NCERT Exemplar MCQs
Quiz Summary
0 of 10 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 10 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 10
1. Question
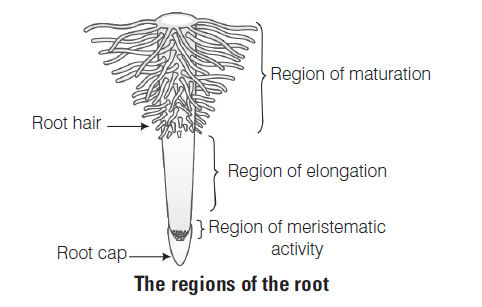
Rearrange the following zones as seen in the root in vertical section and choose the correct option.
A. Root hair zone
B. Zone of meristems
C. Rootcap zone
D. Zone of maturation
E. Zone of elongationCorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Root Cap Zone protective covering at the root apex, secretes mucilage to soften the hard soil for the growth of the root.
Zone of Meristem region of actively dividing densely packed cells resulting in root growth.
Zone of Elongation divided cells grow in size and elongate increasing the length of the root. They cannot divide further.
Root Hair Zone root hair arises and grows in this region, helps in water and mineral absorption from the soil.
Zone of Maturation the cells of the root at this region are fully differentiated and mature, performing different functions of the root.
-
Question 2 of 10
2. Question
In an inflorescence where flowers are borne laterally in an acropetal succession, the position of the youngest floral bud in the floral axis shall be
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) In an inflorescence where flowers are borne laterally in an acropetal succession the position of the youngest floral bud shall be distal.
-
Question 3 of 10
3. Question
The mature seeds of plants such as gram and peas, possess no endosperm, because
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Endosperm is a nourishing tissue of seed that provides nourishment to the developing embryo either before or after germination. In gram and peas, the endosperm gets used up at the time of development of the seed. So, the seed is non-endospermic, i.e., the endosperm is not present in the mature seed.
-
Question 4 of 10
4. Question
Roots developed from parts of the plant other than radicle are called
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Adventitious roots are those which develop from any part of the plant other than radicle.
-
Question 5 of 10
5. Question
Venation is a term used to describe the pattern of arrangement of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The arrangement of veins and veinlets on the lamina of the leaf is called venation. The veins are the part of the leaf which possess vascular tissues, i.e., xylem and phloem. They are meant for the conduction of water, minerals, and food to and from the leaf.
-
Question 6 of 10
6. Question
Endosperm, a product of double fertilization in angiosperms is absent in the seeds of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Orchid seed is a non-endospermic seed, i.e., endosperm is absent in it. Endosperm is a nourishing tissue present in the seed which nourishes the developing embryo. In orchid, seed endosperm is absent because it is used up during the time of seed development. Nourishment for germinating seeds is provided by the food material present in cotyledons. Rest of the options are examples of endospermic seeds.
-
Question 7 of 10
7. Question
Many pulses of daily use belong to one of the families below (tick the correct answer)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Fabaceae is a subfamily of Leguminosae which was earlier called Papilionoideae. Plants of this family are the source of pulses and edible oils. Pulses are rich in protein contents.
-
Question 8 of 10
8. Question
The placenta is attached to the developing seed near the
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) The placenta is attached to the developing seed near hilum. It is the scar located near the edge where the seed breaks from the stalk of the funiculus, i.e., connecting the seed with the fruit wall and placenta.
Rest of the options are incorrect as Testa is the outermost covering of a seed, micropyle is a small opening in the seed coat through which water enters the seed and chalaza is a tissue where nucellus and integument are joined. Nutrients from the plant travel through vascular tissue in the funiculus and outer integuments through the chalaza into the nucellus.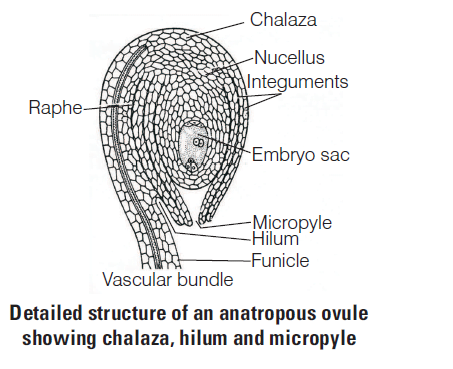
-
Question 9 of 10
9. Question
Which of the following plants is used to extract the blue dye?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) Indigo (blue dye) is obtained from the leaves of Indigofera tinctoria and \(\)I\(\). suffruticosa. The leaves contain a colourless chemical which on exposure to air turns bluish.
The other options are incorrect as
Trifolium is used as fodder.
Lupin is an ornamental plant.
Cassia is a shrub usually grown on the roadside as an ornamental plant. -
Question 10 of 10
10. Question
Match the following and choose the correct option
Column I Column IIA. Aleurone layer i. without fertilization
B. Parthenocarpic fruit ii. Nutrition
C. Ovule iii. Double fertilization
D. Endosperm iv. SeedCorrectIncorrectHint
(b) It is the correct sequence of the options in the two columns. Aleurone layer surrounds the tissue of the monocot seed and is morphologically and biochemically distinct from the seed. It is a proteinaceous layer (surrounding the endosperm and separating the embryo) that provides nutrition and helps in germination.
Parthenocarpic fruit is seedless fruit that develops without the fertilisation of egg cells present in the ovule of the plants.The ovule contains the female reproductive unit, i.e., embryo sac that develops into a seed after it is fertilised.
Endosperm is formed during the process of double fertilisation by the fusion of one male gamete with the two polar nuclei at the centre of the embryo sac.