Basic Mathematics
Quadratic Equation
Roots of \(a x^{2}+b x+c=0\) are \(x=\frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4 a c}}{2 a}\)
Sum of roots \(x_{1}+x_{2}=-\frac{b}{a}\);
Product of roots \(x_{1} x_{2}=\frac{\mathrm{c}}{\mathrm{a}}\)
For real roots, \(b^{2}-4 a c \geq 0\)
For imaginary roots, \(b^{2}-4 a c<0\)
Logarithm
\(\begin{array}{ll}
\log _{10} N=x \Rightarrow 10^{\mathrm{x}}=\mathrm{N} & \\
\log _{b} N=\log _{\mathrm{b}}\mathrm{a}^{*} \log _{\mathrm{a}}\mathrm{N} & \\
\log _{\mathrm{b}} 1=0, \log _{\mathrm{a}} \mathrm{a}=1 & \\
\log \mathrm{mn}=\log \mathrm{m}+\log \mathrm{n} & \log \frac{\mathrm{m}}{\mathrm{n}}=\log \mathrm{m}-\log \mathrm{n} \\
\log \mathrm{m}^{\mathrm{n}}=\mathrm{n} \log \mathrm{m} & \log _{e} \mathrm{~m}=2.303 \log _{10} \mathrm{~m} \\
\log 2=0.3010 & \log 3=0.4771
\end{array}
\)
Logarithmic Expansion
\(\ln (1+x)=x-\frac{1}{2} x^{2}+\frac{1}{3} x^{3}-\ldots(|x|<1)\)Arithmetic progression-AP
\(a, a+d, a+2 d, a+3 d, \ldots \ldots a+(n-1) d\), here \(\mathrm{d}=\) common difference
Sum of \(n\) terms \(S_{n}=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\), \(n^{\text {th }}\) term: \(a_{n}=a+(n-1) d\)
(i) \(1+2+3+4+5 \ldots+\mathrm{n}=\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{n}+1)}{2} \\\)
(ii) \(1^{2}+2^{2}+3^{2}+\ldots+\mathrm{n}^{2}=\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{n}+1)(2 \mathrm{n}+1)}{6} \\\)
(iii) \(1^{3}+2^{2}+3^{2}+\ldots+\mathrm{n}^{3}=\left[\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{n}+1)}{2}\right]^{2}\)
Binomial Theorem
\((1+x)^{n}=1+n x+\frac{n(n-1)}{2} x^{2}+\frac{n(n-1)(n-2)}{6} x^{3}+\ldots \\\)
\((1-\mathrm{x})^{\mathrm{n}}=1-\mathrm{nx}+\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{n}-1)}{2} \mathrm{x}^{2}-\frac{\mathrm{n}(\mathrm{n}-1)(\mathrm{n}-2)}{6} \mathrm{x}^{3}+\ldots \ldots \left(x^{2}<1\right)\\\)
\((1-x)^{-n}=1 – \frac{n x}{1 !}+\frac{n(n+1) x^{2}}{2 !}+\ldots . .\left(x^{2}<1\right) \\\)
\(\text { If } x<<1 \text { then }(1+x)^{n} \approx 1+n x \&(1-x)^{n} \approx 1-n x\)
Exponential Expansion
\(e^{x}=1+x+\frac{x^{2}}{2 !}+\frac{x^{3}}{3 !}+\ldots \ldots\)Trigonometric Expansion (\(\theta\) in radians)
\(\begin{aligned}
&\sin \theta=\theta-\frac{\theta^{3}}{3 !}+\frac{\theta^{5}}{5 !}-\ldots . \\
&\cos \theta=1-\frac{\theta^{2}}{2 !}+\frac{\theta^{4}}{4 !}-\ldots . \\
&\tan \theta=\theta+\frac{\theta^{3}}{3}+\frac{2 \theta^{5}}{15}-\ldots .
\end{aligned}
\)
Componendo and dividendo theorem
\(\text { If } \frac{p}{q}=\frac{a}{b} \text { then } \frac{p+q}{p-q}=\frac{a+b}{a-b}\)Geometrical progression-GP
\(\mathrm{a}, \mathrm{ar}, \mathrm{ar}^{2}, \mathrm{ar}^{3}, \ldots \ldots\) here, \(\mathrm{r}=\mathrm{common}\) ratio, \(n^{\text {th }}\) term, \(a_{n}=a \cdot r^{n-1} \\\)
Sum of \(n\) terms \(S_{n}=\frac{a\left(1-r^{n}\right)}{1-r} \\\)
Sum of \(\infty\) terms \(S_{\infty}=\frac{a}{1-r} \quad\) [where \(|r|<1\) ]
Trigonometry
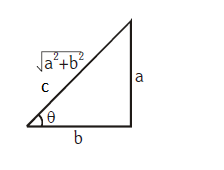
Pythagorean Theorem: In this right triangle, \(a^{2}+b^{2}=c^{2}\)
\(\begin{array}{l|l|l}
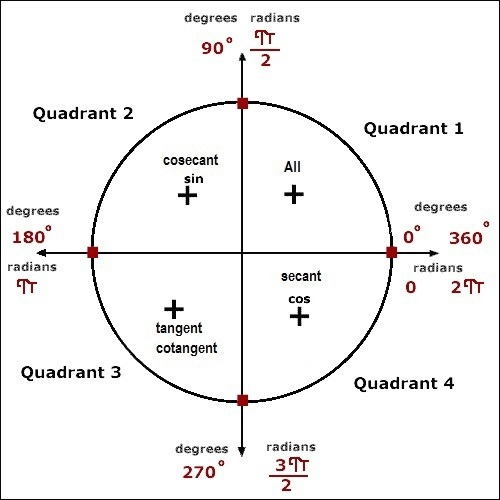
{2 \pi \text { radian }=360^{\circ} \Rightarrow 1 \mathrm{rad}=57.3^{\circ}} \\
\sin \theta=\frac{\text { perpendicular }}{\text { hypotenuse }} & \cos \theta=\frac{\text { base }}{\text { hypotenuse }} & \tan \theta=\frac{\text { perpendicular }}{\text { base }} \\
\cot \theta=\frac{\text { base }}{\text { perpendicular }} & \sec \theta=\frac{\text { hypotenuse }}{\text { base }} & \operatorname{cosec} \theta=\frac{\text { hypotenuse }}{\text { perpendicular }} \\
\sin \theta=\frac{a}{\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}} & \cos \theta=\frac{b}{\sqrt{a^{2}+b^{2}}} & \tan \theta=\frac{a}{b} \\
\operatorname{cosec} \theta=\frac{1}{\sin ^{2}} & \sec \theta=\frac{1}{\cos ^{2} \theta} & \cot \theta=\frac{1}{\tan ^{2} \theta} \\
\sin ^{2} \theta+\cos ^{2} \theta=1 & 1+\tan ^{2} \theta=\sec ^{2} \theta & 1+\cot ^{2} \theta=\operatorname{cosec}^{2} \theta
\end{array}
\)
\begin{array}{ll}
\sin (A \pm B)=\sin A \cos B \pm \cos A \sin B & \cos (A \pm B)=\cos A \cos B \mp \sin A \sin B \\
\tan (A \pm B)=\frac{\tan A \pm \tan B}{1 \mp \tan A \tan B} & \sin 2 A=2 \sin A \cos A \\
\cos 2 A=\cos ^{2} A-\sin ^{2} A=1-2 \sin ^{2} A=2 \cos ^{2} A-1 \\
\tan 2 A=\frac{2 \tan A}{1-\tan ^{2} A} & \sin 3 \alpha=3 \sin \alpha-4 \sin ^{3} \alpha \\
\cos 3 \alpha=4 \cos ^{3} \alpha-3 \cos \alpha & 2 \sin A \sin B=\cos (A-B)-\cos (A+B) \\
2 \cos A \cos B=\cos (A-B)+\cos (A+B) & 2 \sin A \cos B=\sin (A+B)+\sin (A-B)
\end{array}
\)
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline \theta & \begin{array}{c}
0^{\circ} \\
(0)
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
30^{\circ} \\
(\pi / 6)
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
45^{\circ} \\
(\pi / 4)
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
60^{\circ} \\
(\pi / 3)
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
90^{\circ} \\
(\pi / 2)
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
120^{\circ} \\
(2 \pi / 3)
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
135^{\circ} \\
(3 \pi / 4)
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
150^{\circ} \\
(5 \pi / 6)
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
180^{\circ} \\
(\pi)
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
270^{\circ} \\
(3 \pi / 2)
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
360^{\circ} \\
(2 \pi)
\end{array} \\
\hline \sin \theta & 0 & \frac{1}{2} & \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} & \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} & 1 & \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} & \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} & \frac{1}{2} & 0 & -1 & \mathbf{0} \\
\hline \cos \theta & 1 & \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} & \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} & \frac{1}{2} & 0 & -\frac{1}{2} & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} & -\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} & -1 & 0 & \mathbf{1} \\
\hline \tan \theta & \mathbf{0} & \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} & \mathbf{1} & \sqrt{3} & \infty & -\sqrt{3} & -\mathbf{1} & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} & \mathbf{0} & \infty & \mathbf{0} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
\(
\begin{array}{|llll|}
\hline \sin \left(90^{\circ}+\theta\right)=\cos \theta & \sin \left(180^{\circ}-\theta\right)=\sin \theta & \sin (-\theta)=-\sin \theta & \sin \left(90^{\circ}-\theta\right)=\cos \theta \\
\cos \left(90^{\circ}+\theta\right)=-\sin \theta & \cos \left(180^{\circ}-\theta\right)=-\cos \theta & \cos (-\theta)=\cos \theta & \cos \left(90^{\circ}-\theta\right)=\sin \theta \\
\tan \left(90^{\circ}+\theta\right)=-\cot \theta & \tan \left(180^{\circ}-\theta\right)=-\tan \theta & \tan (-\theta)=-\tan \theta & \tan \left(90^{\circ}-\theta\right)=\cot \theta \\
\sin \left(180^{\circ}+\theta\right)=-\sin \theta & \sin \left(270^{\circ}-\theta\right)=-\cos \theta & \sin \left(270^{\circ}+\theta\right)=-\cos \theta & \sin \left(360^{\circ}-\theta\right)=-\sin \theta \\
\cos \left(180^{\circ}+\theta\right)=-\cos \theta & \cos \left(270^{\circ}-\theta\right)=-\sin \theta & \cos \left(270^{\circ}+\theta\right)=\sin \theta & \cos \left(360^{\circ}-\theta\right)=\cos \theta \\
\tan \left(180^{\circ}+\theta\right)=\tan \theta & \tan \left(270^{\circ}-\theta\right)=\cot \theta & \tan \left(270^{\circ}+\theta\right)=-\cot \theta & \tan \left(360^{\circ}-\theta\right)=-\tan \theta \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
sine law
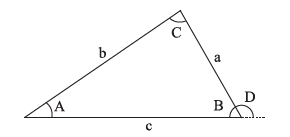
Trlangles
Angles are \(A, B, C\)
Opposite sides are \(a, b, c\)
Angles \(A+B+C=180^{\circ}\)
\(
\frac{\sin A}{a}=\frac{\sin B}{b}=\frac{\sin C}{c}
\)
\(c^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2 a b \cos C\)
Exterior angle \(D=A+C\)
cosine law
\(\cos A=\frac{b^{2}+c^{2}-a^{2}}{2 b c}, \cos B=\frac{c^{2}+a^{2}-b^{2}}{2 c a}, \cos C=\frac{a^{2}+b^{2}-c^{2}}{2 a b}\)For small \(\theta\)
\(\sin \theta \approx \theta \quad \cos \theta \approx 1 \quad \tan \theta \approx \theta \quad \sin \theta \approx \tan \theta\)Differentiation
\(y=x^{n} \rightarrow \frac{d y}{d x}=n x^{n-1} \quad \quad y=\ell n x \rightarrow \frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{1}{x} \\\)
\(y=\sin x \rightarrow \frac{d y}{d x}=\cos x \quad \quad y=\cos x \rightarrow \frac{d y}{d x}=-\sin x \\\)
\(y=e^{\alpha x+\beta} \rightarrow \frac{d y}{d x}=\alpha e^{\alpha x+\beta} \quad \quad y=u v \rightarrow \frac{d y}{d x}=u \frac{d v}{d x}+v \frac{d u}{d x} \\\)
\(y=f(g(x)) \Rightarrow \frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{d f(g(x))}{d g(x)} \times \frac{d(g(x))}{d x} \\\)
\(\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{k}(\) constant \() \Rightarrow \frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}=0 \\\)
\(y=\frac{u}{v} \Rightarrow \frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{v \frac{d u}{d x}-u \frac{d v}{d x}}{v^{2}} \\\)
Integration
\(\mathrm{C}=\) Arbitrary constant, \(k=\) constant
\(\int f(x) d x=g(x)+C \\\)
\(\quad \frac{d}{d x}(g(x))=f(x) \\\)
\(\int k f(x) d x=k \int f(x) d x \\\)
\(\int(u+v+w) d x=\int u d x+\int v d x+\int w d x \\\)
\(\int e^{x} d x=e^{x}+C \\\)
\(\int x^{n} d x=\frac{x^{n+1}}{n+1}+C, n \neq-1 \\\)
\(\int \frac{1}{\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{dx}=\ln \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{C} \\\)
\(\int \sin x d x=-\cos x+C\)
\(\int \cos x d x=\sin x+C \\\)
\(\int e^{\alpha x+\beta} d x=\frac{1}{\alpha} e^{\alpha x+\beta}+C \\\)
\(\int(\alpha x+\beta)^{n} d x=\frac{(\alpha x+\beta)^{n+1}}{\alpha(n+1)}+C \\\)
Definite Integration
\(\int_{a}^{b} f(x) d x=|g(x)|_{a}^{b}=g(b)-g(a) \\\)
Area under the curve \(y=f(x)\) from \(x=a\) to \(a=b\) is
\(
A=\int_{a}^{b} f(x) d x
\)
Maxima & Minima of a function y=f(x)
For maximum value \(\frac{d y}{d x}=0 \& \frac{d^{2} y}{d x^{2}}=-v e \\\)
For minimum value \(\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dx}}=0 \& \frac{\mathrm{d}^{2} \mathrm{y}}{\mathrm{dx}^{2}}=+v e \\\)
Average of a varying quantity
\(\text { If } y=f(x) \text { then }\langle y\rangle=\bar{y}=\frac{\int_{x_{1}}^{x_{2}} y d x}{\int_{x_{1}}^{x_{2}} d x}=\frac{\int_{x_{1}}^{x_{2}} y d x}{x_{2}-x_{1}}
\)
Formulae For Determination Of Area
Area of a square \(=(\text { side })^{2} \\\)
Area of rectangle \(=\) length \(\times\) breadth
Area of a triangle \(=\frac{1}{2} \times\) base \(\times\) height
Area of a trapezoid \(=\frac{1}{2} \times(\) distance between parallel sides \() \times(\) sum of parallel sides \() \\\)
Area enclosed by a circle \(=\pi \mathrm{r}^{2} \quad(\mathrm{r}=\) radius \() \\\)
Surface area of a sphere \(=4 \pi \mathrm{r}^{2}\) ( \(\mathrm{r}=\) radius \() \\\)
Area of a parallelogram \(=\) base \(\times\) height
Area of curved surface of cylinder \(=2 \pi \mathrm{r} \ell \), where \(r=\) radius and \(\ell=\) length
Area of whole surface of cylinder \(=2 \pi r(r+\ell)\) where \(\ell=\) length
Area of ellipse \(=\pi \mathrm{ab}\), (a & b are semi-major and semi-minor axis respectively)
Surface area of a cube \(=6(\text { side })^{2} \\\)
Total surface area of a cone \(=\pi r^{2}+\pi r \ell \\\)
where \(\pi r \ell=\pi r \sqrt{r^{2}+h^{2}}=\) lateral area
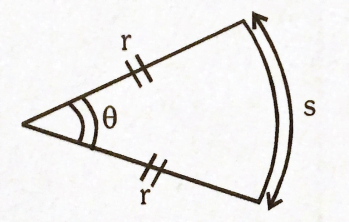
Arc length \(s=r . \theta \\\)
Area of sector \(=\frac{r^{2} \theta}{2} \\\)
Plane angle, \(\theta=\frac{\mathrm{s}}{\mathrm{r}}\) radian
Solid angle, \(\Omega=\frac{\mathrm{A}}{\mathrm{r}^{2}}\) steradian
Formulae for Determination of Volume
Volume of a rectangular slab\(=\) length \(\times\) breadth \(\times\) height
\(=\mathrm{l w h}\\ \)
Volume of a cube \(=(\text { side })^{3} \\\)
Volume of a sphere \(=\frac{4}{3} \pi r^{3}\) \((r=\) radius)
Volume of a cylinder \(=\pi r^{2} \ell \\\)
( \(\mathrm{r}=\) radius and \(\ell=\) length)
Volume of a cone \(=\frac{1}{3} \pi r^{2} h \\\)
( \(\mathrm{r}=\) radius and \(\mathrm{h}=\) height \()\)
Key Points to Remember
To convert an angle from degree to radian, we have to multiply it by \(\frac{\pi}{180^{\circ}}\) and to convert an angle from radian to degree, we have to multiply it by \(\frac{180^{\circ}}{\pi}\).
By help of differentiation, if \(y\) is given, we can find \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) and by help of integration, if \(\frac{d y}{d x}\) is given, we can find \(y\).
The maximum and minimum values of the function
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\quad A \cos \theta+B \sin \theta \text { are } \sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}} \text { and }-\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}} \text { respectively. } \\(a+b)^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}+2 a b & (a-b)^{2}=a^{2}+b^{2}-2 a b \\
(a+b)(a-b)=a^{2}-b^{2} & (a+b)^{3}=a^{3}+b^{3}+3 a b(a+b) \\
(a-b)^{3}=a^{3}-b^{3}-3 a b(a-b) &
\end{array}
\)