Practice Corner MCQ
Quiz Summary
0 of 85 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 85 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 85
1. Question
Microbes are present in
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Microbes are omnipresent, found in soil, water, air, ice, inside bodies of human beings, animals and plants. Some are found in hot springs (upto \(80^{\circ} \mathrm{C}-100^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) ) and even in geysers (thermal vents).
-
Question 2 of 85
2. Question
Which of the following microbes is a proteinaceous infectious agent?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Prions are highly resistant glycoprotein particles which function as infectious agents. They can also act as catalyst converting normal protein into prion state. Prions are not affected by proteases, nucleases, temperature upto \(800^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\), UV radiations and formaldehyde.
-
Question 3 of 85
3. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { a } & \text { Rod shaped virus } & 1 & \text { Adenovirous } \\
\hline \text { b } & \text { Respiratory infections } & 2 & \text { Bacteriophage } \\
\hline \text { c } & \text { Proteinaceous infectious agents } & 3 & \text { Prions } \\
\hline \text { d } & \text { Bacterial virus } & 4 & \text { Tobacco mosaic virus } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 4 of 85
4. Question
Refer to the given figure and select the correct match.
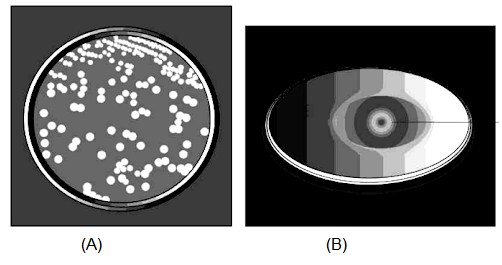 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : The given figures \((A)\) and \((B)\) respectively shows bacteria and fungal colonies growing in petri dishes.
-
Question 5 of 85
5. Question
The nutritive medium for growing bacteria and many fungi in laboratory is called
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 6 of 85
6. Question
The inoculum is added to the fresh milk in order to convert milk into curd, the term ‘inoculum’ here refers to
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 7 of 85
7. Question
Study the following statements regarding lactic acid bacteria (LAB) which are used to convert milk into curd.
(i) They produce acids that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins.
(ii) A small amount of curd added to the fresh milk as an inoculum contains millions of LAB, which at suitable temperature, multiply and convert milk into curd.
(iii) Conversion of milk into curd improves its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin \(B_{12}\).
(iv) LAB may result in acidity in the stomach of human beings.
Which of the given statements are correct?CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Microbes such as Lactobacillus and others commonly called lactic acid bacteria (LAB) grow in milk and convert it into curd. During growth, such bacteria produce acids (mainly lactic acid) that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins. A small amount of curd, known as starter, is added to the milk and kept at suitable temperature, where lactic acid bacteria multiply in millions and converts milk into curd that also improves its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin \(\mathrm{B}_{12}\). It also check growth of disease causing microbes in the stomach.
-
Question 8 of 85
8. Question
Read the following statements and select the incorrect one.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : The large holes in ‘Swiss cheese’ are due to production of large amount of \(\mathrm{CO}_2\) by a bacterium named Propionibacterium shermanii.
-
Question 9 of 85
9. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Besides curdling of milk, LAB also improve its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin \(\mathrm{B}_{12}\).
Statement 2 : LAB, when present in human stomach, check disease causing microbes.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Microbes such as Lactobacillus and others commonly called lactic acid bacteria (LAB) grow in milk and convert it into curd. During growth, such bacteria produce acids (mainly lactic acid) that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins. A small amount of curd, known as starter, is added to the milk and kept at suitable temperature, where lactic acid bacteria multiply in millions and converts milk into curd that also improves its nutritional quality by increasing vitamin \(\mathrm{B}_{12}\). It also check growth of disease causing microbes in the stomach.
-
Question 10 of 85
10. Question
Which one of the following combinations of organisms are responsible for the formation and flavour of yogurt?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Yogurt is produced by curdling milk with the help of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus. The temperature is maintained at about \(45^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\left(40^{\circ}-46^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\right)\) for about four to six hours. It has a flavour of lactic acid and acetaldehyde.
-
Question 11 of 85
11. Question
Which of the following food items is produced by the fermenting activity of microbes?
A. Idli
B. Dosa
C. Toddy
D. CheeseCorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Cheese is one of the oldest milk products prepared with the help of microbes. The curd is separated from liquid part or whey to form cheese. Dosa, Upma and Idli are fermented preparation of rice and black gram. The two are allowed to ferment for 3-12 hours with air borne Leuconostoc and Streptococcus species of bacteria. Toddy is a traditional drink of some parts of South India which is made by fermentation of sap of palms.
-
Question 12 of 85
12. Question
Study the following flow chart depicting the formation of curd from milk. Identify the missing parts X and Y.
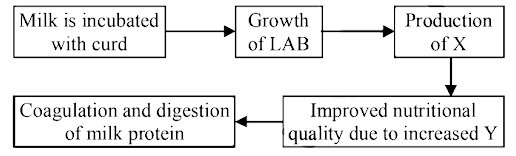 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 13 of 85
13. Question
Match different organisms in column I with their uses in column II and select the correct option from the given below codes.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|c|l|}
\hline & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Column I } \\
\text { (Organisms) }
\end{array} & & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Column II } \\
\text { (Uses) }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { A. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Lactobacillus } \\
\text { acidophilus }
\end{array} & \text { (i) } & \text { Formation of dough } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Saccharomyces } \\
\text { cerevisiae }
\end{array} & \text { (ii) } & \text { Single cell proteins } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Propionibacterium } \\
\text { shermanii }
\end{array} & \text { (iii) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Conversion of milk into } \\
\text { curd }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Spirulina } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Formation of Swiss cheese } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 14 of 85
14. Question
Which of the following organisms is used in the production of beverages?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, commonly known as brewer’s yeast, is used for fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices to produce ethanol (ethyl alcohol). Microbes (yeasts in particular) have been used for the production or Beverages, such as wine, beer, whisky, brandy and rum.
-
Question 15 of 85
15. Question
Identify the blank spaces A, B, C and D in the following table and select the correct option.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \begin{array}{c}
\text { Type of } \\
\text { microbe }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Scientific } \\
\text { name }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Commercial } \\
\text { product }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Bacterium } & \text { A } & \text { Lactic acid } \\
\hline \text { Fungus } & \text { B } & \text { Cyclosporin A } \\
\hline \text { Bacterium } & \text { Acetobacter aceti } & \text { C } \\
\hline \text { Fungus } & \text { Penicillium notatum } & \text { D } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 16 of 85
16. Question
Wine and beer are produced directly by fermentation whereas brandy and whisky require both fermentation and distillation. This is because
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 17 of 85
17. Question
The chemical substances produced by some microbes which can kill or retard the growth of other microbes are called
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Antibiotics are chemical substances secreted by certain microbes which can kill or inhibit the growth and development of harmful microbes. Most of them are produced by actinomycetes (specially the genus Streptomyces) and filamentous fungi. Some important antibiotics are : tetracycline, chloramphenicol, streptomycin, etc.
-
Question 18 of 85
18. Question
Antibiotics are obtained from
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Antibiotics are obtained from lichens, fungi, eubacteria and actinomycetes.
-
Question 19 of 85
19. Question
Which of the following antibiotics was extensively used to treat American soldiers wounded in world war II?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : In 1940, E. Chain and H. Florey obtained a relatively stable preparation of penicillin, which was extensively used to treat wounded American soldiers in world war II.
-
Question 20 of 85
20. Question
Read the following statements regarding antibiotics and select the incorrect option from codes given below.
(i) Antibiotics are the attenuated microorganisms which in small concentration can kill or retard the growth of other harmful microorganisms.
(ii) Penicillin was the first antibiotic discovered by Alexander Fleming (1928) while working on bacterium Staphylococcus aureus.
(iii) The full potential of penicillin as an effective antibiotic was established by Ernst Chain and Howard Florey.
(iv) Fleming, Chain and Florey were awarded the Nobel Prize in 1945.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Antibiotics are chemical substances secrereu dy certain microbes which can kill or inhibit the growth and development of harmful microbes. Most of them are produced by actinomycetes (specially the genus Streptomyces) and filamentous fungi. Some important antibiotics are : tetracycline, chloramphenicol, streptomycin, etc.
-
Question 21 of 85
21. Question
Which of the following diseases are treated by antibiotics?
(i) Plague
(ii) Diphtheria
(iii) Leprosy
(iv) Whooping coughCorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 22 of 85
22. Question
Streptomycin is obtained from
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : S. cerevisiae is used in the formation of dough while \(S\).venezuelae is used in obtaining chloramphenicol drug. Oxytetracycline is obtained from S.rimosus.
-
Question 23 of 85
23. Question
Which of the following antibiotics is not correctly matched with the source from which it is obtained?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Streptomycin is obtained from Streptomyces griseus. It is found useful in meningitis, pneumonia, tuberculosis and local infections.
-
Question 24 of 85
24. Question
Select the correct option to fill up the blanks.
(i) \(\qquad\) are used in detergent formulations and are helpful in removing oily stains from the laundry.
(ii) \(\qquad\) are ripened by growing Penicillium roqueforti on them.
(iii) \(\qquad\) are produced without distillation whereas, \(\qquad\) are produced by distillation of the fermented broth.
(iv) \(\qquad\) antibiotic was used to treat American soldiers wounded in world war II.
(v) \(\qquad\) is also called as kusht rog.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 25 of 85
25. Question
\(\qquad\)
produced by bacterium Streptococcus and modified by genetic engineering is used as a “clot buster” for removing clots from the blood vessels of patients who have undergone myocardial infarction leading to heart attack.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Streptokinase (Tissue Plasminogen Activator or TPA) is an enzyme obtained from the cultures of some haemolytic bacterium Streptococcus and modified genetically to function as clot buster. It has fibrinolytic effect. Therefore, it helps in clearing blood clots inside the blood vessels in patients who have undergone myocardial infarction leading to heart attack, through dissolution of intravascular fibrin.
-
Question 26 of 85
26. Question
Enzyme which has the fibrinolytic effect is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Streptokinase (Tissue Plasminogen Activator or TPA) is an enzyme obtained from the cultures of some haemolytic bacterium Streptococcus and modified genetically to function as clot buster. It has fibrinolytic effect. Therefore, it helps in clearing blood clots inside the blood vessels in patients who have undergone myocardial infarction leading to heart attack, through dissolution of intravascular fibrin.
-
Question 27 of 85
27. Question
Identify the blank spaces A, B, C and D in the following table and select the correct option.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline \begin{array}{c}
\text { Type of } \\
\text { microbe }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Scientific } \\
\text { name }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Commercial } \\
\text { product }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Bacterium } & \text { A } & \text { Streptokinase } \\
\hline \text { B } & \text { Aspergillus niger } & \text { Citric acid } \\
\hline \text { Fungus } & \text { Trichoderma polysporum } & \text { C } \\
\hline \text { Bacterium } & \text { D } & \text { Butyric acid } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)\(
\begin{array}{lll}
\text { (a) } & \text { A-Streptococcus } & \text { B-Fungus } \\
& \text { C-Cyclosporin A } & \text { D-Clostridium butylicum } \\
\text { (b) } & \text { A-Clostridium butylicum } & \text { B-Streptococcus } \\
& \text { C-Fungus } & \text { D-Cyclosporin A } \\
\text { (c) } & \text { A-Streptococcus } & \text { B-Yeast } \\
& \text { C-Cyclosporin A } & \text { D-Lactobacillus } \\
\text { (d) } & \text { A-Streptococcus } & \text { B-Cyclosporin A } \\
& \text { C-Statins } & \text { D-Clostridium butylicum }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 28 of 85
28. Question
A drug used for patient ‘ A ‘ is obtained from the organism ‘ B ‘. Identify A and B in the above statement and select the correct option.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Cyclosporin A is a cyclic oligopeptide obtained through fermentative activity of fungus Trichoderma polysporum. It has anti-fungal, anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. It inhibits activation of T -cells and therefore, prevents rejection reactions in organ transplantation.
-
Question 29 of 85
29. Question
Statins used for lowering blood cholesterol level are extracted from
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Statins are products of fermentation by yeast Monascus purpureus which resemble mevalovate and are competitive inhibitors of \(\beta\)-hydroxy- \(\beta\)-methylglutaryl or HMG COA reductase. This inhibits cholesterol synthesis. Statins are, therefore, used in lowering blood cholesterol, e.g., lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin.
-
Question 30 of 85
30. Question
Monascus purpureus is a yeast commercially used in the production of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Statins are products of fermentation by yeast Monascus purpureus which resemble mevalovate and are competitive inhibitors of \(\beta\)-hydroxy- \(\beta\)-methylglutaryl or HMG COA reductase. This inhibits cholesterol synthesis. Statins are, therefore, used in lowering blood cholesterol, e.g., lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin.
-
Question 31 of 85
31. Question
Identify the blank spaces A, B, C and D in the given table and select the correct option.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline \begin{array}{c}
\text { Type of } \\
\text { microbe }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Scientific } \\
\text { name }
\end{array} & \text { Product } & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Medical } \\
\text { application }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { Fungus } & \text { A } & \text { CyclosporinA } & \text { B } \\
\hline \text { C } & \begin{array}{c}
\text { Monascus } \\
\text { purpureus }
\end{array} & \text { Statin } & \text { D } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 32 of 85
32. Question
Which of the following options contains the end products formed during anaerobic respiration in yeast?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Anaerobic respiration in yeast results in the production of ethyl alcohol, carbon dioxide and energy.
-
Question 33 of 85
33. Question
Which of the following is the first step of sewage treatment?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Primary treatment in sewage treatment involves physical removal of particles (large and small) from the sewage through filtration and sedimentation. Initially floating debris is removed by sequential filtration. Then the grit (soil and small pebbles) are removed by sedimentation.
-
Question 34 of 85
34. Question
During the primary treatment of sewage, solid particles that settle down are called
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Primary or physical treatment is the process of removal of small and large, floating and suspended solids from sewage through two processes of filtration and sedimentation. First floating and suspended matter is removed through sequential filtration with progressively smaller pore filters. The sediment is called primary sludge while the supernatant is called effluent. The primary sludge traps a lot of microbes and debris. It is subjected to composting, land fill or anaerobic digestion to produce biogas and manure.
-
Question 35 of 85
35. Question
The purpose of biological treatment of waste water is to
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Secondary treatment of sewage (or biological treatment) depletes about 90-95 % of the BOD and many pathogens are removed. Reduction of BOD by \(90 \%\) is achieved through mineralisation of small fraction of organic matter and conversion of large proportion to removable solids.
-
Question 36 of 85
36. Question
The masses of bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures are called
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Flocs are masses of bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures.
-
Question 37 of 85
37. Question
The purpose of biological treatment of waste water is to
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Secondary treatment of sewage (or biological treatment) depletes about \(90-95 \%\) of the BOD and many pathogens are removed. Reduction of BOD by \(90 \%\) is achieved through mineralisation of small fraction of organic matter and conversion of large proportion to removable solids.
-
Question 38 of 85
38. Question
The masses of bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures are called
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Flocs are masses of bacteria held together by slime and fungal filaments to form mesh-like structures.
-
Question 39 of 85
39. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: BOD represents the amount of dissolved oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidised by microorganisms.
Statement 2 : High value of BOD indicates that water is highly polluted by organic matter.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : BOD (biochemical oxygen demand) refers to the amount of the oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidised by bacteria. The BOD test measures the rate of update of oxygen by microorganisms in a sample of water and thus, indirectly BOD is the measure of the organic matter present in the water. The greater the BOD of wastewater, more is its polluting potential.
-
Question 40 of 85
40. Question
Read the following statements and select the incorrect one.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 41 of 85
41. Question
Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) in a river water
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 42 of 85
42. Question
Sewage water is treated before release into water bodies. The type of microbes used to treat sewage water is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Heterotrophic microbes are naturally present in sewage water. These microbe digest organic matter of sewage water.
-
Question 43 of 85
43. Question
A sewage treatment process in which a part of decomposer bacteria present in the wastes is recycled into the starting of the process is called
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : The activated sludge system, a part of secondary treatment, is one of the widely used aerobic treatment systems for waste water in which very vigorous aeration of the sewage is done. The sewage is passed into an aeration tank from primary settling tank.
The flocs are allowed to settle down in secondary settling tank. In settling tank, the bacterial flocs are allowed to undergo sedimentation. The effluent or supernatant is generally passed into natural water bodies like rivers and streams. The sediment of settling tank is called activated sludge. A part of it is used as inoculum in aeration tanks. The remaining part is passed into a large tank called anaerobic sludge digesters. -
Question 44 of 85
44. Question
Which of the following steps is taken by the Ministry of Environment and Forests to protect rivers from water pollution?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : The Ministry of Environment and Forests has initiated Ganga Action Plan and Yamuna Action Plan to save these major rivers of our country from pollution. Under these plans, it is proposed to build a large number of sewage treatment plants so that only treated water may be discharged in the rivers.
-
Question 45 of 85
45. Question
BOD is _____ in polluted water and _____ in potable water.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : B O D (biochemical oxygen demand) refers to the amount of the oxygen that would be consumed if all the organic matter in one litre of water were oxidised by bacteria. The BOD test measures the rate of update of oxygen by microorganisms in a sample of water and thus, indirectly BOD is the measure of the organic matter present in the water. The greater the BOD of wastewater, more is its polluting potential.
-
Question 46 of 85
46. Question
Select the correct statement regarding activated sludge formed during secondary sewage treatment.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : The activated sludge system, a part of secondary treatment, is one of the widely used aerobic treatment systems for waste water in which very vigorous aeration of the sewage is done. The sewage is passed into an aeration tank from primary settling tank.
The flocs are allowed to settle down in secondary settling tank. In settling tank, the bacterial flocs are allowed to undergo sedimentation. The effluent or supernatant is generally passed into natural water bodies like rivers and streams. The sediment of settling tank is called activated sludge. A part of it is used as inoculum in aeration tanks. The remaining part is passed into a large tank called anaerobic sludge digesters. -
Question 47 of 85
47. Question
In the sewage treatment, bacterial flocs are allowed to sediment in a settling tank. This sediment is known as
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Activated sludge is formed during secondary sewage treatment. It possess flocs of decomposer microbes. Formation of activated sludge requires aeration.
-
Question 48 of 85
48. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Methanogens } & \text { (i) } & \text { BOD } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Fermentors } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Methane rich fuel gas } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Organic waste } \\
\text { in water }
\end{array} & \text { (iii) } & \text { Production of methane } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Biogas } & \text { (iv) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Large vessels for growing } \\
\text { microbes }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 49 of 85
49. Question
Study the following statements and select the incorrect ones.
(i) Methanococcus and Methanobacterium grow anaerobically on cellulosic material.
(ii) Secondary sewage treatment is mainly a mechanical process.
(iii) Activated sludge sediment in a sewage treatment plant is a rich source of aerobic bacteria.
(iv) Biogas, commonly called as gobar gas, is pure methane.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Secondary treatment is also called biological treatment or microbial degradation. It is mainly a biological process. Biogas is a mixture of gases, containing predominantly methane \((50-70 \%), \mathrm{CO}_2(30-40 \%)\) and traces of hydrogen, \(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~S}\) and nitrogen.
-
Question 50 of 85
50. Question
Methanogens, growing anaerobically on cellulosic material produce
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Methanobacterium is found in the rumen (a part of the stomach) of cattle. A lot of cellulosic material is also available in the rumen. In rumen, these bacteria help in the breakdown of cellulose and play an important role in nutrition of cattle.
-
Question 51 of 85
51. Question
Which of the following bacteria is present in the rumen of cattle?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Methanobacterium is found in the rumen (a part of the stomach) of cattle. A lot of cellulosic material is also available in the rumen. In rumen, these bacteria help in the breakdown of cellulose and play an important role in nutrition of cattle.
-
Question 52 of 85
52. Question
Process of biogas production is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Biogas is a methane rich fuel gas produced by anaerobic breakdown or digestion of biomass with the help of methanogenic bacteria. Biogas is made up of methane ( \(50-70 \%\) ), carbon dixide (30-40 %) with traces of nitrogen, hydrogen sulphide and hydrogen.
-
Question 53 of 85
53. Question
Biogas is produced by anaerobic breakdown of biomass of agricultural waste by methanogenic bacteria. It is a
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 54 of 85
54. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Statins } & \text { (i) } & \text { Biogas } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Dung } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Saccharomyces cerevisiae } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Ethanol production } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Monascus purpureus } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Decomposition of } \\
\text { organic matter }
\end{array} & \text { (iv) } & \text { Methanothrix } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 55 of 85
55. Question
These bacteria grow anaerobically on cellulosic material, produce large amount of methane along with \(\mathrm{CO}_2\) and \(\mathrm{H}_2\), and are collectively called methanogens. Examples of such bacteria are
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Methanogens are microorganisms that produce methane as a metabolic byproduct in anoxic condition. They include Methanobacterium, Methanobrevibacter and Methanococcus.
-
Question 56 of 85
56. Question
The given figure represents a typical biogas plant. Select the correct option for A, B and C respectively.
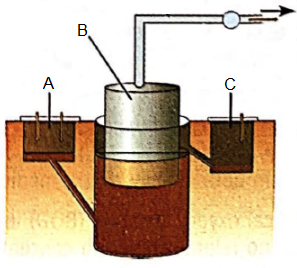 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : The given figure is of a biogas plant, in which \(A\) is Inlet for cattle dung and water; B is Gas holder and C is Outlet for leftover slurry.
-
Question 57 of 85
57. Question
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : In the biogas generation, organic acids, i.e., acetic acid, are acted upon by methanogenic bacteria.
-
Question 58 of 85
58. Question
Biogas generation is a three stage anaerobic digestion of animal and other organic wastes. Study the following flow chart and select the correct option for stages I, II and III.
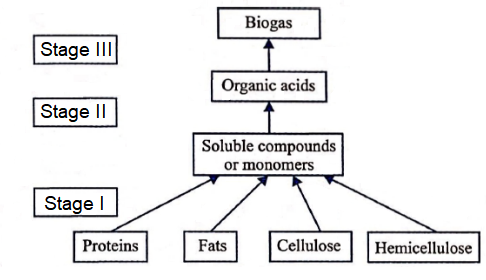 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 59 of 85
59. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Biocontrol refers to the use of biological methods for controlling plant diseases and pests.
Statement 2 : Use of biocontrol measures will greatly reduce our dependence on toxic chemicals and pesticides.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 60 of 85
60. Question
Biopesticides are
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Biopesticides are those biological agents or their products that are used for control of weeds and insects (pathogens). Most important example is the soil bacterium, Bacillus thuringiensis.
-
Question 61 of 85
61. Question
When a natural predator (living organism) is applied on the other pathogen organisms to control them, this process is called as
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 62 of 85
62. Question
Dragonflies are used to get rid of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 63 of 85
63. Question
A microbial biocontrol agent that can be used to control butterfly caterpillars is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : An example of microbial biocontrol agent that can be introduced in order to control butterfly caterpillars is the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis ( Bt ). These are available in sachets as dried spores which are mixed with water and sprayed onto vulnerable plants such as Brassica and fruit trees, where these are eaten by the insect larvae. In the gut of the larvae, the toxin is released and the larvae get killed. The bacterial disease will kill the caterpillars, but leave other insects unharmed.
-
Question 64 of 85
64. Question
Bacillus thuringiensis is used to control
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 65 of 85
65. Question
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) strains have been used for designing novel
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Bioinsecticides are those biological agents that are used to control harmful insects. Because of development of methods of genetic engineering, B. thuringiensis toxic genes are introduced into plants. Such plants are resistant to attack by insect pests. Bt cotton is one such example.
-
Question 66 of 85
66. Question
Fill up the blanks by selecting the correct option.
(i) Biogas is a mixture of gases which predominantly contains ____ and is used as ______.
(ii) Methanogens are commonly found in the ____ during sewage treatment.
(iii) _____ species are free-living fungi and effective biocontrol agents of several plant pathogens.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 67 of 85
67. Question
Which of the following statements is correct with regard to biocontrol agents?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 68 of 85
68. Question
Trichoderma harzianum has proved to be a useful microorganism for
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 69 of 85
69. Question
Baculoviruses (Nucleopolyhedrovirus) do not show
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Nucleopolyhedrovirus are excellent candidates for species-specific, narrow spectrum insecticidal applications. They have been shown to have no negative impacts on plants, mammals, birds, fish or even on non-target insects. This is especially desirable when beneficial insects are being conserved to aid in an overall integrated pest management (IPM) programme, or when an ecologically sensitive area is being treated.
-
Question 70 of 85
70. Question
Which of the following statements regarding baculoviruses as biocontrol agents is/are correct?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 71 of 85
71. Question
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) discourages the excessive use of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an effective and environmental sensitive approach for pest management. IPM programs use current, comprehensive information on the life cycles of pest and their interaction with the environment. This information in combination with available pest control methods, is used to manage pest damage by the most economical means, and with the least possible hazard to people, property and the environment.
-
Question 72 of 85
72. Question
Which of the following is not used as a biopesticide?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Xanthomonas campestris is not used as a biopesticide. Bacillus thuringiensis is used as a microbial biocontrol agent. Trichoderma harzianum is a free-living fungi, common in soil and root ecosystems. It is an effective biocontrol agent of several plant pathogens. Viruses of the family Baculoviruses are pathogens that attack insects and other arthropods. The majority of baculoviruses used as biological control agents belong to genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus.
-
Question 73 of 85
73. Question
The reason that the chemical/synthetic fertilisers should be replaced by biofertilisers is that the former
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Chemical fertilisers are being used in increasing amounts in order to increase output in high yielding varieties of crop plants. However, chemical fertilisers cause pollution of water bodies as well as groundwater, besides getting stored in crop plants. They are expensive and also require lot of energy resources in their manufacture.
-
Question 74 of 85
74. Question
Organic farming does not include
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Organic farming includes several methods to enhance soil fertility. In such farming, methods of biological origin are used, e.g., biopesticides, biofertilisers, IPM (Integrated Pest Management) green manure, bioherbicides, keeping pests and pathogens under control, etc. Chemical fertilisers are not used in organic farming.
-
Question 75 of 85
75. Question
Organic farming includes
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Organic farming includes several methods to enhance soil fertility. In such farming, methods of biological origin are used, e.g., biopesticides, biofertilisers, IPM (Integrated Pest Management) green manure, bioherbicides, keeping pests and pathogens under control, etc. Chemical fertilisers are not used in organic farming.
-
Question 76 of 85
76. Question
Living organisms used to enrich the nutrient quality of the soil are known as
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Biofertilisers are microorganisms which bring about nutrient enrichment of soil by enhancing the availability of nutrients to crops. Microorganisms which act as biofertilisers are bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue green algae) and mycorrhizal fungi. Bacteria and cyanobacteria have the property of nitrogen fixation while mycorrhizal fungi preferentially withdraw minerals from organic matter for the plant with which they are associated. They maximise ecological benefits and minimise environmental hazards.
-
Question 77 of 85
77. Question
Biofertilisers are organisms that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil. Which of the following can be used as biofertilisers?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Biofertilisers are microorganisms which bring about nutrient enrichment of soil by enhancing the availability of nutrients to crops. Microorganisms which act as biofertilisers are bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue green algae) and mycorrhizal fungi. Bacteria and cyanobacteria have the property of nitrogen fixation while mycorrhizal fungi preferentially withdraw minerals from organic matter for the plant with which they are associated. They maximise ecological benefits and minimise environmental hazards.
-
Question 78 of 85
78. Question
Biofertilisers are
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 79 of 85
79. Question
Biofertilisers are the living organisms which
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Biofertilisers are microorganisms which bring about nutrient enrichment of soil by enhancing the availability of nutrients to crops. Microorganisms which act as biofertilisers are bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue green algae) and mycorrhizal fungi. Bacteria and cyanobacteria have the property of nitrogen fixation while mycorrhizal fungi preferentially withdraw minerals from organic matter for the plant with which they are associated. They maximise ecological benefits and minimise environmental hazards.
-
Question 80 of 85
80. Question
Unicellular symbiotic organisms improve yield of legumes by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria form a mutually beneficial association with the plants. The bacteria obtain food and shelter from plants. In return, they give a part of their fixed nitrogen to the plants. The most important of the symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria is Rhizobium. It forms nodule on the roots of legume plants. They develop the ability to fix nitrogen only when they are present inside the root nodules. In the nodule cells, bacteria (bacteroids) lie in groups surrounded by membrane of the host which is lined by a pink-red pigment called leghaemoglobin.
-
Question 81 of 85
81. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Trichoderma } & \text { (i) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Free living nitrogen fixing } \\
\text { bacteria }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Streptomyces } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Biocontrol agent } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Azospirillum } & \text { (iii) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Free living nitrogen fixing } \\
\text { cyanobacteria }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Anabaena } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Source of antibiotic } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 82 of 85
82. Question
Which one of the following can be used as biofertiliser in cotton field?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Cotton is a dicotyledonous crop. Ine for cotton is Bacillus cereus and Azotobacter chroococcum. These are free living \(N_2\) fixing bacteria and enhance the fertility of soil.
-
Question 83 of 85
83. Question
The symbiotic association between fungi and roots of higher plants is referred to as
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 84 of 85
84. Question
Which one of the following microorganisms forms symbiotic association with plants and helps them in their nutrition?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Several fungi are known to form symbiotic associations with plants, i.e., mycorrhiza. The most common fungal partners of mycorrhiza are Glomus species.
-
Question 85 of 85
85. Question
Which of the following statements is not correct regarding mycorrhiza?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)