NCERT Exemplar MCQs
Summary
- By a sequence, we mean an arrangement of number in definite order according to some rule. Also, we define a sequence as a function whose domain is the set of natural numbers or some subsets of the type \(\{1,2,3, \ldots . k\}\). A sequence containing a finite number of terms is called a finite sequence. A sequence is called infinite if it is not a finite sequence.
- Let \(a_1, a_2, a_3, \ldots\) be the sequence, then the sum expressed as \(a_1+a_2+a_3+\ldots\) is called series. A series is called finite series if it has got finite number of terms.
- An arithmetic progression (A.P.) is a sequence in which terms increase or decrease regularly by the same constant. This constant is called common difference of the A.P. Usually, we denote the first term of A.P. by \(a\), the common difference by \(d\) and the last term by \(l\). The general term or the \(n^{\text {th }}\) term of the A.P. is given by \(a_n=a+(n-1) d\).
- The sum \(S _n\) of the first \(n\) terms of an A.P. is given by
\(S _n=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]=\frac{n}{2}(a+l) .\)
- The arithmetic mean \(A\) of any two numbers \(a\) and \(b\) is given by \(\frac{a+b}{2}\) i.e., the sequence \(a, A , b\) is in A.P.
- A sequence is said to be a geometric progression or G.P., if the ratio of any term to its preceding term is same throughout. This constant factor is called the common ratio. Usually, we denote the first term of a G.P. by \(a\) and its common ratio by \(r\). The general or the \(n^{\text {th }}\) term of G.P. is given by \(a_n=a r^{n-1}\). The sum \(S _n\) of the first \(n\) terms of GP. is given by
\(S _n=\frac{a\left(r^n-1\right)}{r-1} \text { or } \frac{a\left(1-r^n\right)}{1-r} \text {, if } r \neq 1\)
- The geometric mean (G.M.) of any two positive numbers \(a\) and \(b\) is given by \(\sqrt{a b}\) i.e., the sequence \(a, G , b\) is G.P.
Quiz Summary
0 of 58 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 58 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 58
1. Question
The first term of an A.P.is \(a\), and the sum of the first \(p\) terms is zero, what is the sum of its next \(q\) terms?
CorrectIncorrectHint
Given that \(a_1=a\) and \(S _p=0\)
Sum of next \(q\) terms of the given A.P. \(= S _{p+q}- S _p\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \therefore \quad S _{p+q}=\frac{p+q}{2}[2 a+(p+q-1) d] \\
& \text { and } \quad S _p=\frac{p}{2}[2 a+(p-1) d]=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 2 a+(p-1) d=0 \Rightarrow(p-1) d=-2 a \\
& \Rightarrow \quad d=\frac{-2 a}{p-1} \\
&
\end{aligned}
\)
Sum of next \(q\) terms \(= S _{p+q}- S _p\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& =\frac{p+q}{2}[2 a+(p+q-1) d]-0 \\
& =\frac{p+q}{2}\left[2 a+(p+q-1)\left(\frac{-2 a}{p-1}\right)\right] \\
& =\frac{p+q}{2}\left[2 a+\frac{(p-1)(-2 a)}{p-1}-\frac{2 a q}{p-1}\right] \\
& =\frac{p+q}{2}\left[2 a-2 a-\frac{2 a q}{p-1}\right]=\frac{(p+q)}{2}\left(\frac{-2 a q}{p-1}\right) \\
& =\frac{-a(p+q) q}{p-1}
\end{aligned}
\)
Hence, the required sum \(=\frac{-a(p+q) q}{p-1}\) -
Question 2 of 58
2. Question
A man saved Rs 66000 in 20 years. In each succeeding year after the first year he saved Rs 200 more than what he saved in the previous year. How much did he save in the first year?
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let \(₹ x\) be saved in first year.
Annual increment \(=₹ 200\), which forms an A.P.
first term \(=a\) and common difference \(d=200\) \(n=20\) years
\(
\therefore \quad S _n=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d] \Rightarrow S _{20}=\frac{20}{2}[2 a+(20-1) 200]
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
66000 & =10[2 a+3800] \Rightarrow 6600=2 a+3800 \\
2 a & =6600-3800 \Rightarrow 2 a=2800 \Rightarrow a=1400
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 3 of 58
3. Question
A man accepts a position with an initial salary of Rs 5200 per month. It is understood that he will receive an automatic increase of Rs 320 in the very next month and each month thereafter.
(a) Find his salary for the tenth month
(b) What is his total earnings during the first year?CorrectIncorrectHint
Given that fixed increment in the salary of a man
\(
=₹ 320 \text { each month }
\)
Initial salary \(=₹ 5200\) which makes an A.P.
whose first term \((a)=₹ 5200\) and common difference \((d)=₹ 320\)
(i) Salary for the tenth month
\(
\begin{aligned}
a_{10} & =a+(n-1) d \\
& =5200+(10-1) \times 320=5200+2880=₹ 8080
\end{aligned}
\)
(ii) Total earning during the first year ( 12 months)
\(
S_{12}=\frac{12}{2}[2 \times 5200+(12-1) \times 320] \left[\because \quad S _n=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]\right]
\)
\(
=6[10400+3520]=6 \times 13920=₹ 83520
\)
Hence, the required amount is (i) ₹ 8080 (ii) ₹ 83520 . -
Question 4 of 58
4. Question
If the \(p\) th and \(q\) th terms of a G.P. are \(q\) and \(p\) respectively, what is its \(\)(p+q)^{\text {th }}\(\) term?
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let the first term and common ratio of G.P. be \(a\) and \(r\), respectively.
Given that, \(p\) th term \(=q \quad \Rightarrow a r^{p-1}=q \dots(i)\)
\(
\text { and } \quad q \text { th term }=p \Rightarrow a r^{q-1}=p \dots(ii)
\)
On dividing Eq. (i) by Eq. (ii), we get
\(
\frac{a r^{p-1}}{a r^{q-1}}=\frac{q}{p} \Rightarrow r^{p-q}=\frac{q}{p} \Rightarrow r=\left(\frac{q}{p}\right)^{\frac{1}{p-q}}
\)
On substituting the value of \(r\) in Eq. (i), we get
\(
a\left(\frac{q}{p}\right)^{\frac{p-1}{p-q}}=q \Rightarrow a=q\left(\frac{p}{q}\right)^{\frac{p-1}{p-q}}
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
(p+q) \text { th term, } T_{p+q} & = a \cdot r^{p+q-1} \\
& =q\left(\frac{p}{q}\right)^{\frac{p-1}{p-q}}\left(\frac{q}{p}\right)^{\frac{p+q-1}{p-q}}=q\left(\frac{p}{q}\right)^{\frac{p-1}{p-q}-\frac{p+q-1}{p-q}} \\
& =q\left(\frac{q}{p}\right)^{\frac{q}{p-q}}=\frac{q^{\frac{q}{p-q}+1}}{p^{\frac{q}{p-q}}}=\frac{q^{\frac{p}{p-q}}}{p^{\frac{q}{p-q}}}=\left(\frac{q^p}{p^q}\right)^{\frac{1}{p-q}}
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 5 of 58
5. Question
A carpenter was hired to build 192 window frames. The first day he made five frames and each day, thereafter he made two more frames than he made the day before. How many days did it take him to finish the job?
CorrectIncorrectHint
Here, \(a=5\) and \(d=2\)
Let the carpenter finish the job in \(n\) days. Then, \(S_n=192\)
\(
192=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d] \Rightarrow 192=\frac{n}{2}[2 \times 5+(n-1) 2]
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& 192=n[5+n-1] \Rightarrow n^2+4 n-192=0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad(n-12)(n+16)=0 \\
& n=12
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 6 of 58
6. Question
We know the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is \(180^{\circ}\). Show that the sums of the interior angles of polygons with \(3,4,5,6, \ldots\) sides form an arithmetic progression. Find the sum of the interior angles for a 21 sided polygon.
CorrectIncorrectHint
We know that, sum of interior angles of a polygon of side \(n\) is \((n-2) \times 180^{\circ}\).
Let \(t_n=(n-2) \times 180^{\circ}\)
Since \(t_n\) is linear in \(n\), it is \(n\)th term of some A.P.
\(
t_3=a=(3-2) \times 180^{\circ}=180^{\circ}
\)
Common difference, \(d=180^{\circ}\)
Sum of the interior angles for a 21 sided polygon is:
\(
t_{21}=(21-2) \times 180^{\circ}=3420^{\circ}
\) -
Question 7 of 58
7. Question
A side of an equilateral triangle is \(20 cm\) long. A second equilateral triangle is inscribed in it by joining the mid points of the sides of the first triangle. The process is continued as shown in the accompanying diagram. Find the perimeter of the sixth inscribed equilateral triangle.
CorrectIncorrectHint
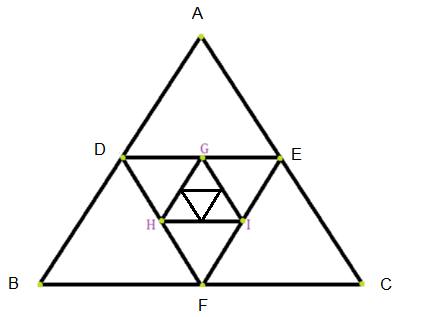
The side of the first equilateral \(\triangle ABC =20 cm\)
By joining the mid points of the sides of this triangle, we get the second equilateral triangle which each side \(=\frac{20}{2}=10 cm\)
\([\because \quad\) The line joining the mid-points of two sides of a triangle is \(1 / 2\) and parallel to third side of the triangle]
Similarly each side of the third equilateral triangle \(=\frac{10}{2}=5 cm\)
\(\therefore\) Perimeter of first triangle \(=20 \times 3=60 cm\)
Perimeter of the second triangle \(=10 \times 3=30 cm\)
and the perimeter of the third triangle \(=5 \times 3=15 cm\)
Therefore, the series will be \(60,30,15, \ldots\)
which is G.P. in which \(a=60\), and \(r=\frac{30}{60}=\frac{1}{2}\)
Now, we have to find the perimeter of the sixth inscribed equilateral triangle
\(
\begin{aligned}
\therefore \quad a_6 & =a r^{6-1} \\
& =60 \times\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^5=60 \times \frac{1}{32}=\frac{15}{8} cm
\end{aligned}
\)
Hence, the required perimeter \(=\frac{15}{8} cm\) -
Question 8 of 58
8. Question
In a potato race 20 potatoes are placed in a line at intervals of 4 metres with the first potato 24 metres from the starting point. A contestant is required to bring the potatoes back to the starting place one at a time. How far would he run in bringing back all the potatoes?
CorrectIncorrectHint
We have,
the distance travelled to bring the first potato, \(a_1=2 \times 24=48 m\), the distance travelled to bring the second potato, \(a_2=2 \times(24+4)=56 m\), the distance travelled to bring the third potato, \(a_3=2 \times(24+4+4)=64 m\),
As, \(a_2-a_1=56-48=8\) and \(a_3-a_2=64-56=8\) i. e. \(a_2-a_1=a_3-a_2\)
So, \(a_1, a_2, a_3, \ldots\) are in A.P.
Also, \(a=48, d=8, n=20\)
Now,
\(
\begin{aligned}
& S_{20}=\frac{20}{2}[2 a+(20-1) d] \\
& =10[2 \times 48+19 \times 8] \\
& =10 \times(96+152) \\
& =10 \times 248 \\
& =2480
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 9 of 58
9. Question
In a cricket tournament 16 school teams participated. A sum of Rs 8000 is to be awarded among themselves as prize money. If the last placed team is awarded Rs 275 in prize money and the award increases by the same amount for successive finishing places, how much amount will the first place team receive?
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let the prize amount got by first place team be \(₹ a\)
Since, the prize money increases by the same amount for successive finishing places, therefore the series will be A.P.
\(
\therefore \quad \begin{aligned}
a_n & =275, n=16 \text { and } S _{16}=8000 \\
a_n & =a+(n-1) d \\
275 & =a+(16-1)(-d)
\end{aligned}
\)
\([\because\) Common difference \(d\) is \((-)\) as the series is decreasing \(]\)
\(
\Rightarrow \quad 275=a-15 d \dots(i)
\)
Now
\(
\begin{aligned}
S _n & =\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d] \\
S _{16} & =\frac{16}{2}[2 a+15(-d)]
\end{aligned}
\)
\(
\Rightarrow \quad 8000=8[2 a-15 d] \Rightarrow 2 a-15 d=1000 \dots(ii)
\)
Solving eq. (i) and eq. (ii) we get
\(
a=725 \text { and } d=30
\)
Hence, the required award received by first place term \(=₹ 725\). -
Question 10 of 58
10. Question
If \(a_1, a_2, a_3, \ldots, a_n\) are in A.P., where \(a_i>0\) for all \(i\), What is the value of
\(
\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_1}+\sqrt{a_2}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_2}+\sqrt{a_3}}+\ldots+\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_{n-1}}+\sqrt{a_n}}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
Given that \(a_1, a_2, a_3, a_4, \ldots, a_n\) are in A.P.
\(\therefore\) Common difference \(d=a_2-a_1=a_3-a_2=a_4-a_3=\ldots=a_n-a_{n-1}\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \text { If } a_2-a_1=d \text { then } \sqrt{a_2^2}-\sqrt{a_1^2}=d \\
& \Rightarrow \quad\left(\sqrt{a_2}-\sqrt{a_1}\right)\left(\sqrt{a_2}+\sqrt{a_1}\right)=d \quad\left[\because \quad a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b)\right]
\end{aligned}
\)
\(
\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_1}+\sqrt{a_2}}=\frac{\sqrt{a_2}-\sqrt{a_1}}{d}
\)
Similarly
\(
\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_2}+\sqrt{a_3}}=\frac{\sqrt{a_3}-\sqrt{a_2}}{d}
\)
\(
\begin{array}{cc}
\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_3}+\sqrt{a_4}}= & \frac{\sqrt{a_4}-\sqrt{a_3}}{d} \\
\cdots & \cdots \\
\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_{n-1}}+\sqrt{a_n}}= & \frac{\sqrt{a_n}-\sqrt{a_{n-1}}}{d}
\end{array}
\)
Adding the above terms, we get
\(
\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_1}+\sqrt{a_2}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_2}+\sqrt{a_3}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_3}+\sqrt{a_4}}+\cdots+\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_{n-1}}+\sqrt{a_n}}
\)
\(
\begin{gathered}
=\frac{1}{d}\left[\sqrt{a_2}-\sqrt{a_1}+\sqrt{a_3}-\sqrt{a_2}+\sqrt{a_4}-\sqrt{a_3}+\cdots \sqrt{a_n}-\sqrt{a_{n-1}}\right] \\
=\frac{1}{d}\left[\sqrt{a_n}-\sqrt{a_1}\right] \dots(i)
\end{gathered}
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Now } \quad a_n=a_1+(n-1) d \\
& \Rightarrow \quad a_n-a_1=(n-1) d \\
& \Rightarrow \quad \sqrt{a_n^2}-\sqrt{a_1^2}=(n-1) d \\
& \Rightarrow \quad\left(\sqrt{a_n}+\sqrt{a_1}\right)\left(\sqrt{a_n}-\sqrt{a_1}\right)=(n-1) d \\
& \Rightarrow \quad \sqrt{a_n}-\sqrt{a_1}=\frac{(n-1) d}{\sqrt{a_n}+\sqrt{a_1}} \\
& \Rightarrow \quad \frac{\sqrt{a_n}-\sqrt{a_1}}{d}=\frac{n-1}{\sqrt{a_n}+\sqrt{a_1}} \dots(ii)\\
&
\end{aligned}
\)
From Eq. (i) and eq. (ii) we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{1}{\sqrt{a_1}+\sqrt{a_2}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_2}+\sqrt{a_3}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_3}+\sqrt{a_4}} \\
& +\cdots+\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_{n-1}}+\sqrt{a_n}}=\frac{n-1}{\sqrt{a_n}+\sqrt{a_1}}
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 11 of 58
11. Question
Find the sum of the series \(\left(3^3-2^3\right)+\left(5^3-4^3\right)+\left(7^3-6^3\right)+\ldots\) to (i) \(n\) terms (ii) 10 terms
CorrectIncorrectHint
Given series
\(
\Rightarrow \quad\left(3^3-2^3\right)+\left(5^3-4^3\right)+\left(7^3-6^3\right)+\cdots
\)
\(
=\left(3^3+5^3+7^3+\cdots\right)-\left(2^3+4^3+6^3+\cdots\right)
\)
\(
\Rightarrow\left[3^3+5^3+7^3+\ldots(2 n+1)^3\right]-\left[2^3+4^3+6^3+\cdots(2 n)^3\right]
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \therefore \quad T _n=(2 n+1)^3-(2 n)^3 \\
& =(2 n+1-2 n)\left[(2 n+1)^2+(2 n+1)(2 n)+(2 n)^2\right] \\
& {\left[\because a^3-b^3=(a-b)\left(a^2+a b+b^2\right)\right]} \\
& =1 \cdot\left[4 n^2+1+4 n+4 n^2+2 n+4 n^2\right] \\
& =12 n^2+6 n+1 \\
&
\end{aligned}
\)
(i)
\(
\begin{aligned}
S _n & =\sum T _n=12 \sum n^2+6 \sum n+n \\
& =12 \cdot \frac{n(n+1)(2 n+1)}{6}+\frac{6 n(n+1)}{2}+n \\
& =2 n(n+1)(2 n+1)+3 n(n+1)+n \\
& =n[2(n+1)(2 n+1)+3(n+1)+1] \\
& =n\left[2\left(2 n^2+3 n+1\right)+3 n+3+1\right] \\
& =n\left[4 n^2+6 n+2+3 n+4\right]=n\left[4 n^2+9 n+6\right] \\
& =4 n^3+9 n^2+6 n
\end{aligned}
\)
(ii)
\(
\begin{aligned}
S _{10} & =4(10)^3+9(10)^2+6(10)=4 \times 1000+900+60 \\
& =4000+960=4960
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 12 of 58
12. Question
Find the \(r^{ th }\) term of an A.P. sum of whose first \(n\) terms is \(2 n+3 n^2\).
CorrectIncorrectHint
\(
\text { [Hint: } a_n= S _n- S _{n-1} \text { ] }
\)
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\text { Given that } & S _n=2 n+3 n^2 \\
\Rightarrow & S _1=2 \times 1+3(1)^2=5 \\
\Rightarrow & S _2=2 \times 2+3 \times 4=16 \\
\Rightarrow & S _3=2 \times 3+3 \times 9=33
\end{array}
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
S_1 & =a_1=5 \\
S_2-S_1 & =a_2=16-5=11 \\
d & =a_2-a_1=11-5=6
\end{aligned}
\)
Now
\(
\begin{aligned}
T _r & =a_1+(r-1) d \\
& =5+(r-1) 6=5+6 r-6=6 r-1
\end{aligned}
\)
Hence, the required \(r\) th term is \(6 r-1\) -
Question 13 of 58
13. Question
If \(A\) is the arithmetic mean and \(G _1, G _2\) be two geometric means between any two numbers, calculate \(\frac{ G _1^2}{ G _2}+\frac{ G _2^2}{ G _1}\)
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let the numbers be \(a\) and \(b\).
Then, \(A=\frac{a+b}{2}\) or \(2 A=a+b \dots(i)\)
Also, \(G_1\) and \(G_2\) are geometric means between \(a\) and \(b\), then \(a, G_1, G_2, b\) are in G.P.
Let \(r\) be the common ratio.
Then, \(b=a r^{4-1}=a r^3 \Rightarrow \frac{b}{a}=r^3 \Rightarrow r=\left(\frac{b}{a}\right)^{1 / 3}\)
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\therefore & G_1=a r=a\left(\frac{b}{a}\right)^{1 / 3}=a^{2 / 3} b^{1 / 3} \\
\text { and } & G_2=a r^2=a\left(\frac{b}{a}\right)^{2 / 3}=a^{1 / 3} b^{2 / 3} \\
\therefore & \frac{G_1^2}{G_2}+\frac{G_2^2}{G_1}=\frac{G_1^3+G_2^3}{G_1 G_2}=\frac{a^2 b+a b^2}{a b}=a+b=2 A
\end{array}
\) -
Question 14 of 58
14. Question
If \(\theta_1, \theta_2, \theta_3, \ldots, \theta_n\) are in A.P., whose common difference is \(d\), Calculate \(\sec \theta_1 \sec \theta_2+\sec \theta_2 \sec \theta_3+\ldots+\sec \theta_{n-1} \sec \theta_n\)
CorrectIncorrectHint
Since \(\theta_1, \theta_2, \theta_3, \ldots, \theta_n\) are in A.P., we get
\(
\theta_2-\theta_1=\theta_3-\theta_2=\ldots=\theta_n-\theta_{n-1}=d \dots(i)
\)
Now,
\(
\begin{aligned}
\sec \theta_1 \sec \theta_2 & =\frac{1}{\sin d} \cdot \frac{\sin d}{\cos \theta_1 \cos \theta_2}=\frac{1}{\sin d} \cdot \frac{\sin \left(\theta_2-\theta_1\right)}{\cos \theta_1 \cos \theta_2} \\
& =\frac{1}{\sin d} \cdot \frac{\left(\sin \theta_2 \cos \theta_1-\cos \theta_2 \sin \theta_1\right)}{\cos \theta_1 \cos \theta_2}=\frac{\tan \theta_2-\tan \theta_1}{\sin d}
\end{aligned}
\)
Similarly, \(\sec \theta_2 \sec \theta_3=\frac{\tan \theta_3-\tan \theta_2}{\sin d} ; \sec \theta_3 \sec \theta_4=\frac{\tan \theta_4-\tan \theta_3}{\sin d}\); and so on.
\(
\therefore \quad \sec \theta_1 \sec \theta_2+\sec \theta_2 \sec \theta_3+\ldots+\sec \theta_{n-1} \sec \theta_n=\frac{\tan \theta_n-\tan \theta_1}{\sin d}
\) -
Question 15 of 58
15. Question
If the sum of \(p\) terms of an A.P. is \(q\) and the sum of \(q\) terms is \(p\), show that the sum of \(p+q\) terms is \(-(p+q)\). Also, find the sum of first \(p-q\) terms \((p>q)\).
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let first term and common difference of the A.P. be a and \(d\), respectively. Given, \(S_p=q\)
\(
\frac{p}{2}[2 a+(p-1) d]=q \quad \Rightarrow \quad 2 a+(p-1) d=\frac{2 q}{p} \dots(i)
\)
Also, \(S_q=p\)
\(
\Rightarrow \quad \frac{q}{2}[2 a+(q-1) d]=p \quad \Rightarrow \quad 2 a+(q-1) d=\frac{2 p}{q} \dots(ii)
\)
On subtracting Eq. (ii) from Eq. (i), we get
\(
(p-q) d=\frac{2 q}{p}-\frac{2 p}{q} \text { or }(p-q) d=\frac{2\left(q^2-p^2\right)}{p q}
\)
\(
\therefore \quad d=\frac{-2(p+q)}{p q} \dots(iii)
\)
On substituting the value of \(d\) into Eq. (i), we get
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
& 2 a+(p-1)\left(\frac{-2(p+q)}{p q}\right)=\frac{2 q}{p} \\
\Rightarrow & a=\frac{q}{p}+\frac{(p+q)(p-1)}{p q} \dots(iv)
\end{array}
\)
Now
\(
\begin{aligned}
S_{p+q} & =\frac{p+q}{2}[2 a+(p+q-1) d] \\
& =\frac{p+q}{2}\left[\frac{2 q}{p}+\frac{2(p+q)(p-1)}{p q}-\frac{2(p+q-1)(p+q)}{p q}\right] \\
& =(p+q)\left[\frac{q}{p}+\frac{(p+q)(p-1-p-q+1)}{p q}\right] \\
& =(p+q)\left[\frac{q}{p}+\frac{(p+q)(-q)}{p q}\right] \\
& =(p+q)\left[\frac{q}{p}-\frac{p+q}{p}\right]=-(p+q)
\end{aligned}
\)
Also,
\(
\begin{aligned}
S_{p-q} & =\frac{p-q}{2}[2 a+(p-q-1) d] \\
& =\frac{p-q}{2}\left[\frac{2 q}{p}+\frac{2(p+q)(p-1)}{p q}-\frac{(p-q-1) 2(p+q)}{p q}\right] \\
& =(p-q)\left[\frac{q}{p}+\frac{(p+q)(p-1-p+q+1)}{p q}\right] \\
& =(p-q)\left[\frac{q}{p}+\frac{(p+q) q}{p q}\right] \\
& =(p-q)\left[\frac{q}{p}+\frac{p+q}{p}\right]=(p-q) \frac{(p+2 q)}{p}
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 16 of 58
16. Question
If \(p\) th, \(q\) th and \(r\) th terms of an A.P. and G.P. are both \(a, b\), and \(c\) respectively. Calculate
\(
a^{b-c} \cdot b^{c-a} \cdot c^{n-b}=1
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
Let \(A\) and \(d\) be the first term and common difference of \(A\).P., respectively. Also, let \(B\) and \(R\) be the first term and common ratio of G.P., respectively.
It is given that,
\(
\begin{aligned}
& A+(p-1) d=a \dots(i) \\
& A+(q-1) d=b \dots(ii) \\
& A+(r-1) d=c \dots(iii)
\end{aligned}
\)
Also,
\(
\begin{aligned}
& a=B R^{p-1} \dots(iv) \\
& b=B R^{q-1} \dots(v) \\
& c=B R^{r-1} \dots(vi)
\end{aligned}
\)
On subtracting Eq. (ii) from Eq. (i), we get
\(
a-b=d(p-q)
\)
On subtracting Eq. (iii) from Eq. (ii), we get
\(
b-c=d(q-r)
\)
On subtracting Eq. (i) from Eq. (iii), we get
\(
c-a=d(r-p)
\)
\(
\therefore \quad a^{b-c} \cdot b^{c-a} \cdot c^{a-b}
\)
\(
=\left(B R^{(p-1)}\right)^{d(q-r)}\left(B R^{(q-1)}\right)^{d(r-p)}\left(B R^{(r-1)}\right)^{d(p-q)}
\)
\(
=B^{d[(q-r)+(r-p)+(p-q)]} R^{d[(p-1)(q-r)+(q-1)(r-p)+(r-1)(p-q)]}
\)
\(
=B^0 R^0=1
\) -
Question 17 of 58
17. Question
If the sum of \(n\) terms of an A.P. is given by \(S _n=3 n+2 n^2\), then the common difference of the A.P. is
CorrectIncorrectHint
Given that
\(
\text { hat } \begin{aligned}
S _n & =3 n+2 n^2 \\
S _1 & =3(1)+2(1)^2=5 \\
S _2 & =3(2)+2(4)=14 \\
S _1 & =a_1=5 \\
S _2- S _1 & =a_2=14-5=9
\end{aligned}
\)
\(\therefore\) Common difference \(d=a_2-a_1=9-5=4\) -
Question 18 of 58
18. Question
The third term of GP. is 4 . The product of its first 5 terms is
CorrectIncorrectHint
\(
\begin{aligned}
\text { Given that } & T _3 =4 \\
\Rightarrow & a r^{3-1} & =4 \left[\because \quad T _n=a r^{n-1}\right] \\
\Rightarrow & a r^2 =4
\end{aligned}
\)
Product of first 5 terms \(=a \cdot a r \cdot a r^2 \cdot a r^3 \cdot a r^4\)
\(
=a^5 r^{10}=\left(a r^2\right)^5=(4)^5
\) -
Question 19 of 58
19. Question
If 9 times the \(9^{\text {th }}\) term of an A.P. is equal to 13 times the \(13^{\text {th }}\) term, then the \(22^{\text {nd }}\) term of the A.P. is
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let the first term and common difference of given A.P. be a and d, respectively.
\(
\begin{aligned}
& & T _n & =a+(n-1) d \\
\therefore & & T _9 & =a+8 d \\
\text { and } & & T _{13} & =a+12 d
\end{aligned}
\)
As per the given condition
\(
\begin{aligned}
& & 9[a+8 d] & =13[a+12 d] \\
\Rightarrow & & 9 a+72 d & =13 a+156 d \Rightarrow-4 a=84 d \\
\Rightarrow & & a & =-21 d \dots(i)
\end{aligned}
\)
Now \(\quad T _{22}=a+21 d=-21 d+21 d=0 \quad\) [from eq. (i)] -
Question 20 of 58
20. Question
If \(x, 2 y, 3 z\) are in A.P., where the distinct numbers \(x, y, z\) are in G.P. then the common ratio of the G.P. is
CorrectIncorrectHint
Since \(x, 2 y, 3 z\) are in A.P.
\(
\begin{aligned}
\therefore & 2 y-x =3 z-2 y \\
\Rightarrow & 4 y =x+3 z \dots(i)
\end{aligned}
\)
Now \(x, y, z\) are in G.P.
\(\therefore \quad\) Common ratio \(r=\frac{y}{x}=\frac{z}{y} \dots(ii)\)
\(
\therefore \quad y^2=x z
\)
putting the value of \(x\) from eq. (i), we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
& y^2=(4 y-3 z) z \Rightarrow y^2=4 y z-3 z^2 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 3 z^2-4 y z+y^2=0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad 3 z^2-3 y z-y z+y^2=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3 z(z-y)-y(z-y)=0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad(3 z-y)(z-y)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 3 z-y=0 \text { and } z-y=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 3 z=y \text { and } z \neq y [\because \quad z \text { and } y \text { are distinct numbers }] \\
&
\end{aligned}
\)
\(
\frac{z}{y}=\frac{1}{3} \Rightarrow r=\frac{1}{3} \quad \text { (from eq. (ii)) }
\) -
Question 21 of 58
21. Question
If in an A.P., \(S _n=q n^2\) and \(S _m=q m^2\), where \(S _r\) denotes the sum of \(r\) terms of the A.P., then \(S _q\) equals
CorrectIncorrectHint
The given series is A.P. whose first term is \(a\) and common difference is \(d\)
\(
\begin{array}{rlrl}
\therefore & & S _n & =\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]=q n^2 \\
\Rightarrow & & =2 a+(n-1) d=2 q n \dots(i) \\
& & S _m & =\frac{m}{2}[2 a+(m-1) d]=q m^2 \\
& & 2 a+(m-1) d & =2 q m \dots(ii)
\end{array}
\)
Solving eq. (i) and eq. (ii) we get
\(
\begin{array}{rlr}
2 a+(m-1) d & =\quad 2 q m \\
2 a+(n-1) d & =\quad 2 q n \\
\hline(-) \quad(-) \quad \quad & (-) \\
(m-n) d & =2 q m-2 q n \\
(m-n) d & =2 q(m-n) \\
\therefore \quad d & =2 q
\end{array}
\)
Putting the value of \(d\) in eq. (ii) we get
\(
2 a+(m-1) \cdot 2 q=2 q m \Rightarrow 2 a=2 q m-(m-1) 2 q
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
2 a & =2 q(m-m+1) \Rightarrow 2 a=2 q \Rightarrow a=q \\
S _q & =\frac{q}{2}[2 a+(q-1) d]=\frac{q}{2}[2 q+(q-1) 2 q] \\
& =\frac{q}{2}\left[2 q+2 q^2-2 q\right]=\frac{q}{2} \times 2 q^2=q^3
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 22 of 58
22. Question
Let \(S _n\) denote the sum of the first \(n\) terms of an A.P. If \(S _{2 n}=3 S _n\) then \(S _{3 n}: S _n\) is equal to
CorrectIncorrectHint
\(
\begin{aligned}
S _n & =\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d] \\
\therefore \quad S _{2 n} & =\frac{2 n}{2}[2 a+(2 n-1) d] \\
S _{3 n} & =\frac{3 n}{2}[2 a+(3 n-1) d]
\end{aligned}
\)
As per the condition of the question, we have
\(
\begin{array}{rlrl}
& & S _{2 n}=3 \cdot S _n \\
\Rightarrow & & \frac{2 n}{2}[2 a+(2 n-1) d] & =3 \cdot \frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d] \\
\Rightarrow & & 2[2 a+(2 n-1) d] & =3[2 a+(n-1) d] \\
\Rightarrow & & 4 a+(4 n-2) d & =6 a+(3 n-3) d
\end{array}
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
6 a+(3 n-3) d-4 a-(4 n-2) d & =0 \\
2 a+(3 n-3-4 n+2) d & =0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad 2 a+(-n-1) d=0
\end{aligned}
\)
\(
2 a-(n+1) d=0 \Rightarrow 2 a=(n+1) d \dots(i)
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
\text { Now } S _{3 n}: S _n & =\frac{3 n}{2}[2 a+(3 n-1) d]: \frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d] \\
& =\frac{\frac{3 n}{2}[2 a+(3 n-1) d]}{\frac{n}{2}[2 a+(n-1) d]}=\frac{3[2 a+(3 n-1) d]}{2 a+(n-1) d} \\
& =\frac{3[(n+1) d+(3 n-1) d]}{(n+1) d+(n-1) d}
\end{aligned}
\)
\(
=\frac{3 d[n+1+3 n-1]}{d(n+1+n-1)}=\frac{3[4 n]}{2 n}=6
\) -
Question 23 of 58
23. Question
The minimum value of \(4^x+4^{1-x}, x \in R\), is
CorrectIncorrectHint
We know that \(AM \geq GM\)
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\therefore & \frac{4^x+4^{1-x}}{2} \geq \sqrt{4^x \cdot 4^{1-x}} \Rightarrow 4^x+4^{1-x} \geq 2 \sqrt{4^{x+1-x}} \\
\Rightarrow & 4^x+4^{1-x} \geq 2 \cdot 2 \Rightarrow 4^x+4^{1-x} \geq 4
\end{array}
\) -
Question 24 of 58
24. Question
Let \(S _n\) denote the sum of the cubes of the first \(n\) natural numbers and \(s_n\) denote the sum of the first \(n\) natural numbers. Then \(\sum_{r=1}^n \frac{ S _r}{s_r}\) equals
CorrectIncorrectHint
Given that \(\sum_{i=1}^n \frac{ S _r}{ s _r}=\frac{ S _1}{s_1}+\frac{ S _2}{s_2}+\frac{ S _3}{s_3}+\cdots+\frac{ S _n}{s_n}\)
Let \(T _n\) be the \(n\)th term of the above series
\(
\therefore \quad T _n=\frac{ S _n}{s_n}=\frac{\left[\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\right]^2}{\frac{n(n+1)}{2}}=\frac{n(n+1)}{2}=\frac{n^2+n}{2}
\)
Now sum of the given series
\(
\begin{aligned}
\sum T _n & =\frac{1}{2} \sum\left[n^2+n\right]=\frac{1}{2}\left[\sum n^2+\sum n\right] \\
& =\frac{1}{2}\left[\frac{n(n+1)(2 n+1)}{6}+\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\right] \\
& =\frac{1}{2} \cdot \frac{n(n+1)}{2}\left[\frac{2 n+1}{3}+1\right]=\frac{n(n+1)}{4}\left[\frac{2 n+1+3}{3}\right] \\
& =\frac{n(n+1)}{4} \cdot \frac{(2 n+4)}{3}=\frac{n(n+1)(n+2)}{6}
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 25 of 58
25. Question
If \(t_n\) denotes the nth term of the series \(2+3+6+11+18+\ldots\) then \(t_{50}\) is
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let \(S _n=2+3+6+11+18+\cdots+t_{50}\)
Using method of difference, we get
\(
\text { and } \quad \begin{aligned}
& S _n=2+3+6+11+18+\cdots+t_{50} \dots(i) \\
& S _n=0+2+3+6+11+\cdots+t_{49}+t_{50} \dots(ii)
\end{aligned}
\)
Subtracting eq. (ii) from eq. (i), we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
& 0=2+1+3+5+7+\cdots-t_{50} \text { terms } \\
& \Rightarrow \quad t_{50}=2+(1+3+5+7+\cdots \text { upto } 49 \text { terms }) \\
& \Rightarrow \quad t_{50}=2+\frac{49}{2}[2 \times 1+(49-1) 2]=2+\frac{49}{2}[2+96] \\
& =2+\frac{49}{2} \times 98=2+49 \times 49=49^2+2 \\
&
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 26 of 58
26. Question
The lengths of three unequal edges of a rectangular solid block are in G.P. The volume of the block is \(216 cm ^3\) and the total surface area is \(252 cm ^2\). The length of the longest edge is
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let the length, breadth and height of a rectangular block be \(\frac{a}{r}, a\) and \(a r\). [Since they are is G.P]
\(
\begin{aligned}
\text { Volume } & =l \times b \times h \\
216 & =\frac{a}{r} \times a \times a r \\
a^3 & =216 \Rightarrow a=6
\end{aligned}
\)
Now total surface area \(=2[l b+b h+l h]\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& 252=2\left[\frac{a}{r} \cdot a+a \cdot a r+\frac{a}{r} \cdot a r\right] \Rightarrow 252=2\left[\frac{a^2}{r}+a^2 r+a^2\right] \\
& 252=2 a^2\left[\frac{1}{r}+r+1\right] \Rightarrow 252=2 \times(6)^2\left[\frac{1+r^2+r}{r}\right] \\
& 252=72\left[\frac{1+r^2+r}{r}\right] \Rightarrow \frac{252}{72}=\frac{1+r+r^2}{r}
\end{aligned}
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{7}{2}=\frac{1+r+r^2}{r} \Rightarrow 2+2 r+2 r^2=7 r \\
& 2 r^2-5 r+2=0 \Rightarrow 2 r^2-4 r-r+2=0 \\
& 2 r(r-2)-1(r-2)=0 \quad \Rightarrow \quad(r-2)(2 r-1)=0
\end{aligned}
\)
\(
\begin{array}{rlrl}
\Rightarrow & r-2 & =0 \text { and } & 2 r-1=0 \\
\therefore & r & =2, \frac{1}{2}
\end{array}
\)
Therefore, the three edge are:
If \(r=2\) then edges are \(3,6,12\)
If \(r=\frac{1}{2}\) then edges are \(12,6,3\)
So, the length of the longest edge \(=12\) -
Question 27 of 58
27. Question
For \(a, b, c\) to be in GP. the value of \(\frac{a-b}{b-c}\) is equal to _____.
CorrectIncorrectHint
Since \(a, b\) and \(c\) are in G.P \(\therefore \quad \frac{b}{a}=\frac{c}{b}=r \quad\) (constant)
\(
\begin{array}{lrl}
\Rightarrow & b=a r \text { and } c=b r \Rightarrow c=a r \cdot r=a r^2 \\
\text { So } & \frac{a-b}{b-c}=\frac{a-a r}{a r-a r^2}=\frac{a(1-r)}{a r(1-r)}=\frac{1}{r}=\frac{a}{b}=\frac{b}{c}
\end{array}
\)
Hence, the correct value of the filler is \(\frac{a}{b}\) or \(\frac{b}{c}\) -
Question 28 of 58
28. Question
The sum of terms equidistant from the beginning and end in an A.P. is equal to
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let A.P be \(a, a+d, a+2 d, a+3 d, \ldots, a+(n-1) d\)
Taking first and last term
\(
a_1+a_n=a+a+(n-1) d=2 a+(n-1) d
\)
Taking second and second last term
\(
a_2+a_{n-1}=(a+d)+[a+(n-2) d]=2 a+(n-1) d=a_1+a_n
\)
Taking third from the beginning and the third from the end
\(
a_3+a_{n-2}=(a+2 d)+[a+(n-3) d]=2 a+(n-1) d=a_1+a_n
\)
From the above pattern, we observe that the sum of terms equidistant from the beginning and the end in an A.P is equal to the [first term + last term]
Hence, the correct value of the filler is first term + last term. -
Question 29 of 58
29. Question
The third term of a G.P. is 4 , the product of the first five terms is ____.
CorrectIncorrectHint
\(
\begin{array}{lr}
\text { Given } & T _3=4 \\
\therefore & a r^2=4 \dots(i)
\end{array}
\)
Product of first five terms \(=a \cdot a r \cdot a r^2 \cdot a r^3 \cdot a r^4\)
\(=a^5 r^{10}=\left(a r^2\right)^5=(4)^5\) [from eq. (i)]
Hence, the correct value of the filler is \((4)^5\). -
Question 30 of 58
30. Question
Two sequences cannot be in both A.P. and G.P. together.
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let us consider a G.P, \(a, a r\) and \(a r^2\)
If it is in A.P then \(a r-a \neq a r^2-a r\)
Hence, the given statement is True. -
Question 31 of 58
31. Question
Every progression is a sequence but the converse, i.e., every sequence is also a progression need not necessarily be true
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let us consider a sequence of prime numbers \(2,3,5,7,11, \ldots\) It is clear that this progression is a sequence but sequence is not a progression because it does not follow a specific pattern. Here, the given statement is True.
-
Question 32 of 58
32. Question
Any term of an A.P. (except first) is equal to half the sum of terms which are equidistant from it.
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let us consider an A.P \(a, a+d, a+2 d, \ldots\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \therefore \quad a_2+a_4=a+d+a+3 d=2 a+4 d=2 a_3 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad a_3=\frac{a_2+a_4}{2} \\
& \frac{a_3+a_5}{2}=\frac{a+2 d+a+4 d}{2}=\frac{2 a+6 d}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \quad=a+3 d=a_4 \\
&
\end{aligned}
\)
Hence, the given statement is True. -
Question 33 of 58
33. Question
The sum or difference of two G.P.s, is again a G.P.
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let us consider two G.P.’s
\(
\begin{aligned}
& a_1, a_1 r_1, a_1 r_1^2, a_1 r_1^3 \cdots a_1 r_1^{n-1} \\
\text { and } & a_2, a_2 r_2, a_2 r_2^2, a_2 r_2^3, \cdots a_2 r_2^{n-1}
\end{aligned}
\)
Now Sum of two G.Ps
\(
\left(a_1+a_2\right)+\left(a_1 r_1+a_2 r_2\right)+\left(a_1 r_1^2+a_2 r_2^2\right) \cdots
\)
Now
\(
\frac{T_2}{T_1}=\frac{a_1 r_1+a_2 r_2}{a_1+a_2} \text { and } \frac{T_3}{T_2}=\frac{a_1 r_1^2+a_2 r_2^2}{a_1 r_1+a_2 r_2}
\)
But \(\frac{a_1 r_1+a_2 r_2}{a_1+a_2} \neq \frac{a_1 r_1^2+a_2 r_2^2}{a_1 r_1+a_2 r_2}\)
Now let us consider the difference G.P’s
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \left(a_1-a_2\right)+\left(a_1 r_1-a_2 r_2\right)+\left(a_1 r_1^2-a_2 r_2^2\right) \\
& \therefore \quad \frac{T_2}{T_1}=\frac{a_1 r_1-a_2 r_2}{a_1-a_2} \text { and } \frac{T_3}{T_2}=\frac{a_1 r_1^2-a_2 r_2^2}{a_1 r_1-a_2 r_2} \\
& \text { But } \quad \frac{T_2}{T_1} \neq \frac{T_3}{T_2}
\end{aligned}
\)
Hence, the given statement is False. -
Question 34 of 58
34. Question
If the sum of \(n\) terms of a sequence is quadratic expression then it always represents an A.P.
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let \(\quad S _n=a n^2+b n+c \quad\) (quadratic expression)
\(
S _1=a+b+c
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& a_1=a+b+c \\
& S _2=4 a+2 b+c \\
& a_2= S _2- S _1=(4 a+2 b+c)-(a+b+c)=3 a+b \\
& S _3=9 a+3 b+c \\
& a_3= S _3- S _2=(9 a+3 b+c)-(4 a+2 b+c)=5 a+b
\end{aligned}
\)
Common difference
\(
\begin{aligned}
d & =a_2-a_1=(3 a+b)-(a+b+c) \\
& =2 a-c \\
\text { and } d & =a_3-a_2=(5 a+b)-(3 a+b)=2 a
\end{aligned}
\)
Here, we observe that \(a_2-a_1 \neq a_3-a_2\)
So it does not represent an A.P
Hence, the given statement is False. -
Question 35 of 58
35. Question
Match the questions given under Column I with their appropriate answers given under the Column II.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline \text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & 4,1, \frac{1}{4}, \frac{1}{16} & \text { (i) } & \text { A.P. } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & 2, 3, 5, 7 & \text { (ii) } & \text { Sequence } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & 13,8,3,-2,-7 & \text { (iii) } & \text { G.P. } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) \(4,1, \frac{1}{4}, \frac{1}{16}\)
Here, \(\frac{a_2}{a_1}=\frac{1}{4}, \frac{a_3}{a_2}=\frac{1 / 4}{1}=\frac{1}{4}\) and \(\frac{a_4}{a_3}=\frac{1 / 16}{1 / 4}=\frac{1}{4}\)
Hence it is G.P
\(\therefore \quad(a) \leftrightarrow(i i i)\)
(b) \(2,3,5,7\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Here } \quad a_2-a_1=3-2=1 \\
& a_3-a_2=5-3=2 \\
& \therefore \quad a_2-a_1 \neq a_3-a_2 \\
&
\end{aligned}
\)
Hence it is not A.P
\(
\frac{a_2}{a_1}=\frac{3}{2}, \frac{a_3}{a_2}=\frac{5}{3}
\)
So, \(\quad \frac{3}{2} \neq \frac{5}{3}\)
So it is not G.P
Hence it is sequence
\(
\therefore \quad(b) \leftrightarrow(i i)
\)
(c) \(13,8,3,-2,-7\)
Here
\(
a_2-a_1=8-13=-5
\)
So, \(\quad \begin{aligned} & a_3-a_2=3-8=-5 \\ & a_2-a_1=a_3-a_2=-5\end{aligned}\)
So, it is an A.P
Hence \((c) \leftrightarrow(i)\) -
Question 36 of 58
36. Question
Match the questions given under Column I with their appropriate answers given under the Column II.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline \text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & 1^2+2^2+3^2+\ldots+n^2 & \text { (i) } & {\left[\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\right]^2} \\
\hline \text { (b) } & 1^3+2^3+3^3+\ldots+n^3 & \text { (ii) } & n(n+1) \\
\hline \text { (c) } & 2+4+6+\ldots+2 n & \text { (iii) } & \frac{n(n+1)(2 n+1)}{6} \\
\hline \text { (d) } & 1+2+3+\ldots+n & \text { (iv) } & \frac{n(n+1)}{2} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Let \(S _n=1^2+2^2+3^2+\cdots+n^2\)
\(K ^3-( K -1)^3=3 K ^2-3 K +1\)
For \(K=1\), \(1^3-0^3=3(1)^2-3(1)+1\)
For \(K=2\),
\(2^3-1^3=3(2)^2-3(2)+1\)
For \(K=3\),
\(
3^3-2^3=3(3)^2-3(3)+1
\)
For \(K =n, \quad n^3-(n-1)^3=3(n)^2-3(n)+1\)
Adding Column wise, we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
& n^3-0^3=3\left(1^2+2^2+3^2+\cdots+n^2\right) \\
& -3(1+2+3+\cdots+n)+n \\
& \Rightarrow \quad n^3=3 \cdot S _n-\frac{3 n(n+1)}{2}+n \\
& \Rightarrow \quad n^3+\frac{3 n(n+1)}{2}-n=3 \cdot S _n \\
& \Rightarrow \frac{2 n^3+3 n^2+3 n-2 n}{2}=3 \cdot S _n \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 6 \cdot S _n=2 n^3+3 n^2+n \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 6 \cdot S _n=n\left(2 n^2+3 n+1\right) \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 6 \cdot S _n=n\left[2 n^2+2 n+n+1\right] \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 6 \cdot S _n=n(n+1)(2 n+1) \\
& \Rightarrow \quad S _n=\frac{n(n+1)(2 n+1)}{6} \\
&
\end{aligned}
\)
Here \((a) \leftrightarrow\) (iii).
(b) Let \(S _n=1^3+2^3+3^3+\cdots+n^3\)
\(
K ^4-( K -1)^4=4 K ^3-6 K ^2+4 K -1
\)
For \(K =1 \quad 1^4-0^4=4(1)^3-6(1)^2+4(1)-1\)
For \(K=2 \quad 2^4-1^4=4(2)^3-6(2)^2+4(2)-1\)
For \(K=3 \quad 3^4-2^4=4(3)^3-6(3)^2+4(3)-1\)
For \(K =n \quad n^4-(n-1)^4=4(n)^3-6\left(n^2\right)+4(n)-1\)
Adding column wise, we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
\Rightarrow \quad n^4-0^4= & 4\left(1^3+2^3+3^3+\cdots n^3\right) \\
& -6\left(1^2+2^2+3^2+\cdots+n^2\right) \\
& +4(1+2+3+\ldots n)-n
\end{aligned}
\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad n^4=4 \cdot S _n-\frac{6 n(n+1)(2 n+1)}{6}+\frac{4 n(n+1)}{2}-n\)
\(
\begin{array}{cc}
\Rightarrow & n^4=4 \cdot S _n-n(n+1)(2 n+1)+2 n(n+1)-n \\
\Rightarrow & n^4+n(n+1)(2 n+1)-2 n(n+1)+n=4 \cdot S _n \\
\Rightarrow & n\left[n^3+(n+1)(2 n+1)-2 n-2+1\right]=4 \cdot S _n \\
\Rightarrow & n\left[n^3+2 n^2+3 n+1-2 n-1\right]=4 \cdot S _n \\
\Rightarrow & n\left[n^3+2 n^2+n\right]=4 \cdot S _n \\
\Rightarrow & \frac{n^2\left(n^2+2 n+1\right)}{4}= S _n \\
\Rightarrow & \frac{n^2(n+1)^2}{4}= S _n
\end{array}
\)
\(
S _n=\left[\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\right]^2
\)
Hence \((b) \leftrightarrow(i)\)
(c) Let
\(
\begin{aligned}
S _n & =2+4+6+\ldots .+2 n \\
& =2(1+2+3+\ldots .+n) \\
& =2 \frac{n(n+1)}{2} \\
& =n(n+1)
\end{aligned}
\)
Hence \((c) \leftrightarrow\) (ii)
(d) Let \(S _n=1+2+3+\cdots+n=\frac{n(n+1)}{2}\)
Hence \((d) \leftrightarrow(i v)\) -
Question 37 of 58
37. Question
The first term of an A.P. is \(a\), the second term is \(b\) and the last term is \(c\). The sum of the A.P. is ____.
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let \(d\) be the common diffrence and \(n\) be the number of terms of the A.P.
Since the first term is \(a\) and the second term is \(b\)
Therefore,
\(
d=b-a
\)
Also, the last term is \(c\), so
\(
\begin{aligned}
& c=a+(n-1)(b- a )(\text { since } \quad d=b-a) \\
& \Rightarrow \\
& n-1=\frac{c-a}{b-a} \\
& n=1+\frac{c-a}{b-a}=\frac{b-a+c-a}{b-a}=\frac{b+c-2 a}{b-a} \\
& \text { Therefore, } \\
& S _n=\frac{n}{2}(a+l)=\frac{(b+c-2 a)}{2(b-a)}(a+c) \\
&
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 38 of 58
38. Question
The \(p^{\text {th }}\) term of an A.P. is \(a\) and \(q^{\text {th }}\) term is \(b\). Calculate the sum of its \((p+q)\) terms
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let \(A\) be the first term and \(D\) be the common difference of the A.P. It is given that
\(
\begin{gathered}
t_p=a \Rightarrow A +(p-1) D =a \dots(1) \\
t_q= b \Rightarrow A +(q-1) D =b \dots(2)
\end{gathered}
\)
Subtracting (2) from (1), we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
(p-1-q+1) D & =a-b \\
D & =\frac{a-b}{p-q} \dots(3)
\end{aligned}
\)
Adding (1) and (2), we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
& 2 A +(p+q-2) D =a+b \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 2 A +(p+q-1) D =a+b+ D \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 2 A +(p+q-1) D =a+b+\frac{a-b}{p-q} \dots(4) \\
& S _{p+q}=\frac{p+q}{2}[2 A +(p+q-1) D ] \\
& =\frac{p+q}{2}\left[a+b+\frac{a-b}{p-q}\right] \text { [(using … (3) and (4)] } \\
&
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 39 of 58
39. Question
If there are \((2 n+1)\) terms in an A.P.,Find the ratio of the sum of odd terms and the sum of even terms is _____.
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let \(a\) be the first term and \(d\) the common difference of the A.P. Also let \(S _1\) be the sum of odd terms of A.P. having \((2 n+1)\) terms. Then
\(
\begin{aligned}
& S _1=a_1+a_3+a_5+\ldots+a_{2 n+1} \\
& S _1=\frac{n+1}{2}\left(a_1+a_{2 n+1}\right) \\
& S _1=\frac{n+1}{2}[a+a+(2 n+1-1) d]
\end{aligned}
\)
\(
=(n+1)(a+n d)
\)
Similarly, if \(S _2\) denotes the sum of even terms, then
\(
\begin{aligned}
& S _2=\frac{n}{2}[2 a+2 n d]=n(a+n d) \\
& \frac{ S _1}{ S _2}=\frac{(n+1)(a+n d)}{n(a+n d)}=\frac{n+1}{n}
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 40 of 58
40. Question
At the end of each year the value of a certain machine has depreciated by \(20 \%\) of its value at the beginning of that year. If its initial value was Rs 1250 , find the value at the end of 5 years.
CorrectIncorrectHint
After each year the value of the machine is \(80 \%\) of its value the previous year so at the end of 5 years the machine will depreciate as many times as 5 .
Hence, we have to find the \(6^{\text {th }}\) term of the GP. whose first term \(a_1\) is 1250 and common ratio \(r\) is . 8 .
Hence, value at the end 5 years \(=t_6=a_1 r^5=1250(.8)^5=409.6\) -
Question 41 of 58
41. Question
Find the sum of first 24 terms of the A.P. \(a_1, a_2, a_3, \ldots\) if it is known that \(a_1+a_5+a_{10}+a_{15}+a_{20}+a_{24}=225\).
CorrectIncorrectHint
We know that in an A.P., the sum of the terms equidistant from the beginning and end is always the same and is equal to the sum of first and last term.
Therefore
\(
d=b-a
\)
\(
\text { i.e., } \quad a_1+a_{24}=a_5+a_{20}=a_{10}+a_{15}
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \text { It is given that }\left(a_1+a_{24}\right)+\left(a_5+a_{20}\right)+\left(a_{10}+a_{15}\right)=225 \\
& \Rightarrow\left(a_1+a_{24}\right)+\left(a_1+a_{24}\right)+\left(a_1+a_{24}\right)=225 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 3\left(a_1+a_{24}\right)=225 \\
& \Rightarrow \quad a_1+a_{24}=75
\end{aligned}
\)
We know that \(S _n=\frac{n}{2}[a+l]\), where \(a\) is the first term and \(l\) is the last term of an A.P.
Thus, \(S _{24}=\frac{24}{2}\left[a_1+a_{24}\right]=12 \times 75=900\) -
Question 42 of 58
42. Question
The product of three numbers in A.P. is 224, and the largest number is 7 times the smallest. Find the numbers.
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let the three numbers in A.P. be \(a-d, a, a+d(d>0)\)
\(
\begin{array}{lr}
\text { Now } & (a- d ) a(a+ d )=224 \\
\Rightarrow & a\left(a^2-d^2\right)=224 \dots(1)
\end{array}
\)
Now, since the largest number is 7 times the smallest, i.e., \(a+d=7(a- d )\)
Therefore,
\(
d=\frac{3 a}{4}
\)
Substituting this value of \(d\) in (1), we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
a\left(a^2-\frac{9 a^2}{16}\right) & =224 \\
a & =8
\end{aligned}
\)
and \(d=\frac{3 a}{4}=\frac{3}{4} \times 8=6\)
Hence, the three numbers are \(2,8,14\). -
Question 43 of 58
43. Question
If \(x, y\) and \(z\) are in A.P. then \(\left(x^2+x y+y^2\right),\left(z^2+x z+x^2\right)\) and \(\left(y^2+y z+z^2\right)\) are consecutive terms of an A.P.. Is this true?
CorrectIncorrectHint
The terms \(\left(x^2+x y+y^2\right),\left(z^2+x z+x^2\right)\) and \(\left(y^2+y z+z^2\right)\) will be in A.P. if
\(
\left(z^2+x z+x^2\right)-\left(x^2+x y+y^2\right)=\left(y^2+y z+z^2\right)-\left(z^2+x z+x^2\right)
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
z^2+x z-x y-y^2 & =y^2+y z-x z-x^2 \\
x^2+z^2+2 x z-y^2 & =y^2+y z+x y
\end{aligned}
\)
\(
(x+z)^2-y^2=y(x+y+z)
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
x+z-y & =y \\
x+z & =2 y
\end{aligned}
\)
which is true, since \(x, y, z\) are in A.P. Hence \(x^2+x y+y^2, z^2+x z+x^2, y^2+y z+z^2\) are in A.P. -
Question 44 of 58
44. Question
If \(a, b, c, d\) are in G.P., then \(a^2-b^2, b^2-c^2, c^2-d^2\) are also in G.P.. Is this statement true?
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let \(r\) be the common ratio of the given GP. Then
\(
\begin{aligned}
\frac{b}{a}= & \frac{c}{b}=\frac{d}{c}=r \\
b & =a r, c=b r=a r^2, d=c r=a r^3 \\
a^2-b^2 & =a^2-a^2 r^2=a^2\left(1-r^2\right)
\end{aligned}
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& b^2-c^2=a^2 r^2-a^2 r^4=a^2 r^2\left(1-r^2\right) \\
& c^2-d^2=a^2 r^4-a^2 r^6=a^2 r^4\left(1-r^2\right)
\end{aligned}
\)
Therefore,
\(
\frac{b^2-c^2}{a^2-b^2}=\frac{c^2-d^2}{b^2-c^2}=r^2
\)
Hence, \(a^2-b^2, b^2-c^2, c^2-d^2\) are in G.P. -
Question 45 of 58
45. Question
If the sum of \(m\) terms of an A.P. is equal to the sum of either the next \(n\) terms or the next \(p\) terms, then \((m+n)\left(\frac{1}{m}-\frac{1}{p}\right)=(m+p)\left(\frac{1}{m}-\frac{1}{n}\right)\). Is this statement true?
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let the A.P. be \(a, a+d, a+2 d, \ldots\). We are given
\(
a_1+a_2+\ldots+a_m=a_{m+1}+a_{m+2}+\ldots+a_{m+n} \dots(1)
\)
Adding \(a_1+a_2+\ldots+a_m\) on both sides of (1), we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
& 2\left[a_1+a_2+\ldots+a_m\right]=a_1+a_2+\ldots+a_m+a_{m+1}+\ldots+a_{m+n} \\
& 2 S _m= S _{m+n}
\end{aligned}
\)
Therefore, \(2 \frac{m}{2}\{2 a+(m-1) d\}=\frac{m+n}{2}\{2 a+(m+n-1) d\}\) Putting \(2 a+(m-1) d=x\) in the above equation, we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
m x & =\frac{m+n}{2}(x+n d) \\
\Rightarrow \quad(2 m-m-n) x & =(m+n) n d \\
(m-n) x & =(m+n) n d \dots(2)
\end{aligned}
\)
Similarly, if \(a_1+a_2+\ldots+a_m=a_{m+1}+a_{m+2}+\ldots+a_{m+p}\)
Adding \(a_1+a_2+\ldots+a_m\) on both sides
we get,
\(
2\left(a_1+a_2+\ldots+a_m\right)=a_1+a_2+\ldots+a_{m+1}+\ldots+a_{m+p}
\)
or, \(2 S _m= S _{m+p}\)
\(\Rightarrow \quad 2\left[\frac{m}{2}\{2 a+(m-1) d\}\right]=\frac{m+p}{2}\{2 a+(m+p-1) d\}\) which gives
i.e., \((m-p) x=(m+p) p d \dots(3)\)
Dividing (2) by (3), we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
\frac{(m-n) x}{(m-p) x} & =\frac{(m+n) n d}{(m+p) p d} \\
\Rightarrow \quad(m-n)(m+p) p & =(m-p)(m+n) n
\end{aligned}
\)
Dividing both sides by \(m n p\), we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
& (m+p)\left(\frac{1}{n}-\frac{1}{m}\right)=(m+n)\left(\frac{1}{p}-\frac{1}{m}\right) \\
= & (m+n)\left(\frac{1}{m}-\frac{1}{p}\right)=(m+p)\left(\frac{1}{m}-\frac{1}{n}\right)
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 46 of 58
46. Question
If \(a_1, a_2, \ldots, a_n\) are in A.P. with common difference \(d\) (where \(d \neq 0\) ); then the sum of the series \(\sin d\left(\operatorname{cosec} a_1 \operatorname{cosec} a_2+\operatorname{cosec} a_2 \operatorname{cosec} a_3+\ldots+\operatorname{cosec}\right.\) \(\left.a_{n-1} \operatorname{cosec} a_n\right)\) is equal to
CorrectIncorrectHint
We have
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \sin d\left(\operatorname{cosec} a_1 \operatorname{cosec} a_2+\operatorname{cosec} a_2 \operatorname{cosec} a_3+\ldots+\operatorname{cosec} a_{n-1} \operatorname{cosec} a_n\right) \\
& =\sin d\left[\frac{1}{\sin a_1 \sin a_2}+\frac{1}{\sin a_2 \sin a_3}+\ldots+\frac{1}{\sin a_{n-1} \sin a_n}\right] \\
& =\frac{\sin \left(a_2-a_1\right)}{\sin a_1 \sin a_2}+\frac{\sin \left(a_3-a_2\right)}{\sin a_2 \sin a_3}+\ldots+\frac{\sin \left(a_n-a_{n-1}\right)}{\sin a_{n-1} \sin a_n} \\
& =\frac{\left.\sin a_2 \cos a_1-\cos a_2 \sin a_1\right)}{\sin a_1 \sin a_2}+\frac{\left.\sin a_3 \cos a_2-\cos a_3 \sin a_2\right)}{\sin a_2 \sin a_3}+\ldots+\frac{\left.\sin a_n \cos a_{n-1}-\cos a_n \sin a_{n-1}\right)}{\sin a_{n-1} \sin a_n} \\
& =\left(\cot a_1-\cot a_2\right)+\left(\cot a_2-\cot a_3\right)+\ldots+\left(\cot a_{n-1}-\cot a_n\right) \\
& =\cot a_1-\cot a_n
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 47 of 58
47. Question
If \(a, b, c, d\) are four distinct positive quantities in A.P., then
CorrectIncorrectHint
\(
\text { Since } a, b, c, d \text { are in A.P., then A.M. > G.M., for the first three terms. }
\)
Therefore, \(b>\sqrt{a c}\) \(\left(\text { Here } \frac{a+c}{2}=b\right)\)
Squaring, we get
\(
b^2>a c \dots(1)
\)
Similarly, for the last three terms
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
AM > GM & \\
c>\sqrt{b d} & \left(\text { Here } \frac{b+d}{2}=c\right) \\
c^2>b d & \dots(2)
\end{array}
\)
Multiplying (1) and (2), we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
& b^2 c^2>(a c)(b d) \\
\Rightarrow & b c>a d
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 48 of 58
48. Question
If \(a, b, c, d\) are four distinct positive quantities in GP., then
CorrectIncorrectHint
Since \(a, b, c, d\) are in G.P.
again A.M. > G.M. for the first three terms
\(
\begin{array}{ll}
\frac{a+c}{2}>b & (\text { since } \sqrt{a c}=b)
\end{array}
\)
\(
\Rightarrow a+c>2 b \dots(1)
\)
Similarly, for the last three terms
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{b+d}{2}>c & \text { (since } \sqrt{b d}=c \text { ) } \\
& \Rightarrow b+d>2 c \dots(2) \\
&
\end{aligned}
\)
Adding (1) and (2), we get
\(
\begin{aligned}
& (a+c)+(b+d)>2 b+2 c \\
& a+d>b+c
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 49 of 58
49. Question
If \(a, b, c\) are three consecutive terms of an A.P. and \(x, y, z\) are three consecutive terms of a G.P. Then \(x^{b-c} \cdot y^{c-a}\cdot z^{a-b}=?\)
CorrectIncorrectHint
We have \(a, b, c\) as three consecutive terms of A.P. Then
\(
b-a=c-b=d \text { (say) }
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& c-a=2 d \\
& a-b=-d
\end{aligned}
\)
Now \(x^{b-c} \cdot y^{c-a} \cdot z^{a-b}=x^{-d} \cdot y^{2 d} \cdot z^{-d}\)
\(
\left.=x^{-d}(\sqrt{x z})^{2 d} \cdot z^{-d} \quad \text { (since } y=(\sqrt{x z})\right) \text { as } x, y, z \text { are GP.) }
\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& =x^{-d} \cdot x^d \cdot z^d \cdot z^{-d} \\
& =x^{-d+d} \cdot z^{d-d} \\
& =x^{\circ} z^{\circ}=1
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 50 of 58
50. Question
Find the natural number \(a\) for which \(\sum_{k=1}^n f(a+k)=16\left(2^n-1\right)\), where the function \(f\) satisfies \(f(x+y)=f(x)\). \(f(y)\) for all natural numbers \(x, y\) and further \(f(1)=2\).
CorrectIncorrectHint
Given that \(f(x+y)=f(x) \cdot f(y) \text { and } f(1)=2\)
Therefore,
\(
\begin{aligned}
& f(2)=f(1+1)=f(1) \cdot f(1)=2^2 \\
& f(3)=f(1+2)=f(1) \cdot f(2)=2^3 \\
& f(4)=f(1+3)=f(1) \cdot f(3)=2^4
\end{aligned}
\)
and so on. Continuing the process, we obtain
\(
\begin{aligned}
f(k) & =2^k \text { and } f(a)=2^a \\
\sum_{k=1}^n f(a+k) & =\sum_{k=1}^n f(a) \cdot f(k) \\
& =f(a) \sum_{k=1}^n f(k) \\
& =2^a\left(2^1+2^2+2^3+\ldots+2^n\right) \\
& =2^a\left\{\frac{2 \cdot\left(2^n-1\right)}{2-1}\right\}=2^{a+1}\left(2^n-1\right)
\end{aligned} \dots(1)
\)
But, we are given
\(
\begin{aligned}
\sum_{k=1}^n f(a+k) & =16\left(2^n-1\right) \\
2^{a+1}\left(2^n-1\right) & =16\left(2^n-1\right) \\
2^{a+1} & =2^4 \Rightarrow a+1=4 \\
a & =3
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 51 of 58
51. Question
A sequence may be defined as a
CorrectIncorrectHint
(C) is the correct answer. A sequence is a function \(f: N \rightarrow X\) having domain \(\subseteq N\)
-
Question 52 of 58
52. Question
If \(x, y, z\) are positive integers then value of expression \((x+y)(y+z)(z+x)\) is
CorrectIncorrectHint
since
A.M. \(>\) GM., \(\frac{x+y}{2}>\sqrt{x y}, \frac{y+z}{2}>\sqrt{y z}\) and \(\frac{z+x}{2}>\sqrt{z x}\)Multiplying the three inequalities, we get
\(
\frac{x+y}{2} \cdot \frac{y+z}{2} \cdot \frac{y+z}{2}>\sqrt{(x y)(y z)(z x)}
\)
or, \(\quad(x+y)(y+z)(z+x)>8 x y z\) -
Question 53 of 58
53. Question
In a G.P. of positive terms, if any term is equal to the sum of the next two terms. Then the common ratio of the G.P. is
CorrectIncorrectHint
\(
\begin{aligned}
& t_n=t_{n+1}+t_{n+2} \\
& \Rightarrow \quad a r^{n-1}=a r^n+a r^{n+1} \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 1=r+r^2 \\
& r=\frac{-1 \pm \sqrt{5}}{2} \text {, since } r>0 \\
& r=2 \frac{\sqrt{5}-1}{4}=2 \sin 18^{\circ} \\
&
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 54 of 58
54. Question
In an A.P. the \(p\) th term is \(q\) and the \((p+q)^{\text {th }}\) term is 0 . Then the \(q\) th term is
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let \(a, d\) be the first term and common difference respectively.
Therefore,
\(
\begin{aligned}
T _p & =a+(p-1) d=q \text { and } \dots(1)\\
T _{p+q} & =a+(p+q-1) d=0 \dots(2)
\end{aligned}
\)
Subtracting (1), from (2) we get \(q d=-q\)
Substituting in (1) we get \(a=q-(p-1)(-1)=q+p-1\)
Now
\(\)
\begin{aligned}
T _q & =a+(q-1) d=q+p-1+(q-1)(-1) \\
& =q+p-1-q+1=p
\end{aligned} -
Question 55 of 58
55. Question
Let \(S\) be the sum, \(P\) be the product and \(R\) be the sum of the reciprocals of 3 terms of a GP. Then \(P^2 R^3: S^3\) is equal to
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let us take a G.P. with three terms \(\frac{a}{r}, a, a r\). Then
\(
\begin{aligned}
& S =\frac{a}{r}+a+a r=\frac{a\left(r^2+r+1\right)}{r} \\
& P =a^3, R =\frac{r}{a}+\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{a r}=\frac{1}{a}\left(\frac{r^2+r+1}{r}\right) \\
& \frac{ P ^2 R ^3}{ S ^3}=\frac{a^6 \cdot \frac{1}{a^3}\left(\frac{r^2+r+1}{r}\right)^3}{a^3\left(\frac{r^2+r+1}{r}\right)^3}=1
\end{aligned}
\)Therefore, the ratio is \(1: 1\)
-
Question 56 of 58
56. Question
The 10th common term between the series \(3+7+11+\ldots\) and \(1+6+11+\ldots\) is
CorrectIncorrectHint
The first common term is 11 .
Now the next common term is obtained by adding L.C.M. of the common difference 4 and 5 , i.e., 20 .
Therefore, \(10^{\text {th }}\) common term \(= T _{10}\) of the AP whose \(a=11\) and \(d=20\)
\(
T _{10}=a+9 d=11+9(20)=191
\) -
Question 57 of 58
57. Question
In a G.P. of even number of terms, the sum of all terms is 5 times the sum of the odd terms. The common ratio of the G.P. is
CorrectIncorrectHint
Let us consider a GP. \(a, a r, a r^2, \ldots\) with \(2 n\) terms. We have \(\frac{a\left(r^{2 n}-1\right)}{r-1}=\frac{5 a\left(\left(r^2\right)^n-1\right)}{r^2-1}\)
(Since common ratio of odd terms will be \(r^2\) and number of terms will be \(n\) )
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \Rightarrow \frac{a\left(r^{2 n}-1\right)}{r-1}=5 \frac{a\left(r^{2 n}-1\right)}{\left(r^2-1\right)} \\
& \Rightarrow a(r+1)=5 a, \text { i.e., } r=4
\end{aligned}
\) -
Question 58 of 58
58. Question
The minimum value of the expression \(3^x+3^{1-x}, x \in R\), is
CorrectIncorrectHint
We know A.M. \(\geq\) GM. for positive numbers.
Therefore, \(\frac{3^x+3^{1-x}}{2} \geq \sqrt{3^x \cdot 3^{1-x}}\)
\(
\begin{aligned}
& \Rightarrow \quad \frac{3^x+3^{1-x}}{2} \geq \sqrt{3^x \cdot \frac{3}{3^x}} \\
& \Rightarrow \quad 3^x+3^{1-x} \geq 2 \sqrt{3}
\end{aligned}
\)