CH5- Morphology of Flowering Plants
Q1. Direct elongation of the radicle leads to the formation of….. root.
Answer: Primary
Q2. Lateral roots includes \(\ldots\) (a) \(\ldots\). and (b) \(\ldots\) roots
Answer: (a) secondary (b) tertiary
Q3. The primary root and its branches constitute the
Answer: Tap root system
Q4. When the primary root is short lived and replaced by large number of thin roots which originates from base of the stem and constitutes the
Answer: Fibrous root system
Q5. The roots which arise from the parts of the plant other than the radicle are called
Answer: Adventitious roots
Q6. The root apex is covered by thimble like structure called
Answer: Root cap
Q7. The region of meristematic activity is situated few millimeters above root cap. True or false?
Answer: True
Q8. Match the following
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline 1 & \text { Tap root } & \text { a } & \text { Monstera } \\
\hline 2 & \text { Fibrous root system } & \text { b } & \text { Wheat } \\
\hline 3 & \text { Adventitious root } & \text { c } & \text { Mustard } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|}
\hline 1-c \\
\hline 2-b \\
\hline 3-a \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Q9. Which region of the root-tip have very small cells, thin walled and with dense protoplasm?
Answer: Meristematic zone
Q10. Which part of root-tip is responsible for the growth of the root in length?
Answer: Region of elongation
Q11. Region of elongation is present –(a)– to the region of meristem
and region of maturation is present — (b)– to the region of elongation.
Answer: a – Proximal, b – Proximal
Q12. Match the following root modifications
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline 1 & \text { For storage } & \text { a } & \text { Maize } \\
\hline 2 & \text { Prop root } & \text { b } & \text { Sugarcane } \\
\hline 3 & \text { Stilt root } & \text { c } & \text { Sweet potato } \\
\hline 4 & \text { For respiration } & \text { d } & \text { Turnip } \\
\hline & & \text { e } & \text { Banyan } \\
\hline & & f & \text { Rhizophora } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|}
\hline 1-c, d \\
\hline 2-e \\
\hline 3-a, b \\
\hline 4-f \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Q13. Stilt roots arise from
Answer: Lower node of the stem
Q14. Hanging structures which provide support to branches of banyan trees are called
Answer: Prop roots
Q15. In Rhizophora, pneumatophores help in
Answer: Respiration
Q16. Shoot develops from the —(a) — of the embryo
Answer: a-plumule
Q17. Part of the plant which bears nodes and internodes is known as
Answer: Stem
Q18. Stem is generally –(a) — when young and later often becomes woody and dark —–(b)——
Answer: a – Green, b-Brown
Q19. Match the following
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline 1 & \text { Organ of perennation } & \text { a } & \text { Opuntia } \\
\hline 2 & \text { Stem tendril } & \text { b } & \text { Citrus } \\
\hline 3 & \text { Stem thorn } & \text { c } & \text { Euphorbia } \\
\hline 4 & \text { Phylloclade } & \text { d } & \text { Bougainvillea } \\
\hline & & \text { e } & \text { Zaminkand } \\
\hline & & f & \text { Cucumber } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|}
\hline 1-e \\
\hline 2-f \\
\hline 3-b, d \\
\hline 4-a, c \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Q20. Stem modified into flattened structure in —(a)— or fleshy cylindrical green structure in —-(b)– and perform photosynthesis.
Answer: a-Opuntia, b – Euphorbia/Casuarina
Q21. In which plants each node bears a rosette of leaves and a tuft of roots?
Answer: Pistia and Eichhornia
Q22. Which type of sub-aerial modification occur in Jasmine.
Answer: Stolon
Q23. In banana, the growing lateral branch come out ————- giving rise to leafy shoots.
Answer: Obliquely upward
Q24. Recognise a, b and c.
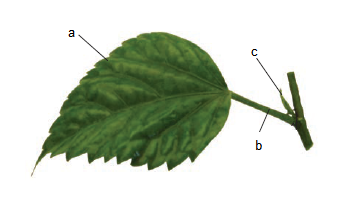
Answer: a – Lamina, b – Petiole, c – Stipule
Q25. Leaves originate from …………….. meristem.
Answer: Shoot apical
Q26. Leaf develops at the —-(a)—- and bears a —-(b)—- in its axil.
Answer: a – Node, b – Bud
Q27. The axillary bud later develops into a
Answer: Branch or flower
Q28. The leaves are arranged in ———– manner on stem.
Answer: Acropetal
Q29. Leaf may bear two lateral small leaf like structures which are known as
Answer: Stipules
Q30. Sheathing leaf base is found in monocots, true or false.
Answer: True
Q31. In some –(a)— plants the leaf base may become swollen which is known as —- (b) ——
Answer: a-leguminous, b-pulvinus
Q32. Vein provide –(a)– to the leaf blade and act as channels of —–(b)—- for water minerals and food materials
Answer: a – Rigidity, b – Transport
Q33. The arrangement of veins and veinlets in the lamina of leaf is termed as ———-
Answer: Venation
Q34. When the veinlets form a network, the venation is known as
Answer: Reticulate venation
Q35. When the veins run parallel to each other within a lamina the venation is termed as
Answer: Parallel venation
Q36. In a leaf, when its lamina is entire or when incised, the incisions do not touch the midrib then this type of leaf is known as
Answer: Simple leaf
Q37. When the incisions of leaf lamina reach upto the midrib the leaf is known as
Answer: Compound leaf
Q38. A ———— is present in the axil of petiole in both simple and compound leaves but not in the axil of leaflets.
Answer: Bud
Q39. Rachis is found in —– leaf.
Answer: Pinnately compound
Q40. In neem plant, which type of leaf is present
Answer: Pinnately compound leaf
Q41. In palmately compound leaf, the leaflets are attached at the —(a)— as in silk cotton.
Answer: a – Common point i.e. tip of Petiole
Q42. Match the following
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline 1 & \text { Alternate phyllotaxy } & \text { a } & \text { Alstonia } \\
\hline 2 & \text { Opposite phyllotaxy } & \text { b } & \text { Mustard, Chinarose } \\
\hline 3 & \text { Whorled phyllotaxy } & \text { c } & \text { Guava, Calotropis } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|}
\hline 1-b \\
\hline 2-c \\
\hline 3-a \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Q43. Match the following
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline 1 & \text { Leaf tendril } & \text { a } & \text { Venus fly trap } \\
\hline 2 & \text { Leaf spine } & \text { b } & \text { Pea } \\
\hline 3 & \text { Insectivorous plant } & \text { c } & \text { Cactus } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|}
\hline 1-b \\
\hline 2-c \\
\hline 3-a \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Q44. Name the plant in which, the leaves are small and short lived and petiole modify in leafy structure and perform photosynthesis.
Answer: Australian acacia
Q45. Flower is a modified
Answer: Shoot
Q46. The arrangement of flower on floral axis is known as
Answer: Inflorescence
Q47. In —(a)–inflorescence the main axis continuous to grow.
Whereas in –(b)–inflorescence main axis terminates in a flower.
Answer: a-Racemose, b-Cymose
Q48. In racemose type of inflorescence the flowers are arranged in
Answer: Acropetal manner
Q49. In a typical flower, calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium are attached on
Answer: Thalamus
Q50. Calyx and corolla are —(a)— whorls while androecium, and gynoecium are —–(b)—– whorls organs.
Answer: a-Accessory, b – Reproductive or essential
Q51. When calyx and corolla are not distinct then they are known as
Answer: Perianth
Q52. If a flower has both androecium and gynoecium, it is a. ——– flower.
Answer: Bisexual
Q53. If a flower having either only stamens or only carpels then it is a. ———- flower.
Answer: Unisexual
Q54. Match the following
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline 1 & \text { Actinomorphic flower } & \text { a } & \text { Mustard, Datura } \\
\hline 2 & \text { Zygomorphic flower } & \text { b } & \text { Canna } \\
\hline 3 & \text { Asymmetric flower } & \text { c } & \text { Chilli } \\
\hline & & \text { d } & \text { Cassia } \\
\hline & & \text { e } & \text { Pea, Bean } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|}
\hline 1-a, c \\
\hline 2-d, e \\
\hline 3-b \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Q55. Given figure represents which type of inflorescence
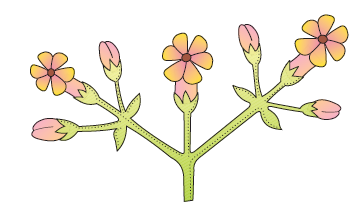
Answer: Cymose inflorescence
Q56. Given figure represents which type of flower.

Answer: Perigynous flower
Q57. Match the following
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline 1 & \text { Hypogynous flower } & \text { a } & \text { Cucumber } \\
\hline 2 & \text { Perigynous flower } & \text { b } & \text { Mustard } \\
\hline 3 & \text { Epigynous flower } & \text { c } & \text { Chinarose } \\
\hline & & \text { d } & \text { Plum } \\
\hline & & \text { e } & \text { Guava } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|}
\hline 1-b, c \\
\hline 2-d \\
\hline 3-a, e \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Q58. In case of perigynous flower, the ovary is
Answer: Half inferior
Q59. When the sepals are united then condition is known as
Answer: Gamosepalous condition
Q60. When the petals are free then condition is known as
Answer: Polypetalous condition
Q61. The mode of arrangement of sepals or petals in floral bud with respect to other members of the same whorl is
Answer: Aestivation
Q62. If the margins of sepals or petals overlap one another but not in any particular direction, then this type of aestivation is known as
Answer: Imbricate aestivation
Q63. Recognise the type of aestivation in a, b, c and d
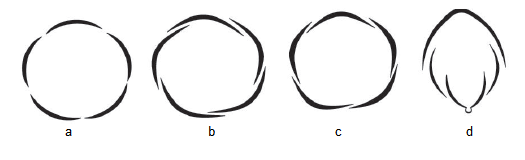
Answer: a – Valvate, b – Twisted, c-Imbricate, d – Vexillary
Q64. Match the following with respect to aestivation in petals
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline 1 & \text { Valvate } & \text { a } & \text { Cassia } \\
\hline 2 & \text { Twisted } & \text { b } & \text { Pea } \\
\hline 3 & \text { Imbricate } & \text { c } & \text { Calotropis } \\
\hline 4 & \text { Vexillary } & \text { d } & \text { China rose } \\
\hline & & \text { e } & \text { Lady finger } \\
\hline & & \text { f } & \text { Gulmohar } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|}
\hline 1-c \\
\hline 2-d, e \\
\hline 3-a, f \\
\hline 4-b \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Q65. The pollen grains are produced in (Pollensac / Ovule)
Answer: Pollen sac
Q66. A sterile stamen is known as
Answer: Staminode
Q67. When the stamens are attached to the petals, they are known as
Answer: Epipetalous
Q68. Match the following
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline 1 & \text { Epitepalous stamen } & \text { a } & \text { Citrus } \\
\hline 2 & \text { Monoadelphous stamen } & \text { b } & \text { Pea } \\
\hline 3 & \text { Diadelphous stamen } & \text { c } & \text { China rose } \\
\hline 4 & \text { Polyadelphous stamen } & \text { d } & \text { Lily } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|}
\hline 1-d \\
\hline 2-c \\
\hline 3-b \\
\hline 4-a \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Q69. In rose and lotus, the condition of carpels is (Apocarpous/Syncarpous)
Answer: Apocarpous
Q70. After fertilisation, the ovules develop into –(a)— and the ovary matures into a —–(b)—-
Answer: a – Seeds, b – Fruit
Q71. The arrangement of ovules within the ovary is known as
Answer: Placentation
Q72. Ripened or mature ovary is known as
Answer: Fruit
Q73. If a fruit is formed without fertilisation of ovary, it is called
Answer: Parthenocarpic fruit
Q74. Which of the following is not correct?
1. Axile placentation – Primrose
2. Parietal placentation – Mustard, Argemone
3. Free central placentation-Dianthus
4. Basal placentation – Sunflower, Marigold
Answer: 1 (Note : Primrose has free central placentation)
Q75. Ovary is one chambered but it becomes two chambered due to formation of the false septum in …(a)….. and …..(b)…..
Answer: (a) Mustard (b) Argemone
Q76. Generally, the fruit is consist of —-(a)—- and —(b)—-
Answer: a – Pericarp, b – Seeds
Q77. In mango and coconut the fruit is known as
Answer: Drupe
Q78. The drupe fruits are developed from ——- and superior ovary.
Answer: Monocarpellary gynoecium
Q79. The edible part of mango is
Answer: Mesocarp
Q80. The mesocarp of coconut is
Answer: Fibrous
Q81. A seed is generally made up of
Answer: Seed coat and an embryo
Q82. The seed coat has two layers, the outer –(a)– and the inner —-(b) —-
Answer: a – Testa, b-Tegmen
Q83. Recognise the a , b and c in the below diagram.
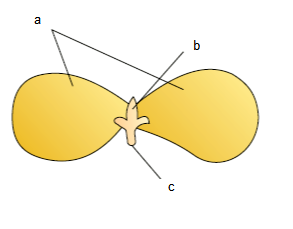
Answer: a – Cotyledon, b- Plumule, c-Radicle
Q84. Orchid seed is (non endospermic or endospermic)
Answer: Non-endospermic
Q85. In the seeds of cereal the seed coat and fruit wall are (Fused/Free)
Answer: Fused
Q86. In maize, the outer covering of endosperm separates the embryo by a proteinous layer called
Answer: Aleurone layer
Q87. In monocots, one large and shield shaped cotyledon is known as
Answer: Scutellum
Q88. The plumule and radicle are enclosed in sheaths which are —-(a)—– and —–(b)—– respectively
Answer: a – Coleoptile, b-Coleorhiza
Q89. Recognise a and b
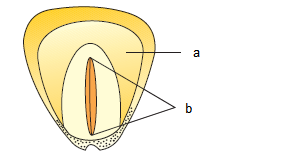
Answer: a – Endosperm, b – Embryo
Q90. Recognise a, b and c in the given diagram
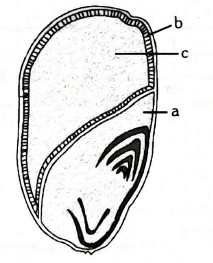
Answer: a – Scutellum, b – Aleurone layer, c-Endosperm
Q91. Floral formula of mustard is
Answer:
![]()
Q92. Papilionatae is a subfamily of
Answer: Leguminosae
Q93. Which structure of petals encloses the stamen and pistil.
Answer: Keel
Q94. Floral formula of Pea is
Answer:
![]()
Q95. In fabaceae family, the gynoecium is monocarpellary, unilocular with many ovules, single style and superior ovary. (True/False)
Answer: True
Q96. How many of the plants given below are comes under fabaceae family – Moong, Soyabean, Indigofera, Sunhemp, Sesbania, Lupinus, Mulaithi
Answer: All
Q97. Solanaceae family commonly known as
Answer: Potato family
Q98. The floral formula of Petunia is
Answer:
![]()
Q99. Persistent calyx is found in the members of (Solanaceae/Liliaceae)
Answer: Solanaceae
Q100. How many of the plants given below are comes under solanaceae family :- Tobacco, Tomato, Chilli, Belladona, Ashwagandha, Petunia, Makoi
Answer: All
Q101. Family Liliaceae is commonly called
Answer: Lily family
Q102. Epitepalous condition is found in (Fabaceae/Liliaceae)
Answer: Liliaceae
Q103. In the members of family liliaceae the gynoecium is tricarpellary, syncarpous, trilocular with many ovules and superior ovary. (True/False)
Answer: True
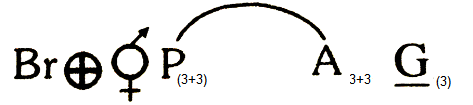
Q104. Floral formula of onion is
Answer:
Q105. How many of the plants given below are comes under family
Liliaceae :- Aloe, Asparagus, Tulip, Gloriosa, Colchicum
Answer: All
Q106. In vexillary aestivation, posterior petal is known as
Answer: Standard or Vexillum
Q107. Underground modification of stem i.e. bulbs, corms and rhizomes comes under…. family.
Answer: Liliaceae
Q108. Fruit of liliaceae family is
Answer: Capsule, rarely berry
Q109. Recognise the family which is related to above floral diagram.
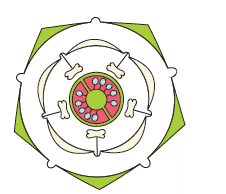
Answer: Solanaceae family
Q110. Match the following
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline 1 & \text { Fabaceae } & \text { i } & \text { Swollen placenta } \\
\hline 2 & \text { Solanaceae } & \text { ii } & \text { Diadelphous stamens } \\
\hline 3 & \text { Liliaceae } & \text { iii } & \text { Epitepalous condition } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Answer:
\(
\begin{array}{|l|}
\hline 1-ii \\
\hline 2-i \\
\hline 3 – iii \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)