\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\textbf{Options:} & \\
(1) A – (iii), B – (ii), C – (iv), D – (i) \\
(2) A – (ii), B – (iii), C – (iv), D – (i) \\
(3) A – (iii), B – (iv), C – (i), D – (ii) \\
(4) A – (iii), B – (ii), C – (i), D – (iv) \\
\end{array}
\)
UNIT I: DIVERSITY IN THE LIVING WORLD
CH2-Biological Classification
2 Quizzes
UNIT II: STRUCTURAL ORGANISATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS
CH5- Morphology of Flowering Plants
2 Quizzes
CH-6- Anatomy of Flowering Plants
2 Quizzes
CH7- Structural Organisation in Animals
2 Quizzes
UNIT III: CELL : STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS
CH10- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
2 Quizzes
UNIT IV: PLANT PHYSIOLOGY
CH11- Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
2 Quizzes
CH13- Plant Growth and Development
2 Quizzes
UNIT V: HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY
CH14- Breathing and Exchange of Gases
2 Quizzes
CH15- Body Fluids and Circulation
2 Quizzes
CH18- Neural Control and Coordination
2 Quizzes
Unit-1: REPRODUCTION
Biomolecules NCERT
Time limit: 0
Quiz Summary
0 of 45 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Quiz complete. Results are being recorded.
Results
0 of 45 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 45
1. Question
Match each item in Column I with only one item in Column II and select the correct match from the codes given:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { COLUMN I } \\
\text { [Component] }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { COLUMN II } \\
\text { [% of the total cellular mass] }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { A. Protein } & \text { P. } 2 \\
\hline \text { B. Carbohydrates } & \text { Q. } 1 \\
\hline \text { C. Lipids } & \text { R. } 5-7 \\
\hline \text { D. Nucleic acids } & \text { S. } 3 \\
\hline & \text { T. } 10-15 \\
\hline & \text { U. } 70-90 \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline 1 . & \text { U } & \text { P } & \text { R } & \text { Q } \\
\hline 2 . & \text { T } & \text { S } & \text { P } & \text { R } \\
\hline 3 . & \text { T } & \text { P } & \text { S } & \text { R } \\
\hline 4 . & \text { P } & \text { Q } & \text { R } & \text { S } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
NCERT TABLE
-
Question 2 of 45
2. Question
Consider the given two statements:
I: Palmitic acid has 16 carbons including the carboxyl carbon.
II: Arachidonic acid has 20 carbons including the carboxyl carbon.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 3 of 45
3. Question
Consider the given two statements:
I: Gingelly oil remains as oil in winters.
II: The fatty acid components of the oil are all saturated.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
The statement “The fatty acid components of the oil are all saturated” is incorrect because most oils contain a mix of both saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Oils are typically liquid at room temperature due to the presence of unsaturated fatty acids, which have at least one double bond in their carbon chain.
-
Question 4 of 45
4. Question
Match each item in Column I with one item in Column II and chose your answer from the codes given below.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { Column I } \\
\text { (type of secondary metabolite) }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Column II } \\
\text { (example) }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { I. Alkaloid } & \text { 1. Abrin } \\
\text { II. Toxin } & \text { 2. Morphine } \\
\text { III. Lectin } & \text { 3. Vinblastin } \\
\text { IV. Drug } & \text { 4. Concanavalin A } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)\(
\begin{aligned}
&\text { Codes: }\\
&\begin{array}{lllll}
&\text { I } & \text { II } & \text { III } & \text { IV } \\
\text { 1. } & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \\
\text { 2. } & 2 & 1 & 4 & 3 \\
\text { 3. } & 2 & 1 & 3 & 4 \\
\text { 4. } & 1 & 2 & 4 & 3
\end{array}
\end{aligned}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 5 of 45
5. Question
Consider the given statements regarding some important secondary metabolites:
I. Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium and is mainly used as a pain medication.
II. Ricin is a toxin and a highly potent toxin produced in the seeds of the castor oil plant.
III. Concanavalin A is a lectin and is widely used in biology and biochemistry to characterize glycoproteins and other sugar-containing entities on the surface of various cells.
IV. Vinblastin is an anti-cancer drug typically used with other medications, to treat a number of types of cancer.CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
All are correct
-
Question 6 of 45
6. Question
Consider the given two statements:
Statement 1: Secondary metabolites derived from plant, fungal and microbial cells do not have a use in human welfare.
Statement 2: We do not, at the moment, understand the role or functions of all the secondary metabolites in host organisms.CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
The statement I is false. Secondary metabolites derived from plant, fungal, and microbial cells do have significant uses in human welfare. These metabolites are utilized in diverse applications, including medicine, agriculture, food industry, and chemical industries.
-
Question 7 of 45
7. Question
Consider the given two statements:
Statement 1: Lipids are a part of acid insoluble fraction or the macromolecular fraction during chemical analysis of a cell.
Statement 2:Lipids have a molecular weight running in thousands of Dalton.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
The statement II is incorrect. Lipids typically have molecular weights less than 800 Daltons and are considered micromolecules. While they can be part of the acid-insoluble fraction due to their role in cell membranes, this is due to their structural organization, not high molecular weight
-
Question 8 of 45
8. Question
Consider the given two statements:
I. Arachidonic acid is a conditionally essential fatty acid.
II. It does become essential if a deficiency in linoleic acid exists.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 9 of 45
9. Question
Consider the given two statements:
Statement 1: A protein is a heteropolymer.
Statement 2: There are 20 types of proteinogenic amino acids and they are linked by peptide bonds to form polypeptidesCorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 10 of 45
10. Question
Consider the given two statements:
Statement 1: Certain amino acids are essential for our health.
Statement 2: Only such amino acids are used to make proteins in our body according to our own genetic code.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
only essential amino acids specified by our genetic code are used to make proteins is incorrect. While the genetic code specifies a set of 20 (Essential +Non Essential) amino acids that are most commonly incorporated into proteins,
-
Question 11 of 45
11. Question
Identify the correctly matched pair:-
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|}
\hline \text { I. } & \text { GLUT-4 } & \text { Enables glucose transport out of the cells } \\
\hline \text { II. } & \text { Collagen } & \text { Most abundant protein in animal world } \\
\hline \text { III. } & \text { RuBisCO } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Most abundant protein in the whole of the } \\
\text { biosphere }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
glut 4 Enables glucose transport into the cells
-
Question 12 of 45
12. Question
Change in an amino acid located distantly from the active site of an enzyme can affect the specificity of the enzyme towards its substrate by:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Even if an amino acid is located far from the active site, it can still influence the overall three-dimensional structure (conformation) of the enzyme. This is because protein structure is maintained by complex interactions throughout the molecule — changes in one region can affect the shape and dynamics of distant parts, including the active site. This in turn can alter substrate binding or enzyme specificity.
The other options are less likely or not directly related to specificity:
-
1. Making the enzyme unstable – could affect activity, but not necessarily specificity.
-
2. Cause a relocation of the enzyme within a cell – affects localization, not substrate specificity.
-
4. Changing the optimum pH and temperature values – might affect activity, but not directly substrate specificity.
-
Question 13 of 45
13. Question
Consider the given two statements:
Statement 1: The right end of the glycogen molecule is called the reducing end and the left end is called the nonreducing end.
Statement 2: Glycogen is a homopolymer of alpha glucose.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 14 of 45
14. Question
Consider the given two statements:
Statement 1: Iodine test can detect the presence of starch but not of cellulose in a given sample.
Statement 2: Starch forms helical secondary structure and can hold iodine molecules while cellulose does not contain complex helices and hence cannot hold iodine.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 15 of 45
15. Question
Quaternary structure is seen in proteins that:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
why the other options are incorrect or incomplete:
-
1. Act as biochemical catalysts – Many enzymes have quaternary structure, but not all. Also, catalytic activity isn’t exclusive to quaternary-structured proteins.
-
2. Are embedded within the plasma membrane – Some membrane proteins have quaternary structure, but again, not all. This doesn’t define quaternary structure.
-
4. Do not have any structural role in the cell – This is unrelated to quaternary structure.
-
Question 16 of 45
16. Question
Identify the correct statements:
I. The level of protein structure organization that provides the positional information of amino acids in a protein is called as the primary structure.
II. Only right handed helices are observed in proteins seen in living organisms.
III. Tertiary structure is absolutely necessary for the many biological activities of proteins.\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { 1. Only I and II } & \text { 2. Only I and III } \\
\hline \text { 3. Only II and III } & \text { 4. I, II and III } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
All are NCERT correct statements
-
Question 17 of 45
17. Question
Consider the given two statements:
Statement 1: In a double stranded DNA molecule, the amount of Guanine should be equal to Cytosine and the amount of Adenine should be equal to Thymine.
Statement 2: There are two hydrogen bonds between Adenine and Thymine and three hydrogen bonds between Guanine and Cytosine.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
Statement 2 does not explain Statement 1 — the number of hydrogen bonds does not determine the equality of base amounts. That equality comes from specific base pairing rules, not from the number of hydrogen bonds.
-
Question 18 of 45
18. Question
In a nucleic acid:
I: A phosphate moiety links the 5′ carbon of one sugar of one nucleotide to the 1′ carbon of the sugar of the succeeding nucleotide.
II: The backbone of the strand is made up of alternate sugar and nitrogenous bases.CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
Both statements are incorrect
Incorrect (I) – In nucleic acids, the phosphate group links the 5′ carbon of one sugar to the 3′ carbon of the next sugar, not the 1′ carbon. This forms the phosphodiester bond, which creates the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA or RNA.
Incorrect(II) -The backbone of a nucleic acid strand is composed of alternating sugar and phosphate groups, not nitrogenous bases. The nitrogenous bases project from the sugar-phosphate backbone.
-
Question 19 of 45
19. Question
Consider the given two statements:
I. Any exposure to extreme stresses can disrupt a protein’s interaction and inevitably lead to denaturation.
II. Protein folding consists of a balance between a substantial amount of weak intra-molecular interactions within a proteinCorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 20 of 45
20. Question
The metabolic pathways in a living system:
I. are linear or circular
II. are series of linked reactions
III. are characterized by a definite rate and direction of flow of metabolites through themCorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
All are correct
-
Question 21 of 45
21. Question
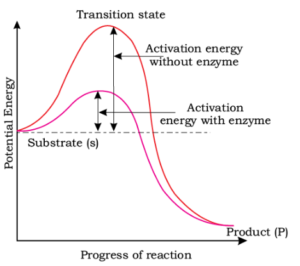
The figure given below shows the conversions of a substrate into product by an enzyme. In which one of the four options (1-4), the components of reaction labelled as A , B , C and D are identified correctly:

\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline
& A & B & C & D \\
\hline
1. & \text{Transition state} & \text{Potential energy} & \text{Activation energy without enzyme} & \text{Activation energy with enzyme} \\
\hline
2. & \text{Potential energy} & \text{Transition state} & \text{Activation energy with enzyme} & \text{Activation energy without enzyme} \\
\hline
3. & \text{Activation energy with enzyme} & \text{Transition state} & \text{Activation energy without enzyme} & \text{Potential energy} \\
\hline
4. & \text{Potential energy} & \text{Transition state} & \text{Activation energy without enzyme} & \text{Activation energy with enzyme} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
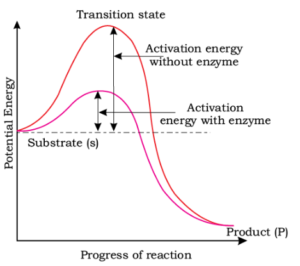
-
Question 22 of 45
22. Question
Consider the following two statements regarding enzyme action:
I. Co-factors play a crucial role in the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
II. Catalytic activity is reduced when the co-factor is removed from the enzyme.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
Statement II is incorrect according to NCERT Lost is written instead of reduced
Catalytic activity is lost when the co-factor is removed from the enzyme
which testifies that they play a crucial role in the catalytic activity of the
enzyme. -
Question 23 of 45
23. Question
The enzymes that catalyse removal of groups from substrates by mechanisms other than hydrolysis leaving double bonds are called as:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 24 of 45
24. Question
Which of the following categories of enzyme classification are correctly matched?
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { EC 1 } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Oxidoreductases: catalyze oxidation/reduction } \\
\text { reactions }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { EC 2 } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Hydrolases: catalyze the hydrolysis of various } \\
\text { bonds }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { EC 3 } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Transferases: transfer a functional group (e.g. a } \\
\text { methyl or phosphate group) }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { EC 4 } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Lyases: cleave various bonds by means other than } \\
\text { hydrolysis and oxidation }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { EC 5 } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Isomerases: catalyze isomerization changes within } \\
\text { a single molecule }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { EC 6 } & \text { Ligases: join two molecules with covalent bonds. } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
EC 2 should be Transferases, not Hydrolases.
-
EC 3 should be Hydrolases, not Transferases.
-
Question 25 of 45
25. Question
Consider the following enzymes:
I. Catalase
II. Peroxidase
III. Carboxypeptidase
Which of these enzymes require haem as a co-factor for their activity?CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
Catalase
-
✅ Requires haem.
-
Catalase is a haem-containing enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
II. Peroxidase
-
✅ Requires haem.
-
Peroxidases (such as horseradish peroxidase) contain a haem group and use hydrogen peroxide to oxidize various substrates.
III. Carboxypeptidase
-
❌ Does NOT require haem.
-
Carboxypeptidase is a metalloenzyme, but it typically uses zinc (Zn²⁺) as a cofactor, not haem
-
Question 26 of 45
26. Question
Select the right option regarding the given graph
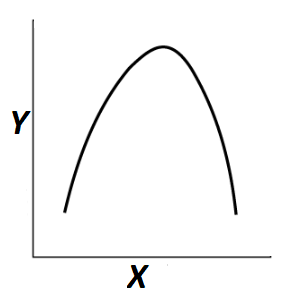
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\textbf{X-axis} & \textbf{Y-axis} \\
(1)\ \text{Rate of reaction} & \text{Enzymatic activity} \\
(2)\ \text{Enzymatic activity} & \text{Rate of reaction} \\
(3)\ \text{Temperature} & \text{Enzymatic activity} \\
(4)\ \text{Enzymatic activity} & \text{pH}
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 27 of 45
27. Question
Identify A, B, C in the given graph for an enzyme mediated reaction:-
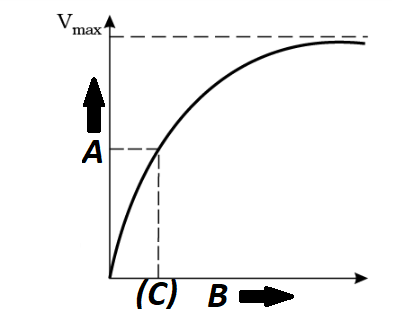
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
(1) \ A – \text{Velocity of reaction} & B – \text{Product concentration} \\
(2) \ \mathrm{C} – K_{\mathrm{m}} \ \text{value} & B – \text{Product concentration} \\
(3) \ \mathrm{C} – K_{\mathrm{m}} \ \text{value} & B – \frac{V_{\text{max}}}{2} \\
(4) \ A – \text{Velocity of reaction} & B – \text{Substrate concentration}
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 28 of 45
28. Question
Read the following statements (A-F)
(A) Km value increases in presence of competitive inhibitor
(B) Km value of enzyme is substrate concentration at 1/2 Vmax
(C) The cofactors of many enzymes are proteins
(D) Most abundant protein in animal world is trypsin
(E) Lactose gives two molecules of glucose on hydrolysis
(F) Chitin is nitrogen containing polysaccharide
How many of the above statements are correct ?CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
❌ (C) The cofactors of many enzymes are proteins
-
Incorrect.
-
Cofactors are non-protein molecules (e.g., metal ions, vitamins, coenzymes). Enzymes are proteins, but cofactors are not.
❌ (D) Most abundant protein in animal world is trypsin
-
Incorrect.
-
The most abundant protein in the animal world is collagen, not trypsin.
❌ (E) Lactose gives two molecules of glucose on hydrolysis
-
Incorrect.
-
Lactose hydrolyzes into glucose + galactose, not two glucose molecules.
Correct statements: A, B, F
✔️ Final Answer: 3 statements are correct
-
Question 29 of 45
29. Question
Identify the statements as True(T) or False(F)
I. In a protein the amino acids are linked by glycosidic bonds
II. Malonate is a competitive inhibitor of succinic dehydrogenase
III. Enzymes require optimum pH for maximal activity
IV. Zwitter ionic form of amino acid has only positive charge\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { I } & \text { II } & \text { III } & \text { IV } \\
\hline(1) & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~F} \\
\hline(2) & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~T} \\
\hline(3) & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~F} \\
\hline(4) & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~F} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
I. In a protein the amino acids are linked by glycosidic bonds
-
❌ False
-
In proteins, amino acids are linked by peptide bonds, not glycosidic bonds (which are found in carbohydrates).
IV. Zwitter ionic form of amino acid has only positive charge
- ❌ False
- A zwitterion has both a positive and a negative charge, making it overall neutral in charge.
-
Question 30 of 45
30. Question
\[
\begin{array}{l}
\textbf{Statement A:} \ \text{A protein with } \alpha\text{-helix or } \beta\text{-pleated sheet represents a secondary protein structure} \\
\textbf{Statement B:} \ \text{The } \beta\text{-pleated protein structure is due to coiling of the polypeptide chains} \\
\\
\text{(1) Only statement A is correct} \\
\text{(2) Both statements A and B are correct} \\
\text{(3) Only statement B is correct} \\
\text{(4) Both statements A and B are incorrect}
\end{array}
\]CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
❌ Statement B:
The β-pleated protein structure is due to coiling of the polypeptide chains
-
Incorrect.
-
The β-pleated sheet is formed by extended (not coiled) polypeptide chains lying side-by-side, connected by hydrogen bonds.
-
Coiling refers to the α-helix, not the β-sheet.
-
Question 31 of 45
31. Question
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|}
\hline
\textbf{Column A} & \textbf{Column B} \\
\hline
\text{(A) Basic amino acid} & (i) \ \text{Lysine} \\
\text{(B) Acidic amino acid} & (ii) \ \text{Aspartic acid}, \ (iii) \ \text{Glutamic acid} \\
\text{(C) Neutral amino acid} & (iv) \ \text{Alanine}, \ (v) \ \text{Glycine}, \ (vi) \ \text{Valine} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\textbf{Options:} & \\
(1) & A – v ; B – iii, vi ; C – i, ii, iv \\
(2) & A – iii, vi ; B – iv, v ; C – i, ii \\
(3) & A – i ; B – ii, iii ; C – iv, v, vi \\
(4) & A – v, i ; B – i, ii ; C – iii, iv \\
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 32 of 45
32. Question
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|}
\hline
\textbf{Column A} & \textbf{Column B} \\
\hline
\text{(A) Insulin} & \text{(iii) Protein} \\
\text{(B) Inulin} & \text{(ii) Fructose polymer} \\
\text{(C) Uridine} & \text{(iv) Nucleoside} \\
\text{(D) Glycine} & \text{(i) Simplest amino acid} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 33 of 45
33. Question
Which of the following statements is incorrect regarding action of an enzyme?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
All enzymes are not of protein , there are some enzymes are made of nucleic acids like Ribozymes
-
Question 34 of 45
34. Question
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|}
\hline
\textbf{Column A} & \textbf{Column B} \\
\hline
\text{(A) Prosthetic group} & \text{(i) Starch} \\
\text{(B) Reducing sugar} & \text{(ii) Sucrose} \\
\text{(C) Storage product} & \text{(iii) Galactose} \\
\text{(D) Zn} & \text{(iv) Haem} \\
\text{} & \text{(v) Carboxypeptidase} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\textbf{Options:} & \\
(1) & A – (v), B – (iii), C – (i), D – (ii) \\
(2) & A – (iv), B – (iii), C – (i), D – (v) \\
(3) & A – (iii), B – (ii), C – (i), D – (v) \\
(4) & A – (iv), B – (ii), C – (i), D – (v) \\
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 35 of 45
35. Question
Lower value of Michaelis constant (Km) shows
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)- Km and Affinity:
The Michaelis constant (Km) represents the substrate concentration needed to reach half of the maximum reaction rate (Vmax).-
Lower Km, Higher Affinity:A lower Km value means the enzyme can achieve half its maximum velocity at a lower substrate concentration, indicating a higher affinity for the substrate.
Why other options are incorrect:-
(2) Less affinity of the enzyme for the substrate:This is the opposite of the correct interpretation. A higher Km value indicates lower affinity, while a lower Km value indicates higher affinity.
-
(3) Enzyme is allosteric:Allosteric enzymes have multiple active sites that can be influenced by binding of a molecule other than the substrate (allosteric activator or inhibitor). The Km value itself doesn’t define whether an enzyme is allosteric or not. Allosteric regulation affects the enzyme’s shape and activity, but it’s a separate mechanism from Km.
-
(4) Enzyme is non-competitive:Non-competitive inhibition affects the Vmax of an enzyme by binding to a site other than the active site, but it doesn’t change the Km value. The question is asking about the meaning of a lower Km value, and non-competitive inhibition is irrelevant to that.
-
Question 36 of 45
36. Question
In the following structure, what does R1, R2 and R3 represent?
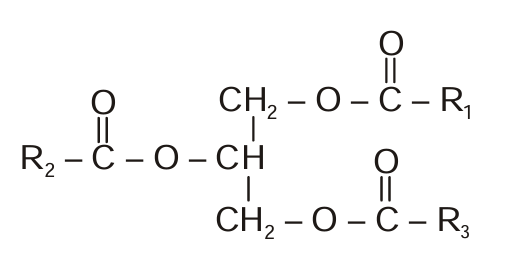 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 37 of 45
37. Question
Read the following statements (A–F)
(A) Carbohydrates, lipids and proteins are primary metabolites
(B) The relative abundance of carbon and hydrogen with respect to other elements is higher in any living
organisms than in earth crust
(C) Flavonoids and alkaloids are secondary metabolites
(D) Most of the elements present in a sample of earth’s crust are also present in a sample of living tissue
(E) The three essential fatty acids are linoleic acid, linolenic acid and palmitic acid
(F) The components common to nucleoside as well as nucleotides are sugar and nitrogenous base
How many of the following statements are true ?CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
(E) The three essential fatty acids are linoleic acid, linolenic acid and palmitic acid
❌ False — Palmitic acid is a saturated fatty acid and not essential. The three essential fatty acids are:-
Linoleic acid (omega-6)
-
α-Linolenic acid (omega-3)
-
Arachidonic acid (conditionally essential)
-
Question 38 of 45
38. Question
Identify the statements as true (T) or false (F)
I. In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor molecule is not chemically changed by the enzyme
II. The presence of a competitive inhibitor decreases the Km of the enzyme for the substrate
III. In proteins right handed helices are observed
IV. Proteins can not form quarternary structures\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { I } & \text { II } & \text { III } & \text { IV } \\
\hline(1) & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~T} \\
\hline(2) & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~F} \\
\hline(3) & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~T} \\
\hline(4) & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{~F} & \mathrm{~T} & \mathrm{~F} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
II. The presence of a competitive inhibitor decreases the Km of the enzyme for the substrate
❌ False (F) — Competitive inhibition increases the apparent Km (decreased substrate affinity) but Vmax remains unchanged.IV. Proteins cannot form quaternary structures
❌ False (F) — Many functional proteins do have quaternary structure, composed of multiple polypeptide chains (e.g., hemoglobin). -
Question 39 of 45
39. Question
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|}
\hline
\textbf{Column A} & \textbf{Column B} \\
\hline
\text{(A) Glucose} & \text{(iv) Hexose sugar} \\
\text{(B) RuBisCO} & \text{(i) Protein} \\
\text{(C) Chitin} & \text{(ii) Arthropods} \\
\text{(D) NAD} & \text{(iii) Niacin} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 40 of 45
40. Question
In a DNA molecule, the phosphate group is attached to ___I___ carbon of the sugar residue of First
nucleotide and __II___ carbon of the sugar residue of the succeeding or next nucleotide by __III
bond\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|}
\hline
\textbf{Option} & \textbf{Statement} \\
\hline
\text{(1)} & \text{I – 5’, II – 3’, III – phosphodiester} \\
\text{(2)} & \text{I – 5’, II – 3’, III – glycosidic} \\
\text{(3)} & \text{I – 3’, II – 5’, III – phosphodiester} \\
\text{(4)} & \text{I – 3’, II – 5’, III – glycosidic} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
In DNA, nucleotides are linked together via phosphodiester bonds.
-
The phosphate group connects the 5′ carbon of one nucleotide’s sugar to the 3′ carbon of the next nucleotide’s sugar.
-
Glycosidic bonds, on the other hand, connect the sugar to the nitrogenous base, not two sugars.
-
Question 41 of 45
41. Question
When we homogenize any tissues in an acid the acid soluble pool represents
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 42 of 45
42. Question
The given compound:-
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
NCERT diagram
NCERT statement:- These are phospholipids. They are found in cell membrane. Lecithin is
one example -
Question 43 of 45
43. Question
Why is cellulose so difficult for most animals to digest?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
❌ Cellulose is made up of chitin, which is indigestible
-
Incorrect. Cellulose and chitin are distinct polysaccharides. Chitin contains N-acetylglucosamine, while cellulose is made of glucose.
-
-
❌ The bonds holding cellulose subunits together are extremely strong, stronger than in any other macromolecule
-
Incorrect. While cellulose is structurally strong, the key issue is enzyme specificity, not exceptional bond strength.
-
-
⚠️ There are many hydrogen bonds holding the subunits together
-
Partially true, but this is not the main reason for indigestibility. Hydrogen bonds contribute to structural rigidity, not enzymatic inaccessibility alone.
-
-
Question 44 of 45
44. Question
Identify the incorrect statement regarding enzyme action:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
“Substrate need not go through a transition state if the enzyme catalyzed reaction is endothermic.”
-
❌ This implies that endothermic reactions skip the transition state, which violates fundamental principles of reaction kinetics and enzyme catalysis.
-
✅ All reactions proceed via a transition state, regardless of their heat exchange profile.
-
Question 45 of 45
45. Question
Statement I: To analyze organic compounds in living organisms, we first take living tissue and grind it with trichloroacetic acid using a mortar and pestle.
Statement II: Al the carbon compounds that we get from living tissues can be called ‘biomolecules’.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)