CH3- Plant Kingdom
Q1. Which taxonomy is based on following points :
- chromosome number
- chromosome structure
- chromosome behaviour
Answer: Cytotaxonomy
Q2. Match the Column I with Column II:
\(\begin{aligned}
&\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { Column-I } & & \text { Column-II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Unicellular } & \text { (i) } & \text { Spirogyra } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Colonial } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Kelps } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Filamentous } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Volvox } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Massive plant bodies } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Chlamydomonas} \\
\hline
\end{array}\\
\end{aligned}
\)
Answer: A-iv, B-iii, C-i, D-ii
Q3. Identify A, B, C and D in given flow chart :
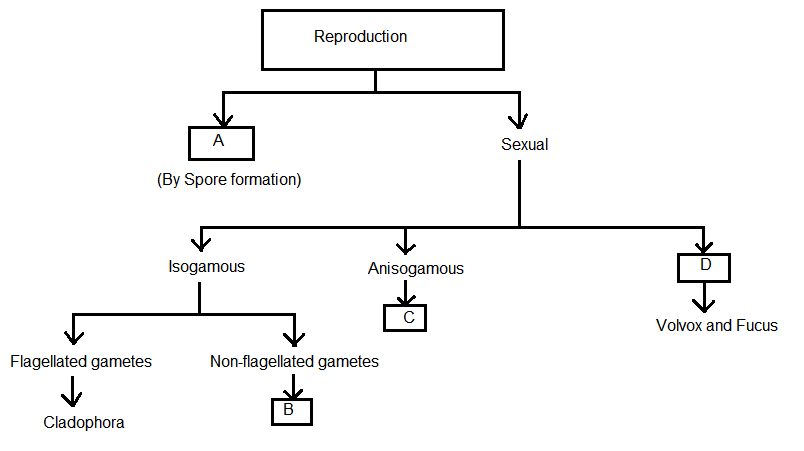
Answer: A-Asexual, B-Spirogyra, C-Eudorina, D-Oogamous
Q4. Numerical taxonomy which is now easily carried out using computers is based on _____.
Answer: All observable characteristics
Q5. Which type of sexual reproduction is found in Fucus?
Answer: Oogamous
Q6. Identify the given figure with \(A, B, C \& D\) :
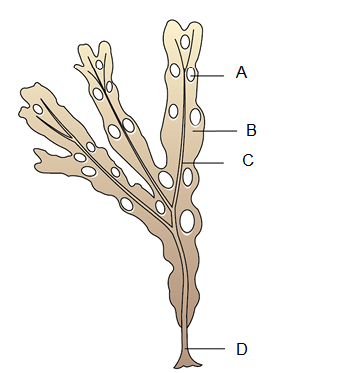
Answer: Fucus: A-Air bladder, B-Frond, C-Midrib, D-Holdfast
Q7. Identify the given figures with \(A, \& B\) :

Answer: A-Volvox, B-Ulothrix
Q8. Write down the algal class of following figures :
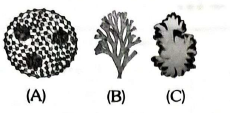
Answer: A-Chlorophyceae B-Phaeophyceae C-Rhodophyceae
Q9. Study the following table and identify (i) (ii) & (iii) :
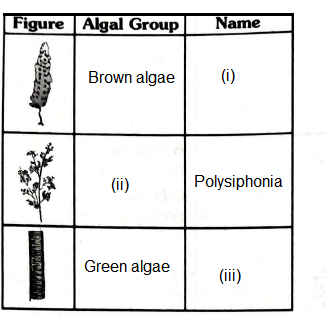
Answer: (i) Laminaria, (ii) Red algae, (iii) Ulothrix
Q10. Porphyra & Dictyota are belong which algal class respectively
Answer: Rhodophyceae, Phaeophyceae
Q11. Agar, one of the commercial products obtained from A and Gracilaria are used to grow microbes and in preparations of ice-creams and jellies.
Answer: A-Gelidium
Q12. Which are the pigments found in phaeophyceae?
Answer: Chlorophyll-a,c, Fucoxanthin
Q13. Write the name of eukaryotic unicellular algae which is rich in proteins and used as food supplements :
Answer: Chlorella
Q14. Most of the green algae have one or more storage bodies, which are located in the chloroplasts are called :
Answer: Pyrenoids
Q15. Certain marine brown and red algae produce large amounts of hydrocolloids eg. A and B , respectively which are used commercially.
Answer: A-Algin, B-Carrageen
Q16. Identify \(A , B\) & C in given table :
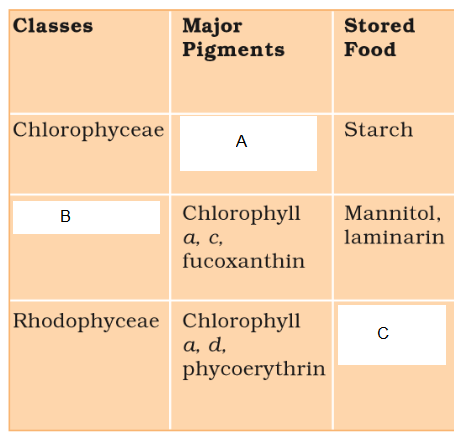
Answer: A-Chlorophyll a, b; B-Phaeophyceae; C-Floridean starch
Q17. In phaeophyceae, the vegetative cells have a cellulosic cell wall usually covered on the outside by a gelatinous coating of _____.
Answer: Algin
Q18. Why are the members of Rhodophyceae commonly called red algae?
Answer: Due to pre-dominance of r-phycoerythrin
Q19. Floridean starch is similar to A and glycogen in structure.
Answer: A-Amylopectin
Q20. In which class of algae, gametes are pyriform (pear-shaped) and bear two unequal laterally attached flagella?
Answer: Phaeophyceae
Q21. In which class of algae sexual reproduction is oogamous and accompanied by complex post fertilization developments?
Answer: Rhodophyceae
Q22. Identify the given figure with \(A, B, C \& D\) :
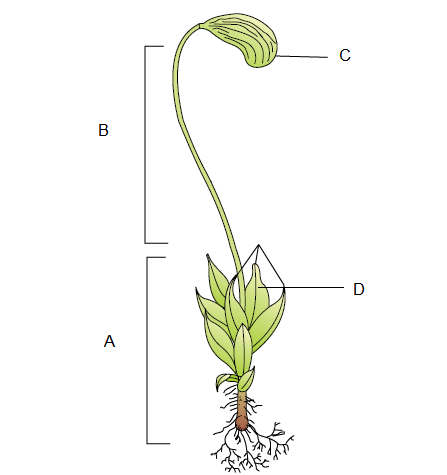
Answer: Funaria: A-Gametophyte, B-Sporophyte, C-Capsule, D-Leaves
Q23. Gracilaria and Porphyra are the members of which algae class?
Answer: Rhodophyceae
Q24. Identify the given figure and also identify the part which produce specialised asexual reproductive structures?
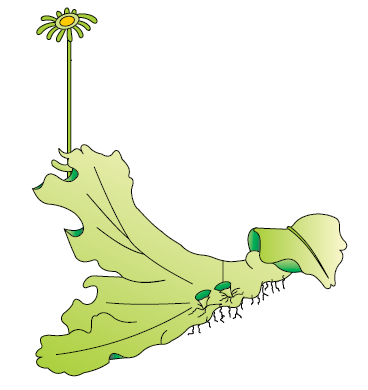
Answer: Marchantia, Gemma cup
Q25. Identify the plants in figures (A & B)
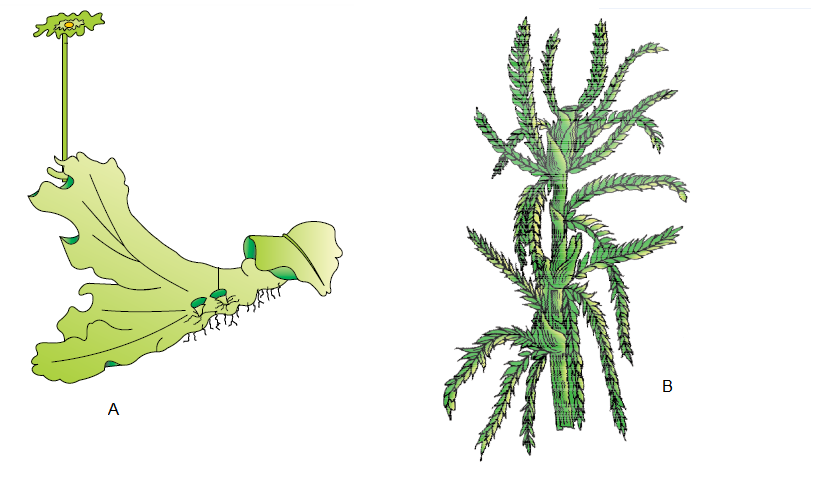
Answer: A-Marchantia (Dioecious), B-Sphagnum(Monoecious)
Q26. Bryophytes are called amphibians of the plant kingdom. Why?
Answer: Because they can live in the moist soil but depend on water for sexual reproduction.
Q27. Study the given flow chart and identify A, B, C & D :
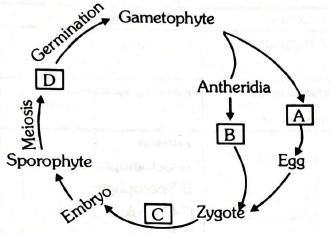
Answer: A-Archegonia, B-Antherozoids, C-Mitosis, D-Spores
Q28. In liverworts, A are green, multicellular, asexual buds, which develop in small receptacles called B located on thallus :
Answer: A-Gemmae, B-Gemma cups
Q29. In bryophytes, zygotes do not undergo reduction division immediately. (True/False)
Answer: True
Q30.
\(\begin{aligned}
&\text { Find the ploidy level of followings with respect to bryophytes :}\\
&\begin{array}{ll}
\text { A-Gametophyte } & \text { B-Sporophyte } \\
\text { C-Spore } & \text { D-Antherozoids } \\
\text { E-Gemmae } & \text { F-Rhizoids }
\end{array}
\end{aligned}
\)
Answer:
\(\begin{array}{ll}
\text { A-n } & \text { B-2n } \\
\text { C-n } & \text { D-n } \\
\text { E-n } & \text { F-n }
\end{array}
\)
Q31. The moss gametophyte consists of two predominant stages, what they are, and they develop from?
Answer:
\(\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Stages } & \text { Develop from } \\
\hline \text { Protonema } & \text { Spore } \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { Leafy } \\
\text { gametophyte }
\end{array} & \text { Bud } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Q32. In bryophytes, the dominant phase in the life cycle is the ______ plant body but in pteridophytes, the main plant body is _______.
Answer: Gametophytic, Sporophytic
Q33. Which of the following term is not related with mosses?
Capsule, Buds, Prothallus, Rhizoids, Archegonia, Protonema
Answer: Prothallus
Q34. Which part of gametophytic plant body of a moss bears sex organs-antheridia & archegonia?
Answer: At the apex of the leafy shoots
Q35. Identify the following figure :
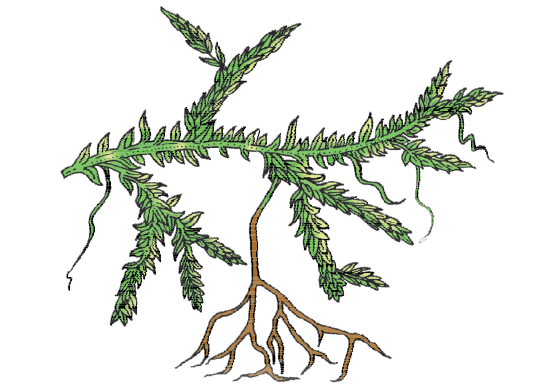
Answer: Selaginella
Q36. Label the \(A, B, C \& D\) in given figure :
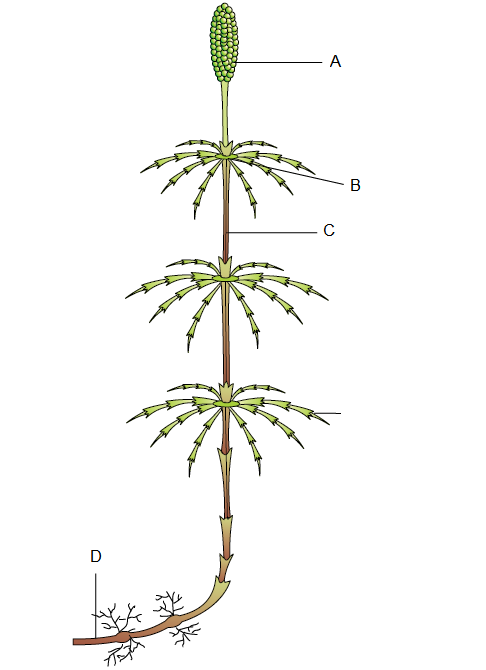
Answer: A-Strobilus B-Node C-Internode D-Rhizome
Q37. Identify the following figures \(( A \& B)\) :
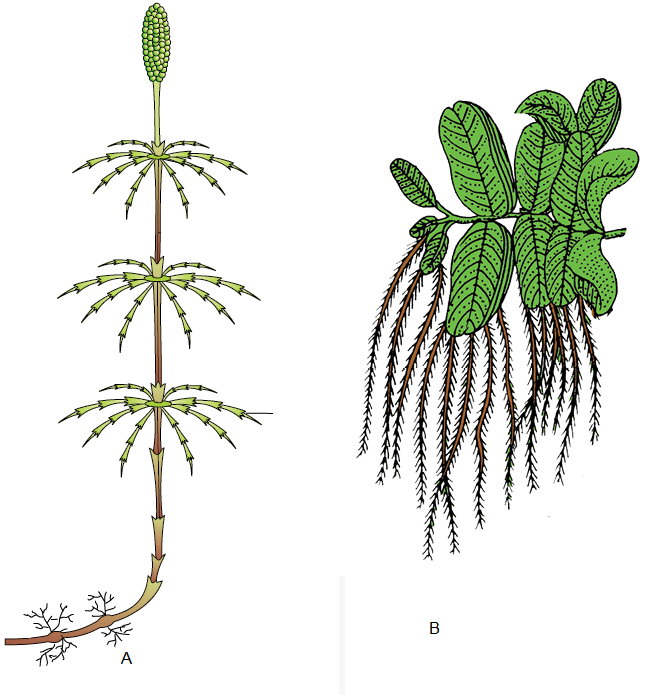
Answer: A-Equisetum, B-Salvinia
Q38. Match the column I with column II:
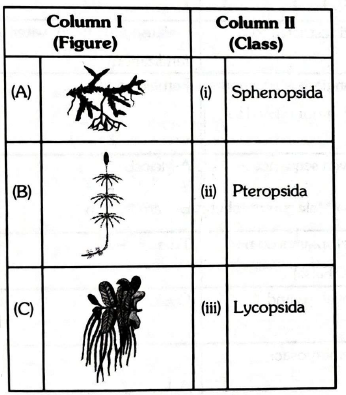
Answer: A-iii, B-i, C-ii
Q39. How many of the following have heterosporous nature? Selaginella, Equisetum, Salvinia
Answer: Two (Selaginella, Salvinia)
Q40. Study the following life cycle of Pteridophytes:
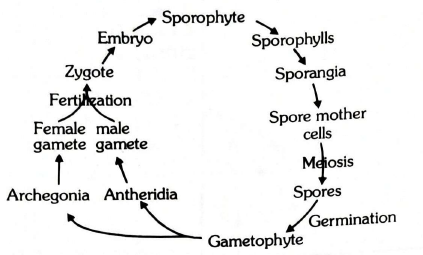
How many structures represent gametophytic & sporophytic generations, respectively?
Answer: Gametophytic structures = Six [Spore, Gametophyte, antheridia, archegonia, male gamete and female gamete]
Sporophytic structures =Six [Zygote, embryo, sporophyte, sporophylls, sporangia and spore mother cells]
Q41. Read the following informations and identify the genus :-
- Coralloid roots are with BGA
- Unbranched stem
- Lack ovary wall
- Pinnate leaves
Answer: Cycas
Q42. Match the column I with Column II:
\(\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { (A) } & \text { Pinus } & \text { (i) } & \text { Precursor of seed habit } \\
\hline \text { (B) } & \text { Cycas } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Coralloid roots } \\
\hline \text { (C) } & \text { Selaginella } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Mycorrhizal association } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer: A-iii, B-ii, C-i
Q43. The spread of living pteridophytes is limited and restricted to narrow geographical regions. why?
Answer: because they need water for fertilization
Q44. Female cone \(\rightarrow\) Mega sporophylls \(\rightarrow\) Megasporangia \(\rightarrow\) Megaspores
For above terms, which one is related to Pinus but not related to Cycas?
Answer: Female cone
Q45. Identify the name of processes \(( A \& B)\) in the given sequence :
Microspore mother cell \(\xrightarrow{ A }\) Microspore \(\xrightarrow{ B }\) Male gametophyte
Answer: A-Meiosis, B-Germination
Q46. In gymnosperms, the male and the female gametophytes do not have an independent free-living existence. (True/False)
Answer: True
Q47. In gymnosperms, the nucellus is protected by envelops and the composite structure is called?
Answer: Ovule
Q48. How many of the following cells are present in emoryosac:
A – Egg cell
B – Synergids
C – Antipodals
D – Central cell
Answer:
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \text { A-1 } \\
& \text { B-2 } \\
& \text { C-3 } \\
& \text { D-1 }
\end{aligned}
\)
Q49. Write the names of male and female sex organs of angiosperms respectively :
Answer: Stamen, Carpel or Pistil
Q50. In how many classes angiosperms are divided?
Answer: Two (Dicotyledonae and monocotyledonae)
Q51. Ovules, stamen, ovary, carpel, anther, antipodals, synergids. pollen grains How many structures are NOT produced by female plant of angiosperm?
Answer: Three: Stamen, Anther, Pollen grains
Q52. Angiosperms range in size from tiny, almost microspic e.g. A to tall trees of e.g. B.
Answer: A-Wolffia, B-Eucalyptus
Q53. How many nuclei are involved in double fertilization?
Answer: Five [2 male nuclei, 2 polar nuclei. 1 egg nucleus]
Q54. Write down the ploidy level of followings regarding typical angiosperm :- (A) Endosperm (B) Synergids (C) Embryo
(D) Pollen grain (E) Embryosac
Answer: \(A-3 n, B-n, C-2 n, D-n, E-n\)
Q55. After fertilization, what is the future of the following :
(A) Ovule
(B) Synergieds
(C) Ovary
(D) Antipodals
Answer: A-Seed, B-Degenerate, C-Fruit, D-Degenerate
Q56. Identify the \(A , B , C , D \& E\) in given life cycle of an angiosperm:
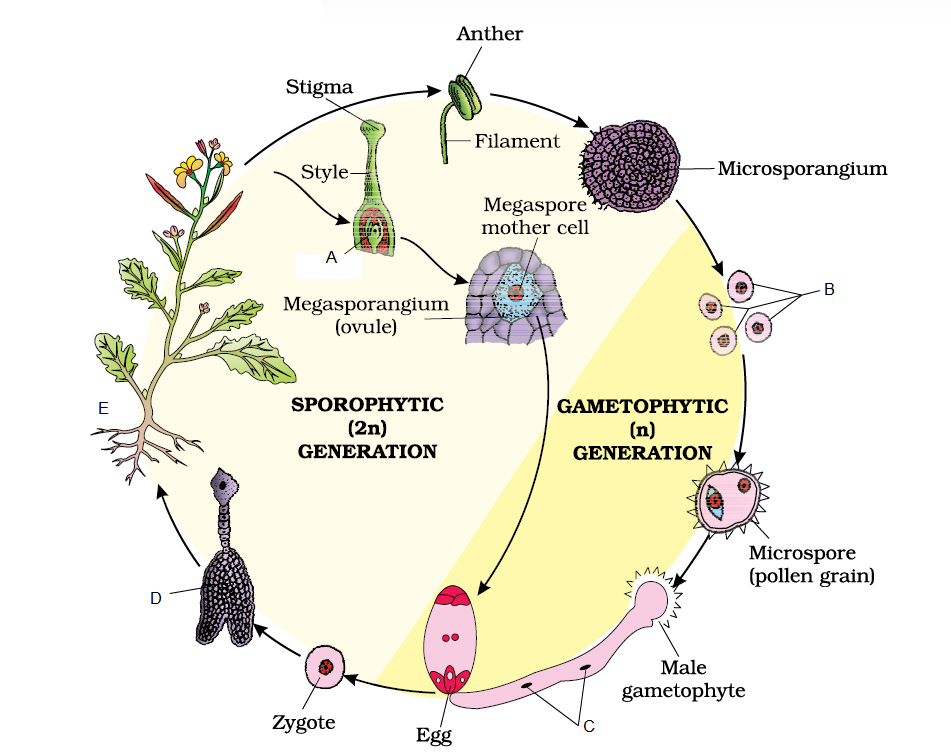
Answer: A-Ovary, B-Microspore, C-Male gametes, D-Embryo, E-Sporophyte
Q57. Many algae such as Volvox, Spirogyra and some species of Chlamydomonas represent ________ pattern of life cycle.
Answer: Haplontic
Q58. Which kind of life cycle pattern is shown by all seed-bearing plants?
Answer: Diplontic
Q59. The life cycle of any sexually reproducting plant, there is an alternation of generation between A producing by haploid gametophyte and B producing by diplod Sporophyte.
Answer: A-Gametes, B-Spore
Q60. Which processes are essential for alteration of generation in plant life cycle?
Answer:
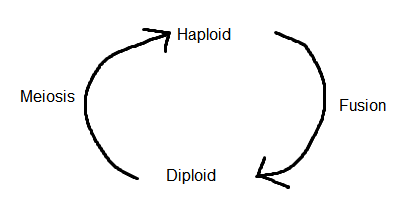
Meiosis and fusion of gametes
Q61. In bryophytes, what is the dominant phase of life cycle?
Answer: Gametophytic phase
Q62. “The diploid sporophyte is represented by a dominant, independent, photosynthetic, vascular plant body. It alternates with multicellular saprophytic/autotrophic, independent but short-lived haploid gametophytes”
Above pattern of life cycle is represented by which group of plants?
Answer: Pteridophyta
Q63. “The short-lived multicellular sporophyte totally or partially dependent on the gametophyte”
Above statement is related to which group of kingdom plantae?
Answer: Bryophyta
Q64. Which type of life cycle is found in Fucus?
Answer: Diplontic
Q65. Algae usually reproduce vegetatively by A, asexually by formation of B and sexually by fusion of C .
Answer: A-Fragmentation, B-Spores, C-Gametes
Q66. Match the column-I (Process) with column II (Result)
\(\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Column I (Process) } & \text { Column II (Result) } \\
\text { (A) Fusion of male } & \text { (i) Spores } \\
\text { (B) Mitosis in zygote } & \text { (ii) Zygote } \\
\text { (C) Meiosis in sporophyte } & \text { (iii) Gametophyte } \\
\text { (D) Germination of spores } & \text { (iv) Embryo }
\end{array}
\)
Answer: A-ii, B-iv, C-i, D-iii