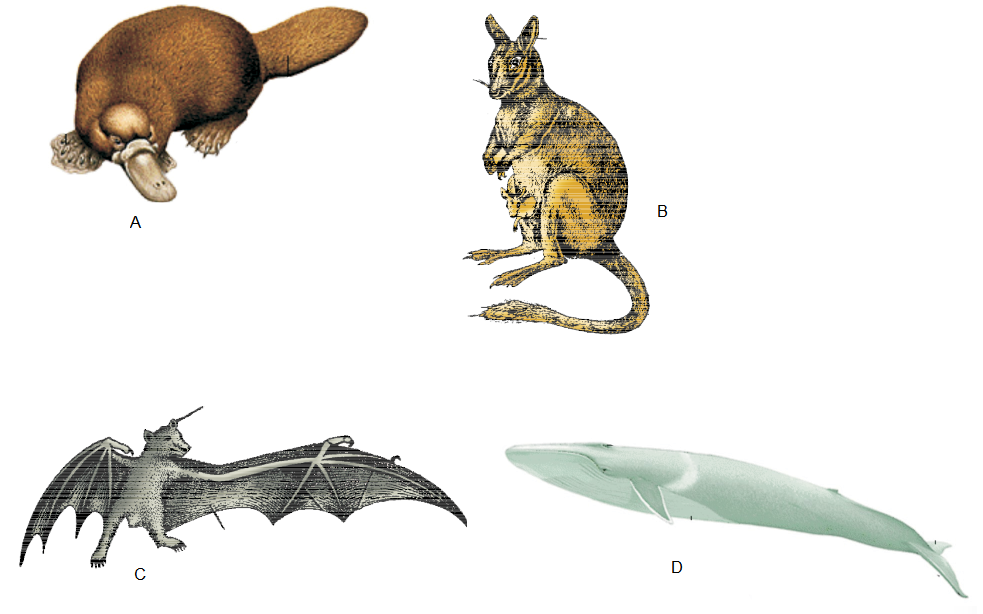
Answer: Some mammals : (A) Ornithorhynchus (B) Macropus (C) Pteropus (D) Balaenoptera