Set-I: Past Entrance Papers
Quiz Summary
0 of 76 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 76 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 76
1. Question
Match List-I with List-II [NEET 2021]
\(
\begin{array}{lll}
\hline {\text { List-I }} & \text { List-II } \\
\hline \text { A. Cristae } & \text { 1. } \begin{array}{l} \text { Primary constriction in chromosome } \\
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { B. Thylakoids } & \text { 2. Disc-shaped sacs in Golgi apparatus } \\
\hline \text { C. Centromere } & \text { 3. } \begin{array}{l}
\text { Infoldings in mitochondria } \\
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { D. Cisternae } & \text { 4. Flattened membranous sacs in stoma of plastids} \\
& \begin{array}{l}
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The inner membrane of mitochondria forms a number of infolding of the cristae.
These dramatically increases the surface area available for hosting the enzymes responsible for cellular respiration.The lamellae, in chloroplast after separation from the inner membrane, usually take the form of closed, flattened, ovoid sacs, the thylakoids, which lie closely packed in piles, the grana.
Primary constriction in the chromosome forms the centromere. Cisternae are a series of flattened, curved membrane saccules of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. -
Question 2 of 76
2. Question
Which of the following is an incorrect statement? [NEET 2021]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Mature sieve tube elements contain structural phloem-specific proteins (P-proteins), mitochondria, ER, and sieve elements plastids but not the conspicuous nucleus.
-
Question 3 of 76
3. Question
The organelles that are included in the endomembrane system are [NEET 2021]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) The endomembrane system is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package and transport protein and lipids.
The endomembrane system include-Nuclear envelope, Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, Lysosomes, Vacuoles, and Plasma membrane.
-
Question 4 of 76
4. Question
When the centromere is situated in the middle of two equal arms of chromosomes, the chromosome is referred as [NEET 2021]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Metacentric chromosomes have the centromere in the center, such that both
sections are of equal length, e.g. human chromosomes 1 and 3 . Other options can be explained as :
Telocentric chromosomes have the centromere at the very end of the chromosome.
Sub-metacentric chromosomes have the centromere slightly offset from the center leading to a slight asymmetry in the length of the two sections.
Acrocentric chromosomes have centromere which is severely offset from the center leading to one very long and one very short section. -
Question 5 of 76
5. Question
Inclusion bodies of blue-green,purple and green photosynthetic bacteria are [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Gas vacuoles are the inclusion bodies in many aquatic prokaryotes like blue-green, purple, and green photosynthetic bacteria. These are generally small, hollow cylindrical
structure that facilitates air permeability. Gas vacuoles are membrane-bound inclusion bodies that contain an array of substructures referred to as gas vesicles. The membrane of gas vacuoles is rigid, impermeable to water, and freely permeable to all gases. -
Question 6 of 76
6. Question
The biosynthesis of ribosomal RNA occurs in [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) The biosynthesis of ribosomal RNA occurs in the nucleolus of the nucleus. It helps the nucleus of the cell to control cell metabolism and other activities. The other two types of RNA, i.e. mRNA and tRNA are also synthesised here.
-
Question 7 of 76
7. Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option from the codes given below. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { a } & \text { Smooth endoplasmic reticulum } & \text { i } & \text { Protein synthesis } \\
\hline \text { b } & \text { Rough endoplasmic reticulum } & \text { ii } & \text { Lipid synthesis } \\
\hline \text { c } & \text { Golgi complex } & \text { iii } & \text { Glycosylation } \\
\hline \text { d } & \text { Centriole } & \text { iv } & \text { Spindle formation } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Codes:CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Option (a) is the correct match, which is as follows
Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum is the major site for the synthesis of lipid. Rough Endoplasmic reticulum is actively involved in protein synthesis and secretion. Golgi complex is an important site of the formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids, i.e. glycosylation. Centrioles help in spindle formation in the cell. -
Question 8 of 76
8. Question
Which of the following elements helps in maintaining the structure of ribosomes? [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Each ribosome consists of two unequal subunits, a larger and a smaller one. \(\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}\) ions are required for binding the two subunits. Below \(0.0001 \mathrm{M} \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}\), the two subunits dissociate while above this strength, the two subunits form the dimer.
-
Question 9 of 76
9. Question
Which is the important site of the formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids in eukaryotic cells? [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Golgi bodies are the site of the formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids in eukaryotic cells. Glycoproteins are simply proteins with a sugar attached to them. The sugars can be attached to a protein in two locations in the cell, the endoplasmic reticulum, which produces \(\mathrm{N}\)-linked sugars, and the Golgi apparatus, which produces 0 -linked sugars. Glycolipids are components of cellular membranes comprised of a hydrophobic lipid tail and one or more hydrophilic sugar groups linked by a glycosidic bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane.
-
Question 10 of 76
10. Question
Which of the following statements about inclusion bodies is incorrect? [NEET 2020]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Inclusion bodies are nuclear or cytoplasmic aggregates which are stainable substances, usually proteins, and formed due to viral multiplication or genetic disorders in human beings these bodies are either intracellular or extracellular abnormalities and they are specific to certain diseases. These are not involved in the ingestion of food particles.
-
Question 11 of 76
11. Question
What will be the direction of flow of water when a plant cell is placed in a hypotonic solution? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The behaviour of the plant cells with regard to water movement depends on the surrounding solution. When a plant cell is placed in hypotonic solution then the water will flow into the cell and the cell will swell.
-
Question 12 of 76
12. Question
Which of the following organic compounds is the main constituent of lecithin? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Phospholipids are the main constituents of lecithin. These molecules are composed of choline and inositol. It is found in all living cells as a major component of the cell membrane.
-
Question 13 of 76
13. Question
The concept of ‘Omnis cellula-e-cellula’ regarding cell division was first proposed by [NEET (National) 2019]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Rudolf Virchow proposed the concept of “Omnis cellula-e-cellula”, i.e. all cells are derived from the pre-existing cells.
-
Question 14 of 76
14. Question
Match column I with column II. [NEET Odisha 2019]
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { (a) Golgi apparatus } & \text { (i) Synthesis of protein } \\
\hline \text { (b) Lysosomes } & \text { (ii) Trap waste and excretory products } \\
\hline \text { (c) Vacuoles } & \text { (iii) Formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids } \\
\hline \text { (d) Ribosomes } & \text { (iv) Digesting biomolecules } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Choose the right match from the options given below:CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 15 of 76
15. Question
Which of the following cell organelles is present in the highest number in secretory cells? [NEET Odisha) 2019]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) The important function of Golgi apparatus is to process, package, and transport the materials for secretion. Therefore secretory cells have Golgi apparatus in highest number.
-
Question 16 of 76
16. Question
Non-membranous nucleoplasmic structures in the nucleus are the site for active synthesis of [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Non-membranous nucleoplasmic structure in the nucleus of the cell are the site for active synthesis of rRNA. These structures are called the nucleolus. Larger and more numerous nucleoli are present in the cell actively carrying out protein synthesis.
-
Question 17 of 76
17. Question
Which of the following pairs of organelles does not contain DNA? [NEET (National) 2019]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Lysosomes and vacuoles do not contain DNA. Lysosomes are single membrane-bound small vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes. Vacuoles are large membranous sac found in the cytoplasm. These contain substances that are not essentially useful for the cell-like water, sap, excretory products, and other materials. Chloroplast and
mitochondria are semi-autonomous organelles because they contain their own DNA and are believed to be prokaryotic symbionts. -
Question 18 of 76
18. Question
Which of the following statements is not correct? [NEET (National) 2019]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The statement”lysosomes are formed by the process of packaging in the endoplasmic reticulum” is incorrect. The correct form of the statement is ‘lysosomes are actually formed by the budding off from the trans-face of Golgi bodies. These membrane-bound structures contain hydrolytic enzymes whose precursors are synthesised by the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Rest statements are correct.
-
Question 19 of 76
19. Question
Which of the following statements regarding mitochondria is incorrect? [NEET (National) 2019]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) The statement “enzymes of electron transport are embedded in the outer membrane” is incorrect. The correct form of statement is
Enzymes of electron transport are embedded in the inner membrane of mitochondria. An electron transport chain is a series of coenzymes and cytochromes that take part in the passage of electrons from a chemical to its ultimate acceptor. Rest statements are correct.
-
Question 20 of 76
20. Question
Which one of the following elements is responsible for maintaining turgor in cells? [NEET 2018]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Among the given elements, potassium \(\left(\mathrm{K}^{+}\right)\)is responsible for maintaining turgor pressure in cell because it regulates the proton pumps involved in opening and closing of stomata.
Magnesium \(\left(\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}\right)\) is a constituent of chlorophyll pigment which helps in photosynthesis in green plants. Calcium \(\left(\mathrm{Ca}^{2+}\right)\) provides selective permeability to the cell membrane. All of these, i.e. \(\mathrm{K}^{+}, \mathrm{Ca}^{2+}\) and \(\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}\) are essential elements.
Sodium ( \(\mathrm{Na}^{+}\)) is involved in membrane permeability. It is a non-essential element. -
Question 21 of 76
21. Question
Which among the following is not a prokaryote? [NEET 2018]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Among the given options, Saccharomyces is a fungus, i.e. it is a eukaryote. They possess a well-defined nucleus and other cell organelles.
Nosto \(c\) and Oscillatioria are cyanobacteria while Mycobacterium is a true bacterium. Cyanobacteria and bacteria both are prokaryotes as they lack a well-defined nucleus and other cell organelles. -
Question 22 of 76
22. Question
The Golgi complex participates in [NEET 2018]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Golgi complex participates in the formation of secretory vesicles. It is a cytoplasmic structure found in eukaryotic cells. It is made up of four parts; cisternae, tubules, vesicles, and vacuoles.
The forming face or cisternae receives vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum. Their contents pass through various cisternae with the help of coated vesicles and intercisternal connectives.
They ultimately reach the maturing face where they are budded off as coated
secretory or Golgian vesicles or vacuoles.
In bacteria, respiration occurs with the help of mesosomes. The breakdown of fatty acid occurs in peroxisomes and mitochondria. Activation of amino acid is an important step of protein synthesis and it occurs in the cytoplasm. In this process, amino acids get attached to tRNA molecules. -
Question 23 of 76
23. Question
Which of the following is true for nucleolus? [NEET 2018]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Nucleolus is a naked, round, or slightly irregular structure in the nucleus. It lacks a membrane and its contents are in direct contact with the nucleoplasm. It is a site for active ribosomal RNA(rRNA) synthesis. Microtubules take part in the spindle formation. Mitochondria, vacuoles, and plastids, etc. are membrane-bound structures. The dividing cells possess a large number of mitochondria.
-
Question 24 of 76
24. Question
Nissl bodies are mainly composed of [NEET 2018]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Nissl granules are found in the cell body of neurons. These granules are composed of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) that bears free ribosomes. The latter acts as the site of protein synthesis. These granules were named after its discoverer Franz Nissl.
-
Question 25 of 76
25. Question
Which one of the following events does not occur in the rough endoplasmic reticulum? [NEET 2018]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Phospholipid synthesis does not occur in RER. It occurs inside the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER). A signal peptide is a short peptide present at the \(N\)-terminus of the newly synthesised proteins. It targets them to the ER and is then cleaved off. RER synthesises proteins. It bears enzymes for modifying polypeptides synthesised by attached ribosomes, e.g. glycosylation.
-
Question 26 of 76
26. Question
Many ribosomes may associate with a single mRNA to form multiple copies of a polypeptide simultaneously. Such strings of ribosomes are termed as [NEET 2018]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Polysome is a string of ribosomes associated with a single mRNA. Polysome helps to produce a number of copies of the same polypeptide. Nucleosome is the unit of eukaryotic DNA that consists of a DNA segment wrapped around a core of eight
histone proteins. Nucleosome chain gives a ‘beads on string’ appearance under an electron microscope. Plastidome refers to all the plastids of a cell that work as a functional unit. -
Question 27 of 76
27. Question
Which of the following cell organelles is responsible for extracting energy from carbohydrates to form ATP? [NEET 2017]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Mitochondria are miniature biochemical factories where foodstuffs or respiratory substrates are completely oxidised to carbon dioxide and water. The energy liberated in the process is initially stored in the form of reduced coenzymes and reduced prosthetic groups. The latter soon undergo oxidation and form energy-rich ATP. ATP comes out of mitochondria and helps perform various energy-requiring processes of the cell-like muscle contraction, nerve impulse conduction, biosynthesis, membrane transport, cell division, movement, etc. Because of the formation of ATP, the mitochondria are called the powerhouses of the cell.
-
Question 28 of 76
28. Question
Which of the following components provides sticky character to the bacterial cell? [NEET 2017]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Glycocalyx is the outer most mucilage layer of the cell envelope. It gives sticky
character to the bacterial cell. -
Question 29 of 76
29. Question
Select the mismatch. [NEET-II 2016]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Large central vacuole is the characteristic of the plant cell, not an animal cell which may have many small scattered vacuoles.
-
Question 30 of 76
30. Question
Select the wrong statement. [NEET-II 2016]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Pili and fimbriae are bacterial appendages that are not involved in locomotion. Actually, pili are long fewer and thicker tubular outgrowths which develop in response to \(\mathrm{F}^{+}\) or fertility factor in Gram-negative bacteria. Being long they are helpful in attaching to the recipient cell and forming a conjugation tube. Fimbriae are small bristle-like fibres sprouting from cell surfaces in large numbers. There are 300-400 of them per cell. They are involved in attaching bacteria to solid surfaces.
-
Question 31 of 76
31. Question
A cell organelle containing hydrolytic enzymes is [NEET-II 2016]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Lysosomes are small vesicles which are bounded by a single membrane and contain hydrolytic enzymes in the form of minute crystalline or semicrystalline granules of \(5-8 \mathrm{~nm}\). About 50 enzymes have been recorded to occur in them. All the enzymes do not occur in the same lysosome but there are different sets of enzymes in different types of lysosomes. The important enzymes are acid phosphatases, sulphatases, proteases, peptidases, nucleases, lipases, and carbohydrases. They are also called acid hydrolases because these digestive enzymes usually function in an acidic medium or \(\mathrm{pH}\) of 4-5.
-
Question 32 of 76
32. Question
Mitochondria and chloroplast are [NEET-I 2016]
(A) semi-autonomous organelles
(B) formed by division of pre-existing organelles and they contain DNA but lack protein synthesising machinery.
Which one of the following options is correct?CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Both mitochondria and chloroplast are semiautonomous organelles. They have their own DNA which produces its own, \(m\) RNA, \(t\) RNA, and \(r\) RNA. These organelles also possess their own ribosomes and hence are able to synthesise some of their proteins.
-
Question 33 of 76
33. Question
Microtubules are the constituents of [NEET-I 2016]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Microtubules are unbranched hollow submicroscopic tubules of protein tubulin which develop on specific nucleating regions. It can undergo quick growth or dissolution at their ends by assembly or disassembly of monomers. They are present in the cytoplasm as well as in specialised structures like centrioles, basal bodies, cilia or flagella, sensory hair, an equatorial ring of thrombocytes, spindle apparatus, chromosome fibres, nerve processes, sperm tails, axostyle of parasitic flagellates, fibre system of Stentor, cyto-pharyngeal basket of Nassula, etc.
-
Question 34 of 76
34. Question
Which one of the following cell organelles is enclosed by a single membrane? [NEET-I 2016]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Lysosomes are small vesicles bounded by a single membrane and contain hydrolytic enzymes. Nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts are double membrane-bound cell organelles.
-
Question 35 of 76
35. Question
Water-soluble pigments found in plant cell vacuoles are [NEET-I 2016]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Anthocyanins are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that may appear red, purple, or blue depending on \(\mathrm{pH}\). It is impermeable to the cell membranes of plants and can leak out only when the membrane is damaged or dead.
-
Question 36 of 76
36. Question
Select the mismatch. [NEET-II 2016]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Animal cells do not have a large central vacuole. Instead, these have 2-3 small vacuoles. The presence of such large central vacuoles is the characteristic feature of plant cells.
Concept Enhancer The presence of a large vacuole is an indication of irregular growth, i.e. growth in the cell membrane is synchronised with growth in protoplasmic content.
-
Question 37 of 76
37. Question
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Column – I } & & \text { Column – II } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & \text { Thylakoids } & \text { (i) } & \text { Disc-shaped sacs in Golgi apparatus } \\
\hline \text { (b) } & \text { Cristae } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Condensed structure of DNA } \\
\hline \text { (c) } & \text { Cisternae } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Flat membranous sacs in stroma } \\
\hline \text { (d) } & \text { Chromatin } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Infoldings in mitochondria } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 38 of 76
38. Question
Which of the following structures is not found in a prokaryotic cell? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) A prokaryotic cell is characterised by the absence of an organised nucleus and membrane-bound cell organelles. DNA is naked i.e., without a nuclear envelope, and lies variously coiled in the cytoplasm. It is commonly called nucleoid or genophore. Mesosomes, plasma membrane, and \(70 \mathrm{~S}\) ribosomes are present in a prokaryotic cell.
-
Question 39 of 76
39. Question
Cellular organelles with membranes are [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Endoplasmic reticulum, nuclei, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles whereas ribosomes are naked ribonucleoprotein protoplasmic particles. Chromosomes are the hereditary particles present in the nucleus.
-
Question 40 of 76
40. Question
Which of the following are not membrane-bound? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Endoplasmic reticulum, nuclei, Lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria are membrane-bound cell organelles whereas ribosomes are naked ribonucleoprotein protoplasmic particles. Chromosomes are the hereditary particles present in the nucleus.
-
Question 41 of 76
41. Question
DNA is not present in [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Ribosome is a small spherical body within a living cell that is the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes consist of two subunits, one large and one small, each of which comprises some RNA (called ribosomal RNA) and protein. They do not have any DNA.
-
Question 42 of 76
42. Question
Nuclear envelope is a derivative of [CBSE AIPMT 2013]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Recent developments have shown that nuclear membrane is derived from the rough endoplasmic reticulum. During cell division, the nuclear membrane is disintegrated. The nuclear envelope transmembrane proteins are absorbed in the RER. Once the division is completed, RER reassembles the nuclear envelope.
-
Question 43 of 76
43. Question
The structures that are formed by stacking of organised flattened membranous sacs in the chloroplasts are [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) A chloroplast is a vesicle, bound by an envelope of two unit membranes and filled with a fluid matrix called the stroma. The lamellae, after separation from the inner membrane, usually take the form of closed, flattened, ovoid sacs, the thylakoids, which lie closely packed in piles, the grana.
-
Question 44 of 76
44. Question
Select the correct matching in the following pairs. [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is a system of smooth membranes (i.e., membranes not having ribosomes) within the cytoplasm of plant and animal cells. It forms a link between the cell and nuclear membranes. It is the site of important metabolic reactions, including phospholipid and fatty acid synthesis. In animal cells, lipid-like steroidal hormones are also synthesized.
-
Question 45 of 76
45. Question
The chromosomes in which centromere is situated close to one end are [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Centromere is a part of a chromosome that attaches to the spindle during cell division. A chromosome with the centromere close to one end is acrocentric.
-
Question 46 of 76
46. Question
Which one of the following is not an inclusion body found in prokaryotes? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Polysome is not an inclusion body. It is an aggregation of ribosomes formed under conditions of high concentration of magnesium. An inclusion body is any of various particulate structures, usually, proteins, formed after viral infections in a prokaryotic or eukaryotic cell.
-
Question 47 of 76
47. Question
The structures that help some bacteria to attach to rocks and/or host tissues are [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Fmbriae are small bristle-like fibres sprouting out of the cell. In some bacteria, they are known to help in attachment to rocks in streams and also to the host tissues.
-
Question 48 of 76
48. Question
A protoplast is a cell [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) A protoplast is a cell without a cell wall. It is a plant, bacterial or fungal cell that had its cell wall completely or partially removed using either mechanical or enzymatic means.
-
Question 49 of 76
49. Question
The solid linear cytoskeletal elements having a diameter of \(6 \mathrm{~nm}\) and made up of a single type of monomer are known as [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Microtubules are hollow microscopic tubular structures with an external diameter of \(24 \mathrm{~nm}\) and of variable length. They are composed of tubulin. Intermediate filaments are the numerous microscopic protein fibres of about \(10 \mathrm{~nm}\) thickness that form part of the cytoskeleton. They are made up of a variety of proteins e.g. keratin in nails.
-
Question 50 of 76
50. Question
The osmotic expansion of a cell kept in water is chiefly regulated by [NEET 2023]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Vacuoles are non-cytoplasmic areas present inside the cytoplasm and separated from the latter by tonoplast. They are believed to be formed by expansion and pinching off from ER. There occurs a large central vacuole and many small vacuoles in plant cells. They play a major role in the osmotic expansion of cell.
-
Question 51 of 76
51. Question
Match the following and select the correct answer. [NEET 2024]
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { (A) Centriole } & \text { (i) } \begin{array}{l}
\text { Infoldings in } \\
\text { mitochondria }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { (B) Chlorophyll } & \text { (ii) Thylakoids } \\
\hline \text { (C) Cristae } & \text { (iii) Nucleic acids } \\
\hline \text { (D) Ribozymes } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { (iv) Basal body cilia } \\
\text { or flagella }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 52 of 76
52. Question
The Golgi complex plays a major role [NEET 2022]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Post-translational modification (PTM) is a step in protein biosynthesis. Proteins are created on ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains. These polypeptide chains undergo PTM, such as folding, cutting, and other processes, before becoming the mature protein product. Proteins synthesized by the rough endoplasmic reticulum and lipids synthesized by the smooth endoplasmic reticulum reach the cisternae of the Golgi apparatus. Here, they combine with carbohydrates to form glycoproteins and glycolipids. This process is called glycosylation.
-
Question 53 of 76
53. Question
Which one of the following organelle in the figure correctly matches with its function? [NEET 2024]
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) The given figure shows endoplasmic reticulum bearing ribosomes on their surface. It is called rough endoplasmic reticulum or RER. RER is actively involved in protein synthesis and secretion.
-
Question 54 of 76
54. Question
A major site for synthesis of lipids is [NEET 2023]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) is the major site for synthesis of lipids. RER is actively involved in protein synthesis and secretion. The nucleolus is the site for active ribosomal RNA synthesis. Simplest is the system of interconnected protoplast through, which water movement occurs.
-
Question 55 of 76
55. Question
The term ‘glycocalyx’ is used for [Karnataka NEET 2013]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Glycocalyx is a sticky, gelatinous material that collects outside the cell wall of bacteria to form an additional surface layer. When this layer is firmly attached to the surface of the cell, it is called a capsule. If it is loosely distributed around the cell, the glycocalyx is called a slime layer.
-
Question 56 of 76
56. Question
Which of the following types of plastid does not contain stored food material? [NEET 2023]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Chromoplasts are yellow or reddish in colour because of the presence of carotenoid pigments. They do not contain stored food material. Chromoplasts are formed either from leucoplasts or chloroplasts. Chromoplasts provide colour to many flowers for attracting pollinating insects. They provide bright red or orange colour to fruits for attracting animals for dispersal.
-
Question 57 of 76
57. Question
Which of the following best illustrates “feedback” in development? [Karnataka NEET 2013]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) As tissue X develops it secretes something that induces tissue Y to develop indicating a positive feedback mechanism.
-
Question 58 of 76
58. Question
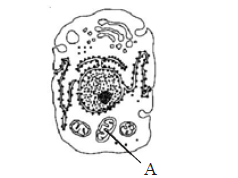
Select the alternative giving the correct identification and function of the organelle ‘A’ in the diagram. [Karnataka NEET 2013]
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Mitochondria are small spheres or short rod-like structures. It is a vesicle bounded by an envelope of two unit membranes and filled with a fluid matrix. Mitochondria are the main sites of cell respiration. They bring about complete oxidation of foodstuffs or respiratory substrates into carbon dioxide and water and form energy-rich ATP which helps in performing various energy-requiring processes. On this account, mitochondria are often described as the powerhouse or storage batteries or ATP mills of the cell.
-
Question 59 of 76
59. Question
Select the correct statement from the following regarding cell membrane. [NEET 2022]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) According to the fluid mosaic model of cell membrane structure proposed by Singer and Nicolson (1972) plasma membrane contains about \(50-60 \%\) proteins and \(50-40 \%\) lipids. Lipids form a bilayer with hydrophilic heads pointing outwards. The cell membrane allows the transport of some molecules by passive transport e.g., water, and neutral solutes while some are transported actively e.g., \(\mathrm{Na}^{+} / \mathrm{K}^{+}\)pump.
-
Question 60 of 76
60. Question
What is true about ribosomes? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Ribosome is a small spherical body within a living cell that is the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes consist of two subunits, one large and one small, each of which comprises a type of RNA (called ribosomal RNA) and protein. They are found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. In prokaryotes \(70 \mathrm{~S}\) ribosomes and in eukaryotes \(80 \mathrm{~S}\) ribosomes are found where ‘S’ denotes Svedberg Unit.
-
Question 61 of 76
61. Question
Which one of the following does not differ in E.coli and Chlamydomonas? [NEET 2023]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) E.coli (bacteria) is a prokaryote while Chlamydomonas (algae) is a eukaryote. Ribosomes of both groups differ being \(70 \mathrm{~S}\) in prokaryotes and \(80 \mathrm{~S}\) in eukaryotes. Prokaryotic chromosomes lack histone protein, unlike eukaryotic ones. Cell wall organization also differs as bacterial cell wall is rich in muramic acid while algal cell wall is cellulosic. It is the cell membrane that has similar organization in both the groups.
-
Question 62 of 76
62. Question
Which one of the following cellular parts is correctly described? [NEET 2022]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Thylakoid are the flattened sac-like membranous structures that are stacked on top of one another to form the grana of plant chloroplast. Chlorophyll and other photosynthetic pigments are situated in the thylakoid membranes, which are the site for the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
-
Question 63 of 76
63. Question
Which one of the following structures is an organelle within an organelle? [NEET 2023]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Ribosomes occur in all living cells except mammalian erythrocytes or red blood corpuscles. Depending upon the place of their occurrence, ribosomes are of two types-cytoplasmic ribosomes and organelle ribosomes. The cytoplasmic ribosomes (cytoribosomes) may remain free in the cytoplasmic matrix or attached to the cytosolic surface of the endoplasmic reticulum with the help of special ribophorin or SRP protein. The organelle ribosomes are found in plastids (plastiribosomes) and mitochondria (mitoribosomes) Cytoplasmic ribosomes are of \(80 \mathrm{~S}\) type in eukaryotic cell whereas organelle ribosomes are of \(70 \mathrm{~S}\) type.
-
Question 64 of 76
64. Question
Ribosomal RNA is actively synthesised in [NEET 2024]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) In eukaryotes, the site of synthesis of most of the ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is the nucleolus. The nucleolar organiser contains many copies of ribosomal DNA (repetitive DNA). The RNA cistron of nucleolar DNA forms \(45 S\) precursor with the help of RNA polymerase. This 45 S RNA undergoes cleavage with the help of nucleases to give \(18 \mathrm{~S}, 28 \mathrm{~S}\), and 5.8S rRNA units. Out of different rRNAs, the \(5 S\) rRNA is not synthesised in the nucleolus. It is synthesised outside it.
-
Question 65 of 76
65. Question
Peptide synthesis inside a cell takes place in [NEET 2024]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Peptide synthesis inside a cell takes place in ribosome. Ribosomes are found in all cells and are involved in protein synthesis. The major constituents of ribosomes are RNA and proteins present in approximately equal amounts.
-
Question 66 of 76
66. Question
Important site for formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids is [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Eukaryotic cells contain a unique cluster of membrane vesicles known as Golgi apparatus. It principally performs the function of packaging materials. The newly synthesized proteins are handed over to the Golgi apparatus which is catalysed by the addition of carbohydrates, lipid, or sulphates moieties to the proteins. Golgi apparatus is the important site of formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
-
Question 67 of 76
67. Question
Which one of the following is not considered as a part of the endomembrane system? [Mains 2011]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) While each of the membranous organelles is distinct in terms of its structure and function, many of these are considered together as an endomembrane system because their functions are coordinated. The endomembrane system includes the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi complex, lysosomes, and vacuoles. Since the functions of the mitochondria, chloroplast, and peroxisomes are not coordinated with the above components, these are not considered part of the endomembrane system.
-
Question 68 of 76
68. Question
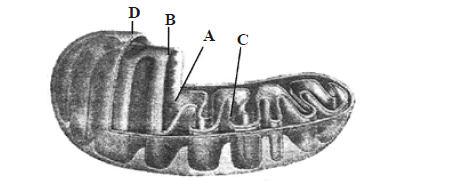
The figure below shows the structure of a mitochondrion with its four parts labelled A, B, C and D. Select the part correctly matched with its function. [Mains 2011]
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Each mitochondrion is a double membrane-bound structure with the outer membrane and the inner membrane dividing its lumen distinctly into two aqueous compartments, i.e., the outer compartment and the inner compartment. The inner compartment is called the matrix. The outer membrane forms the continuous limiting boundary of the organelle. The inner membrane forms a number of infoldings called the cristae towards the matrix. The cristae increase the surface area. The two membranes have their own specific enzymes associated with mitochondrial function.
-
Question 69 of 76
69. Question
Which one of the following organisms is not an example of eukaryotic cells? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) The bacterium E. coli is a prokaryote. It is a Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium. It is the most widely studied prokaryotic model organism.
-
Question 70 of 76
70. Question
Which one of the following also acts as a catalyst in a bacterial cell? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) \(23S\) rRNA in bacteria is the enzyme ribozyme for the formation of peptide bond. 23S rRNA is found in a large sub-unit (70S) of the ribosome of bacteria.
-
Question 71 of 76
71. Question
The plasma membrane consists mainly of [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Plasma membrane consists of lipids \((20-79 \%)\), proteins \((20-70 \%)\), carbohydrates (1-5\%) and water \((20 \%)\). Lipid molecules possess both hydrophobic and hydrophilic ends and are thus arranged in the form of the lipid bilayer. The most common lipid of the bilayer is phospholipid. Protein molecules occur at places both inside (intrinsic proteins) and on the outer side (extrinsic proteins) of the phospholipid bilayer.
-
Question 72 of 76
72. Question
The main area of various types of activities of a cell is [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Cytoplasm is a granular, crystallo-colloidal complex that forms the living protoplasm of a cell excluding its nucleus. It consists of proteins, nucleic acids, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals, waste metabolites, and all the organelles. It is the main area for various types of activities of a cell-like respiration, nutrition, storage, etc.
-
Question 73 of 76
73. Question
Which one of the following has its own DNA? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Mitochondrion is a structure within the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that carries out aerobic respiration. It is the site of the Krebs’ cycle and electron transport chain, and therefore the cell’s energy production. Mitochondria vary greatly in shape, size, and number but are typically oval or sausage-shaped and bounded by two membranes, the inner one being folded into finger-like projections (cristae); they contain their own DNA and 70S ribosomes.
-
Question 74 of 76
74. Question
Which one of the following structures between two adjacent cells is an effective transport pathway? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Plasmodesmata are fine cytoplasmic strands that connect the protoplasts of adjacent plant cells by passing through their cell walls. Plasmodesmata are cylindrical in shape (about 20-40 \(\mathrm{nm}\) in diameter) and are lined by the plasma membrane of the two adjacent cells. They permit the passage between cells of substances including ions, sugars, amino acids, and macromolecules.
-
Question 75 of 76
75. Question
An elaborate network of filamentous proteinaceous structures present in the cytoplasm which helps in the maintenance of cell shape is called [Mains 2010]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) The eukaryotic cell is composed of a network of protein fibres that is known as the cytoskeleton. It is responsible for the movement of organelles around the cytoplasm (organelles are attached to the cytoskeleton). This network of proteins consists of protein microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. So, the correct answer is ‘Cytoskeleton’.
-
Question 76 of 76
76. Question
Identify the components labelled A, B, C and D in the diagram below from the list (i) to (viii) given along with Components:
(i) Cristae of mitochondria
(ii) Inner membrane of mitochondria
(iii) Cytoplasm
(iv) Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
(v) Rough endoplasmic reticulum
(vi) Mitochondrial matrix
(vii) Cell vacuole
(viii) Nucleus
The correct components are: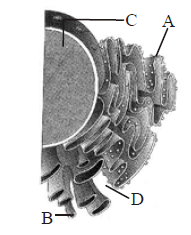 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
A – Rough endoplasmic reticulum
B- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
C- Nucleus
D – Cytoplasm