14.1 Respiratory Organs
Mechanisms of breathing vary among different groups of animals depending mainly on their habitats and levels of organisation. Lower invertebrates like sponges, coelenterates, flatworms, etc., exchange \(\mathrm{O}_2\) with \(\mathrm{CO}_2\) by simple diffusion over their entire body surface. Earthworms use their moist cuticle and insects have a network of tubes (tracheal tubes) to transport atmospheric air within the body. Special vascularised structures called gills (branchial respiration) are used by most of the aquatic arthropods and molluscs whereas vascularised bags called lungs (pulmonary respiration) are used by the terrestrial forms for the exchange of gases. Among vertebrates, fishes use gills whereas amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals respire through lungs. Amphibians like frogs can respire through their moist skin (cutaneous respiration) also.
Human Respiratory System
We have a pair of external nostrils opening out above the upper lips. It leads to a nasal chamber through the nasal passage. The nasal chamber opens into the pharynx, a portion of which is the common passage for food and air. The pharynx opens through the larynx region into the trachea. Larynx is a cartilaginous box which helps in sound production and hence called the sound box. During swallowing glottis can be covered by a thin elastic cartilaginous flap called epiglottis to prevent the entry of food into the larynx. Trachea is a straight tube extending up to the mid-thoracic cavity, which divides at the level of 5 th thoracic vertebra into a right and left primary bronchi. Each bronchi undergoes repeated divisions to form the secondary and tertiary bronchi and bronchioles ending up in very thin terminal bronchioles. The tracheae, primary, secondary and tertiary bronchi, and initial bronchioles are supported by incomplete cartilaginous rings. Each terminal bronchiole gives rise to a number of very thin, irregular-walled and vascularised bag-like structures called alveoli. The branching network of bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli comprise the lungs (Figure 14.1). We have two lungs which are covered by a double layered pleura, with pleural fluid between them. It reduces friction on the lung-surface. The outer pleural membrane is in close contact with the thoracic lining whereas the inner pleural membrane is in contact with the lung surface. The part starting with the external nostrils up to the terminal bronchioles constitute the conducting part whereas the alveoli and their ducts form the respiratory or exchange part of the respiratory system. The conducting part transports the atmospheric air to the alveoli, clears it from foreign particles, humidifies and also brings the air to body temperature. Exchange part is the site of actual diffusion of \(\mathrm{O}_2\) and \(\mathrm{CO}_2\) between blood and atmospheric air.
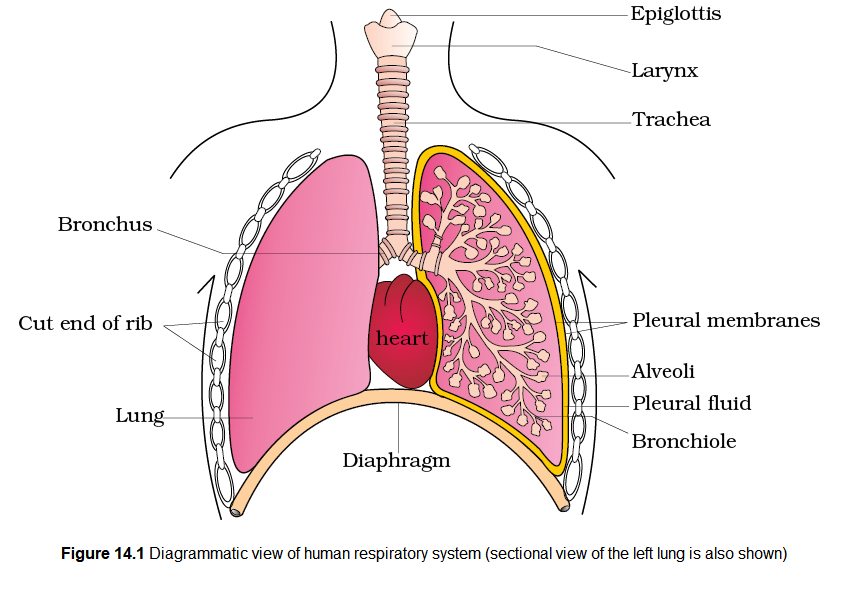
The lungs are situated in the thoracic chamber which is anatomically an air-tight chamber. The thoracic chamber is formed dorsally by the vertebral column, ventrally by the sternum, laterally by the ribs and on the lower side by the dome-shaped diaphragm. The anatomical setup of lungs in thorax is such that any change in the volume of the thoracic cavity will be reflected in the lung (pulmonary) cavity. Such an arrangement is essential for breathing, as we cannot directly alter the pulmonary volume.
Respiration involves the following steps:
- Breathing or pulmonary ventilation by which atmospheric air is drawn in and \(\mathrm{CO}_2\) rich alveolar air is released out.
- Diffusion of gases \(\left(\mathrm{O}_2\right.\) and \(\left.\mathrm{CO}_2\right)\) across alveolar membrane.
- Transport of gases by the blood.
- Diffusion of \(\mathrm{O}_2\) and \(\mathrm{CO}_2\) between blood and tissues.
- Utilisation of \(\mathrm{O}_2\) by the cells for catabolic reactions and resultant release of \(\mathrm{CO}_2\) (cellular respiration as dealt in the Chapter 12).