Practice Corner MCQ
Quiz Summary
0 of 98 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 98 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 98
1. Question
Which of the following factors affect human health?
(i) Infections
(ii) Silent mutations
(iii) Lifestyle
(iv) Genetic disordersCorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Human health is affected by following three factors: genetic disorders, infections and lifestyle, including food and water, rest and exercise we give to our bodies and habits.
-
Question 2 of 98
2. Question
Read the following statements about health and select the incorrect one.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Health increases longevity of people and reduces infant and maternal mortality.
-
Question 3 of 98
3. Question
Which one of the following diseases is non-communicable?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 4 of 98
4. Question
Which of the following pairs contains an infectious and a non-infectious disease respectively?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Infectious diseases are those diseases that can spread from one person to another, e.g., AIDS. Non-infectious diseases are those diseases that cannot spread from one person to another, e.g., cancer.
-
Question 5 of 98
5. Question
Typhoid fever in human beings is caused by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Salmonella typhi, a rod shaped bacterium causes typhoid.
-
Question 6 of 98
6. Question
Which of the following statements regarding the disease typhoid is/are correct?
(i) Salmonella typhi a pathogenic bacterium which enter human intestine through contaminated food and water and migrate to other organs through blood.
(ii) Sustained high fever \(\left(39^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\right.\) to \(\left.40^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\right)\), weakness, stomach pain, constipation, headache and loss of appetite are some common symptoms of typhoid.
(iii) Typhoid vaccine is available as DPT vaccine.
(iv) Widal test is used for diagnosis of typhoid fever.
(v) The patient of this disease is not required to be treated with antibiotics.CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Frequency of dominant allele \((A)=0.4\)
Applying Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium; \(p+q=1\)
\(
q=1-0.4=0.6 ; p^2+q^2+2 p q=1
\)Frequency of homozygous dominant genotype \(=p^2\)
\(
\therefore \quad A A=(0.4)^2=0.16
\)Frequency of heterozygous genotype \(=2 p q\)
\(
\therefore \quad A a=2 \times 0.4 \times 0.6=0.48
\)Frequency of homozygous recessive genotype \(=q^2\)
\(
\therefore \quad \text { aa }=(0.6)^2=0.36
\) -
Question 7 of 98
7. Question
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Darwin finches are an excellent example of the way in which the species gene pool have adapted in order for long term survival via their offspring. Finches were formed due to divergent evolution (adaptive radiation) to avoid interspecific competition. The common birds of Galapagos islands, the finches were markedly different from the finches of mainland. The closely related species of finches had beak of different shapes and sizes and were adapted for feeding on completely different diets.
-
Question 8 of 98
8. Question
Which of the following is the bacterial disease in humans?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 9 of 98
9. Question
Which of the following pathogens causes whooping cough?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : In 1953, S.L. Miller, an American scientist created similar conditions in a laboratory scale. He created electric discharge in a closed flask containing \(\mathrm{CH}_4, \mathrm{H}_2, \mathrm{NH}_3\) and water vapour at \(800^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\) and observed formation of amino acids.
-
Question 10 of 98
10. Question
Which one of the following sets includes only bacterial diseases?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c): Charles Robert Darwin returned to England in October 1836 from his 5 -year expedition. On returning, he analysed and processed his observations made during the journey. Meanwhile, he came across Malthus’s theory of human population and received a brief essay from Alfred Wallace. He combined all his studies and finally in November 1859, Darwin published his observations and conclusions in the form of book. The full title of his book was ‘On the origin of species by means of Natural Selection : The Preservation of Races in the Struggle for life’.
-
Question 11 of 98
11. Question
The main reason why antibiotics could not always treat the bacteria-mediated diseases is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : In response to antibiotics, bacteria develop mutant strains that become resistant to the antibiotics. Thus, these antibiotics become incapable against bacterial mediated diseases.
-
Question 12 of 98
12. Question
The common cold is caused by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 13 of 98
13. Question
Common cold differs from pneumonia as
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Pneumonia is caused by bacteria, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae. It is a serious disease of lungs infecting alveoli and bronchioles. Common cold is a viral disease caused by Rhinoviruses. It affects the nose and respiratory passage but not the lungs. Both are communicable diseases.
-
Question 14 of 98
14. Question
Hepatitis B is transmitted through
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Hepatitis B is a viral disease, transmitted through both blood transfusion and sexual intercourse.
-
Question 15 of 98
15. Question
A toxic substance, responsible for the chills and high fever recurring every three to four days in malarial fever, is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : In malaria, chills and shivers are caused by the release of toxic substance, haemozoin into the blood at the time of RBC rupture. It is generally followed by fever.
-
Question 16 of 98
16. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Malarial parasite requires two hosts humans and mosquitoes to complete its life cycle.
Statement 2 : Haemozoin is a toxic substance produced by the rupturing of liver cells during malarial infection.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Haemozoin is a toxic substance produced by the rupturing of red blood cells.
-
Question 17 of 98
17. Question
During the life cycle of Plasmodium, sexual reproduction takes place in which of the following hosts?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasite. It requires two hosts to complete its life cycle. Female Anopheles mosquito is the primary host in which the sexual phase of the parasite occurs. Human being is the secondary host in which the asexual phase of the parasite occurs.
-
Question 18 of 98
18. Question
Where will you look for the sporozoites of malarial parasite?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a): When a female Anopheles mosquito bites an infected person, Plasmodium enters the mosquito’s body and undergoes further development. The parasites multiply within them to form sporozoites that are stored in their salivary glands.
-
Question 19 of 98
19. Question
Arrange these stages of life cycle of Plasmodium in the correct sequence and select the correct option.
1. Sporozoites leave the blood stream and enter the liver cells of man.
2. Sporozoites present in the salivary glands of female Anopheles mosquito are injected into the blood stream of man.
3. The parasite reproduces asexually in RBCs, resulting in bursting of RBCs and causing the cycles of fever; released parasites infect new RBCs.
4. The parasite reproduces asexually in liver cells, ultimately causing the rupturing of cells.
5. Two types of gametocytes i.e., microgametocytes and macrogametocytes develop in the RBCs.
6. Female Anopheles mosquito takes up the gametocytes with blood meal of an infected person.
7. Mature infective stage of the parasite, i.e., sporozoites escape from intestine and migrate to the mosquito’s salivary glands.
8. Fertilisation and developmental stages of the parasite take place in mosquito’s stomach.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 20 of 98
20. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|c|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Amoebiasis } & \text { (i) } & \text { Treponema pallidum } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Diphtheria } & \text { (ii) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Houseflies as mechanical } \\
\text { Carriers }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Cholera } & \text { (iii) } & \text { DPT vaccine } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Syphilis } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Oral rehydration therapy } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 21 of 98
21. Question
Amoebic dysentery (amoebiasis) is caused by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Amoebic dysentery is caused by a monogenic protozoan known as Entamoeba histolytica. The pathogen lives in the large intestine of humans. The patient passes blood along with the faeces and feels pain in the abdomen.
-
Question 22 of 98
22. Question
Which one of the following diseases cannot be cured by taking antibiotics?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial diseases. Plague, leprosy and whooping cough are bacterial diseases. Amoebiasis is a protozoan disease. It cannot be cured by taking antibiotics.
-
Question 23 of 98
23. Question
An intestinal parasite which causes blockage of the intestinal passage and whose eggs are excreted along with the faeces of infected person is \(\qquad\)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Ascaris is an endoparasite of the small intestine. A large number of adult Ascaris worms normally obstruct the intestinal passage and thereby cause abdominal discomfort and colic pain. Other symptoms include impaired digestion, diarrhoea and vomiting. Ascaris’s eggs are excreted along with the faeces of infected person.
-
Question 24 of 98
24. Question
Elephantiasis, a chronic inflammation that results in gross deformities is caused by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Elephantiasis or filariasis is caused by a number of worms. However, in India only two types of worms are responsible for this disease, Wuchereria bancrofti and W. malayi. This disease is transmitted by female Culex mosquitoes. Elephantiasis affects lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs.
-
Question 25 of 98
25. Question
Which of the following is affected by the infection of Wuchereria bancrofti?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Elephantiasis or filariasis is caused by a number of worms. However, in India only two types of worms are responsible for this disease, Wuchereria bancrofti and W. malayi. This disease is transmitted by female Culex mosquitoes. Elephantiasis affects lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs.
-
Question 26 of 98
26. Question
Which of the following diseases is transmitted by the bite of the female mosquito vector?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Elephantiasis or filariasis is caused by a number of worms. However, in India only two types of worms are responsible for this disease, Wuchereria bancrofti and W. malayi. This disease is transmitted by female Culex mosquitoes. Elephantiasis affects lymphatic vessels of the lower limbs.
-
Question 27 of 98
27. Question
Which of the following pairs correctly matches a disease and a pathogen causing it?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Typhoid – Salmonella typhi
Pneumonia – Streptococcus pneumoniae
Malaria – Plasmodium
Ringworm – Trichophyton -
Question 28 of 98
28. Question
The pathogen Microsporum responsible for ringworm disease in humans belongs to the same kingdom as that of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Microsporum and Rhizopus belong to the Kingdom Fungi.
-
Question 29 of 98
29. Question
Appearance of dry, scaly lesions with itching on various parts of the body are the symptoms of \(\qquad\)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Ringworms or tinea is caused by the fungi belonging to the genera Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton. Appearance of dry, scaly lesions with itching on various parts of the body such as skin, nails and scalp are the main symptoms of ringworm. The infection is generally acquired from soil or by using towels, clothes or even the comb of infected persons.
-
Question 30 of 98
30. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Many fungi belonging to genera Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton are responsible for the disease ringworm.
Statement 2 : Ringworm infection is generally acquired from soil or by using towels, clothes, comb, etc. of infected individuals.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Ringworms or tinea is caused by the fungi belonging to the genera Microsporum, Trichophyton and Epidermophyton. Appearance of dry, scaly lesions with itching on various parts of the body such as skin, nails and scalp are the main symptoms of ringworm. The infection is generally acquired from soil or by using towels, clothes or even the comb of infected persons.
-
Question 31 of 98
31. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Leishmania donovani } & \text { (i) } & \text { Malaria } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Wuchereria bancrofti } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Amoebiasis } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Trypanosoma gambiense } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Kala azar } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Entamoeba histolytica } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Sleeping sickness } \\
\hline & & \text { (v) } & \text { Filariasis } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 32 of 98
32. Question
Gambusia is a fish which is being introduced into the ponds in order to check the vector borne diseases such as
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Gambusia feeds on the larvae of mosquitoes that live in water. Mosquito is a vector for all these three diseases: dengue, malaria and chikungunya.
-
Question 33 of 98
33. Question
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|l|c|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Sporozoites } & \text { (i) } & \text { Infectious form of Plasmodium } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Filariasis } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Aedes mosquitoes } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Typhoid } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Wuchereria } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Chikungunya } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Widal test } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 34 of 98
34. Question
Which one of the following pairs of diseases is viral as well as transmitted by mosquitoes?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Yellow fever is caused by flavivirus and dengue is caused by arbovirus. Both are transmitted by the bite of mosquito, Aedes aegypti.
-
Question 35 of 98
35. Question
The term ‘immunity’ refers to
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 36 of 98
36. Question
Which of the following statements regarding different barriers of innate immunity is not correct?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Mucous membrane lining the respiratory, gastrointestinal and urinogenital tracts helps in trapping the microbes and constitute physical barriers of our body.
-
Question 37 of 98
37. Question
MALT is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : MALT (Muscosal Associated Lymphoid Tissue) is located within the lining of the major tracts, i.e., respiratory, urogenital and digestive tracts.
-
Question 38 of 98
38. Question
The lymphoid tissue, located within the lining of digestive tract is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : MALT (Muscosal Associated Lymphoid Tissue) is located within the lining of the major tracts, i.e., respiratory, urogenital and digestive tracts.
-
Question 39 of 98
39. Question
A person has developed interferons in his body. He seems to carry an infection of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Interferons are produced in the body in response to viral infection. Measles is a viral disease.
-
Question 40 of 98
40. Question
Which lymphoid organ atrophies with age?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 41 of 98
41. Question
Primary response produced due to first time encounter with a pathogen is of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Primary immune response is produced by the initial contact of an animal with an antigen. It takes relatively longer time, is of low intensity and declines rapidly.
-
Question 42 of 98
42. Question
Which of the following components does not participate in innate immunity?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Innate immunity is the type of immunity that is present in the organism by birth. Acquired immunity is the immunity that an individual acquires during life. B-lymphocytes are involved in acquired immunity and produce antibodies.
-
Question 43 of 98
43. Question
Antibodies are secreted by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 44 of 98
44. Question
An antibody consists of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Antibodies are immunoglobulins produced by B-lymphocytes in response to antigenic stimulation. An antibody is made up of four peptide chains. Of the four chains, there are two long chains, called heavy chains and two short chains called light chains.
-
Question 45 of 98
45. Question
Identify the marking A, B, C and D in thdye figure given below and select the correct option.
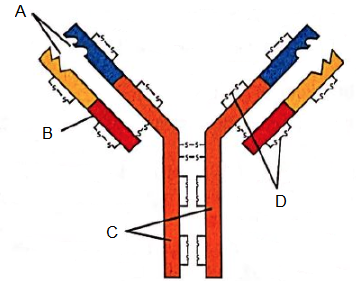 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 46 of 98
46. Question
The antigen binding site of an antibody is present at
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Antibodies are made up of four polypeptide chains two heavy and two light chains. Light and heavy chains are subdivided into variable and constant regions. The variable portion is used for binding to antigen and a constant portion determines its adherence and diffusivity.
-
Question 47 of 98
47. Question
Humoral immunity is associated with
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Humoral immunity consists of antibodies that circulate in the blood and lymph. B-lymphocytes produce antibodies that regulate humoral immunity.
-
Question 48 of 98
48. Question
The antibody which can cross placental barrier is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : lgG is the only maternal immunoglobulin that can cross the placenta and provide natural passive immunity to the fetus. It is the most abundant class of immunoglobulins in the body constituting \(80 \%\) of the igs.
-
Question 49 of 98
49. Question
The most abundant class of immunoglobulins (lgs) in the body is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : lgG is the only maternal immunoglobulin that can cross the placenta and provide natural passive immunity to the fetus. It is the most abundant class of immunoglobulins in the body constituting \(80 \%\) of the igs.
-
Question 50 of 98
50. Question
A protein or polysaccharide molecule that stimulates antibody formation is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 51 of 98
51. Question
Select the correct statements regarding the characteristics of acquired immunity.
(i) Cell-mediated immunity is responsible for acquired immunity.
(ii) It produces a primary response of low intensity.
(iii) Active and passive immunity are types of acquired immunity.
(iv) Polymorphonuclear leucocytes and natural killer cells are involved in acquired immunity.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Polymorphonuclear leucocytes and natural killer cells are Involved in innate Immunity. These cells phagocytose and destroy microbes.
-
Question 52 of 98
52. Question
Which of the given statements are correct?
(i) Innate immunity is a specific type of defence, that is present at the time of birth.
(ii) Malignant malaria is caused by Plasmodium falciparum.
(iii) Malaria could be confirmed by Widal test.
(iv) Active immunity is slow and takes time to give its full effective response.
(v) Saliva in the mouth acts as physiological barrier for pathogens.CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Innate immunity is a non-specific type of defence that is present at the time of birth. Typhoid could be confirmed by Widal test.
-
Question 53 of 98
53. Question
Passive immunity can be conferred directly by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Transfer of immune products like antibodies and immunoglobulins to a recipient is called passive immunity. Colostrum, a yellowish milk secreted by mother during the initial days of lactation has abundant antibodies to protect the infant. In tetanus, we need to directly infect the preformed antibodies or antitoxin (a preparation containing antibodies to the toxin). These both are examples of passive immunity.
-
Question 54 of 98
54. Question
Which one of the following immune system components does not correctly match with its respective role?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c): Macrophages are large phagocytic cells that digest the invading organisms.
-
Question 55 of 98
55. Question
Which form of pathogen is used in vaccination?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Transfer of immune products like antibodies and immunoglobulins to a recipient is called passive immunity. Colostrum, a yellowish milk secreted by mother during the initial days of lactation has abundant antibodies to protect the infant. In tetanus, we need to directly inject the preformed antibodies or antitoxin (a preparation containing antibodies to the toxin). These both are examples of passive immunity.
-
Question 56 of 98
56. Question
Injection of antitoxin in tetanus confers which type of immunisation?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Macrophages are large phagocytic cells that digest the invading organisms.
-
Question 57 of 98
57. Question
Select incorrect option regarding the lymphoid organs labelled as P, Q, R and S in the diagram of human Ivmphatic system.
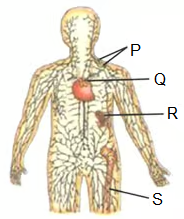 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : In the given diagram, ‘P’-Lymph nodes, ‘Q’-Thymus, ‘R’-Spleen, ‘S’-Bone marrow. Thymus and bone marrow are the primary lymphoid organs where maturation of T-cells and B-cells take place respectively. Lymph nodes and spleen are the secondary lymphoid organs where T-cells and B-cells undergo proliferation and differentiation.
-
Question 58 of 98
58. Question
The term ‘antitoxin’ refers to a preparation containing
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 59 of 98
59. Question
The injection given against the snake venom contains
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 60 of 98
60. Question
The site where lymphocytes interact with antigens and proliferate to become effector cells are
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : After maturation in primary lymphoid organs, B-cells and T-cells migrate via blood and lymph to the secondary lymphoid organs such as spleen, tonsils, Peyer’s patches, etc., where they interact with antigens and proliferate to become effector cells.
-
Question 61 of 98
61. Question
Vaccine against polio viruses is an example of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : When a host is exposed to antigens, which may be in the form of living or dead microbes or other proteins, antibodies are produced in the host body. This type of immunity is called active immunity. Injecting the microbes deliberately during immunisation/ vaccination induces active immunity, e.g., polio vaccine.
-
Question 62 of 98
62. Question
Select the correct option to fill up the blanks.
(i) Diseases which are easily transmitted from one person to another, are called _____ diseases.
(ii) In human body, parasite of malaria initially multiplies within the _____ and then attack the ____.
(iii) ____ is the yellowish fluid secreted by mother during the initial days of lactation.
(iv) ____ and ____ are the primary lymphoid organs.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 63 of 98
63. Question
Use of vaccination and immunisation programmes have controlled which of the following infectious diseases?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 64 of 98
64. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: The exaggerated response of the immune system to certain antigens present in the environment is called as allergy.
Statement 2 : The allergic tendency is genetically passed from the parent to the offspring and is characterised by the presence of large quantities of IgG antibodies in the blood.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 65 of 98
65. Question
An auto-immune disease is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : If the immune system fails to recognise ‘self’ fro ‘non-self’ and starts destroying the body’s own cells, this leads some malfunctions, which are termed as auto-immune diseases. Both theumatoid arthritis and myasthenia gravis are autoimmune diseases.
-
Question 66 of 98
66. Question
Which out of the following groups represent autoimmune disorders?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 67 of 98
67. Question
The drugs used to quickly reduce the symptoms of allergy are
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Anti-histamine, adrenaline and steroids quickly reduce the symptoms of allergy that include sneezing, watery eyes, running nose and difficulty in breathing.
-
Question 68 of 98
68. Question
The primary lymphoid organs are
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Bone marrow and thymus are primary lymphoid organs where differentiation and proliferation of immature lymphocytes occurs.
-
Question 69 of 98
69. Question
The abbreviation AIDS stands for
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 70 of 98
70. Question
The genetic material of HIV is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d): HIV which causes AIDS is a retrovirus that contains single stranded RNA (ssRNA) as its genetic material.
-
Question 71 of 98
71. Question
The human immuno deficiency virus is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 72 of 98
72. Question
Which of the following is not a cause of transmission of HIV?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 73 of 98
73. Question
Viral DNA after being converted from viral RNA by \(X\), incorporates into host genome to undergo replication. What is ‘ \(X\) ‘?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : When HIV enters into the body of a person, it moves into macrophages where RNA genome of the virus replicates to form viral DNA with the help of enzyme reverse transcriptase.
-
Question 74 of 98
74. Question
Which one of the following statements is true?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Dysentery, plague and diphtheria are bacterial diseases. Ringworm appears during summer and rainy season. Widal test is used for confirmation of typhoid.
-
Question 75 of 98
75. Question
The figure given below shows mode of action of AIDS virus. Which step shows formation of viral DNA from RNA by reverse transcription?
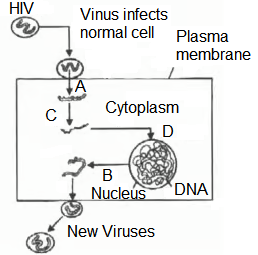 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 76 of 98
76. Question
The cells called ‘HIV factory’ is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : After entering into the host body, HIV moves into macrophages where its RNA replicates to form viral DNA. This viral DNA gets incorporated into the host cell’s DNA and directs the infected cells to produce more viruses. Hence macrophages continue to produce viruses and act as HIV factories.
-
Question 77 of 98
77. Question
HIV is a retrovirus that attacks
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 78 of 98
78. Question
AIDS is characterised by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : AIDS is caused by HIV. When HIV enters into helper T-cells, it replicates and produces other viruses that kill the helper T-cells. Thus, the number of helper T-cells decreases in the body of the infected person and the person starts suffering from various infections.
-
Question 79 of 98
79. Question
AIDS is widely diagnosed by
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : AIDS is diagnosed by ELISA (Enzyme linked Immunosorbent Assay) test.
-
Question 80 of 98
80. Question
Which of the following days is celebrated as ‘World AIDS Day’?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 81 of 98
81. Question
Cancer cells do not exhibit the property of
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Normal cells have the property of contact inhibition. Due to this property they contact with other cells and inhibit their uncontrolled growth. Cancer cells seem to have lost this property and thus undergo uncontrolled growth.
-
Question 82 of 98
82. Question
A person suffering from leukaemia has
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : A person suffering from leukaemia has abnormal increase in the number of WBCs due to their increased formation in the bone marrow.
-
Question 83 of 98
83. Question
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Malignant tumors normally remain confined to their original location, do not spread to other body parts and cause less damage.
Statement 2: Cancer arising from epithelial tissues of internal organs and glands is referred to as sarcoma e.g., breast cancer, cervical cancer etc.CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Benign tumour remains confined to the site of its origin and does not spread to other parts of the body. It causes limited damage to the body and is non-cancerous. Malignant tumor is a cancerous tumour and spreads to other parts of the body from the site of its origin. Cancer arising from epithelial tissues is referred to as carcinoma, e.g., breast cancer, cervical cancer, etc.
-
Question 84 of 98
84. Question
A chemical carcinogen present in tobacco smoke is responsible for
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 85 of 98
85. Question
Complete the given paragraph by selecting correct sequence of words.
Several genes called ____ have been identified in normal cells which when activated will turn into _____ and under certain conditions, could lead to cancerous transformation of the cells.CorrectIncorrectHint
(c)
-
Question 86 of 98
86. Question
Major factors that cause cancer are
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Two major factors known to cause cancer are oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. An oncogene is a gene that sustains some genetic damage and thus, produces a protein capable of cellular transformation. Tumor suppressor gene normally keeps mitosis in check and prevents cancer from occurring. If this gene is inactivated it loses control of cell cycle and initiates cancer.
-
Question 87 of 98
87. Question
Read the following statements regarding the various techniques used in cancer detection and select the incorrect one.
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Computed tomography uses \(X\)-rays to generate a three -dimensional image of the internal structure of an object. MRI uses strong magnetic fields and non-ionising radiations to accurately detect pathological and physiological changes in the living tissues.
-
Question 88 of 98
88. Question
Which of the given statements are not correct regarding cancer?
(i) Cancer causing viruses have genes called viral oncogenes.
(ii) Malignant tumors remain confined to their original location.
(iii) Cancer cells do not exhibit contact inhibition.
(iv) \(X\)-rays and UV rays are not potent carcinogens.
(v) Cancer detection is based on biopsy.CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Benign tumors remain confined to their original location. \(X\)-rays and UV-rays are carcinogenic.
-
Question 89 of 98
89. Question
Which of the following statements is not correct?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Fetus receiving antibodies from mother through placenta is an example of passive immunity.
-
Question 90 of 98
90. Question
Which of the following approaches are used for the treatment of cancer?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 91 of 98
91. Question
The substance given to cancer patients in order to activate their immune system and destroy the tumor is
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Cancer patients are given substances called biological response modifiers like \(\alpha\)-interferon which activate their immune system and help in destroying the tumors.
-
Question 92 of 98
92. Question
In humans, receptors for opioids are present in
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 93 of 98
93. Question
Heroin is commonly called as
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Heroin, is chemically diacetylmorphine which is a white, odourless, bitter crystalline compound commonly called smack. It is obtained by acetylation of morphine which is extracted from the latex of poppy plant (Papaver somniferum).
-
Question 94 of 98
94. Question
Which compound is formed by acetylation of morphine?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Heroin, is chemically diacetylmorphine which is a white, odourless, bitter crystalline compound commonly called smack. It is obtained by acetylation of morphine which is extracted from the latex of poppy plant (Papaver somniferum).
-
Question 95 of 98
95. Question
Which of the following statements is not correct?
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Opioids act as analgesics which relieve pain by acting on the CNS.
-
Question 96 of 98
96. Question
Marijuana is extracted from
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 97 of 98
97. Question
Charas and ganja are the drugs which affect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Charas and ganja are known for their effects on cardiovascular system of the body and generally taken by inhalation and oral ingestion.
-
Question 98 of 98
98. Question
Cocaine is obtained from
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Coca alkaloid or cocaine is obtained from coca plant Enthroxylum (Erythroxylon coca) which is native to South America.