CH-6- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
Q1. On the basis of their….(A) … and …..(B)…., there are three types of
Answer: A-Structure/morphology, B-Location/Position
Q2. Phloem fibre are made up of ….(A)…… cells. These are generally absent in the ….(B)….. .
Answer: A-Sclerenchymatous, B-Primary Phloem
Q3. Epiderrnal cell are …..(A)….. With a small amount of …..(B)….. and large vacuole.
Answer: A-Parenchymatous, B-Cytoplasm
Q4. In dicots, guard cells are. ….(A)…. shaped whereas in grasses quard cells are ….(B)… shaped.
Answer: A-bean, B-dumb-bell
Q5. The stomatal aperture, guard cells and the surrounding subsidiary cells are together called …(A)….
Answer: A-Stomatal apparatus
Q6. The root hairs are …..(A) … elongations of the …(B)…. cells and help absorb water and minerals from the soil.
Answer: A-Unicellular, B-Epidermal
Q7. All tissues except ….(A)…. and Vascular bundles constitute the ground tissue system.
Answer: A-Epidermis
Q8. In ….(A) … the ground tissue consists of thin walled. Chloroplasts containing cells and is called …(B)…
Answer: A-Leaves, B-Mesophyll
Q9. Given figure represents which type of vascular bundle?
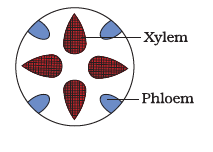
Answer: Radial
Q10. Given figure represents which type of vasculer bundle?
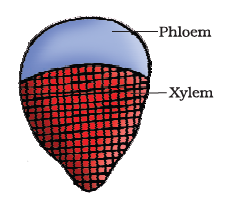
Answer: Conjoint, collateral & closed
Q11. Given figure represents which type of vascular bundle?
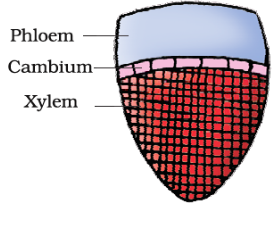
Answer: Conjoint, collateral & open
Q12. Which type of vascular bundles are found in roots?
Answer: Radial
Q13. Some of the terms are given below :
Pericycle, Pith, vascular bundles and medullary rays
Which is not a part of stele in the primary internal structure of Dicot and Monocot roots but part of stele
in the primary internal structure of Dicot stem.
Answer: Medullary rays
Q14. The cross section of a plant material shows the following anatomical features under microscope:-
(a) usually more than six xylem bundles with exarch xylem
(b) pith is large and well developed
(c) Radial arrangement of xylem and phloem bundles.
The plant material should be:
Answer: Monocotyledonous root / Monocotyledonous root
Q15. In the internal structure of roots, casparian strips are present in
Answer: Endodermis
Q16. The cross section of a plant material shows the following anatomical features under microscope.
(a) usually two to four xylem and phloem patches with exarch xylem.
(b) pith in small or inconspicuous.
(c) Radial arrangement of xylem & phloem bundle. The plant material should be.
Answer: Dicotyledonous root
Q17. In flowering plants, lateral roots are endogenous in origin and originates from the cells of …(A)….
Answer: A-Pericycle
Q18. In dicotyledonous stem, which layer is also termed as starch sheath?
Answer: Endodermis
Q19. List of some of the plant materials is given below :
– Dicotyledonous root
– Monocotyledonous root
– Dicotyledonae stem
– Monocotyledonous stem
Which plant material have sclerenchymatous pericycle in patches, located just above phloem bundles in the primary internal structure.
Answer: Dicotyledonous stem
Q20. List of some the plant materials is given below :
– Dicotyledonous root
– Dicotyledonous stem
– Monocotyledonous root
Which plant material have bundle cap in the primary internal structure?
Answer: Dicotyledonous stem
Q21. In the internal structure of sunflower stem, in between the vascular bundles there are a few layers of radially placed …(A)… cells, which constitute…(B)…
Answer: A-Parenchymatous, B-Medullary rays
Q22. Which type of vascular bundles are found in the primary internal structure of dicotyledonous stem (eg. Sunflower stem)?
Answer: Conjoint, collateral & open
Q23. The cross section of a plant material shows the following anatomical features under microscope:
(a) Sclerenchymatous bundle sheath
(b) Many vascular bundles are scattered in parenchymatous ground tissue, each vascular bundle is surrounded by sclerenchymatous bundle sheath
(c) Vascular bundles are usually oval shaped.
(d) Vascular bundles are conjoint, collateral \& closed and xylem is endarch
(e) Phloem parenchyma is absent and water containing cavities are present within the vascular bundles
The plant material should be :
Answer: Monocotyledonous stem
Q24. Look at the given figure and find the position (Adaxial or abaxial) of xylem in the vascular bundle.
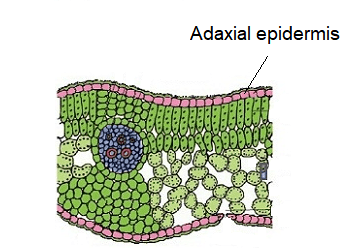
Answer: Adaxial
Q25. In a dorsiventral leaf, palisade parenchyma lies towards …(A)… epidermis and spongy parenchyma lies towards …(B)… epidermis.
Answer: A- Adaxial, B-Abaxial
Q26. In grasses, certain …(A)… epidermal cells along the veins modify themselves into large, empty, colourless cells. These cells are called ——– (B) —– cells.
Answer: A-Adaxial, B-Bulliform
Q27. The …(A)… venation in monocot leaves is reflected in the near similar sizes of vascular bundles (except in main veins) as seen in vertical section of the leaves.
Answer: A-Parallel
Q28. In a isobilateral leaf, two distinct patches of …(A)… are present above and below of each large …(B)… which extend towards upper and lower epidermis, respectively.
Answer: A-Sclerenchyma, B- Vascular bundle
Q29. In dicot stem, the cells of cambium present between primary xylem and primary phloem is the ….(A)….
Answer: A-Intra fascicular cambium
Q30. At some places, the cambium forms a narrow bands of …(A)…, which passes through the secondary xylem and the secondary phloem in the radial directions. These are the …(B)….
Answer: A-Parenchyma, B-Secondary Medullary rays
Q31. Name the lateral meristem which is responsible for the formation of phellem and phelloderm.
Answer: Phellogen (Cork cambium)
Q32. Name the lateral meristem which is responsible for the formation of secondary xylem, secondary phloem and secondary medullary rays.
Answer: Vascular cambium
Q33. In the given figure Labelled Structure ‘ x ‘ is :
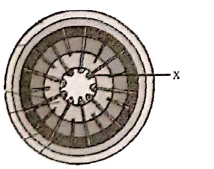
Answer: x= Primary xylem
Q34. Identify what does a, b, c, d & e represents in the figure below:
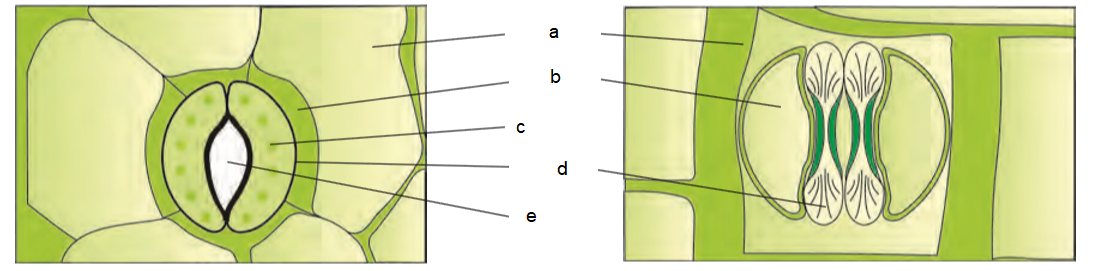
Answer: a – Epidermal cells, b – Subsidiary cells, c – Chloroplast, d – Guard cells, e – Stomatal pore
Q35. The cells of epidermis bear a number of hairs. The root hairs are unicellular elongations of the epidermal cells and help absorb water and minerals from the soil. On the stem the epidermal hairs are called trichomes. The trichomes in the shoot system are usually multicellular. Is this statement True or False?
Answer: True
Q36. All tissues except epidermis and vascular bundles constitute the ———
Answer: ground tissue.
Q37. In leaves, the ground tissue consists of thin-walled chloroplast containing cells and is called ——
Answer: mesophyll.
Q38. Ground tissue consists of what?
Answer: It consists of simple tissues such as parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma. Parenchymatous cells are usually present in cortex, pericycle, pith and medullary rays, in the primary stems and roots.
Q39. Identify what does a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h & i represents in the figure below:
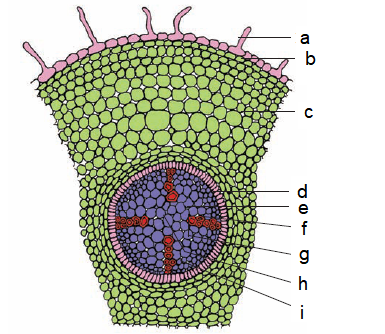
Answer: (T.S.: Dicot root [primary]) a – Root hair, b -Epidermis, c – Cortex, d – Endodermis, e – Pericycle, f – Protoxylem, g – Metaxylem, h -Pith, i – Phloem
Q40. What does the figure shown below represent?
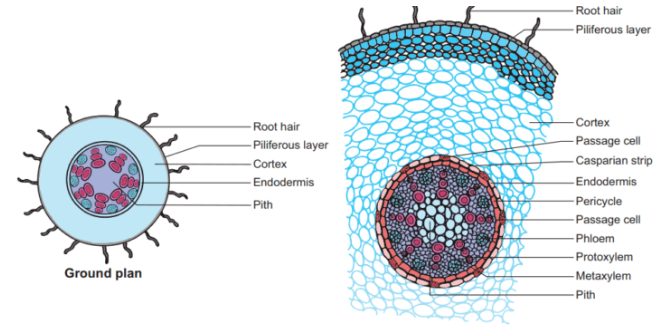
Answer: T. S. : Monocot root
Q41. Indicate T.S. of stem: Dicot
Answer:
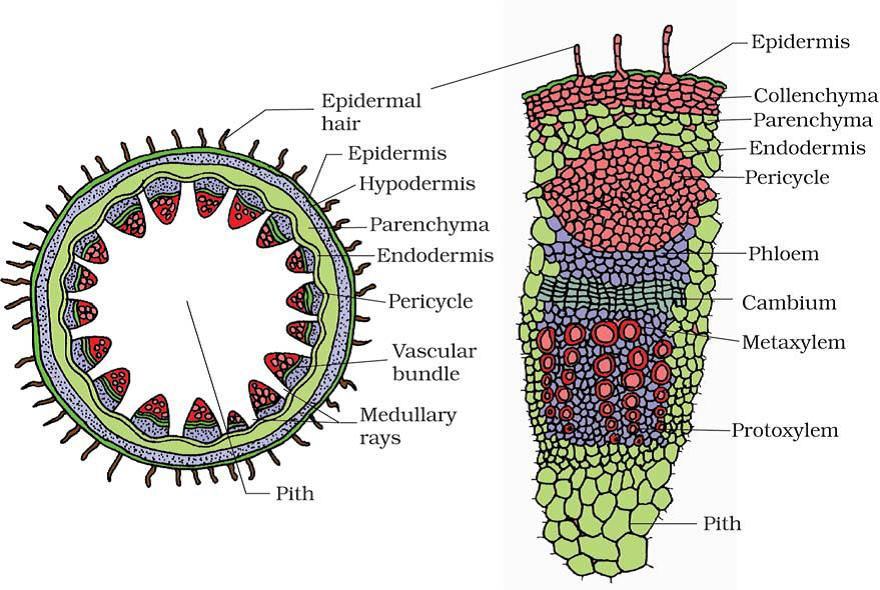
Q42. Indicate T.S. of stem: Monocot
Answer:
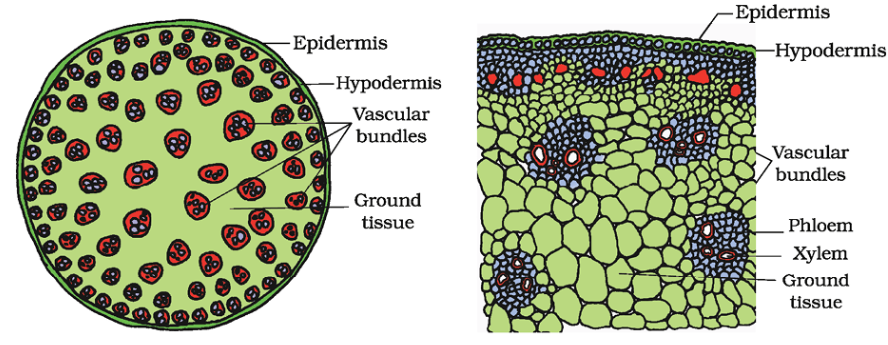
Q43. Identify the items marked in the figure below.
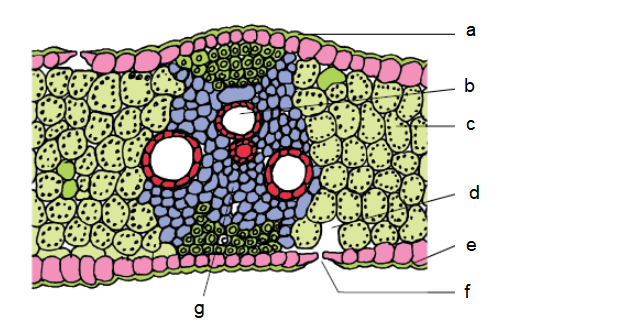
Answer: a- Adaxial epidermis, b – Xylem, c – Mesophyll, d- Sub-stomatal cavity, e – Abaxial epidermis, f- Stoma, g – phloem
Q44. In grasses, certain adaxial epidermal cells along the veins modify themselves into large, empty, colourless cells. These are called —–
Answer: bulliform cells.
Q45. The Dicotyledonous Root outermost layer is called —–
Answer: Epiblema
Q45. The Dicotyledonous Root innermost layer of the cortex is called —–
Answer: Endodermis.
Q46. The tangential as well as radial walls of the endodermal cells have a deposition of water-impermeable, waxy material suberin in the form of ——
Answer: Casparian strips.
Q47. Next to endodermis lies a few layers of thick-walled parenchyomatous cells referred to as —–
Answer: pericycle.
Q48. The parenchymatous cells which lie between the xylem and the phloem are called —–
Answer: Conjuctive tissue.
Q49. All tissues on the inner side of the endodermis such as pericycle, vascular bundles and pith constitute the ——–.
Answer: Stele
Q50. There are usually more than —— xylem bundles in the monocot root.
Answer: six (polyarch)
Q51. Monocotyledonous roots do not undergo any secondary growth. True or False?
Answer: True
Q52. The tissue between the upper and the lower epidermis is called the ———
Answer: mesophyll
Q53. Mesophyll, which possesses chloroplasts and carry out photosynthesis, is made up of parenchyma. It has two types of cells. What are they?
Answer: The palisade parenchyma and the spongy parenchyma.
Q54. The size of the vascular bundles are dependent on the size of the —–
Answer: veins.
Q55. The vascular tissue system is formed by the —–
Answer: xylem and phloem
Q56. The secondary growth occurs in most of the dicotyledonous —–
Answer: roots and stems
Q57. There are three types of tissue systems. What are they?
Answer: epidermal, ground and vascular.
Q58. The ground tissue system forms the main bulk of the plant. It is divided into three zones known as ———
Answer: cortex, pericycle and pith
Q59. The plant tissues are broadly classified into ——– and ——–
Answer: meristematic (apical, lateral and intercalary) and permanent (simple and complex)
Q60. The epidermal tissue systems are made of ———-
Answer: epidermal cells, stomata and the epidermal appendages.