NCERT Exemplar
Quiz Summary
0 of 27 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 27 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 27
1. Question
Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points.
(A) n-butane
(B) 2-methylbutane
(C) n-pentane
(D) 2,2-dimethylpropaneCorrectIncorrectHint
(d) As the number of carbon atom increases, boiling point increases. Boiling point decreases with branching.
Hint: Boiling point inversely proportional to branching
Boiling point of an alkane depends on number of carbon atoms, as the number of carbon atom increases boiling point also increases. It also depends on branching in the alkane, as branching increases boiling point of alkane decreases.Alkanes with even number of carbon atoms have greater melting points than those with odd number of carbon atoms As per both factor the order of boiling point is as follows:
n-butane \(<2,2\)-dimethylpropane \(<2\)-methylbutane \(<\) n-pentane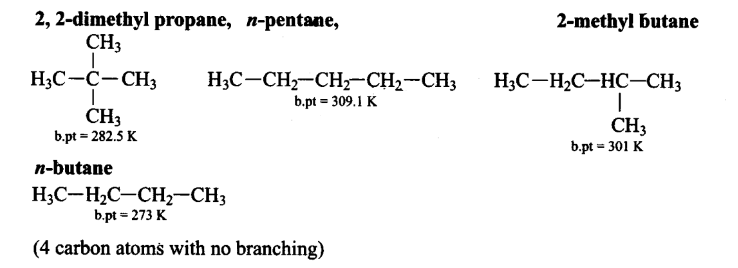
-
Question 2 of 27
2. Question
Arrange the halogens \(\mathrm{F}_2, \mathrm{Cl}_2, \mathrm{Br}_2, \mathrm{I}_2\), in order of their increasing reactivity with alkanes.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) The reactivity order of halogens with alkanes is \(\mathrm{I}_2<\mathrm{Br}_2<\mathrm{Cl}_2<\mathrm{F}_2\)
HINT- High electronegativity means high reactivity with alkanes
EXPLAINATION:
Alkane react with \(\mathrm{F}_2\) is vigorously and with \(\mathrm{I}_2\) the reaction is too slow that it requires a catalyst. It is because of high electronegativity of fluorine. Reactivity decreases with decrease in electronegativity and electronegativity decreases down the group. -
Question 3 of 27
3. Question
The increasing order of reduction of alkyl halides with zinc and dilute \(\mathrm{HCl}\) is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) The reactivity of reduction of alkyl halides with \(\mathrm{Zn} / \mathrm{HCl}\) increases as the strength of the \(\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{X}\) bond decreases, i.e., \(\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{Cl}<\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{Br}<\mathrm{R}-\mathrm{I}\)
HINT: Weaker bond of halogen with carbon gets easily reduced.
-
Question 4 of 27
4. Question
The correct IUPAC name of the following alkane is
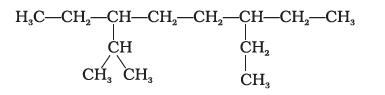 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
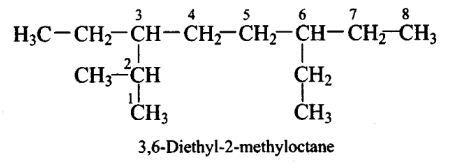
-
Question 5 of 27
5. Question
The addition of \(\mathrm{HBr}\) to 1-butene gives a mixture of products \(\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}\) and \(\mathrm{C}\)
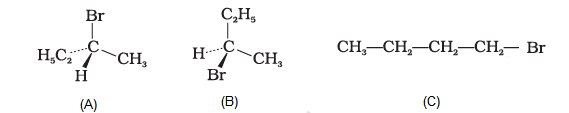
The mixture consists of
CorrectIncorrectHint
Hint: Markownikoff’s rule
(a) The alkene is unsymmetrical, hence will follow Markovnikov rule to give major product.
The alkene is unsymmetrical, hence will follow Markownikoff’s rule to give major product. The major product is 2- bromobutane and minor product is 1bromobutane. The 2 -bromobutane contains a chiral center hence racemic mixture is obtained. So, products A and B are major and product \(\mathrm{C}\) is minor. The reaction is as follows:
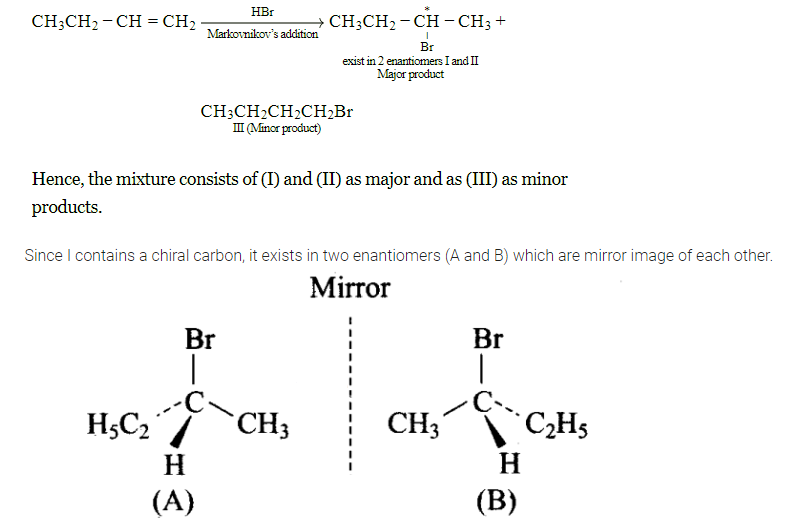
-
Question 6 of 27
6. Question
Which of the following will not show geometrical isomerism?
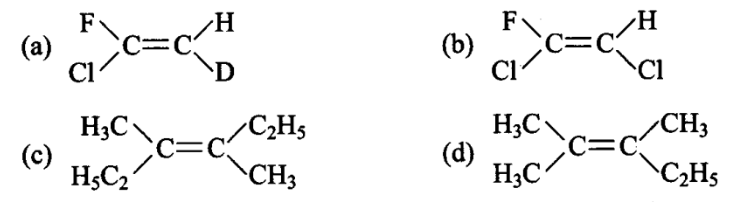 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
HINT: If same groups are attached with any double bonded carbon atom then compound does not show geometrical isomerism.
In option (d), a carbon with double bond has two same functional groups \(\left(\mathrm{CH}_3\right)\) attached. The rotation around carbon will not produce a new compound. Hence, geometrical isomerism is not possible.

-
Question 7 of 27
7. Question
Arrange the following hydrogen halides in order of their decreasing reactivity with propene.
CorrectIncorrectHint
Hint: Reactivity of an acid inversely proportional to the bond energy.
(c) The decreasing order of reactivity of hydrogen halides with propene is \(\mathrm{HI}>\mathrm{HBr}>\mathrm{HCl}\) . As the size of halogen increases, the strength of \(\mathrm{H}-\mathrm{X}\) bond decreases and hence, reactivity increases.
Explanation:
The order of reactivity parallels the order of acidity. The stronger the acid, the more readily it provides \(\mathrm{H}^{+}\)ions for addition to the double bond. The stability of hydrogen halides decreases down the group due to decrease in bond \((\mathrm{H}-\mathrm{X})\) dissociation energy in the order: \(\mathrm{HI}>\mathrm{HBr}>\mathrm{HCl}\)
Bond energy of \(\mathrm{HI}\) is \(296.8 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol}, \mathrm{HBr}\) is \(362.7 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol}\) and \(\mathrm{HCl}\) is \(430.5 \mathrm{~kJ} / \mathrm{mol}\). As bond energy decreases the reactivity of hydrogen halide compound increases. In the case of hydrogen halide, down the group reactivity increases with propene.
Hence, \(\mathrm{HI}>\mathrm{HBr}>\mathrm{HCl}\) is the order of reactivity with propene.
-
Question 8 of 27
8. Question
Arrange the following carbanions in order of their decreasing stability.
(A) \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{C}^{-}\)
(B) \(\mathrm{H}-\mathrm{C} \equiv \mathrm{C}^{-}\)
(C) \(\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH^{-}_2}\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Hint: As the percentage of s character increases electronegativity of carbon increase
EXPLANATION
+ I effect decreases the stability of carbon anion. Since \(\mathrm{CH}_3\) – group has + I-effect, therefore, it intensifies the negative charge and hence destabilises (A) relative to (B). \(\mathrm{sp}\) hybridised carbanion is more stabilised than \(\mathrm{sp}^3\) hybridized carbanion.Thus, the stability order is as follows:
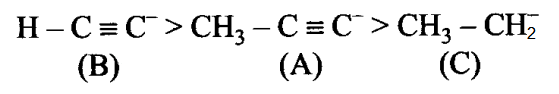
-
Question 9 of 27
9. Question
Arrange the following alkyl halides in decreasing order of the rate of \(\beta\) – elimination reaction with alcoholic \(\mathrm{KOH}\).
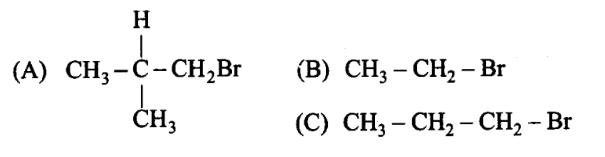 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Hint: Stability of alkene decide the rate of reaction
Alkyl halides on heating with alcoholic potash elminates one molecule of \(\mathrm{HX}\) to form an alkene. Hydrogen is eliminated from \(\beta\)-carbon atom, thus this reaction is know as \(\beta\)-elimination reaction. Stability of product that is alkene determines rate of reaction.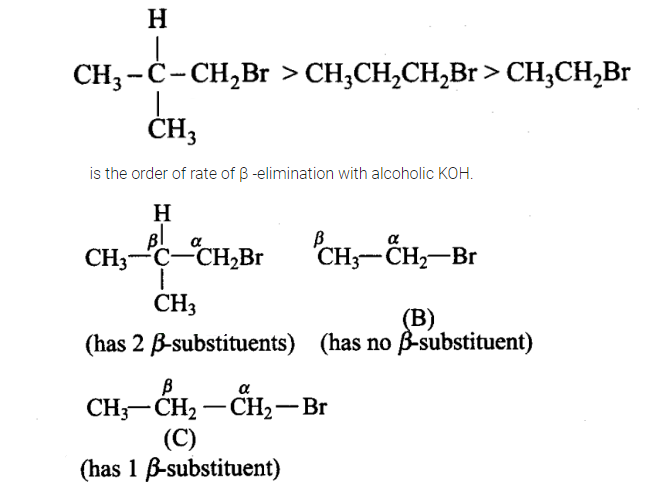
More the number of \(\beta\)-substituents (alkyl groups), more stable alkene will be formed on \(\beta\)-elimination and more will be the reactivity. Thus, the decreasing order of the rate of \(\beta\)-elimination reaction with alcoholic \(K O H\) is: \(A>C>B\).
-
Question 10 of 27
10. Question
Which of the following reactions of methane is incomplete combustion:
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) HINT: Incomplete combustion forms carbon black.
Explanation:
During incomplete combustion of alkanes with insufficient amount of air or dioxygen carbon black is formed which is used in the manufacturing of ink, printer ink, black pigments and as filters. Thus, The incomplete combustion of methane can result in a slew of partially oxidized products, including COCO, but also methanol, formic acid, formaldehyde, and higher hydrocarbons also.
(c) Dining incomplete combustion of alkanes with insufficient amount of air or dioxygen, carbon black is formed which is used in the manufacture of ink, printer ink, black pigments and as filters. Thus,
\(
\mathrm{CH}_4(\mathrm{~g})+\mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \xrightarrow[\text { combustion }]{\text { Incomplete }} \mathrm{C}(\mathrm{s})+2 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(l)
\) -
Question 11 of 27
11. Question
Some oxidation reactions of methane are given below. Which of them is/are controlled oxidation reactions?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c, d)
\(
\mathrm{CH}_4+\mathrm{O}_2 \xrightarrow{\mathrm{Mo}_2 \mathrm{O}_3} \mathrm{HCHO}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}
\)\(
2 \mathrm{CH}_4+\mathrm{O}_2 \xrightarrow[100 \mathrm{~atm}]{\mathrm{Cu} / 523 \mathrm{~K}} 2 \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{OH}
\)Reactions in which methane does not undergo complete combustion to give carbon dioxide and water or incomplete combustion to give carbon and water are controlled oxidation reactions.
-
Question 12 of 27
12. Question
Which of the following alkenes on ozonolysis give a mixture of ketones only?
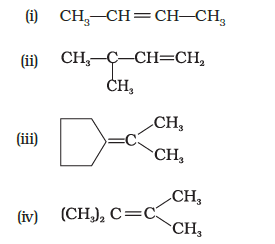 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c, d) Alkenes which have two substituents on each carbon atom of the double bond give a mixture of ketones on ozonolysis. Thus, options (c) and (d) give mixture of ketones.
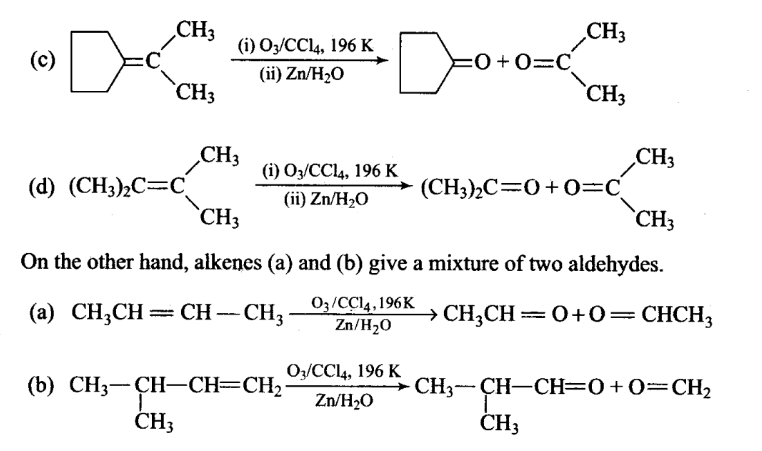
-
Question 13 of 27
13. Question
Which are the correct IUPAC names of the following compound?
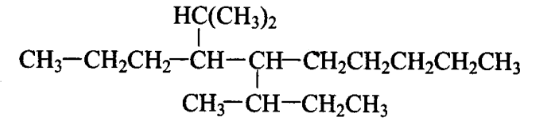 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c,d)
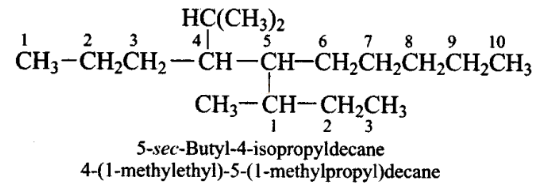
-
Question 14 of 27
14. Question
Which are the correct IUPAC names of the following compound?
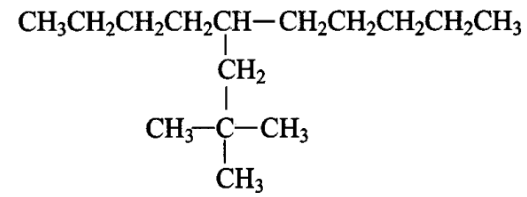 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a,d) The answer is the option (i) 5-(\(2^{\prime}\), \(2^{\prime}\)-Dimethylpropyl)-decane & (iv) 5-neo-Pentyldecane
Explanation: The longest carbon chain has 10 carbon atoms, hence ‘decane’. Sidechain is present on
5th carbon atom, viz., neo-Pentyl or 2′,2′-Dimethylpropyl according to IUPAC. Hence option (i) & (iv). -
Question 15 of 27
15. Question
For an electrophilic substitution reaction, the presence of a halogen atom in the benzene ring _____.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a, c) For an electrophilic substitution reaction, the presence of halogen atom in the benzene ring deactivates the ring by inductive effect and increases the charge density at ortho- and para-position relative to meta-position by resonance. –
When chlorine is attached to benzene ring, chlorine being more electronegative pulls the electrons because of its -I-effect. The electron cloud of benzene becomes less dense. Thus, chlorine makes the benzene ring in aryl halide somewhat deactivated. But due to resonance, the electron density on ortho- and parapositions is greater than on meta-position.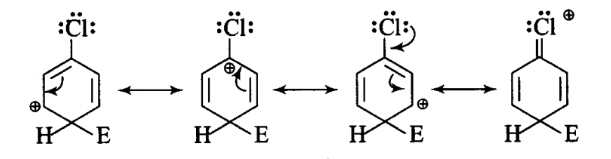
The last structure contributes more to the orientation and hence halogens are \(o\) – and \(p\)-directors.
-
Question 16 of 27
16. Question
In an electrophilic substitution reaction of nitrobenzene, the presence of nitro group ____.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a, c) Nitro group by virtue of-I-effect withdraws electrons from the ring and increases the charge and destabilizes carbocation.
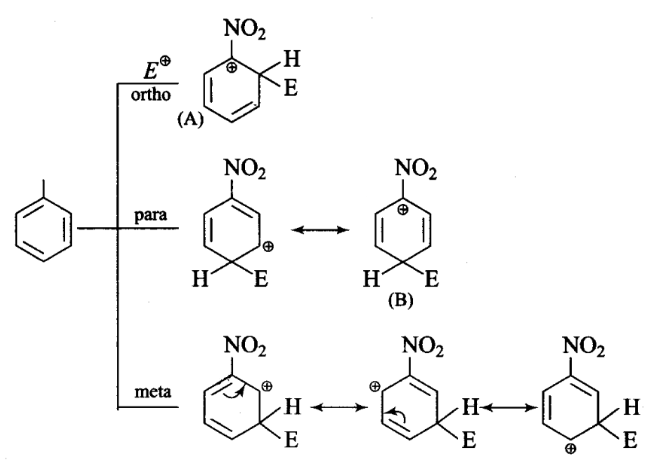
In ortho, para-attack of electrophile on nitrobenzene, we are getting two structures (A) and (B) in which positive charge is appearing on the carbon atom directly attached to the nitro group.
As nitro group is electron withdrawing by nature, it decreases the stability of such product and hence meta attack is more feasible when electron withdrawing substituents are attached. -
Question 17 of 27
17. Question
Which of the following are correct?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a, c)
\(
\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{O}-\mathrm{CH}_2^{\oplus} \text { is more stable than } \mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}_2^{\oplus}
\)
\(
\text { because }+\mathrm{R} \text { effect of } \mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{O} \text { is } \text { greater than }-\mathrm{CH}_3 \text { (stability of carbocation increases due to the }+\mathrm{R} \text { effect). }
\)
(iii) We know that the resonance effect is stronger than +I effect. Here,
\(\mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CH}-\mathrm{CH}_2^{\oplus}\)
is stabilised by resonance effect; whereas \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2^{\oplus}\)
\(\text { is stabilised by }+I \text { effect only . Hence, }\)
\(
\mathrm{CH}_2=\mathrm{CH}-\mathrm{CH}_2^{\oplus} \text { is more stable than } \mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}_2-\mathrm{CH}_2^{\oplus}
\) -
Question 18 of 27
18. Question
Four structures are given in options (i) to (iv). Examine them and select the aromatic structures.
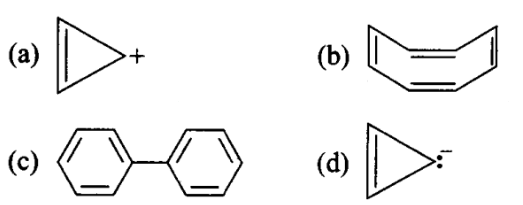 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a, c) Aromaticity requres following condition
(i) Planarity
(ii) Complete delocalisation of \(\pi\) electrons in the ring.
(iii) Presence of \((4 n+2) \pi\) electrons in the ring.
Cyclooctatetraene is non-planar and has \(8 \pi\)-electrons. It is not aromatic. Cyclopropenyl anion is planar but has \(4 \pi\)-electrons. It is not aromatic.
-
Question 19 of 27
19. Question
The molecules having dipole moment are ______.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b,c)
Since, the +I effect of \(\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\) group is higher than that of \(\mathrm{CH}_3\) group, therefore, the dipole moments of \(\mathrm{C-}\) \(\mathrm{CH}_3\) and \(\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\) bonds are unequal. Although these two dipoles oppose each other, yet they do not exactly cancel out each other and hence trans-z-pentene has small but finite dipole moment. In cis-hex-3-ene, although the dipole moments of the two \(\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{CH}_2 \mathrm{CH}_3\) bond are equal, but they are inclined to each other at an angle of \(60^{\circ}\) and hence have a finite dipole moment.
-
Question 20 of 27
20. Question
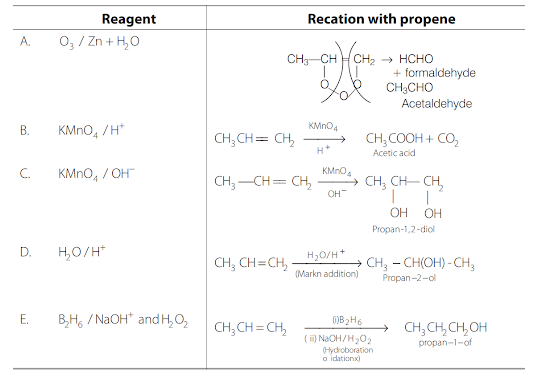
Match the reagent from Column I which on reaction with \(\mathrm{CH}_3-\mathrm{CH}=\mathrm{CH}_2\) gives some product given in Column II as per the codes given below :
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { (i) } \mathrm{O}_3 / \mathrm{Zn}+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} & \text { (a) Acetic acid and } \mathrm{CO}_2 \\
\hline \text { (ii) } \mathrm{KMnO}_4 / \mathrm{H}^{+} & \text {(b) Propan-1-ol } \\
\hline \text { (iii) } \mathrm{KMnO}_4 / \mathrm{OH}^{-} & \text {(c) Propan-2-ol } \\
\hline \text { (iv) } \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} / \mathrm{H}^{+} & \text {(d) Acetaldehyde and formaldehyde } \\
\hline \text { (v) } \mathrm{B}_2 \mathrm{H}_6 / \mathrm{NaOH} \text { and } \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}_2 & \text { (e) Propane-1,2-diol } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 21 of 27
21. Question
Match the hydrocarbons in Column I with the boiling points given in Column II.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { (i) n-Pentane } & \text { (a) } 282.5 K \\
\hline \text { (ii) iso-Pentane } & \text { (b) } 309 K \\
\hline \text { (iii) neo-Pentane } & \text { (c) } 301 K \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Hint: Boiling point inversely proportional to the branching in the molecule
In hydrocarbon as branching increases in the molecule, the boiling point of hydrocarbon decreases in comparable molecular masses.
Explanation:
(i) There are more Vander Waal’s forces in n-pentane, and its boiling point is also high since there is no branching and surface area.
(ii) The boiling point of iso-pentane is less because the molar mass is the same except there’s one brach which reduces the surface area.
(iii) The boiling point of neo-pentane is the lowest because it has two side chains which have the same molar mass. -
Question 22 of 27
22. Question
Match the following reactants in Column I with the corresponding reaction products in Column II.
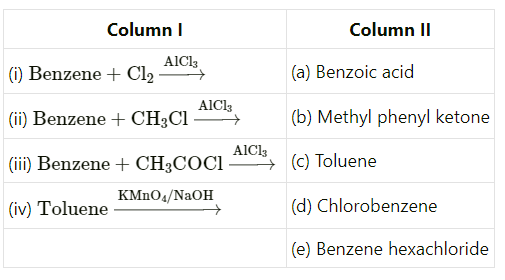 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The first reaction shows benzene undergoes chlorination.
The second reaction is Friedel-Craft alkylation.
The third reaction exhibits friedel-Craft acylation of benzene.
In the fourth reaction shown below, toluene undergoes oxidation with \(\mathrm{KMnO}_4\) to form benzoic acid. -
Question 23 of 27
23. Question
Match the reactions given in Column I with the reaction types in Column II.
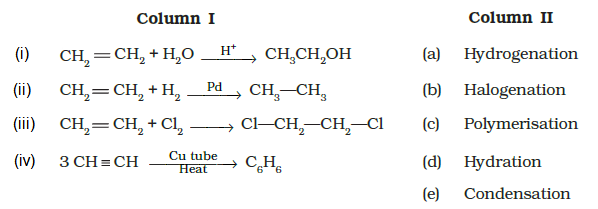 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Hint: Chemical properties of alkenes.
(i) \(\rightarrow\) (d) (ii) \(\rightarrow\) (a) (iii) \(\rightarrow\) (b) (iv) \(\rightarrow\) (c)
-
Question 24 of 27
24. Question
In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : The compound cyclooctane has the following structural formula: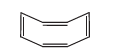
It is cyclic and has conjugated \(8 \pi\)-electron system but it is not an aromatic compound.
Reason (R) : \((4 n+2) \pi\) electrons rule does not hold good and ring is not planar.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Hint: cyclooctatetraene is not a planar compound
According to Huckel rule Aromaticity is shown by compounds possessing the following characteristics
(i) Compound must be planar and cyclic
(ii) Complete delocalization of \(\pi\) electrons in the ring
(iii) Presence of conjugated \((4 n+2) \pi\) electrons in the ring where \(n\) is an integer \((n=0,1,2, \ldots\).
cyclooctatetraene (given) has a tub-like structure. It loses planarity. The number of \(\pi\)-electron delocalized is 8 and \(\mathrm{n}\) is not an integer. Hence, cycloctatetraene is a non-aromatic compound.
Thus, both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion. -
Question 25 of 27
25. Question
In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Toluene on Friedal Crafts methylation gives \(o\)- and \(p\)-xylene.
Reason (R) : \(\quad \mathrm{CH}_3\)-group bonded to benzene ring increases electron density at \(o-\)and \(p-\) position.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Hint: \(\mathrm{CH}_3\) group is an electron-donating group
Toluene has \(-\mathrm{CH}_3\) group attached to benzene. \(-\mathrm{CH}_3\) group activates the benzene for the attack of an electrophile.
In the resonating structure of toluene, electronic density is more on ortho and para position.
Hence, substitution takes place mainly at these positions. Thus, both assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion. -
Question 26 of 27
26. Question
In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
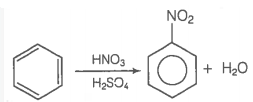
Assertion (A) : Nitration of benzene with nitric acid requires the use of concentrated sulphuric acid.
Reason (R) : The mixture of concentrated sulphuric acid and concentrated nitric acid produces the electrophile, \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\).CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Hint: Nitration mixture contains conc. \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4\) and conc. \(\mathrm{HNO}_3\)
In the nitration of benzene with nitric acid, sulphuric acid acts as a catalyst. It helps in the formation of electrophile i.e., nitronium ion \(\mathrm{NO}_2^{+}\).
The reaction is as follows:
\(
\mathrm{HNO}_3+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{SO}_4 \rightarrow \mathrm{NO}_2^{+}+2 \mathrm{HSO}_4^{-}+\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{O}^{+}
\)
-
Question 27 of 27
27. Question
In the following questions a statement of assertion (A) followed by a statement of reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Assertion (A) : Among isomeric pentanes, 2, 2-dimethylpentane has highest boiling point.
Reason (R) : Branching does not affect the boiling point.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Hint: Boiling point is inversely proportional to branching
As branching increases, the boiling point of alkane decreases in comparable molecular masses. The structures of pentane and 2,2-dimethylpropane are as follows: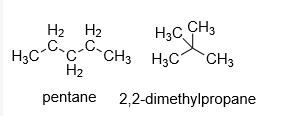
As branching increases the boiling point of the compound decreases but in compounds with comparable molar masses. Hence, 2,2-dimethylpropane boiling point is lower than pentane because it has a higher branching than pentane.
Thus, both assertion and reason are not correct.