Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants NCERT
Quiz Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
In the diagrammatic representation of L.S. of a flower:
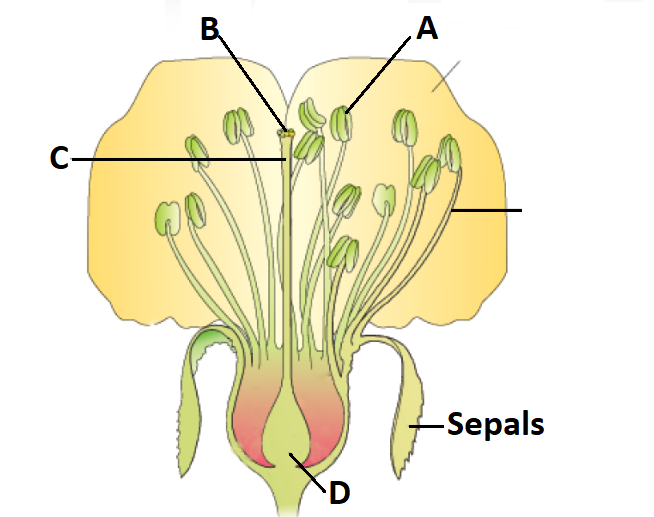
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { Statement } \\
\text { I: }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { A is anther and collectively anthers form the } \\
\text { androecium of the flower. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { Statement } \\
\text { II: }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { B is the site for landing of pollens during } \\
\text { pollination, C is style, and D after fertilisation } \\
\text { becomes a fruit. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(a)
-
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
Cultivation of flowering and ornamental plants for gardens and for commerce and trade is called:
Hint
(c)
-
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
Consider the following statements regarding floral primordium:
I: It is formed at the shoot apical meristem
II: The development of flowers is dependent on genetics, PGR, and environmental conditions.
Of the two statements:Hint
(c)
-
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
In an angiosperm, the structure that develops and becomes a pollen sac is called:
Hint
(c)
-
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
Given below is a three-dimensional cut section of an anther:
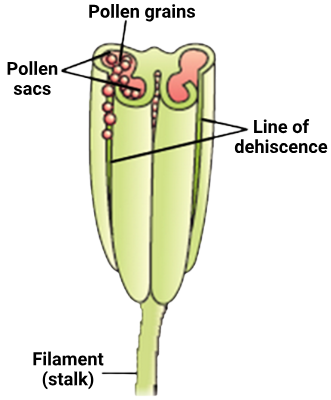
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Statement I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { The bilobed nature of an anther is very } \\
\text { distinct in the given section. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Statement II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { The anther is a two-sided [bigonal] } \\
\text { structure consisting of four } \\
\text { microsporangia located at the corners, two } \\
\text { in each lobe. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(c)
NCERT:-
II:-The anther is a four-sided (tetragonal) structure
consisting of four microsporangia located at the
corners, two in each lobe. -
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
The layers in the walls of the microsporangium that helps in the dehiscence of anther to release the pollen include:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I. } & \text { Epidermis } \\
\hline \text { II. } & \text { Endothecium } \\
\hline \text { III. } & \text { Middle layers } \\
\hline \text { IV. } & \text { Tapetum } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(b)
NCERT:
The outer three (Excluding Tapetum) wall layers perform the function of protection and help in
dehiscence of anther to release the pollen. -
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
Tapetum:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline 1 . & \text { is the outermost layer in the wall of microsporangium } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { helps in the protection of the pollen grains } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { helps in dehiscence of anther } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { has cells that generally have more than one nucleus } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(d)
NCERT: Cells of the
tapetum possess dense cytoplasm and generally have more than one
nucleus -
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
Identify A-D in the given enlarged view of one microsporangium showing wall layers:
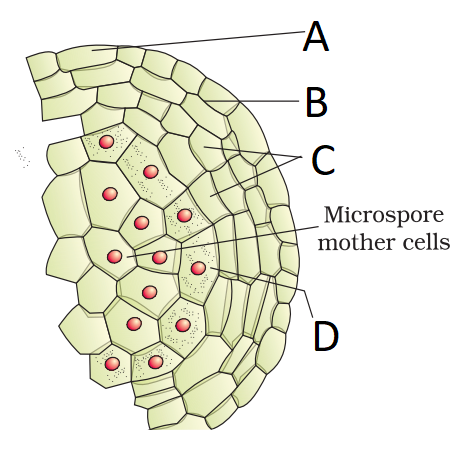
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline \text { 1. } & \text { Epidermis } & \text { Endothecium } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Middle } \\
\text { layers }
\end{array} & \text { Tapetum } \\
\hline \text { 2. } & \text { Epithelium } & \text { Endothelium } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Middle } \\
\text { layers }
\end{array} & \text { Tapetum } \\
\hline \text { 3. } & \text { Endothecium } & \text { Epidermis } & \text { Tapetum } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Middle } \\
\text { layers }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { 4. } & \text { Epithelium } & \text { Endothelium } & \text { Tapetum } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Middle } \\
\text { layers }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(a)
-
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
The given diagram shows a mature dehisced anther.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { Statement } \\
\text { I: }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { This process is coordinated precisely with } \\
\text { pollen differentiation, floral development, and } \\
\text { flower opening. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { Statement } \\
\text { II: }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Anther dehiscence is the final function of the } \\
\text { anther that causes the release of pollen grains. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(b)
-
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
During microsporogenesis, meiosis occurs in:
Hint
(b)
-
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
The outer hard layer of the pollen wall is made up of:
Hint
(b)
-
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
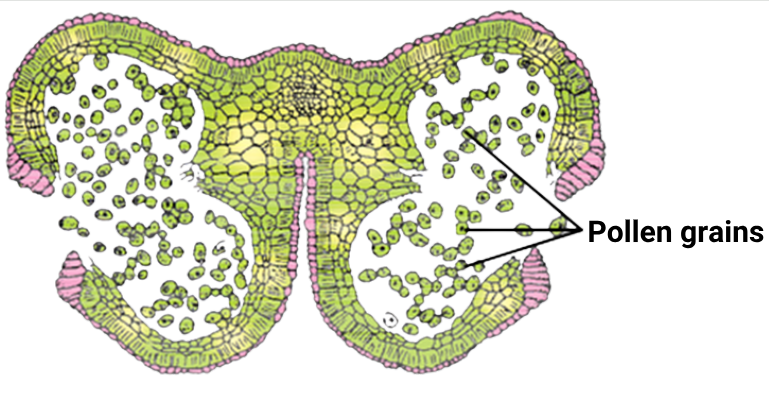
Regarding the given diagram:
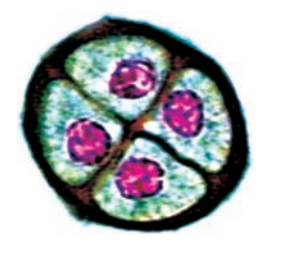
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { Statement } \\
\text { I: }
\end{array} & \text { It shows a pollen tetrad. } \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { Statement } \\
\text { II: }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { The four microspores are contained by } \\
\text { callose walls. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(a)
-
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
Study the stages of maturation of microspore into a pollen grain and select the correct statements:

\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { Statement } \\
\text { I: }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { The spindle formation as seen in A is strictly } \\
\text { symmetric. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { Statement } \\
\text { II: }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { The larger cell [B] is the generative cell and } \\
\text { the smaller cell [C] is the vegetative cell. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(d)
I: Asymmetric
II: B is Vegetative and C is Generative
-
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
‘Germ pore’ in pollen in angiosperms:
Hint
(d)
-
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
What is true about the vegetative cell in the pollen tube?
Hint
(b)
-
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
Identify the incorrect statement regarding Parthenium hysterophorus:
Hint
(d)
-
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
At what temperature pollens can be stored for years in liquid nitrogen?
Hint
(c)
-
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
In a multicarpellary syncarpous ovary:
Hint
(a)
-
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
Match the structure in COLUMN I with the description in COLUMN II and choose your answer from the codes given below:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Column I} \\
\end{array} & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Stigma } & \text { a. } & \text { Landing platform for pollen grains } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Ovary } & \text { b. } & \text { Basal bulged part of the pistil } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Placenta } & \text { c. } & \text { Part of the ovary where funiculus attaches } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Ovule } & \text { d. } & \text { Megasporangium } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Codes:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { a } & \text { b } & \text { c } & \text { d } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { a } & \text { c } & \text { b } & \text { d } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { b } & \text { a } & \text { d } & \text { c } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { d } & \text { c } & \text { b } & \text { a } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(a)
-
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
From among the sets of terms given below, identify those that are associated with the gynoecium.
Hint
(a)
-
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
Match each item in Table I with one in Table II and select the correct match from the codes given:
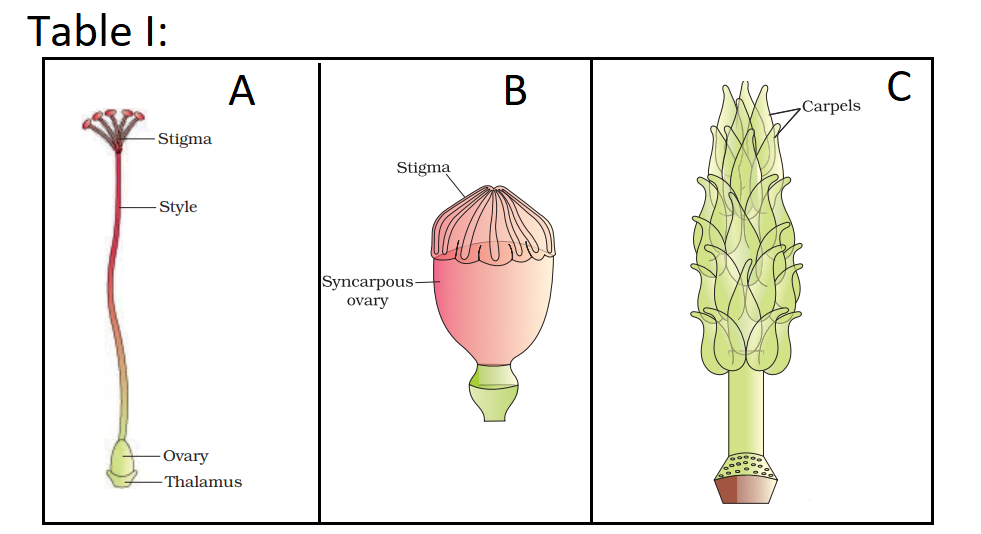
Table II
P. A dissected flower of Hibiscus showing pistil where other floral parts have been removed
Q. Multicarpellary, syncarpous pistil of Papaver
R. Multicarpellary, apocarpous gynoecium of Michelia\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline
& \textbf{A} & \textbf{B} & \textbf{C} \\
\hline
1. & P & Q & R \\
\hline
2. & P & R & Q \\
\hline
3. & Q & R & P \\
\hline
4. & R & P & Q \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(a)
-
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
Starting from the innermost part, the correct sequence of parts in an ovule are:
Hint
(b)
-
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
Consider the following two statements regarding the integuments of an ovule:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Angiosperms are generally bitegmic and } \\
\text { gymnosperms unitegmic }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { The integuments develop into the seed coat when the } \\
\text { ovule matures after } \\
\text { fertilization. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Of the two statements:Hint
(a)
-
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
Regarding the mature monosporic female gametophyte of angiosperms:
Hint
(d)
I: Incorrect — Egg apparatus is at the micropylar end, and antipodals are at the chalazal end.
II: Incorrect — The two polar nuclei are haploid (n each), but they later fuse during double fertilization to form a diploid secondary nucleus, and finally a triploid endosperm nucleus after fertilization.
III: Incorrect -It is 7-celled and 8-nucleate, as per NCERT.
-
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
Regarding part I of the diagram:

\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Statement I: } & \text { A is the Chalazal end. } \\
\hline \text { Statement II: } & \text { B is the microspore mother cell, } \mathrm{C} \text { is the microspore dyad and } \mathrm{D} \text { is the microspore tetrad. } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(d)
A is Mycropylar end
B is Megaspore Mother cell , C is Megaspoe Dyad and D is Megaspore Tetrad
-
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
Choose the correct statement from the following:
Hint
(a)
-
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
Wind-pollinated flowers are characterized by the following except:
Hint
(c)
NCERT:- Wind pollinated flowers often have a single ovule in
each ovary -
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
Regarding part II of the diagram:

\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Statement I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { It shows the two, four, and eighth nucleate } \\
\text { stages of the embryo sac. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Statement II: } & \text { The divisions are mitotic and free nuclear. } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(a)
-
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
The diagram shows stages in embryo development in a dicot where A, B, and C respectively are:

Hint
(b)
-
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
The plant shown in the given diagram is most likely to be pollinated by:
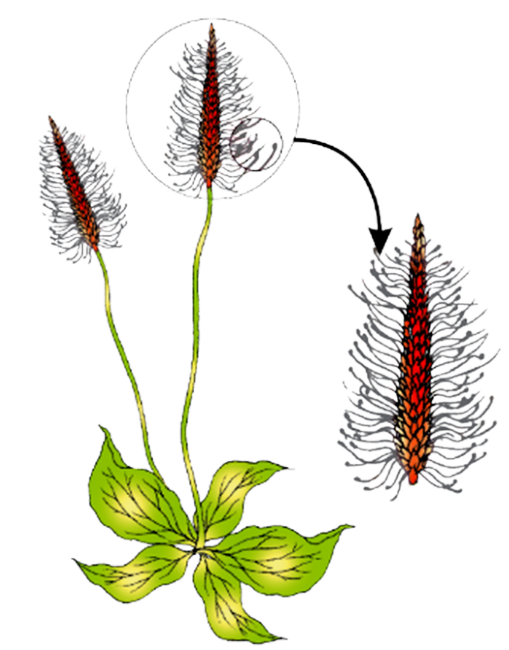
Hint
(b)
-
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
Embryos of monocotyledons possess only one ___A____. In the grass family the cotyledon is called ____B___
that is situated towards one side (lateral) of the embryonal axis. At its lower end, the embryonal axis has the
radical and root cap enclosed in an undifferentiated sheath called ____C___.
The portion of the embryonal axis above the level of attachment of scutellum is the ____D___ which has a shoot apex enclosed in a foliar structure called ____E____.Hint
(a)
-
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
Regarding part III of the diagram:
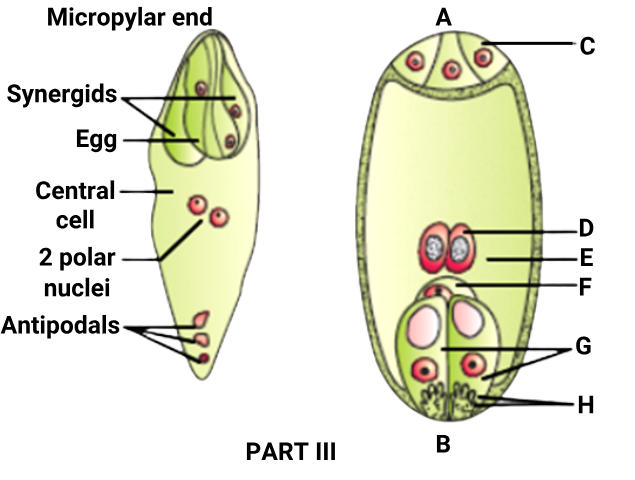
Statement I: It represents mature embryo-sac or the female gametophyte in an angiosperm.
Statement II: A is the micropylar end and B is the Chalazal end
Statement III: C guides the entry of the pollen tube into the embryo sac.
Statement IV: D is the polar nuclei and E is the central cell.
Statement V: F is the egg cell.
Statement VI: G is the antipodals and H is special cellular thickenings.The correct Statements are:
Hint
(c)
II: ❌ False — The labels are actually:
- A = Chalazal end (top in the image)
- B = Micropylar end (bottom in the image)
III: ❌ False — C is labeled as antipodals, which do not guide the pollen tube.
The synergids (G), especially with the filiform apparatus (H), guide the pollen tube.VI: ❌ False — G = Synergids, not antipodals;
H = Filiform apparatus (correct as special thickenings). -
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
From the statements given below, choose the option that is true for a typical female gametophyte of a flowering plant:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { i. } & \text { It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity } \\
\hline \text { ii. } & \text { It is free-nuclear during the development } \\
\hline \text { iii. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { It is situated inside the integument but outside the } \\
\text { nucellus }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { iv. } & \text { It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(c)
3. ❌ False
- The embryo sac is located inside the nucellus, which is in turn surrounded by integuments.
- So, the correct location is: inside both the nucellus and integuments.
4. ❌ False
-
The egg apparatus (egg + 2 synergids) is located at the micropylar end, not the chalazal end.
-
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
In the given diagram showing the structure of a monocot seed:

\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Statement I: } & \text { A is pericarp. } \\
\hline \text { Statement II: } & \text { B is the cotyledon of the monocot seed. } \\
\hline \text { Statement III: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { C is triploid in nature and develops before } \\
\text { B. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(a)
B is Endosperm
C is Scutellum which is cotyledon of monocot seed
-
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
The diagram shows:
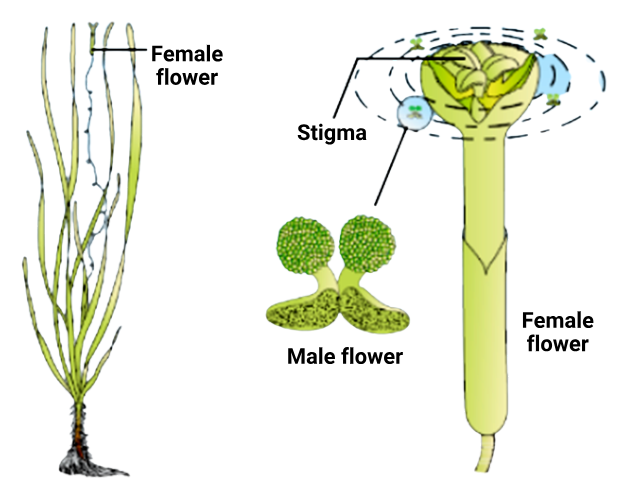
Hint
(a)
-
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
Plants have developed many mechanisms to encourage cross-pollination that include:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Asynchrony between pollen release and stigma } \\
\text { receptivity }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { II. } & \text { Placing of pollen and stigma at different positions } \\
\hline \text { III. } & \text { Self-incompatibility } \\
\hline \text { IV. } & \text { Dioecy } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
What would be true regarding these mechanisms?Hint
(b)
1.
- I (Dichogamy): prevents autogamy (same flower), but not always geitonogamy (different flowers on the same plant).
- II (Herkogamy): prevents autogamy, but geitonogamy can still occur if pollen is transferred to another flower of the same plant.
- 🔸 Verdict: ❌ Incorrect – They prevent autogamy, but not always geitonogamy.
3.
- Dioecy = male and female flowers on separate plants.
- This is not common in flowering plants. Most are hermaphrodite or monoecious.
- 🔸 Verdict: ❌ Incorrect – Dioecy is relatively rare in angiosperms.
4.
- I and II: reduce autogamy, but don’t guarantee xenogamy (they can allow geitonogamy).
- III: strongly promotes xenogamy.
- 🔸 Verdict: ❌ Incorrect – Only III invariably leads to xenogamy.
-
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
From among the situations given below, choose the one that prevents both autogamy and geitonogamy.
Hint
(b)
Plant and flower both should be unisexual
-
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
Whether a pollen grain will be able to germinate on a stigma is primarily decided by:
Hint
(b)
-
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
In the diagram identify A to D :
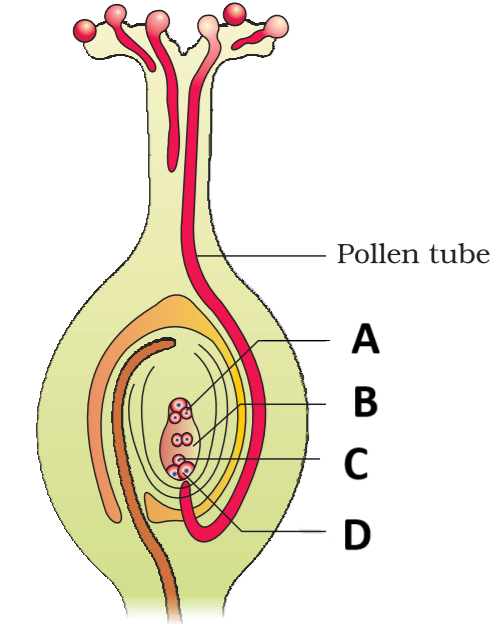
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline \text { 1. } & \text { Synergid } & \text { Polar nuclei } & \text { Male gamete } & \text { Antipodal } \\
\hline \text { 2. } & \text { Synergid } & \text { PEN } & \text { Male gamete } & \text { Antipodal } \\
\hline \text { 3. } & \text { Antipodal } & \text { Polar nuclei } & \text { Egg cell } & \text { Synergid } \\
\hline \text { 4. } & \text { Antipodal } & \text { PEN } & \text { Egg cell } & \text { Synergid } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(c)
-
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
The diagram shows the false fruits of apple and strawberry.
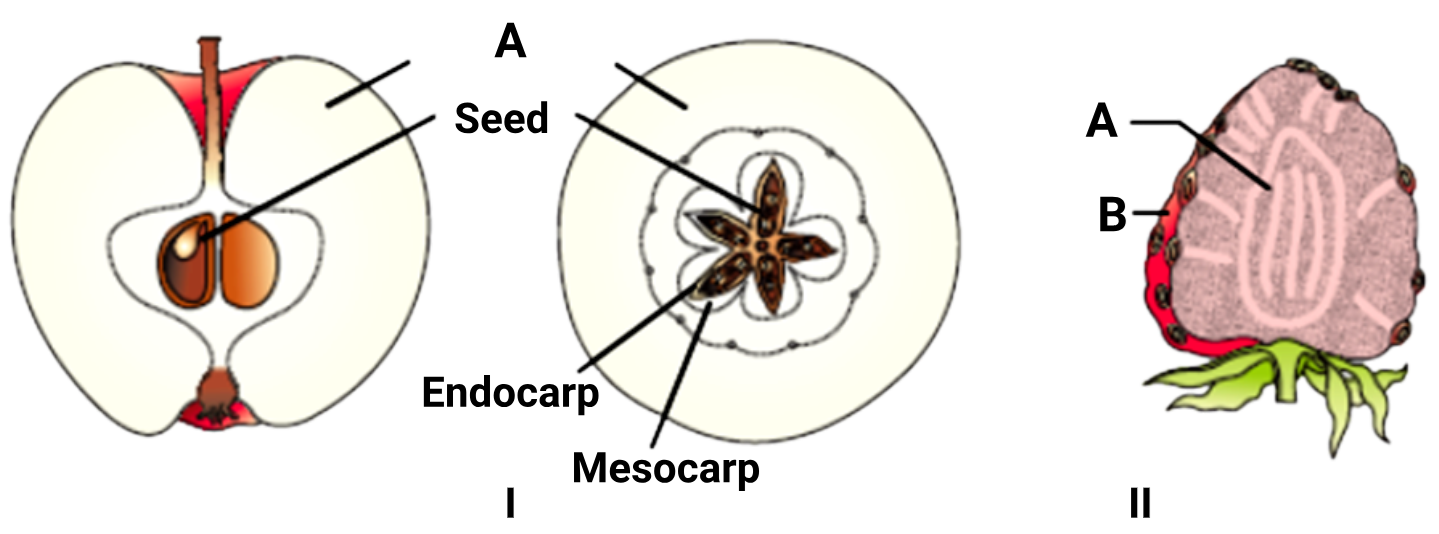
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Statement I: } & \text { False fruits develop only from the ovary. } \\
\hline \text { Statement II: } & \text { A is Thalamus and B is Achene. } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(b)
❌ I: Incorrect
-
False fruits (pseudocarps) are those that develop from floral parts other than the ovary, such as the thalamus.
-
Example: In apple, the fruit develops mainly from the thalamus, not the ovary
-
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
In the given Diagram Identify Correct option regarding A to D
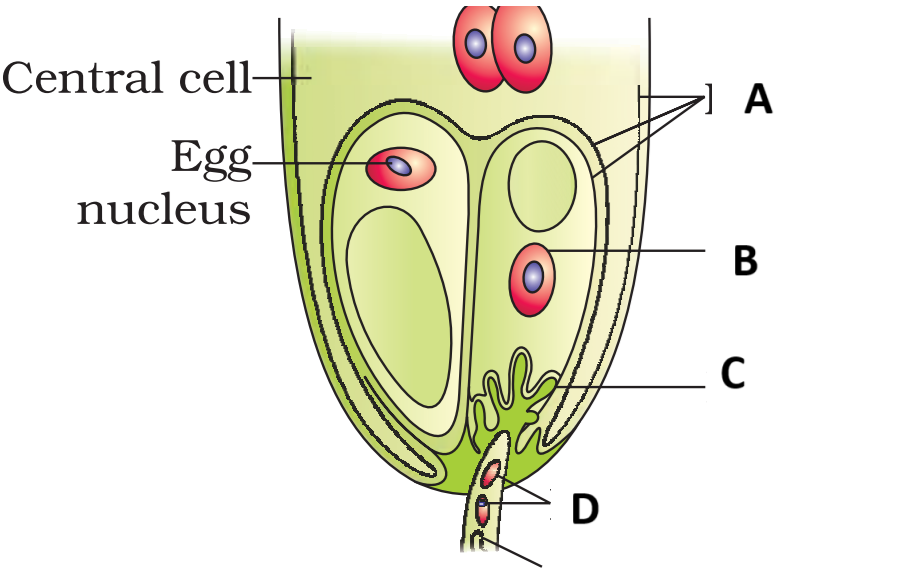
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline
& \text{A} & \text{B} & \text{C} & \text{D} \\
\hline
\text{1.} & \text{Synergid} & \text{Polar nuclei} & \text{Male gamete} & \text{Antipodal} \\
\hline
\text{2.} & \text{Synergid} & \text{PEN} & \text{Male gamete} & \text{Antipodal} \\
\hline
\text{3.} & \text{Antipodal} & \text{Polar nuclei} & \text{Egg cell} & \text{Synergid} \\
\hline
\text{4.} & \text{Plasma membrane} & \text{Synergids} & \text{Filiform apparatus} & \text{Male gametes} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(d)
-
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
The diagram of NCERT given below shows two types of flowers in a certain plant:
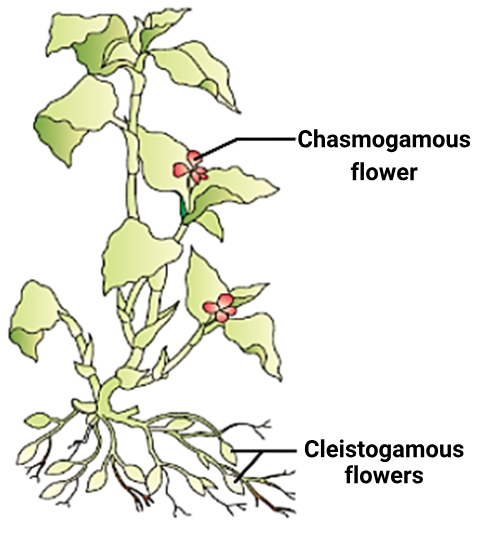
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Statement I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Cleistogamous flowers have an advantage } \\
\text { and a disadvantage over chasmogamous } \\
\text { flowers. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Statement II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Seed set is assured even in the absence of } \\
\text { pollinators but the amount of genetic } \\
\text { variations is less in cleistogamous flowers } \\
\text { when compared to the chasmogamous } \\
\text { flowers. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(b)
-
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R)
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Assertion (A): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { An apomixis is a form of asexual } \\
\text { reproduction that mimics sexual } \\
\text { reproduction. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Reason (R): } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { There is no fertilisation in apomicts } \\
\text { plants and they do not produce any seeds. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :Hint
(a)
Reason is false : -In apomixis seeds are formed without fertilization
-
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
The diagram shows a fertilised embryo sac where:
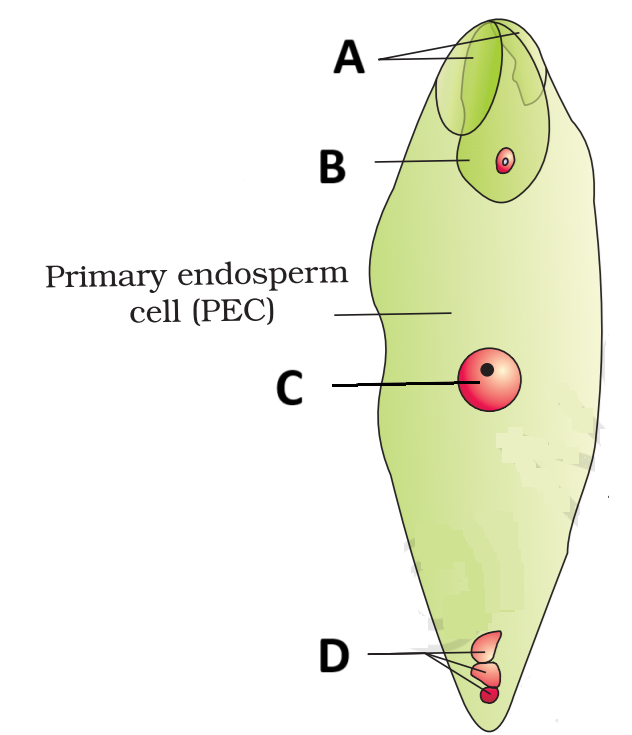
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Statement I: } & \text { A is diploid and B is triploid } \\
\hline \text { Statement II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { C are degenerating antipodal cells and D } \\
\text { are degenerating synergids }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(d)
B is zygote which is diploid that ‘s why Statement I is incorrect
D is antipodal cells and C is Primary Endosperm cell that ‘s why Statement II is also incorrect
-
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
Identify A – D in the diagram showing a typical dicot embryo:
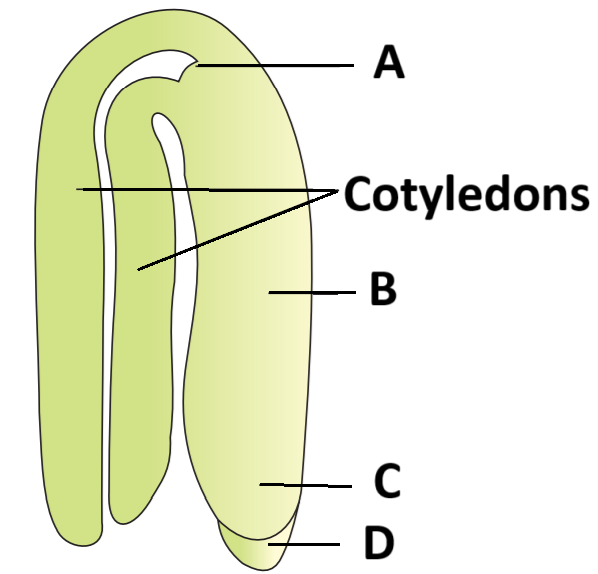
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline \text { 1. } & \text { Radicle } & \text { Epicotyl } & \text { Plumule } & \text { Root cap } \\
\hline \text { 2. } & \text { Radicle } & \text { Epicotyl } & \text { Plumule } & \text { Coleoptile } \\
\hline \text { 3. } & \text { Plumule } & \text { Hypocotyl } & \text { Radicle } & \text { Root cap } \\
\hline \text { 4. } & \text { Plumule } & \text { Hypocotyl } & \text { Radicle } & \text { Coleoptile } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(c)
-
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
Which of the given statement/s regarding embryogenesis in angiosperms is/are correct ?
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Embryo develops at the chalazal end of the embryo } \\
\text { sac where the zygote is situated. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Development of a zygote usually occurs after some } \\
\text { endosperm formation. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(b)
Statement I is incorrect due to the wrong location (chalazal instead of micropylar).
-
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
In the Given Diagram:-
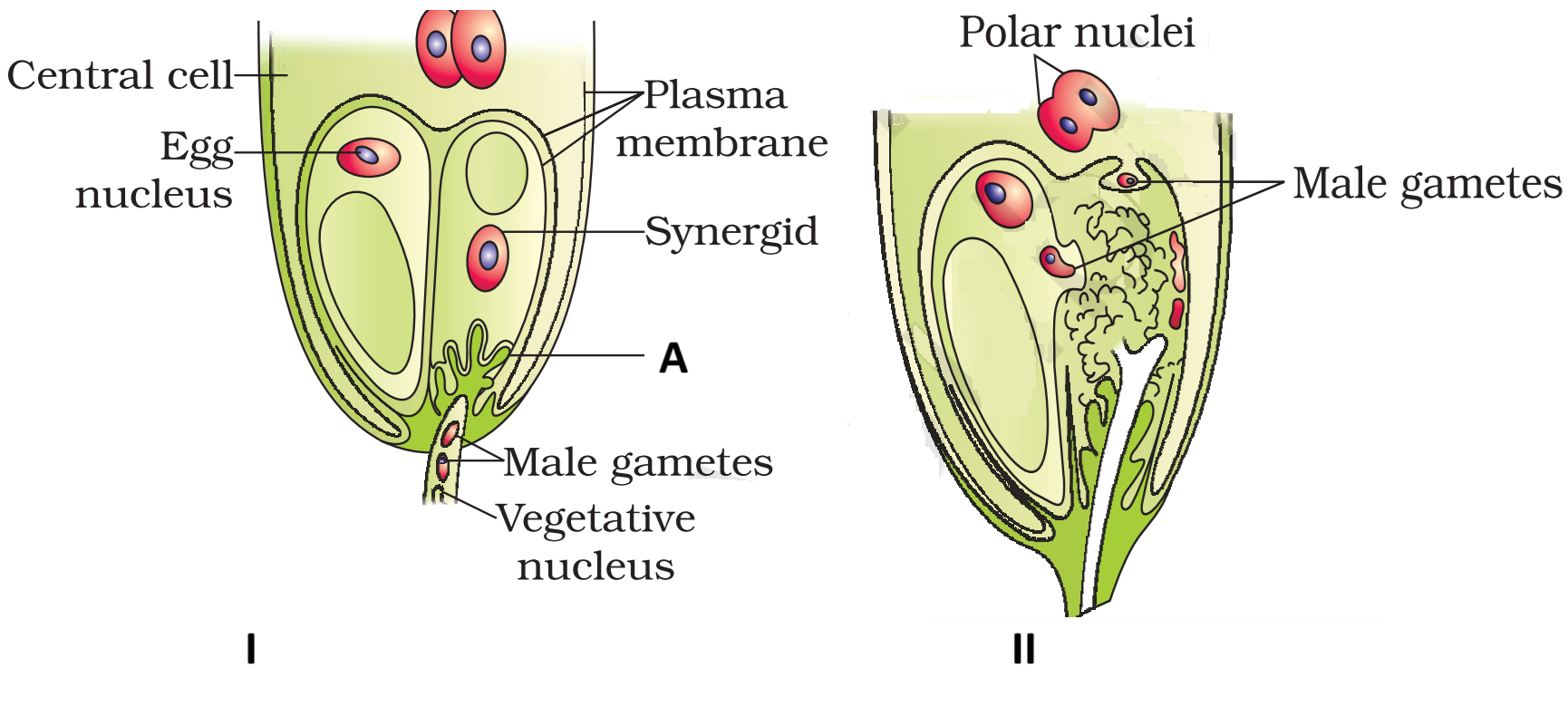
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Statement I: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { I shows the entry of the pollen tube into a } \\
\text { synergid under the guidance of A. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Statement II: } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { II shows the discharge of male gametes } \\
\text { into a synergid. }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(a)
-
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
Identify A – D in the diagram showing L.S. of an embryo of grass:
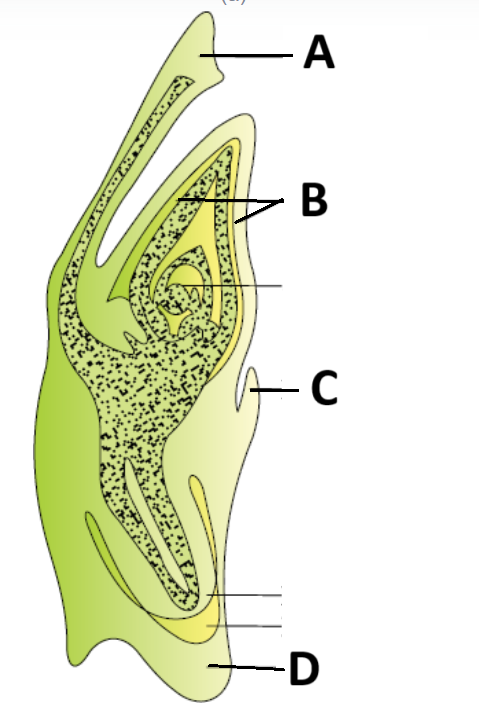
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline \text { 1. } & \text { Perisperm } & \text { Coleoptile } & \text { Epiblast } & \text { Coleorrhiza } \\
\hline \text { 2. } & \text { Scutellum } & \text { Coleoptile } & \text { Epiblast } & \text { Coleorrhiza } \\
\hline \text { 3. } & \text { Scutellum } & \text { Hypocotyl } & \text { Hypoblast } & \text { Coleoptile } \\
\hline \text { 4. } & \text { Scutellum } & \text { Hypocotyl } & \text { Hypoblast } & \text { Coleoptile } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Hint
(b)
-
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
Double fertilization, a characteristic of angiosperms, results in the formation of:
Hint
(a)
-
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
In a fertilised embryo sac, the haploid, diploid, and triploid structures are:
Hint
(a)