Sample Paper
Sample 20 Questions are from JEE Main year 2021 Paper (Section-A)
Q1. The temperature of equal masses of three different liquids \(\mathrm{x}, \mathrm{y}\) and \(\mathrm{z}\) are \(10^{\circ} \mathrm{C}, 20^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and \(30^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) respectively. The temperature of mixture when \(\mathrm{x}\) is mixed with \(\mathrm{y}\) is \(16^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and that when \(\mathrm{y}\) is mixed with \(\mathrm{z}\) is \(26^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). The temperature of mixture when x and z are mixed will be:
(1) \(28.32^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\)
(2) \(25.62^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\)
(3) \(23.84^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\)
(4) \(20.28^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\)
Answer: 3
Q2. The de-Broglie wavelength of a particle having kinetic energy E is λ. How much extra energy must be given to this particle so that the de-Broglie wavelength reduces to 75% of the initial value?
(1) \(\frac{1}{9} \mathrm{E}\)
(2) \(\frac{7}{9} \mathrm{E}\)
(3) \(\mathrm{E}\)
(4) \(\frac{16}{9} \mathrm{E}\)
Answer: 2
Solution:
\(
\begin{aligned}
&\lambda=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\mathrm{mv}}=\frac{\mathrm{h}}{\sqrt{2 \mathrm{mE}}}, \mathrm{mv}=\sqrt{2 \mathrm{mE}} \\
&\lambda \propto \frac{1}{\sqrt{\mathrm{E}}} \\
&\frac{\lambda_{2}}{\lambda_{1}}=\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{E}_{1}}{\mathrm{E}_{2}}}=\frac{3}{4}, \lambda_{2}=0.75 \lambda_{1} \\
&\frac{\mathrm{E}_{1}}{\mathrm{E}_{2}}=\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)^{2} \\
&\mathrm{E}_{2}=\frac{16}{9} \mathrm{E}_{1}=\frac{16}{9} \mathrm{E} \quad\left(\mathrm{E}_{1}=\mathrm{E}\right)
\end{aligned}
\)
Extra energy given \(=\frac{16}{9} \mathrm{E}-\mathrm{E}=\frac{7}{9} \mathrm{E}\)
Q3. A particle of mass m is suspended from a ceiling through a string of length L. The particle moves in a horizontal circle of radius r such that \(\mathrm{r}=\frac{\mathrm{L}}{\sqrt{2}}\). The speed of particle will be:
(1) \(\sqrt{\mathrm{rg}}\)
(2) \(\sqrt{2 \mathrm{rg}}\)
(3) \(2 \sqrt{\mathrm{rg}}\)
(4) \(\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{rg}}{2}}\)
Answer: 1
Q4. A cylindrical container of volume \(4.0 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~m}^{3}\) contains one mole of hydrogen and two moles of carbon dioxide. Assume the temperature of the mixture is \(400 \mathrm{~K}\). The pressure of the mixture of gases is :
[Take gas constant as \(8.3 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1}\) ]
(1) \(249 \times 10^{1} \mathrm{~Pa}\)
(2) \(24.9 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~Pa}\)
(3) \(24.9 \times 10^{5} \mathrm{~Pa}\)
(4) \(24.9 \mathrm{~Pa}\)
Answer: 3
Q5. The angle between vector \((\vec{A})\) and \((\vec{A}-\vec{B})\) is:
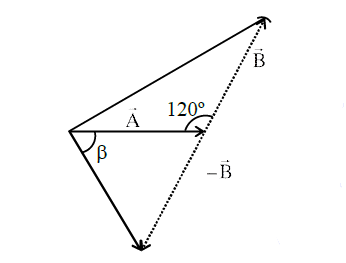
(1) \(\tan ^{-1}\left(\frac{-\frac{B}{2}}{A-B \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}}\right)\)
(2) \(\tan ^{-1}\left(\frac{\mathrm{A}}{0.7 \mathrm{~B}}\right)\)
(3) \(\tan ^{-1}\left(\frac{\sqrt{3} \mathrm{~B}}{2 \mathrm{~A}-\mathrm{B}}\right)\)
(4) \(\tan ^{-1}\left(\frac{\mathrm{B} \cos \theta}{\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{B} \sin \theta}\right)\)
Answer: 3
Q6. A light beam is described by \(E=800 \sin \omega\left(t-\frac{x}{c}\right)\). An electron is allowed to move normal to the propagation of light beam with a speed of \(3 \times 10^{7}\) \(\mathrm{ms}^{-1}\). What is the maximum magnetic force exerted on the electron?
(1) \(1.28 \times 10^{-18} \mathrm{~N}\)
(2) \(1.28 \times 10^{-21} \mathrm{~N}\)
(3) \(12.8 \times 10^{-17} \mathrm{~N}\)
(4) \(12.8 \times 10^{-18} \mathrm{~N}\)
Answer: 4
Q7. The two thin coaxial rings, each of radius ‘a’ and having charges +Q and –Q respectively are separated by a distance of ‘s’. The potential difference between the centers of the two rings is:
(1) \(\frac{\mathrm{Q}}{2 \pi \varepsilon_{0}}\left[\frac{1}{\mathrm{a}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mathrm{s}^{2}+\mathrm{a}^{2}}}\right]\)
(2) \(\frac{Q}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}}\left[\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{s^{2}+a^{2}}}\right]\)
(3) \(\frac{Q}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}}\left[\frac{1}{a}-\frac{1}{\sqrt{s^{2}+a^{2}}}\right]\)
(4) \(\frac{\mathrm{Q}}{2 \pi \varepsilon_{0}}\left[\frac{1}{\mathrm{a}}-\frac{1}{\sqrt{\mathrm{s}^{2}+\mathrm{a}^{2}}}\right]\)
Answer: 4
Q8. If you are provided a set of resistances 2Ω, 4Ω, 6Ω, and 8Ω. Connect these resistances so as to obtain an equivalent resistance of \(\frac{46}{3}\)Ω.
(1) 4Ω and 6Ω are in parallel with 2Ω and 8Ω in series
(2) 6Ω and 8Ω are in parallel with 2Ω and 4Ω in series
(3) 2Ω and 6Ω are in parallel with 4Ω and 8Ω in series
(4) 2Ω and 4Ω are in parallel with 6Ω and 8Ω in series
Answer: 4
Q9. The solid cylinder of length \(80 \mathrm{~cm}\) and mass M has a radius of \(20 \mathrm{~cm}\). Calculate the density of the material used if the moment of inertia of the cylinder about an axis CD parallel to \(A B\) as shown in the figure is \(2.7 \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~m}{ }^{2}\).
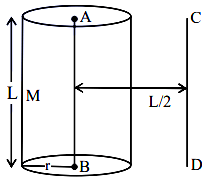
(1) \(14.9 \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\)
(2) \(7.5 \times 10^{1} \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\)
(3) \(7.5 \times 10^{2} \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\)
(4) \(1.49 \times 10^{2} \mathrm{~kg} / \mathrm{m}^{3}\)
Answer: 4
Solution:
Parallel axis theorem: The moment of inertia of a body about an axis parallel to the body passing through its center is equal to the sum of the moment of inertia of the body about the axis passing through the center and the product of the mass of the body times the square of the distance between the two axes.
\(
\begin{aligned}
&\mathrm{I}=\mathrm{I}_{\mathrm{CM}}+\mathrm{Md}^{2} \\
&\mathrm{I}=\frac{\mathrm{Mr}^{2}}{2}+\mathrm{M}\left(\frac{\mathrm{L}}{2}\right)^{2} \\
&2.7=\mathrm{M} \frac{(0.2)^{2}}{2}+\mathrm{M}\left(\frac{0.8}{2}\right)^{2} \\
&2.7=\mathrm{M}\left[\frac{2}{100}+\frac{16}{100}\right] \\
&\mathrm{M}=15 \mathrm{~kg} \\
&\Rightarrow \rho=\frac{\mathrm{M}}{\pi \mathrm{r}^{2} \mathrm{~L}}=\frac{15}{\pi(0.2)^{2} \times 0.8} \\
&=0.1492 \times 10^{3}
\end{aligned}
\)
Q10. A parallel – plate capacitor with plate area A has separation \(\mathrm{d}\) between the plates. Two dielectric slabs of dielectric constant \(\mathrm{K}_{1}\) and \(\mathrm{K}_{2}\) of same area \(\mathrm{A} / 2\) and thickness \(\mathrm{d} / 2\) are inserted in the space between the plates. The capacitance of the capacitor will be given by:
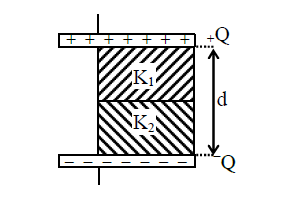
(1) \(\frac{\varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{~A}}{\mathrm{~d}}\left(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{\mathrm{K}_{1} \mathrm{~K}_{2}}{\mathrm{~K}_{1}+\mathrm{K}_{2}}\right)\)
(2) \(\frac{\varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{~A}}{\mathrm{~d}}\left(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{\mathrm{K}_{1} \mathrm{~K}_{2}}{2\left(\mathrm{~K}_{1}+\mathrm{K}_{2}\right)}\right)\)
(3) \(\frac{\varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{~A}}{\mathrm{~d}}\left(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{\mathrm{K}_{1}+\mathrm{K}_{2}}{\mathrm{~K}_{1} \mathrm{~K}_{2}}\right)\)
(4) \(\frac{\varepsilon_{0} \mathrm{~A}}{\mathrm{~d}}\left(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{2\left(\mathrm{~K}_{1}+\mathrm{K}_{2}\right)}{\mathrm{K}_{1} \mathrm{~K}_{2}}\right)\)
Answer: 1
Q11. A bomb is dropped by a fighter plane flying horizontally. To an observer sitting in the plane, the trajectory of the bomb is a:
(1) hyperbola
(2) parabola in the direction of motion of the plane
(3) straight line vertically down the plane
(4) parabola in a direction opposite to the motion of the plane
Answer: 3
Q12. At time \(\mathrm{t}=0\), a material is composed of two radioactive atoms A and B, where \(N_{A}(0)=2 N_{B}(0)\). The decay constant of both kind of radioactive atoms is \(\lambda\). However, A disintegrates to B and B disintegrates to \(\mathrm{C}\). Which of the following figures represents the evolution of \(\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{B}}(\mathrm{t}) / \mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{B}}(0)\) with respect to time \(\mathrm{t}\) ?
\(
\left[\begin{array}{l}
\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{A}}(0)=\text { No. of } \mathrm{A} \text { atoms at } \mathrm{t}=0 \\
\mathrm{~N}_{\mathrm{B}}(0)=\text { No. of } \mathrm{B} \text { atoms at } \mathrm{t}=0
\end{array}\right]
\)
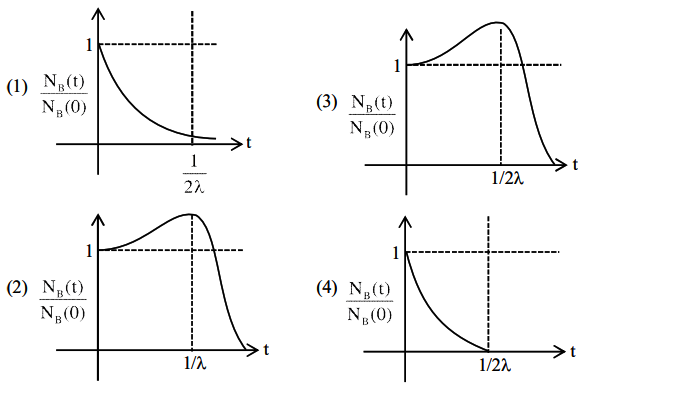
Answer: 3
Q13. A transmitting antenna at top of a tower has a height of 50 m and the height of receiving antenna is 80 m. What is the range of communication for the Line of Sight (LoS) mode?
[Use radius of earth = 6400 km]
(1) 45.5 km
(2) 80.2 km
(3) 144.1 km
(4) 57.28 km
Answer: 4
Q14. A refrigerator consumes an average \(35 \mathrm{~W}\) power to operate between temperature \(-10^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) to \(25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\). If there is no loss of energy then how much average heat per second does it transfer?
(1) \(263 \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{s}\)
(2) \(298 \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{s}\)
(3) \(350 \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{s}\)
(4) \(35 \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{s}\)
Answer: 1
Q15. An electric bulb of 500 watt at 100 volt is used in a circuit having a 200 V supply. Calculate the resistance R to be connected in series with the bulb so that the power delivered by the bulb is 500 W.
(1) 20 Ω
(2) 30 Ω
(3) 5 Ω
(4) 10 Ω
Answer: 1
Q16. Four NOR gates are connected as shown in the figure. The truth table for the given figure is:
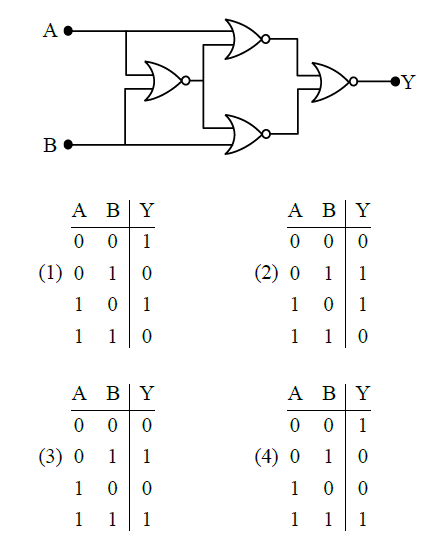
Answer: 4
Q17. Match List–I with List-II.
List-I List-II
(a) Magnetic Induction (i) \( \mathrm{ML}^{2} \mathrm{~T}^{-2} \mathrm{~A}^{-1}\\\)
(b) Magnetic Flux (ii) \( \mathrm{M}^{0} \mathrm{~L}^{-1} \mathrm{~A}\\\)
(c) Magnetic Permeability (iii) \( \mathrm{MT}^{-2} \mathrm{~A}^{-1}\\\)
(d) Magnetization (iv) \( \mathrm{ML}\mathrm{~T}^{-2} \mathrm{~A}^{-2}\\\)
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
(1) (a)-(ii), (b)-(iv), (c)-(i), (d)-(iii)
(2) (a)-(ii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(iii)
(3) (a)-(iii), (b)-(ii), (c)-(iv), (d)-(i)
(4) (a)-(iii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(ii)
Answer: 4
Q18. In the given circuit the \(\mathrm{AC}\) source has \(\omega=100 \mathrm{rad} \mathrm{s}^{-1}\). Considering the inductor and capacitor to be ideal, what will be the current I flowing through the circuit?
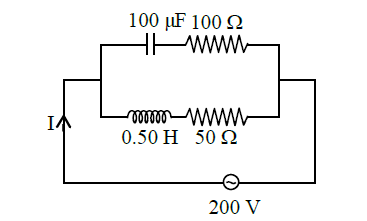
(1) \(5.9 \mathrm{~A}\)
(2) \(3.16 \mathrm{~A}\)
(3) \(0.94 \mathrm{~A}\)
(4) \(6 \mathrm{~A}\)
Answer: 2
Solution:
\(\begin{aligned}&Z_{\mathrm{C}}=\sqrt{\left(\frac{1}{\omega \mathrm{C}}\right)^{2}+\mathrm{R}^{2}} \\
&=\sqrt{\left(\frac{1}{100 \times 100 \times 10^{-6}}\right)^{2}+100^{2}} \\
&\mathrm{Z}_{\mathrm{C}}=\sqrt{(100)^{2}+(100)^{2}} \\
&=100 \sqrt{2} \\
&\mathrm{Z}_{\mathrm{L}}=\sqrt{(\omega \mathrm{L})^{2}+\mathrm{R}^{2}} \\
&\sqrt{(100 \times 0.5)^{2}+50^{2}} \\
&=\sqrt{10}=\sqrt{2+8} \\
&=50 \sqrt{2} \\
&\mathrm{i}_{\mathrm{C}}=\frac{200}{\mathrm{z}_{\mathrm{C}}}=\frac{200}{100 \sqrt{2}}=\sqrt{2} \\
&\mathrm{i}_{\mathrm{L}}=\frac{200}{\mathrm{z}_{\mathrm{L}}}=\frac{200}{50 \sqrt{2}}=2 \sqrt{2} \\
&\cos \phi_{1}=\frac{100}{10 \sqrt{2}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \Rightarrow \phi_{1}=45^{\circ} \\
&\cos \phi_{2}=\frac{50}{50 \sqrt{2}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \Rightarrow \phi_{\mathrm{2}}=45^{\circ}&\\&I=\sqrt{I_{C}^{2}+I_{L}^{2}} \\
&=\sqrt{2+8} \\
&=\sqrt{10} \\
&I=3.16 \mathrm{~A}
\end{aligned}
\)
Q19. If the length of the pendulum in the pendulum clock increases by 0.1%, then the error in time per day is:
(1) 86.4 s
(2) 4.32 s
(3) 43.2 s
(4) 8.64 s
Answer: 3
Solution:
\(\begin{aligned}&\mathrm{T}=2 \pi \sqrt{\frac{\ell}{\mathrm{g}}} \\
&\frac{\Delta \mathrm{T}}{\mathrm{T}}=\frac{1}{2} \frac{\Delta \ell}{\ell} \\
&\Delta \mathrm{T}=\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{0.1}{100} \times 24 \times 3600 \\
&\Delta \mathrm{T}=43.2
\end{aligned}\)
Q20. Two blocks of masses \(3 \mathrm{~kg}\) and \(5 \mathrm{~kg}\) are connected by a metal wire going over a smooth pulley. The breaking stress of the metal is \(\frac{24}{\pi} \times 10^{2} \mathrm{Nm}^{-2}\).
What is the minimum radius of the wire?
\(\left(\right.\) Take \(\left.\mathrm{g}=10 \mathrm{~ms}^{-2}\right)\)
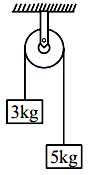
(1) 125 cm
(2) 1250 cm
(3) 12.5 cm
(4) 1.25 cm
Answer: 3