Practice Corner MCQs
Quiz Summary
0 of 110 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 110 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 110
1. Question
Consider the following four statements and select the correct option stating which ones are true \((\mathrm{T})\) and which ones are false (F).
(i) Proteins contribute \(6-8 \%\) of the blood plasma.
(ii) Plasma contains very high amount of minerals.
(iii) Plasma without the clotting factors is called serum.
(iv) Glucose, amino acids, lipids, etc., are also present in the plasma as they are always in transit in the body.
\(
\begin{array}{ccccc}
& \text { (i) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (iv) } \\
\text { (a) } & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{T} \\
\text { (b) } & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{T} \\
\text { (c) } & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{T} & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{F} \\
\text { (d) } & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{F} & \mathrm{T}
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Plasma contains small amounts of minerals like \(\mathrm{Na}^{+}\), \(\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}, \mathrm{Ca}^{2+}, \mathrm{HCO}_3^{-}, \mathrm{Cl}^{-}\), etc.
-
Question 2 of 110
2. Question
The colour of plasma is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Normal plasma is typically straw-colored or pale yellow in appearance. This color is due to the presence of bilirubin, a pigment produced from the breakdown of red blood cells. A phlebotomist should expect to see this color in most blood samples, as it is considered the baseline color of plasma.
-
Question 3 of 110
3. Question
\(\mathrm{pH}\) of blood
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) The pH of the human body ranges between 7.35 to 7.45, with the average at 7.40.
-
Question 4 of 110
4. Question
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
CorrectIncorrectHint
RBCs are the most abundant of all the cells in the blood. A healthy adult man has an average 5 millions to 5.5 millions of RBCs per \(\mathrm{mm}^3\) of blood.
-
Question 5 of 110
5. Question
What is the oxidation state of iron in haemoglobin?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) In its oxygenated state, the iron in haemoglobin exists in the +2 oxidation state (\(\mathrm{Fe}^{2+}\)).
When oxygen binds to the iron atom, it forms a coordination bond, resulting in the formation of oxyhaemoglobin.
In this state, the iron is coordinated to the oxygen molecule, stabilizing the oxygen and allowing it to be transported throughout the body. -
Question 6 of 110
6. Question
Which of the following is an agranulocyte?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Leucocytes that lack granules in their cytoplasm are known as agranulocytes. Since lymphocytes do not have granules in their cytoplasm so, they are called agranulocytes.
-
Question 7 of 110
7. Question
The life span of human granulocytic WBC is approximately
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) White blood cells are continuously made in our bone marrow. They have a short lifespan of just one to three days. The medical term for these cells is leukocytes.
-
Question 8 of 110
8. Question
In a healthy adult man, the smallest type of leucocytes are
CorrectIncorrectHint
\(
\text { (d) Lymphocytes are the smallest }(6-10 \mathrm{~nm}) \text { leucocytes. }
\) -
Question 9 of 110
9. Question
Find the correct descending order of the percentage proportion of leucocytes in human blood.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Neutrophils \((60-65 \%) \rightarrow\) Lymphocytes \((20-25 \%) \rightarrow\) Monocytes \((6-8 \%) \rightarrow\) Acidophils \((2-3 \%) \rightarrow\) Basophils \((0.5-1 \%)\).
-
Question 10 of 110
10. Question
Which of the following match is correct?
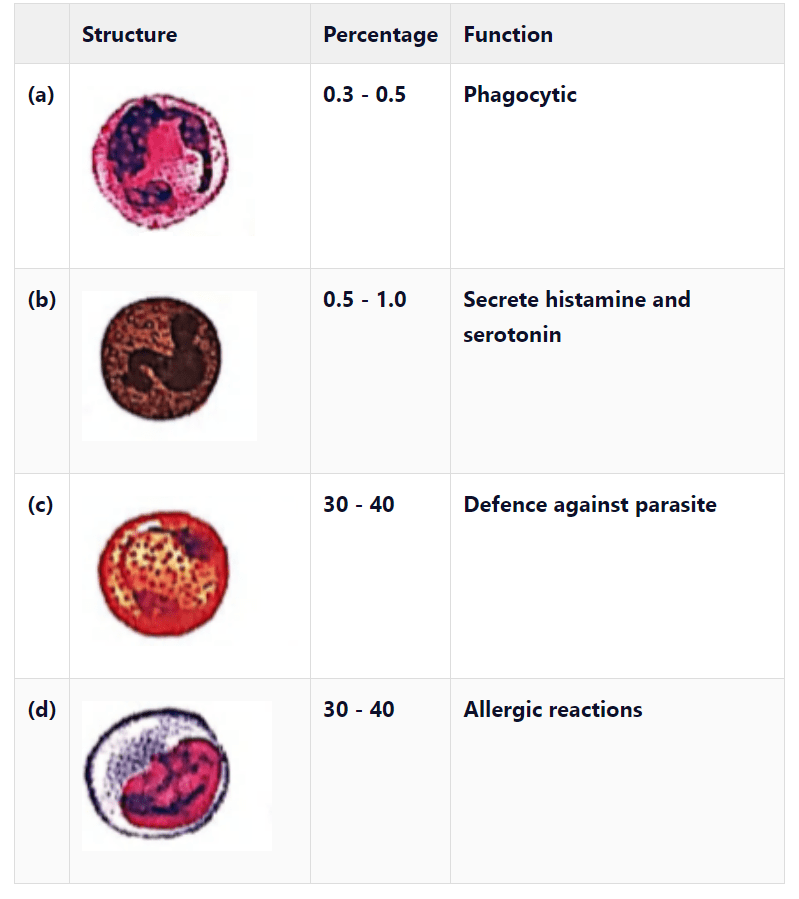 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) The structure given in option ‘b’ is of basophil. Basophils secrete histamine, serotonin, heparin, etc., and are involved in inflammatory reactions. The structure given in option ‘ \(a\) ‘ is of neutrophil. Its percentage is \(60-65 \%\). The structure given in option ‘ \(C\) ‘ is of eosinophil. Its percentage is \(2-3 \%\). The structure given in option ‘ \(d\) ‘ is of monocyte. Its percentage is \(6-8 \%\) and is phagocytic in function.
-
Question 11 of 110
11. Question
Match the types of WBC listed in column I with the shape of nucleus given under column II. Choose the answer which gives the correct combination of alphabets of two columns.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & {\text { Column II }} \\
\hline & \text { Type of WBC } & & \text { Shape of Nucleus } \\
\hline \text { a } & \text { Neutrophils } & \text { p } & \text { Kidney shaped } \\
\hline \text { b } & \text { Eosinophils } & \text { q } & \text { S-shaped } \\
\hline \text { c } & \text { Basophils } & \text { r } & \text { 3-5 lobes } \\
\hline \text { d } & \text { Monocytes } & \text { s } & \text { 2 lobes } \\
\hline & & \text { t } & \text { disc-shaped } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
Hypersegmented neutrophil. When stained, neutrophils have a segmented nucleus and pink/orange cytoplasm under light microscope. The majority of neutrophils have three nuclear segments (lobes) connected by tapering chromatin strands. A small percentage have four lobes, and occasionally five lobes may be seen.
Eosinophils usually have bilobed nuclei
Basophilic granulocytes have a 2 or 3-lobed nucleus. The lobes are usually not as well defined as in neutrophilic granulocytes and the nucleus may appear S-shaped.
Monocytes have one large nucleus, which is usually centrally placed within the cell and often kidney-shaped
So, the correct answer is ‘ \(a=r, b=s, c=q, d=p\) ‘. -
Question 12 of 110
12. Question
Which statement is true for WBCs?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 13 of 110
13. Question
Which of the following statements are incorrect ?
(i) Leucocytes disintegrate in spleen and liver
(ii) RBCs, WBCs and blood platelets are produced by bone narrow
(iii) Neutrophils bring about destruction and detoxification of toxins of proteins origin
(iv) Important function of lymphocytes is to produce antibodies.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Leucocytes disintegrate in blood, liver and lymph nodes. Neutrophils are phagocytic in nature i.e., they engulf harmful germs.
-
Question 14 of 110
14. Question
The life span of thrombocytes is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Thrombocytes are involved in blood clotting. Their life span is 3-7 days.
-
Question 15 of 110
15. Question
In the following table of human \(\mathrm{ABO}\) blood groups, fill up the blanks (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) from the options given below.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { Blood group } & \text { Antigens on RBCs } & \text { Antibody in Plasma } & \text { Donor groups } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { A } & \text { Anti-B } & \text { A, O } \\
\hline \text { B } & \text { B } & \text { Anti-A } & \text { B, O } \\
\hline A B & A B & \text { (ii) } & \text { A, B, AB, O } \\
\hline \text { O } & \text { (i) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (iv) } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
i) for O blood group the antigens are absent on the RBCs, III) the plasma therefore contains antibodies for both antigen \(A\) and antigen \(B\), II) for \(\mathrm{AB}\) blood group the surface of \(\mathrm{RBC}\) has both antigen \(\mathrm{A}\) and \(\mathrm{B}\), therefore no antibodies in the plasma.
iv) the donor group of \(\mathrm{O}\) is only \(\mathrm{O}\) group.
So, the correct answer is ‘ \(\mathrm{i}\) – Nil, ii – Nil, iii – Anti-A, B, iv – O’ -
Question 16 of 110
16. Question
A certain road accident patient with unknown blood group needs immediate blood transfusion. His one doctor friend at once offers his blood. What was the blood group of the doctor?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Persons with blood group ‘ \(O\) ‘ (with no antigens on RBCs) are known as universal donors as they can donate blood to any person of any blood group of \(A B O\) system. Thus the blood group of the donor must be ‘ \(O\) ‘ which can be safely donated to the patient as the patient’s body will not produce any antibody against the person’s blood.
-
Question 17 of 110
17. Question
Which of the following blood groups is a universal recipient in blood transfusion?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Persons having blood group AB, do not have antibodies in their plasma, therefore, they are universal recipients.
-
Question 18 of 110
18. Question
Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies are not found in which of the following blood group?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Persons having blood group AB, do not have antibodies in their plasma, therefore, they are universal recipients.
-
Question 19 of 110
19. Question
Clumping of RBC may occur when blood of one person is mixed with serum or blood of another person. This is due to
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) The RBC membrane contains either antigen \(A\) or antigen \(B\), or both Antigen \(A\) and \(\mathrm{B}\) or no antigen at all, accordingly the blood is classified as blood group A, \(\mathrm{B}, \mathrm{AB}\) and \(\mathrm{O}\) respectively. The blood plasma of blood group \(\mathrm{A}\) will have antibodies for \(\mathrm{B}\), that of \(\mathrm{B}\) will have antibodies for \(\mathrm{A}\), that of \(\mathrm{AB}\) will have non, while that of \(\mathrm{O}\) will have both the antibodies. If blood is transfused at random this will lead to antigen-antibody reaction – like if \(\mathrm{A}\) is the blood group of the recipient while the blood group of the donor happens to be \(\mathrm{B}\), this will lead to clumping of the RBCs.
So, the correct answer is ‘Antigen-antibody reaction’ -
Question 20 of 110
20. Question
Blood of AB group cannot be given to B group patient because
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Persons with blood group B have B antigen on the surface of their RBCs and anti \(A\) antibodies (against \(A\) antigen) in their plasma. The person with \(A B\) blood group possesses both the antigens \(A\) and \(B\) on the surface of RBCs. If \(A B\) blood group is given to \(B\) group patient, agglutination occurs between anti \(A\) antibodies and \(\mathrm{A}\) antigen.
-
Question 21 of 110
21. Question
A drop of each of the following is placed separately on four slides. Which of them will not coagulate?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Blood serum is blood plasma from which the fibrinogens and clotting factors have been removed. So, blood serum will not coagulate.
-
Question 22 of 110
22. Question
Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to the principle of safe blood transfusion?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The correct option is C The recipient’s serum should not contain the antibodies against the RBCs of the donor ” \(A\) ” and ” \(B\) ” are the two surface antigens that are present on the surface of the RBCs. If antigen “A” is found on the RBCs, then anti-B antibodies are developed in the plasma of that individual. If antigen ” \(B\) ” is found on the RBCs, then that individual tends to develop anti-A antibodies in the plasma. The blood transfusion should be done in such a way that the recipient’s serum (plasma without the clotting factors) does not contain antibodies against the antigens present on the surface of the RBCs of the donor. The blood of the donor should properly match with the blood of the recipient. Otherwise, it will result in the destruction or clumping of the red blood cells.
-
Question 23 of 110
23. Question
Detection of blood groups is done by agglutinisation test using antiserum. According to this method, if the blood shows coagulation with
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) If the blood shows coagulation with antiserum B, the blood group is B. Agglutinisation if observed when antiserum B is mixed, will be blood group B. It is the test for checking blood group.
-
Question 24 of 110
24. Question
As per the guidelines of the Indian Red Cross Society, which of the following persons is recommended for blood donation?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Indian Red Cross Society has recommended some guidelines for suitable persons for blood donation, a person who is immunised with live vaccines is one of them.
-
Question 25 of 110
25. Question
Rh factor was discovered by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 26 of 110
26. Question
In which of the following situations, there is a risk factor for children acquiring erythroblastosis fetalis?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) During the first pregnancy, Rh antigens of the fetus do not get exposed to the Rh-ve blood of the mother as the two bloods are well separated by the placenta. However, at the time of delivery, there are chances of exposure of the maternal blood to small amounts of Rh +ve blood of the fetus. Thus, mother’s body starts preparing antibodies against Rh antigens in her blood. In case of subsequent pregnancies, the \(\mathrm{Rh}\) antibodies from the mother can leak into the blood of the Rh +ve fetus and destroy the foetal RBCS. This could be fatal for the fetus or could cause severe anaemia and jaundice. This condition is called erythroblastosis fetalis.
-
Question 27 of 110
27. Question
Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin is catalysed by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Thrombin catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen (factor I) – a soluble plasma protein into long, sticky threads of insoluble fibrin. The fibrin threads form a mesh that traps platelets, blood cells, and plasma. The fibrin mesh work begins to contract in a short period of time and prevents blood loss.
So, the correct answer is ‘Thrombin’ -
Question 28 of 110
28. Question
Which proteolytic enzyme induces lysis of fibrin during fibrinolysis?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Plasmin is a proteolytic enzyme in plasma, which can digest many proteins through the process of hydrolysis. It induces lysis of fibrin during fibrinolysis and is known as fibrinolysin.
-
Question 29 of 110
29. Question
Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) \(\mathrm{Ca}^{2+}\) is necessary for blood coagulation.
(ii) Coagulation in blood vessels is prevented during normal conditions by heparin.
(iii) Clotting of blood involves changes of fibrinogen to fibrin by thrombin.
(iv) Blood clotting involves a cascading process involving a number of factors present always in the active form.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Blood clotting involves cascading process involving a number of factors present in the plasma in an inactive state.
-
Question 30 of 110
30. Question
Consider the following statements \((\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{C}\) ) each with one or two blanks.
(A) (1) are the most abundant cells \((60-65 \%)\) of the total WBCs and (2) are the least \((0.5-1 \%)\) among them.
(B) Platelets are cell fragments produced from (3).
(C) During clot formation, fibrins are formed by the conversion of inactive (4) in the plasma by the enzyme (5).
Which one of the following options, gives the correct fill-ups for the respective blank numbers from (1) to (5) in the statements?CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Blood platelets are cell fragments rather than true cells, they are formed from megakaryocytes (very large cells of bone marrow).
-
Question 31 of 110
31. Question
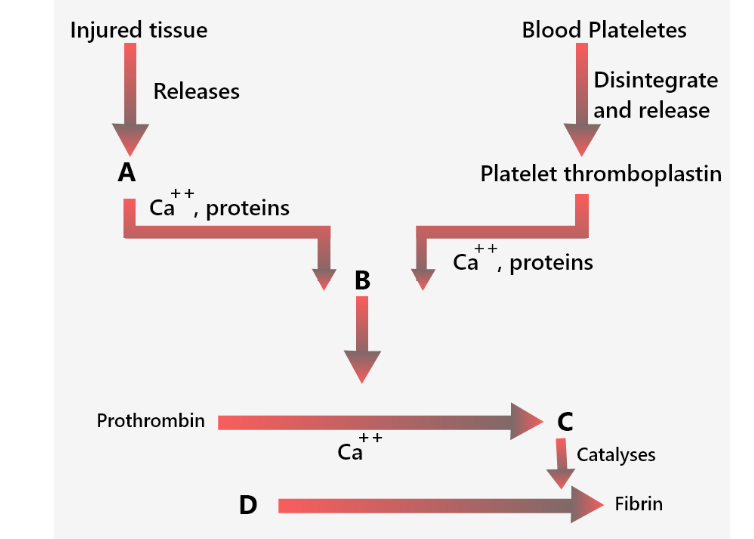
Identify the components labelled (A-D) in the given flow chart of the blood clotting process.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Reason: In the following diagram, the process of blood clotting. In the first step at the site of an injury, the blood platelets disintegrate and release a phospholipid, called platelet factor-3. Injured tissues also release a lipoprotein factor called thromboplastin. These two factors combine with calcium ions and certain proteins of blood plasma to form an enzyme called prothrombinase. In the second step, prothrombinase inactivates heparin in the presence of calcium. Prothrombinase catalyzes the breakdown of prothrombin into an active protein called thrombin. In the third step, thrombin acts as an enzyme and first brings about depolymerization of fibrinogen into its monomers. Later thrombin stimulates repolymerization of these monomers into long insoluble fiber-like polymers called fibrin.
-
Question 32 of 110
32. Question
Prothrombin, which helps in clotting of blood, is released by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Prothrombin is an important plasma protein which is essential for the clotting of blood. It is converted into thrombin at the presence of thromboplastin which is released by blood platelates at the site of injury. The thrombin then converts the protein fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin, which further prevents blood loss by blood arresting, plugging holes in small blood vessels, and by blood clotting.
-
Question 33 of 110
33. Question
Prothrombin required for blood clotting is produced in
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Prothrombin is a plasma protein produced in the liver in the presence of vitamin K. So, the correct answer is ‘Liver’
-
Question 34 of 110
34. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Prothrombin is essential for blood clotting.
Statement 2: Prothrombin is synthesised in the liver in the presence of \(\mathrm{Ca}^{++}\).CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Prothrombin is essential for blood clotting and is synthesised in the liver in the presence of vitamin K.
-
Question 35 of 110
35. Question
During the process of blood coagulation, vitamin \(\mathrm{K}\) helps in
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Prothrombin is essential for blood clotting and is synthesised in the liver in the presence of vitamin K.
-
Question 36 of 110
36. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|c|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Factor II } & \text { (i) } & \text { Thromboplastin } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Factor III } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Prothrombin } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Factor VIII } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Hageman factor } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Factor XII } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Antihaemophilic globulin } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 37 of 110
37. Question
Most of our cells are surrounded by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) All the fluids outside the cells are collectively called the extracellular fluid. The extracellular fluid is mainly present as interstitial fluid and plasma. The interstitial fluid surrounds each cell. The plasma is the non-cellular part of the blood and communicates continuously with the interstitial fluid through the pores of the capillary membranes.
-
Question 38 of 110
38. Question
Which of the following statements is/are incorrect about lymph?
(i) Lymph is colourful as it has haemoglobin but no RBC.
(ii) It contains specialised lymphocytes which are responsible for the immunity of the body.
(iii) Lymph is an important carrier for nutrients and hormones.
(iv) Fats are absorbed through lymph in the lacteals present in the intestinal villi.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Lymph is a colourless fluid containing lymphocytes which are involved in the immune responses of the body.
-
Question 39 of 110
39. Question
Lymph nodes form
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Lymph nodes produce both B-cells and T-cells. B-cells change to plasma cells that produce antibodies against invading antigens.
-
Question 40 of 110
40. Question
The lymph serves to
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Lymph is in contact with the cells/tissues of the organs as interstitial fluid, this fluid is drained in the lymphatic vessels, that connects to the venous system. In this manner interstitial fluid is returned to the blood. So, the correct answer is ‘Return the interstitial fluid to the blood’
-
Question 41 of 110
41. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Lymphatic capillaries are free and blind at one end.
Statement 2: Lymph does not flow in a circular manner.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Lymphatic capillaries lie close to the blood capillaries and end blindly. Lymph does not flow in circular manner. Lymph from the lymphatic capillaries goes into the lymphatic vessels and then from the thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct it does into the left and right subclavian vein respectively.
-
Question 42 of 110
42. Question
Compared to blood our lymph has
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Lymph is a fluid connective tissue containing lymph plasma and cells. The cells in lymph are floating amoeboid cells called WBCs (white blood cells) which are mostly lymphocytes. RBCs and platelets are absent in lymph.
-
Question 43 of 110
43. Question
Which of the following statements is true for lymph?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Lymph differs from blood in lacking RBCs, platelets and some plasma proteins and in having less calcium and phosphorus than the blood.
-
Question 44 of 110
44. Question
Fill the correct option for (i) and (ii).
Open circulatory system is present in (i) and (ii).CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Open circulatory system is present in arthropods and molluscs in which blood pumped by the heart passes through large vessels into open spaces or body cavities called sinuses.
-
Question 45 of 110
45. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The four-chambered heart is present in birds and crocodiles.
Statement 2: Birds have two separate circulatory pathways.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 46 of 110
46. Question
The given figure shows the vertical section of human heart. Identify the parts labelled as A to K.
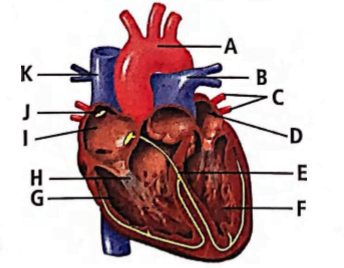
(a) A-Aorta, B-Pulmonary vein, C-Pulmonary arteries, D-Left ventricle, E-Semilunar valves, F-Left auricle, G-Right auricle, H-Superior vena cava, I-Right ventricle, J-Tricuspid valves, K-Inferior vena cava
(b) A-Aorta, B-Pulmonary artery, C-Pulmonary veins, D-Left auricle, E-Bundle of His, F-Left ventricle, G-Right ventricle, H-Chordae tendineae, I-Right auricle, J-Sino-atrial node, K – Vena cava
(c) A-Aorta, B-Superior vena cava, C-Inferior vena cava, D-Right ventricle, E-Bundle of His, F-Right auricle, G-Left auricle, H-Pulmonary vein, I-Right ventricle, J-Sino-atrial node, K-Pulmonary artery
(d) A-Aorta, B-Superior vena cava, C-Inferior vena cava, D-Left ventricle, E-Semilunar valves, F-Left auricle, G-Right auricle, H-Pulmonary artery, I-Right ventricle, J-Tricuspid valves, K-Pulmonary veinCorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 47 of 110
47. Question
Which of the following is correct about human heart?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 48 of 110
48. Question
Which of the following chambers of the heart has the thickest muscular wall?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Left ventricle has the thickest muscular wall as it has to pump the oxygenated blood with great force to all visceral organs and parts of body through aorta.
-
Question 49 of 110
49. Question
Heart pumps blood more forcefully in older persons than younger ones due to
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) As one ages, arteries lose their elasticity. Consequently, the heart has to pump the blood more forcefully in order to fulfill the needs of the body cells.
-
Question 50 of 110
50. Question
Pacemaker is situated in the
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Sino-atrial node, also called pacemaker is situated in the right upper corner of the wall of right atrium.
-
Question 51 of 110
51. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The SA node acts as pacemaker.
Statement 2: The SA node is located in the wall of the right atrium near the interatrial septum.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) The heartbeat originates from the SA node which acts as a pacemaker. SA node lies in the wall of the right atrium near the opening of the superior vena cava.
-
Question 52 of 110
52. Question
In which one of the following pairs, two terms represent the same thing?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The opening between the left atrium and left ventricle is guarded by a bicuspid valve, also known as the mitral valve.
-
Question 53 of 110
53. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) Nodal tissue is specialised cardiac musculature in human heart which has the ability to generate action potential due to an external stimuli.
(ii) Position of SAN – Right corner of right atrium.
(iii) Position of AVN – Right corner of left ventricle.
(iv) AV bundle continues from AVN.
(v) Purkinje fibres are modified cardiac muscle fibres that originate from the atrioventricular node and spread into the two ventricles.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The nodal musculature, has the ability to generate action potential without any external stimuli i.e., it is autoexcitable. AVN is located in the lower left corner of the right atrium close to the atrio-ventricular septum.
-
Question 54 of 110
54. Question
The given figure illustrates a section through the human heart.
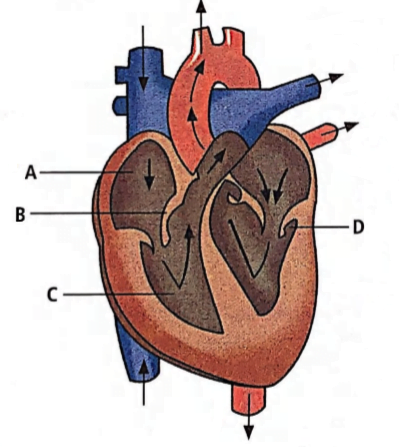
Which labelled part represents the site for the generation of action potential in human heart?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) The SA node is present in the right atrium of the heart which contains pacemaker cells. It is responsible for the generation of action potential. ‘ B ‘ represents the valve present between the right atrium and right ventricle. ‘C’ is the right ventricle. ‘ D ‘ represents the valve between the left atrium and the left auricle.
Thus, the correct answer is ‘A.’ -
Question 55 of 110
55. Question
Chordae tendineae are found in
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Chordae tendineae are the special fibrous cords attached to the flaps of tricuspid valve on one end and on the other end with the special muscles of the ventricular wall, the papillary muscles.
-
Question 56 of 110
56. Question
The problem of electrical discontinuity caused in the normal heart by the connective tissue separating the atria from the ventricles is solved by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) The human heart has an intrinsic conducting system whereby the cardiac muscle is automatically stimulated to contract without the need for a nerve supply from the brain. The components of this system are
(i) \(S A\) node This is small mass of cells located in right atrium. It is often-called pacemaker. It generates < electrical impulse.
(ii) \(A V\) node Small mass of muscular tissue situated in wall of atria septum. Impulse is transferred to it from \(S A\) node.
(iii) Bundle of His It consists of mass of specialized fibres that originate from \(A V\) node. -
Question 57 of 110
57. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|r|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { RBC } & \text { (i) } & \text { Coagulation } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Antibody } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Immunity } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Platelets } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Contraction } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Systole } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Gas transport } \\
\hline & & \text { (v) } & \text { Hypertension } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 58 of 110
58. Question
Blood enters the heart because muscles of the
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Blood enters the heart when the atrium is in a relaxed state. The relaxed state of the atrium increases the volume of the space inside the atrium which creates a suction pull. This results in the blood entering the right atrium.
-
Question 59 of 110
59. Question
During ventricular systole
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Due to contraction of the ventricles (ventricular systole), the pressure inside the ventricles rises, that force open the semilunar valves of aorta and pulmonary artery so that the blood enters into these vessels. Oxygenated blood is pumped into the aorta from the left ventricle while deoxygenated blood is pumped into the pulmonary artery from the right ventricle.
-
Question 60 of 110
60. Question
If due to some injury the chordae tendineae of the tricuspid valve of the human heart is partially nonfunctional, what will be the immediate effect?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Chordae tendineae are cords that prevent the valve from collapsing back into the right atrium during powerful right ventricular contraction. When the right ventricle contracts forcing blood into the pulmonary artery, the tricuspid valve closes the aperture to the right atrium thereby preventing any backflow of blood. Thus, if chordae tendineae of tricuspid valve becomes partially non-functional, then the flow of blood into the pulmonary artery will be reduced.
-
Question 61 of 110
61. Question
The figure given below shows three stages in the cardiac cycle.
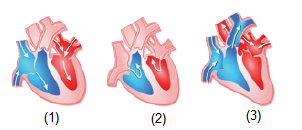
Which of the following sequences is correct regarding this?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) In figure (2), blood is entering into the right auricle through superior and inferior vena cava and blood enters into left auricle through the pulmonary vein. Figure (1) shows the movement of blood from the auricles into the ventricles. Figure (3) shows the movement of blood from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery and from the left ventricle into aorta.
-
Question 62 of 110
62. Question
A red blood cell, entering the right side of the heart passes through the following structures.
1. Atrioventricular valves
2. Semilunar valves
4. Right ventricle
3. Right atrium
5. SAN
Which of the following options represents the correct sequence?CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 63 of 110
63. Question
What happens when the pacemaker becomes non-functional?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The SA node possesses a unique property of selfexcitation, which enables it to act as the pacemaker of the heart. It spontaneously generates a wave of contraction which spreads over both the auricles more or less simultaneously along the muscle fibres that fan out from the pacemaker. The pacemaker establishes the basic rhythm at which the heart beats. Thus, if the pacemaker becomes non-functional, then the cardiac muscles do not undergo co-ordinated rhythmic movements.
-
Question 64 of 110
64. Question
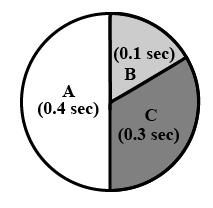
In the given figure the durations of the events of the cardiac cycle are given. Identify these events and select the correct option.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 65 of 110
65. Question
Which of the following statement(s) regarding the cardiac system is/are correct?
(i) Human heart is an ectodermal derivative.
(ii) Mitral valve guards the opening between the right atrium and left ventricle.
(iii) SAN is located on the left upper corner of the right atrium.
(iv) Stroke volume \(\times\) Heart rate \(=\) Cardiac output.CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) During a cardiac cycle, each ventricle pumps out approximately \(70 \mathrm{~mL}\) of blood which is called stroke volume. The stroke volume multiplied by the number of heart beats per minute (heart rate) gives the cardiac output. Therefore, Cardiac output = Stroke volume \(\times\) heart rate \(=70 \times 72=5040 \mathrm{~mL}\) per minute i.e. 5 litres per minute.
-
Question 66 of 110
66. Question
In a cardiac output of \(5250 \mathrm{~mL}\) per minute, with 75 heartbeats per minute, the stroke volume is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Cardiac output \(=\) Stroke volume \(\times\) Heartbeats per minute
\(
\begin{array}{r}
\therefore \text { Stroke volume }=\frac{\text { Cardiac output }}{\text { Heart beats per minute }} \\
\quad=\frac{5250}{75}=70 \mathrm{~mL}
\end{array}
\) -
Question 67 of 110
67. Question
Rate of heartbeat is determined by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 68 of 110
68. Question
Which one of the following is a matching pair?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) During ventricular systole, the contraction of ventricular muscles causes the closure of bicuspid and tricuspid valves (AV valves), producing a low pitched ‘lub’ sound. At the end of ventricular systole, semilunar valves close, producing the second heart sound, the ‘dup’. Pulsation of the radial artery is due to rhythmic contraction and relaxation in the aorta. Initiation of the heartbeat occurs in the SA node.
-
Question 69 of 110
69. Question
The longer heart sound is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) The first heart sound (lub) is caused by the sudden closure of bicuspid and tricuspid valves and is longer than the second heart sound (dup) which is caused by the closure of semilunar valves.
-
Question 70 of 110
70. Question
‘ \(X\) ‘ is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation in the aorta and its main arteries. What is \(X\)?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 71 of 110
71. Question
Which of the following is the diagrammatic representation of standard electrocardiogram (ECG)?
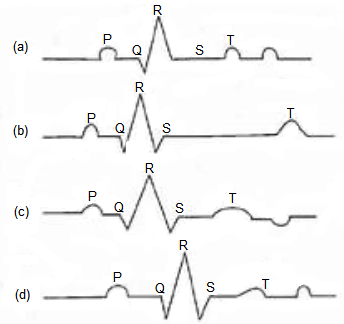 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Reason: A normal electrogram (ECG) is composed of a ‘P’ wave, a QRS wave (complex), and a T wave. The ‘ \(\mathrm{P}\) ‘ wave is a small upward wave that represents electrical excitation or atrial depolarization which leads to contraction of both the atria. \(Q R S\) wave (complex) begins after a fraction of a second of the \(P\) wave. It begins as a small downward deflection \((\mathrm{Q})\) and continues as a larger upright (R) and triangular wave, ending as a downward wave (S) at its base. It represents ventricular depolarization. The ‘ \(T\) ‘ wave is dome-shaped which represents ventricular repolarization. The potential generated by the recovery of the ventricle from the depolarization state is called the repolarization wave. The end of the ‘T’ wave marks the end of the systole.
-
Question 72 of 110
72. Question
In a standard ECG which one of the following alphabets is the correct representation of the respective activity of the human heart?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) In a standard ECG, the P wave is a small upward wave that represents depolarisation of the atria which leads to the contraction of both the atria.
-
Question 73 of 110
73. Question
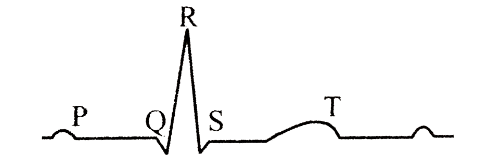
Examine the diagrammatic representation of standard ECG. Select an option with correct matching.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { P-Wave } & \text { QRS complex } & \text { T-wave } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Repolarisation of the } \\
\text { atria }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Repolarisation of the } \\
\text { ventricles }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Depolarisation of the } \\
\text { atria }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { (b) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Depolarisation of the } \\
\text { atria }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Depolarisation of the } \\
\text { ventricles }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Repolarisation of the } \\
\text { ventricles }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { (c) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Repolarisation of the } \\
\text { ventricles }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Repolarisation of the } \\
\text { atria }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Depolarisation of the } \\
\text { ventricles }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { (d) } & \text { Depolarisation of the ventricles } & \text { Depolarisation of the atria } & \text { Repolarisation of the atria } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 74 of 110
74. Question
Which of the following statements is correct?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) In a standard ECG, a patient is connected to the machine with three electrical leads, one to each wrist and one to the left ankle.
-
Question 75 of 110
75. Question
The given figure is the ECG of a normal human. Which one of its components is correctly interpreted below?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) The QRS complex represents the depolarisation of the ventricles, which initiates the ventricular contraction. By counting the number of QRS complexes that occur in a given time period, one can determine the rate of heartbeat of an individual.
-
Question 76 of 110
76. Question
In ECG, P-R interval corresponds to
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) In ECG, P-R interval is the time from the beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex. It corresponds to the time lag from the onset of atrial depolarisation to the onset of ventricular depolarisation. Most of the delay occurs in the AV node.
-
Question 77 of 110
77. Question
Read the following statements carefully.
(i) In fishes, the heart pumps out deoxygenated blood which is oxygenated by the gills and supplied to the body parts from where deoxygenated blood is returned to the heart.
(ii) The openings of the right and the left ventricles into pulmonary artery and aorta respectively are provided with the mitral valves.
(iii) The nodal musculature has the ability to generate action potentials without any external stimuli, i.e., it is autoexcitable.
(iv) The T-wave of ECG represents depolarisation of the ventricles.
Which of the above two statements are incorrect?CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) The openings of the right and the left ventricles into the pulmonary artery and the aorta respectively are provided with semilunar valves. The T-wave of ECG represents repolarisation of ventricles.
-
Question 78 of 110
78. Question
Which of the following parts of heart first receives deoxygenated blood?
CorrectIncorrectHint
The right and left atria are the top chambers of the heart and receive blood into the heart. The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from systemic circulation and the left atrium receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary circulation.
Thus, the correct answer is ‘Right auricle.’ -
Question 79 of 110
79. Question
Which of the following options represents correct systemic circulation in human being?
(a) \(\text { Left ventricle } \xrightarrow[\text { blood }]{\text { Deoxygenated }} \text { Tissues } \xrightarrow[\text { blood }]{\text { Oxygenated }} \text { Right ventricle }\)
(b) \(\text { Right ventricle } \xrightarrow[\text { blood }]{\text { Oxygenated }} \text { Tissues } \xrightarrow[\text { blood }]{\text { Deoxygenated }} \text { Right auricle }\)
(c) \(\text { Left ventricle } \xrightarrow[\text { blood }]{\text { Deoxygenated }} \text { Tissues } \xrightarrow[\text { blood }]{\text { Oxygenated }} \text { Right auricle }\)
(d) \(\text { Left ventricle } \xrightarrow[\text { blood }]{\text { Oxygenated }} \text { Tissues } \xrightarrow[\text { blood }]{\text { Deoxygenated }} \text { Right auricle }\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Oxygen-rich blood flows from the lungs back into the left atrium or the left upper chamber of the heart, through four pulmonary veins.
Oxygen-rich blood then flows through the mitral valve into the left ventricle, or the left lower chamber. The left ventricle pumps the oxygen-rich blood through the aortic valve into the aorta, the main artery that takes oxygen-rich blood out to the rest of the body.
Oxygen-poor blood returns from the body to the heart through the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava, the two main veins that bring blood back to the heart. The oxygen-poor blood enters the right atrium, or the right upper chamber of the heart. -
Question 80 of 110
80. Question
In which of the following points pulmonary artery is different from pulmonary vein?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 81 of 110
81. Question
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) On an average, capillaries are about \(1 \mathrm{~mm}\) long and \(8 \mathrm{~mm}\) in diameter. Although each capillary is very narrow, there are so many of them that the capillaries have the greatest total cross-sectional area of any other type of vessel. Consequently, the blood decreases in velocity as it passes through the capillary beds, allowing more time for it to exchange materials with the surrounding extracellular fluid. Blood also loses most of its pressure in passing through the vast capillary networks and so is under very low pressure when it enters the veins.
-
Question 82 of 110
82. Question
Select the schematic diagram which properly represents pulmonary circulation in humans.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Pulmonary circulation is the movement of blood between heart and lungs. During this pathway deoxygenated blood entering the right atrium, moves into the right ventricle. From here it moves through the pulmonary arch into the lungs for oxygenation. Then from lungs the oxygenated blood moves into the left atrium through pulmonary veins.
-
Question 83 of 110
83. Question
Which of the following sequences is truly a systemic circulation pathway?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Systemic circulation is the movement of the blood between the heart and the rest of the body (tissues) and the back to the heart.
-
Question 84 of 110
84. Question
Given below are the figures of blood vessels. Identify them and select the correct option.
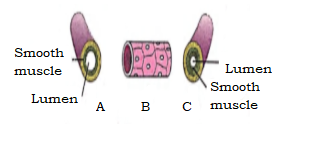
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B complex } & \text { C } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & \text { Capillary } & \text { Vein } & \text { Artery } \\
\hline \text { (b) } & \text { Artery } & \text { Capillary } & \text { Vein } \\
\hline \text { (c) } & \text { Vein } & \text { Capillary } & \text { Artery } \\
\hline \text { (d) } & \text { Vein } & \text { Artery } & \text { Capillary } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) A shows a vein composed of smooth muscles with a characteristic larger lumen. B shows a capillary made up of a single layer of cells. C shows an artery made up of smooth muscles with a smaller lumen. C is the correct answer
-
Question 85 of 110
85. Question
What is the nature of blood passing through blood vessels A, B, C and D respectively?

\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & \text { Deoxygenated } & \text { Oxygenated } & \text { Deoxygenated } & \text { Oxygenated } \\
\hline \text { (b) } & \text { Deoxygenated } & \text { Deoxygenated } & \text { Oxygenated } & \text { Oxygenated } \\
\hline \text { (c) } & \text { Oxygenated } & \text { Oxygenated } & \text { Deoxygenated } & \text { Deoxygenated } \\
\hline \text { (d) } & \text { Oxygenated } & \text { Deoxygenated } & \text { Oxygenated } & \text { Deoxygenated } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) ‘ A ‘ is vena cava that carries deoxygenated blood. ‘ B ‘ is aorta that carries oxygenated blood. ‘ C ‘ is pulmonary artery that carries deoxygenated blood. ‘D’ is pulmonary vein that carries oxygenated blood.
-
Question 86 of 110
86. Question
The given figure is of the circulatory system. Identify the labelled parts (A-D) from the list (i-vii).
(i) Pulmonary circulation
(ii) Systemic circulation
(iii) Superior vena cava
(iv) Inferior vena cava
(v) Aorta
(vi) Veins and venules
(vii) Arterioles and capillaries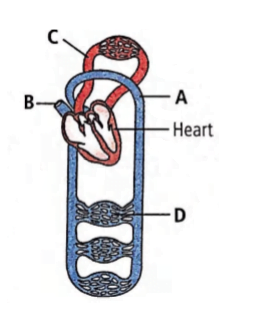
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & \text { (v) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (i) } & \text { (vii) } \\
\hline \text { (b) } & \text { (vii) } & \text { (iv) } & \text { (i) } & \text { (vi) } \\
\hline \text { (c) } & \text { (v) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (vii) } \\
\hline \text { (d) } & \text { (vii) } & \text { (v) } & \text { (i) } & \text { (vii) } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 87 of 110
87. Question
In the given figure of the heart which of the labelled parts (1,2,3,4,5) carries oxygenated blood?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
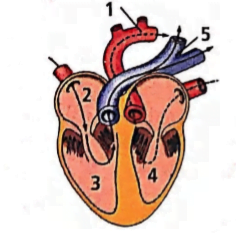
(c) The labelled parts ‘ 1 ‘ and ‘ 4 ‘ are aorta and left ventricle respectively, which carry oxygenated blood.
-
Question 88 of 110
88. Question
Right atrium receives blood from
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) The superior vena cava brings deoxygenated blood from the upper part of the body while the inferior vena cava brings blood from lower part of the body into the right atrium of the heart.
-
Question 89 of 110
89. Question
In the given figure, which blood vessel represents vena cava?
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) In the given figure ‘ D ‘ represents the vena cava.
-
Question 90 of 110
90. Question
Arteries are best defined as the vessels which
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) The correct option is b carry blood away from the heart to different organs Arteries and veins are main blood vessels. Arteries carry blood from the heart to different body parts. Veins bring blood from different parts to the heart.
-
Question 91 of 110
91. Question
Carotid artery supplies
CorrectIncorrectHint
There are two carotid arteries, one on the right and one on the left. In the neck, each carotid artery branches into two divisions: The internal carotid artery supplies blood to the brain. The external carotid artery supplies blood to the face and neck. So, the correct answer is “Oxygenated blood to the brain.”
-
Question 92 of 110
92. Question
All veins carry deoxygenated blood except
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) All veins carry deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body to heart. Pulmonary vein is the only vein that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart.
-
Question 93 of 110
93. Question
In veins, valves are present to check backward flow of blood flowing at
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Veins bring blood from different body parts to the heart. The flow of blood in veins is not so fast because the blood in veins is under low pressure. Veins possess valves which prevent backward flow of blood.
-
Question 94 of 110
94. Question
Which of the following statements is correct regarding veins?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) The veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart. There is an exception, the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart. However, all veins carry blood from some organ to the heart. Thus, the correct answer is option a.
-
Question 95 of 110
95. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Superior vena cava } & \text { (i) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Carries deoxygenated } \\
\text { blood to lungs }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Inferior vena cava } & \text { (ii) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Carries oxygenated } \\
\text { blood from lungs }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Pulmonary artery } & \text { (iii) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Brings deoxygenated } \\
\text { blood from lower part } \\
\text { of body to right atrium }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Pulmonary vein } & \text { (iv) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Bring deoxygenated } \\
\text { blood from upper part } \\
\text { of body to right atrium }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 96 of 110
96. Question
Consider the following four statements (i) – (iv) and select the correct option.
(i) Fish heart contains only oxygenated blood.
(ii) Closure of AV valves produces the second heart sound.
(iii) The vascular connection between the digestive tract and kidney is called hepatic portal system.
(iv) Purkinje fibres are nerve fibres present in the heart wall.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Fish heart contains only deoxygenated blood. Closure of the semilunar valves produces the second heart sound. The vascular connection between the digestive tract and liver is called hepatic portal system.
-
Question 97 of 110
97. Question
The rate of heartbeat is regulated by the integrated activity of inhibiting and accelerating effects occurring in which part of the brain?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) A special neural centre in the medulla oblongata can moderate the cardiac function through autonomic nervous system (ANS). Neural signals through the sympathetic nerves (part of ANS) can increase the rate of heartbeat, the strength of ventricular contraction and thereby the cardiac output. On the other hand, parasympathetic neural signals (another component of ANS) decrease the rate of heartbeat, speed of conduction of action potential and thereby the cardiac output.
-
Question 98 of 110
98. Question
Hormonal regulation of cardiac activity involves the hormones _____ and _____ secreted by the ______.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) The renal medulla secretes two similar hormones: adrenaline( epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) that have almost the same basic effect. Role of epinephrine and norepinephrine- They whip up metabolism for preparing the animal to face special conditions created by physical stress such as fall in BP or blood sugar, anger, fear etc..All these conditions require more energy which is provided by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, sugar level of blood.
So, the correct answer is ‘Epinephrine, norepinephrine, medulla of adrenal glands’.
-
Question 99 of 110
99. Question
Which of the following statements is correct regarding neural regulation of cardiac activity?
CorrectIncorrectHint
Option (a)
– The cardiovascular centre is a component of the human brain that uses the neurological and endocrine systems to control heart rate.
– The medulla oblongata is where it is found.
Option (b)
– The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, both of which are components of the autonomic nervous system, are crucial in this control.
– The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for boosting heart rate and ventricular contraction strength.
– The parasympathetic nervous system, on the other hand, plays a significant role in cardiac activity regulation by lowering the speed of nerve impulse conduction and heart rate.
Option (c)
– Sensory fibres extend from the receptors present in the walls of aortic arch, carotid sinuses and vena cava to the cardiovascular centre in medulla oblongata” which exactly same as it is mentioned
Thus the Correct option is (d). -
Question 100 of 110
100. Question
Which one of the following is correct for ‘atherosclerosis’
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Atherosclerosis is the deposition of fatty substances especially cholesterol and triglycerides in the wall of the arteries. Such a deposition is called a plaque which gradually grows and as a result the lumen of the artery decreases and the flow of the blood is reduced. Sclerosis means hardening.
-
Question 101 of 110
101. Question
If the systolic pressure is \(120 \mathrm{mmHg}\) and diastolic pressure is \(80 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\), the pulse pressure is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) \(120-80=40 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\)
The pulse pressure can be defined as the difference between the diastolic and systolic pressure of an individual’s heart. If the normal diastolic and systolic pressure of the adult human heart is \(120 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\) and \(80 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\) respectively, then the pulse pressure is \(120-80=40 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\). -
Question 102 of 110
102. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Heart failure } & \text { (i) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Heart muscle is suddenly } \\
\text { damaged by an inadequate } \\
\text { blood supply }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Cardiac arrest } & \text { (ii) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Chest pain due to } \\
\text { inadequate } \mathrm{O}_2 \text { reaching } \\
\text { the heart muscles }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Heart attack } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Atherosclerosis } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Coronary } \\
\text { artery disease } \\
\text { (CAD) }
\end{array} & \text { (iv) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Heart not pumping blood } \\
\text { effectively enough to meet } \\
\text { the needs of the body }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { E. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Angina } \\
\text { pectoris }
\end{array} & \text { (v) } & \text { Heart stops beating } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 103 of 110
103. Question
During acute myocardial infarction, which of the following changes occurs in the ECG ?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The S-T segment represents the time between the end of the spread of impulse through ventricles and their repolarisation. The S-T segment becomes elevated in acute myocardial infarction.
-
Question 104 of 110
104. Question
Which one of the following statements is correct regarding blood pressure?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Normal blood pressure is \(120 / 80 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\). Blood pressure of \(190 / 110 \mathrm{~mm} \mathrm{Hg}\) is regarded as high blood pressure. It leads to heart diseases and also affects vital organs like brain and kidney.
-
Question 105 of 110
105. Question
Refer to the given electrocardiogram and select the correct statement.
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
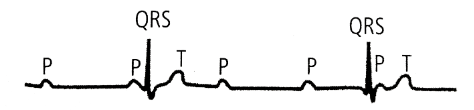
(c) In case of complete A-V block (third degree block), the condition in the AV bundle causes complete block of the impulse from the atria into the ventricles. The ventricles spontaneously establish their own signal usually originating in the AV node or AV bundle. Therefore, the P waves become dissociated from QRS-T complexes and there is no relation between the rhythm of the P waves and that of the QRS-T complexes. The rate of rhythm of the atria in this electrocardiogram is about 100 beats per minute, whereas the rate of ventricular beat is less than 40 per minute.
-
Question 106 of 110
106. Question
Excessively high heart rate (>180) can reduce cardiac output because
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The cardiac output is determined by multiplying the heart rate (HR) – the number of beats per minute, and the stroke volume (SV) – the blood volume ejected by each ventricle during systole. During diastole, normal filling of the ventricles occurs. In the first third period of diastole, there is rapid filling of ventricles. The middle period of diastole, accounts only for a small amount of blood that continues to empty into the atria from the veins and passes through the atria directly into the ventricles. During the last third period of diastole, the atria contract and give an additional thrust to the inflow of blood into the ventricles. The fact that most of ventricular filling is completed during early diastole is of great importance. It ensures that filling is not seriously impaired during periods when the heart is beating very rapidly and the duration of diastole and therefore total filling times are reduced. Furthermore, this leads to a decrease in the blood volume ejected at the time of ventricular systole. Hence, the stroke volume reduces.
-
Question 107 of 110
107. Question
Lungs receive blood from right side of the heart, whereas the branching of systemic arteries result in a parallel pattern. What is the advantage of such of an arrangement?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) The lungs receive all the blood pumped by the right side of the heart, whereas the branching of the systemic arteries results in a parallel pattern so that each of the peripheral organs and tissues receives only a fraction of the blood pumped by the left ventricle. This arrangement guarantees that all systemic tissues receive freshly oxygenated blood and allows for independent variation in blood flow through different tissues as their metabolic activities change.
-
Question 108 of 110
108. Question
The figure represents total period of one cardiac cycle i.e., 0.8 sec and A, B and C represent its stages. Identify A, B and C and select the correct statement regarding them.
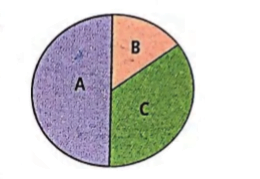 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) In the given figure, A is atrial and ventricular diastole (complete cardiac diastole), B is artrial systole and C is ventricular systole.
-
Question 109 of 110
109. Question
Select the incorrect difference between open and closed circulatory system.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { Open circulatory } \\
\text { system }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Closed circulatory } \\
\text { system }
\end{array} \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { a. Blood flows at high } \\
\text { pressure. }
\end{array} & \text { Blood flows at low pressure } \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { b. Exchange of } \\
\text { materials is direct. }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Exchange of materials } \\
\text { occurs through tissue fluid. }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { c. It is less efficient. } & \text { It is more efficient. } \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { d. Found in arthropods } \\
\text { and molluscs }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Found in annelids and } \\
\text { chordates }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 110 of 110
110. Question
What is the relationship between cholesterol with blood pressure?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) When both high blood pressure and high cholesterol occur together, they can damage blood vessels, greatly increasing the risk of future complications.