Anatomy of Flowering Plants TS
Quiz Summary
0 of 50 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 50 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 50
1. Question
Given below are two statements :
Statement I: In dicotyledonous leaf abaxially placed palisade parenchyma is made up of elongated cells which are arranged only vertically.
Statement-II: In monocotyledonous leaf mesophyll is not differenciated into palisade and spongy parenchyma.
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-93]
In dicotyledonous leaf adaxially placed palisade parenchyma is made up of elongated cells which are arranged vertically and parallel to each other. In monocotyledonous leaf mesophyll is not differenciated into palisade and spongy parenchyma. -
Question 2 of 50
2. Question
Starch sheath is a endodermis which rich starch grains found in :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-92]
Starch sheath is a endodermis which rich starch grains found in dicot stem -
Question 3 of 50
3. Question
Vascular bundle is conjoint, open and with endarch protoxylem found in :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-90]
Vascular bundle is conjoint, open and with endarch protoxylem found in dicot stem -
Question 4 of 50
4. Question
Which of the following structure constitute stele:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-91]
Pericycle, Vascular bundles and Pith constitute stele -
Question 5 of 50
5. Question
The pith is small or inconspicuous in :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-91]
The pith is small or inconspicuous in dicot root -
Question 6 of 50
6. Question
Select the incorrect statement from the followings:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT I-90]
In monocotyledons, the vascular bundles have no cambium present in them. Hence, since they do not form secondary tissue they are referred to as closed. -
Question 7 of 50
7. Question
Match the following columns:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { a. Vessel } & \text { i. Tapering ends } \\
\hline \text { b. Tracheids } & \text { ii. Large central cavity } \\
\hline \text { c. Sclereids } & \text { iii. Special parenchy -matous cell } \\
\hline \text { d. Companion cells } & \text { iv. Very narrow cavity } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-87, 88]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Vessel } & \text { Large central cavity } \\
\text { Tracheids } & \text { Tapering ends } \\
\text { Sclereids } & \text { Very narrow cavity } \\
\text { Companion cells } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Special parenchy -matous cell} \\
\end{array}
\end{array}
\) -
Question 8 of 50
8. Question
Identify A, B, C and D in the following diagrams :
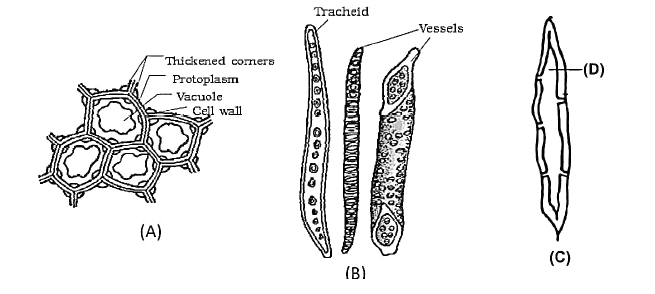 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-86, 87]
A-Collenchyma, B-Xylem, C-Sclerenchyma and D- Lumen
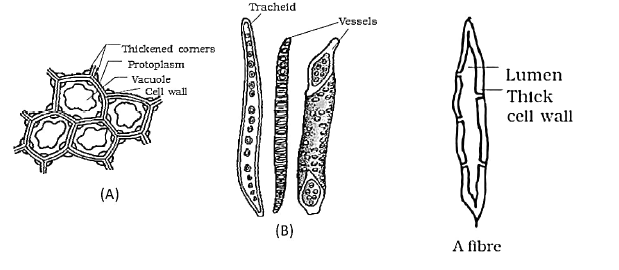
-
Question 9 of 50
9. Question
Given below are two statements :
Statement I : Trichomes in the shoot system are usually unicellular
Statement-II : Trichomes may be branched or unbranched
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-89]
Trichomes in the shoot system are usually multicellular
Trichomes may be branched or unbranched -
Question 10 of 50
10. Question
Apical meristems produce :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I- 84]
The meristems which occur at the tips of roots and shoots and produce primary tissues are called apical meristems. -
Question 11 of 50
11. Question
Read the statements given below carefully and find out the correct ones
a. Bast fibres are made of sclerenchymatous cells
b. Bast fibres are unbranched & with pointed apex
c. Epidermal cells are perenchymatous with small amount of cytoplasm
d. Functions of companion cells are controlled by nucleus of the sieve tubesCorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT – I – 88]
– Bast fibres are made of sclerenchymatous cells
– Bast fibres are unbranched \& with pointed apex
– Epidermal cells are perenchymatous with small amount of cytoplasm
– Functions of sieve tubes are controlled by nucleus of the companion cells -
Question 12 of 50
12. Question
The pith is large and well developed in :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-91]
The pith is large and well developed in Monocot root -
Question 13 of 50
13. Question
Casparian bands (strips) are characteristic feature of :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-91]
Casparian bands (strips) are characteristic feature of endodermis
-
Question 14 of 50
14. Question
The xylem in which protoxylem lies towards the centre (pith) and metaxylem lies towards the periphery is called :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-87]
The xylem in which protoxylem lies towards the centre (pith) and metaxylem lies towards the periphery is called endarch -
Question 15 of 50
15. Question
Examples of lateral meristem :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I- 85]
The meristem that occurs in the mature regions of roots and shoots of many plants, particularly those that produce woody axis and appear later than primary meristem is called the secondary or lateral meristem.
They are cylindrical meristems. Fascicular vascular cambium, interfascicular cambium and cork-cambium are examples of lateral meristems. These are responsible for producing the secondary tissues. -
Question 16 of 50
16. Question
In the given figure A, B and C are :
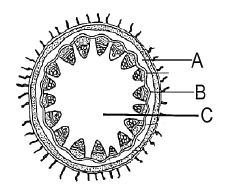 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-92]
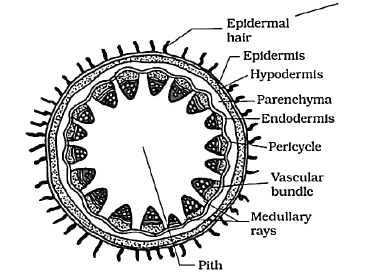
-
Question 17 of 50
17. Question
The parenchymatous cells which lie between the xylem and the phloem are called :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-91]
The parenchymatous cells which lie between the xylem and the phloem are called Conjuctive tissue -
Question 18 of 50
18. Question
One of the following is absent in the monocots :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-90]
Cambium is absent in the monocots -
Question 19 of 50
19. Question
Schlerenchymatous hypodermis is characteristics of :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-93]
Schlerenchymatous hypodermis is characteristics of dicot stem -
Question 20 of 50
20. Question
Which of the following is a part of the epidermal tissue system :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-89]
Epidermal cells, stomata and Trichomes is a part of the epidermal tissue system -
Question 21 of 50
21. Question
In monocot leaf which type of guard cell present:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-89]
In monocot leaf dumb-bell shaped guard cell present -
Question 22 of 50
22. Question
Read the following statements and choose correct answer :
(i) First formed primary xylem elements are called Protoxylem
(ii) The later formed primary xylem is called Metaxylem
(iii) In stem the Protoxylem lies towards the Periphery
(iv) In roots the Protoxylem lies towards centreCorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT – I – 87]
- First formed primary xylem elements are called Protoxylem
- The later formed primary xylem is called Metaxylem
- In stem the Protoxylem lies towards centre
- In roots the Protoxylem lies towards the Periphery
-
Question 23 of 50
23. Question
Type of meristems occur in grasses and regenerate parts removed by the grazing herbivores is :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-85]
Extensive elongation of stem is monocot is due to increase the length between the internodal length. -
Question 24 of 50
24. Question
Trichomes in shoot system are :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT – I – 89]
Trichomes in shoot system are Usually multicellular. -
Question 25 of 50
25. Question
What constitutes the ground tissue of a plant :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-89]
All tissues except epidermis and vascular bundles constitute the ground tissue. It consists of simple tissues such as parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma. Parenchymatous cells are usually present in cortex, pericycle, pith and medullary rays, in the primary stems and roots. In leaves, the ground tissue consists of thin-walled chloroplast containing cells and is called mesophyll. -
Question 26 of 50
26. Question
Protophloem & metaphloem have :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I- 88]
The first formed primary phloem consists of narrow sieve tubes and is referred to as protophloem and the later formed phloem has bigger sieve tubes and is referred to as metaphloem. -
Question 27 of 50
27. Question
Find the correct statements from the statements given below-(about dorsiventral leaf):
(a) Size of the vascular bundle in leaves depends on the size of the veins
(b) Vascular bundle are surrounded by thin walled bundle sheath cells
(c) The veins vary in thickness in the reticulate venation of dicot leaves
(d) Abaxially placed palisade parenchyma in dicot leaf is made up of elongated cellsCorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-93]
Size of the vascular bundle in leaves depends on the size of the veins.The veins vary in thickness in the reticulate venation of dicot leaves
-
Question 28 of 50
28. Question
Companion cells are closely associated with :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-88]
The companion cells are specialised parenchymatous cells, which are closely associated with sieve tube elements. -
Question 29 of 50
29. Question
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A) : Radial vascular bundles present in roots.
Reason (R) : Xylem and phloem with in a vascular bundle are arranged in an alternate manner on different radii.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given belowCorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-90]
Radial vascular bundles present in roots.
Xylem and phloem with in a vascular bundle are arranged in an alternate manner on different radii. -
Question 30 of 50
30. Question
The xylem in which protoxylem lies towards periphery and metaxylem lies towards the centre. Such arrangement of primary xylem is called :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-87]
The xylem in which protoxylem lies towards periphery and metaxylem lies towards the centre. Such arrangement of primary xylem is called exarch -
Question 31 of 50
31. Question
In given figure A and B are :
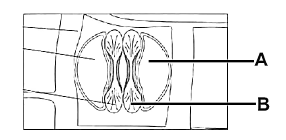 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-89]
-
Question 32 of 50
32. Question
Hypodermis of dicotyledonous plants is made up of :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-92]
Hypodermis of dicotyledonous plants is made up of collenchyma -
Question 33 of 50
33. Question
Elongated or tube-like cells with thick and lignified walls and tapering ends is a character of :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-87]
Elongated or tube-like cells with thick and lignified walls and tapering ends is a character of tracheids -
Question 34 of 50
34. Question
Which of the following is made up of dead cells:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-96]
Phloem fibre is made up of dead cells -
Question 35 of 50
35. Question
In which character a monocot root differs from a dicot root :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) [NCERT-I-91]
In Large pith character a monocot root differs from a dicot root. -
Question 36 of 50
36. Question
According to given figure which of the following is correct :
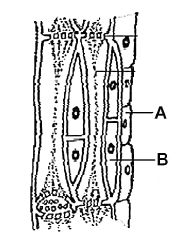 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-87]
-
Question 37 of 50
37. Question
Semilunar patches of sclerenchyma are found in
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-92,93]
Pericycle is present on the inner side of the endodermis and above the phloem in the form of semi-lunar patches of sclerenchyma. -
Question 38 of 50
38. Question
The food material produced in leaves is conducted through the plant with the help of :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NC-I-87-88]
Phloem transports food materials, usually from leaves to other parts of the plant. Phloem in angiosperms is composed of sieve tube elements, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres. Gymnosperms have albuminous cells and sieve cells. They lack sieve tubes and companion cells. -
Question 39 of 50
39. Question
Match the following
a. Lycopsida (i) Dryopteris
b. Pteropsida (ii) Selaginella
c. Sphenopsida (iii) Psilotum
d. Psilopsida (iv) EquisetumCorrectIncorrectHint
[NCERT-I-32]
Psilopsida (Psilotum); Lycopsida (Selaginella, Lycopodium), Sphenopsida (Equisetum) and Pteropsida (Dryopteris, Pteris, Adiantum). -
Question 40 of 50
40. Question
\(
\begin{array}{lll}
& \text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\text { a. } & \text { Nostoc } & \text { i. } \text { Biogas } \\
\text { b. } & \text { Methanogen } & \text { ii. } \text { Heterocysts } \\
\text { c. } & \text { Mycoplasma } & \text { iii. Lack of cell wall } \\
\text { d. } & \text { Heterotrophic } & \text { iv. } \text { Antibiotic } \\
& \text { bacteria } &
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-13]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Nostoc } & – \text { Heterocysts } \\
\text { Methanogen } & – \text { Biogas } \\
\text { Mycoplasma } & – \text { Lack of cell wall } \\
\begin{array}{l}
\text { Heterotrophic } \\
\text { bacteria }
\end{array} & – \text { Antibiotic }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 41 of 50
41. Question
How many matching are correct:
(a) Marchantia – Gemma cup
(b) Funaria – Biflagellate antherozoids
(c) Gymnosperm – Heterosporous
(d) Cedrus – Branched stemCorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-29 to 32]
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Marchantia } & – \text { Gemma cup } \\
\text { Funaria } & – \text { Biflagellate anthero-zoids } \\
\text { Gymnosperm } & – \text { Heterosporous } \\
\text { Cedrus } & – \text { Branched stem }
\end{array}
\) -
Question 42 of 50
42. Question
Given below are two statements :
Statement I : Most member of chlorophyceae have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids.
Statement II : Pyrenoids are located in Mitochondria.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given belowCorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-26]
Statement I: Most member of chlorophyceae have one or more storage bodies called pyrenoids.
Statement II : Pyrenoids are located in chloroplast.
-
Question 43 of 50
43. Question
Which of the following is incorrect for dueteromycetes:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
[NCERT-I-18]
Some member are saprophytes and parasite -
Question 44 of 50
44. Question
Which of the following is correct :
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) [NCERT-I-21]
The RNA of viroid was of low molecular weight -
Question 45 of 50
45. Question
Given below are two statements:
Statement I : Bacteria reproduce mainly by fission
Statement II : The vast majority of bacteria are heterotrophs.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given belowCorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
[NCERT-I-14]
Statement I : Bacteria reproduce mainly by fission
Statement II : The vast majority of bacteria are heterotrophs. -
Question 46 of 50
46. Question
How many matchings are correct:
a. Musca domestica \(\quad\) – Insecta
b. Triticum aestivum \(\quad\) – Poales
c. Solanum nigram \(\quad\) – Polymoniales
d. Panthera leo \(\quad\) – CarnivoraCorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
[NCERT-I-7, 8]
a. Musca domestica – Insecta
b. Triticum aestivum – Poales
c. Solanum nigram – Polymoniales
d. Pantheraleo – Carnivora -
Question 47 of 50
47. Question
How many matching are correct:
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { (a) Diploblastic } & – \text { Mesoderm present } \\
\text { (b) Triploblastic } & – \text { Mesoderm absent } \\
\text { (c) Coelomate } & – \text { Mesoderm present } \\
\text { (d) Coelentrata } & – \text { Mesoglea present }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-38,39]
Diploblastic – Mesoderm absent
Triploblastic – Mesoderm present
Coelomate – Mesoderm present
Coelentrata – Mesoglea present -
Question 48 of 50
48. Question
How many matching are correct:
a. Hermaphrodite – Porifera
b. Unisexual – Aschelminthes
c. Bioluminescence – Ctenophora
d. Bisexual – PlatyhelminthesCorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT-I-40,41,42]
Hermaphrodite – Porifera
Unisexual – Aschelminthes
Bioluminescence – Ctenophora
Bisexual – Platyhelminthes -
Question 49 of 50
49. Question
Recognise the given figure and find out correct statement for it.:
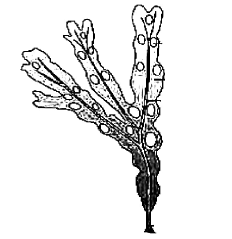
(i) It is a member of Rhodophycea
(ii) Oogamous type reproduction occur.
(iii) Diplontic life cycle present
(iv) It posses chlorophyll a and c as major pigement.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
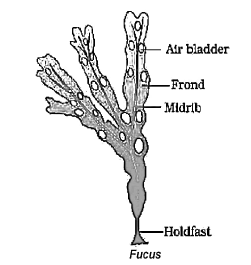
– It is a member of Phaeophycea
– Oogamous type reproduction occur.
– Diplontic life cycle present
– It posses chlorophyll a and c as major pigement. -
Question 50 of 50
50. Question
Read the given name carefully
Ustilago, Puccinia, Neurospora, Claviceps, Alternaria, Trichoderma.
How many fungi is/are imperfectCorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT-I-18]
Member of deuteromycetes are called imperfect fungi. e.g. Alternaria, Colletotrichum, Trichoderma.