Past Entrance Paper
Quiz Summary
0 of 93 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 93 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 93
1. Question
In which blood corpuscles, the HIV undergoes replication and produces progeny viruses? [NEET 2024]
CorrectIncorrectHint
Answer (1)
Sol. The correct answer is option (1) because HIV enters into helper T-lymphocytes \(\left(T_H\right)\), replicates and produces progeny viruses. The progeny viruses released into blood attack other helper lymphocytes. -
Question 2 of 93
2. Question
Match List I with List II.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { LIST-I } & & \text { LIST-II } \\
\hline \text { A. } & \text { Common cold } & \text { I. } & \text { Plasmodium } \\
\hline \text { B. } & \text { Haemozoin } & \text { II. } & \text { Typhoid } \\
\hline \text { C. } & \text { Widal test } & \text { III. } & \text { Rhinoviruses } \\
\hline \text { D. } & \text { Allergy } & \text { IV. } & \text { Dust mites } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: [NEET 2024]CorrectIncorrectHint
Answer (3)
Sol. Correct answer is option (3) because
– Common cold is caused by Rhinoviruses
– Haemozoin is released in blood due to ruptured RBCs after Plasmodium infection.
– Widal test is used to confirm the typhoid fever.
– Allergy is caused due to dust mites. -
Question 3 of 93
3. Question
Match List I with List II.
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { List I } & & \text { List II } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { Ringworm } & \text { I } & \text { Haemophilus influenzae } \\
\hline \text { B } & \text { Filariasis } & \text { II } & \text { Trichophyton } \\
\hline \text { C } & \text { Malaria } & \text { III } & \text { Wuchereria bancrofti } \\
\hline \text { D } & \text { Pneumonia } & \text { IV } & \text { Plasmodium vivax } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: [NEET 2023]CorrectIncorrectHint
Answer (1)
Sol. Option (1) is the correct answer because:
(i) Ringworm is caused by Trichophyton.
(ii) Filariasis is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti.
(iii) Malaria is caused by Plasmodium species.
(iv) Pneumonia is caused by Haemophilus influenzae. -
Question 4 of 93
4. Question
Select the incorrect statement with respect to acquired immunity.[NEET 2022]
CorrectIncorrectHint
Answer (4)
Sol. Option (4) is the correct answer as acquired immunity is a specific type of defence which is not present at the time of birth.
Option (3), (1) and (2) are true statements and hence cannot be the answer.
Anamnestic response or secondary immune response is a highly intensified response due to memory of first encounter.
When our body encounters a pathogen for the first time then the body elicits the primary immune response.
When there is a subsequent encounter with the same pathogen, secondary or anamnestic immune response is elicited. -
Question 5 of 93
5. Question
Transplantation of tissues/organs fails often due to non-acceptance by the patient’s body. Which type of immune response is responsible for such rejections? (NEET 2017)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Transplantation of tissue/organ often fails due to non-acceptance by the patient’s body therefore, tissue matching and blood group matching are essential before undertaking any graft/transplant. When the immune system recognises the protein in the transplanted tissue or organ as foreign, it initiates cellular immunity. As a result of this, there is a rejection of transplanted organs. To suppress the immune response during transplantation, histocompatibility antigen and immunosuppressants play an important role.
-
Question 6 of 93
6. Question
MALT constitutes about _____ percent of the lymphoid tissue in human body. (NEET 2017)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : MALT are significant aggregations of lymphoid tissues which are seen in relation to the mucosa of the major tracts like respiratory, alimentary canal and urinogenital tracts. It constitutes about 50 percent of the lymphoid tissue in human body.
-
Question 7 of 93
7. Question
Which of the following sets of diseases is caused by bacteria? (NEET-II 2016)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a): Cholera is caused by bacterium Vibrio cholerae, tetanus is caused by bacterium Clostridium tetani, typhoid is caused by bacterium Salmonella typhi, small pox is caused by Variola virus, mumps is caused by Paramyxo virus, Herpes is caused by Herpis simplex virus and influenza is caused by Orthomyxovirus.
-
Question 8 of 93
8. Question
Which of the following is correct regarding AIDS causative agent HIV? (NEET-II 2016)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b, d) : HIV is spherical virus with a diameter of about \(90-120 \mathrm{~nm}\). Its genome consists of a singlestranded RNA filament segmented into two identical filaments and associated with reverse transcriptase enzymes. The envelope consists of a lipid bilayer derived from host cell membrane and projecting knob like glycoprotein spikes. It contains two protein coats. HIV is a retrovirus that attacks helper T cells. Without an adequate supply of helper cells, the immune system cannot signal B cells to produce antibodies to kill infected cells, thus body becomes susceptible to infections. This immune deficiency is described by the name acquired immune deficiency syndrome or AIDS.
-
Question 9 of 93
9. Question
Antivenom injection contains preformed antibodies while polio drops that are administered into the body contain (NEET-I 2016)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : The Sabin vaccine or trivalent ‘oral polio vaccine’ consists of attenuated viral strains.
-
Question 10 of 93
10. Question
Which of the following statements is not true for cancer cells in relation to mutations? (NEET-I 2016)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 11 of 93
11. Question
In higher vertebrates, the immune system can distinguish self-cells and non-self. If this property is lost due to genetic abnormality and it attacks self-cells, then it leads to (NEET-I 2016)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Autoimmunity is a disorder of the body’s defence mechanisms in which an immune response is elicited against its own tissues, which are thereby damaged or destroyed. Autoimmunity may be caused due to genetic or environmental factors.
-
Question 12 of 93
12. Question
If you suspect major deficiency of antibodies in a person, to which of the following would you look for confirmatory evidence? (NEET 2015)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Serum globulins are proteins that include gamma globulins (antibodies) and a variety of enzymes and carrier/ transport proteins.The specific profile of the globulins is determined by protein electrophoresis (SPEP), which separates the proteins according to size and charge. There are four major groups that can be identified : alpha-1 globulins, alpha-2 globulins, beta globulins and gamma globulins. Once the abnormal group has been identified, further studies can determine the specific protein excess or deficit. Since the gamma fraction usually makes up the largest portion of the globulins, therefore antibody deficiency is mainly related with the low level of serum globulins.
-
Question 13 of 93
13. Question
Which of the following immunoglobulins does constitute the largest percentage in human milk? (NEET 2015)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : IgA immunoglobulins are the second most abundant class of immunoglobulins, which are mainly found in sweat, tears, saliva, mucus, colostrum and gastrointestinal secretions.
-
Question 14 of 93
14. Question
Grafted kidney may be rejected in a patient due to (NEET 2015)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Cell-mediated immune response (CMIS) consists of T-lymphocytes. It reacts against transplants. Transplantation may result in the rejection of the transplanted organs. The immune system recognises the protein in the transplanted tissue or organ as foreign and initiates cellular immunity against it.
-
Question 15 of 93
15. Question
Match each disease with its correct type of vaccine. [2015]
\(
\begin{array}{|l|c|c|c|}
\hline \text { A } & \text { Tuberculosis } & 1 & \text { Harmless virus } \\
\hline \text { B } & \text { Whooping cough } & 2 & \text { Inactivated toxin } \\
\hline \text { C } & \text { Diphtheria } & 3 & \text { Killed bacteria } \\
\hline \text { D } & \text { Polio } & 4 & \text { Harmless bacteria } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 16 of 93
16. Question
The active form of Entamoeba histolytica feeds upon (2015 Cancelled)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Entamoeba histolytica (Gr., entos : within + amoeba : change + histos : : : : lysue : dissolve) is the causative organism of amoebic dysentery or amoebiasis in man. It is a microscopic endoparasite of man. It is commonly found in the upper part of the large intestine (colon) and is very often lodged in the liver, lungs, brain and testes. In its life cycle, it occurs in three distinct forms (i) trophozoite or magna form, (ii) precystic or minuta form, and (iii) cystic form. Trophozoite is the most active, motile and feeding form which is pathogenic to man. It lives in the mucous and submucous layers of the colon and feeds on these layers and erythrocytes.
-
Question 17 of 93
17. Question
HIV that causes AIDS, first starts destroying (2015 Cancelled)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : The AIDS retrovirus, called human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), mounts a direct attack on \(\mathrm{CD}^{+} \mathrm{T}\) helper cells because it recognizes the CD4 coreceptors associated with these cells.HIV’s attack on \(\mathrm{CD} 4^{+} \mathrm{T}\) cells cripples the immune system in at least three ways. First, HIV-infected cells die only after releasing replicated viruses that infect other \(\mathrm{CD} 4^{+} \mathrm{T}\) cells, until the entire population of \(\mathrm{CD} 4^{+}\) T cell is destroyed. Second, HIV causes infected CD\(4^{+}\) \(\mathrm{T}\) cells, to secrete a soluble suppressing factor that blocks other \(\mathrm{T}\) cells from responding to the HIV antigen. Finally, HIV may block transcription of MHC genes, hindering the recognition and destruction of infected \(\mathrm{CD} 4^{+} \mathrm{T}\) cells, and thus protecting those cells from any remaining vestiges of the immune system. The combined effect of these responses to HIV infection is to wipe out the human immune defense.
-
Question 18 of 93
18. Question
Which is the particular type of drug that is obtained from the plant whose one flowering branch is shown here? [2014]
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a): The plant illustrated in the diagram is Datura. Seeds of Datura stramonium are misused for their hallucinogenic properties because of the presence of anticholinergic alkaloids atropine, hyoscyamine and scopolamine (= hyoscine). However, even in slight excess, they can cause death.
-
Question 19 of 93
19. Question
At which stage of HIV infection does one usually show symptoms of AIDS? (NEET 2014)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : AIDS is a disorder of cell-mediated immune system of the body. Virus responsible for AIDS is HIV (Human immunodeficiency virus). There is a reduction in the number of helper T-cells which stimulate antibody production by B-cells. This results in the loss of natural defence against viral infection.
-
Question 20 of 93
20. Question
Infection of Ascaris usually occurs by (NEET 2013)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c): Man acquires infection of Ascaris by directly ingesting Ascaris eggs, containing the infective second stage larva, with contaminated food or water. Life cycle of Ascaris is monogenetic. There is no vector or intermediate host.
-
Question 21 of 93
21. Question
Which one of the following statements is correct regarding sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)? (Karnataka NEET 2013)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Syphilis is caused by bacterium Treponema pallidum. It is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) which is transferred through sexual intercourse with infected person. Haemophilia is a X-linked genetic disorder of blood. It is not transmitted via any sexual practice. Genital herpes is an STD while sickle-cell anaemia is an autosomal hereditary disorder. The chances of a 5 year boy contracting an STD are very little since he is unlikely to have sex at this age.
-
Question 22 of 93
22. Question
Identify the site where Wuchereria bancrofti is normally found in human body.(Karnataka NEET 2013)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Wuchereria bancrofti is a dreaded human parasite. It is a digenetic parasite completing its life cycle in two hosts, the final host is man harbouring the adult worm.
The disease passes through four stages in human beings:
In the first stage, the patient has increased eosinophils, enlarged lymph nodes. Second or carrier stage is symptomless. Third stage is characterised by filarial fever, inflammation of lymph nodes (lymphadenitis) and lymph vessels (lymphangiectasis) and reversible lymphoedema (excess fluid in tissues due to obstruction of lymph vessels) in various body parts. The fourth or final stage is manifestated by lymphoedema accompanied by thickening of subcutaneous tissues and skin so that there is permanent swelling mostly of feet, legs, thighs, scrotal sacs, breast etc. It is called elephantiasis. -
Question 23 of 93
23. Question
Which one of the following is a hallucinogenic drug? (Karnataka NEET 2013)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : LSD is a psychedelic drug since it causes optical and auditory hallucinations and induces behavioural abnormalities. Opium and morphine are opiate narcotics that suppress brain activity and relieve pain. Caffeine is a stimulant that temporarily stimulates the nervous system.
-
Question 24 of 93
24. Question
Motile zygote of Plasmodium occurs in (NEET 2012)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a): Plasmodium, a tiny protozoan parasite causes malaria in humans, and is transmitted through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquito. When female Anopheles sucks the blood of infected human it takes up gametocytes (sexual stages of parasite) with blood meal. The gametocytes come out of the RBCs into the lumen (cavity) of the stomach of the mosquito. In the stomach, the male gametocyte divides and forms 6 to 8 long, motile, whip-like microgametes (male gametes). The female gametocyte does not divide but undergoes a process of maturation to become the macrogamete (female gamete). A microgamete penetrates a macrogamete and fertilization (syngamy) takes place, resulting in the formation of a zygote. The zygote elongates and becomes worm like motile organism called ookinete. Ookinete further changes into sporozoites (mature infective stage of Plasmodium).
-
Question 25 of 93
25. Question
Widal test is carried out to test (NEET 2012)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Widal test (developed by G.F.I Widal) is an agglutination test for the presence of antibodies against the Salmonella organism that cause typhoid fever. It is used to diagnose the presence of the disease in a patient.
-
Question 26 of 93
26. Question
Common cold differs from pneumonia in that (NEET 2012)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Common cold or rhinitis is one of the most infectious diseases caused by Rhino viruses. It affects nose and respiratory passage but not lungs. It spreads by droplet infection or contaminated objects. Pneumonia, caused by bacteria Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae is a serious disease of lungs, in which fluid collects in the alveoli and bronchioles. The disease spreads by sputum of the patient.
-
Question 27 of 93
27. Question
Which one of the following is not a property of cancerous cells whereas the remaining three are? (NEET 2012)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Contact inhibition is a property of normal cells by virtue of which contact with other cells inhibits their uncontrolled growth. Cancerous cells lack this property.
-
Question 28 of 93
28. Question
Cirrhosis of liver is caused by the chronic intake of (NEET 2012)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Cirrhosis is a condition in which the liver responds to injury or death of some of its cells by producing interlacing strands of fibrous tissuebetween which are nodules of regenerating cells. The liver becomes tawny and characteristically knobbly (due to the nodules). One of the causes include alcoholism (alcoholic cirrhosis).
-
Question 29 of 93
29. Question
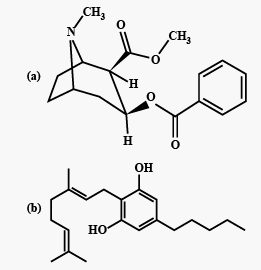
Identify the molecules (a) and (b) shown above and select the right option giving their source and use. (2011)
 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) The given chemical structures (a) and (b) are of morphine and cannabinoid respectively. Morphine is the principal opium alkaloid. It is a strong analgesic. It also has sedative and calming effect. Morphine depresses respiratory centre, it contributes to the fall in blood pressure. Morphine is a very effective sedative and painkiller. It is very useful in patients who have undergone surgery. Natural cannabinoids are obtained from the inflorescence of hemp plant Cannabis sativa, family Cannabinaceae. They affect the cardiovascular system of the body.
-
Question 30 of 93
30. Question
Where will you look for the sporozoites of the malarial parasite? (NEET 2011)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Sporozoites represent the infective forms of malarial parasite. A healthy person acquires infection, when a female Anopheles mosquito, containing sporozoites, bites the person for sucking his blood. The mosquito punctures the host’s skin by its proboscis and first introduces some saliva into the blood stream. Along with saliva, thousands of sporozoites are inoculated in the host also.
-
Question 31 of 93
31. Question
Which one of the following options gives the correct match of a disease with its causative organism and mode of infection? (2011)
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Disease } & \text { Causative Organisms } & \text { Mode of Infection } \\
\hline \mathbf{1} & \text { Malaria } & \text { Plasmodium vivax } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Bite of male Anopheles } \\
\text { mosquito }
\end{array} \\
\hline \mathbf{2} & \text { Typhoid } & \text { Salmonella typhi } & \text { With inspired air } \\
\hline \mathbf{3} & \text { Pneumonia } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Streptococcus } \\
\text { pneumoniae }
\end{array} & \text { Droplet infection } \\
\hline \mathbf{4} & \text { Elephantiasis } & \text { Wuchereria bancrofti } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { With infected water and } \\
\text { food }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Disease – Causative organism – Mode of infection typhoid – Salmonella typhi – contaminated food and water. pneumonia – Streptococcus pneumoniae – droplet infection. elephant iasis – Wuchereria bancrofti – bite of infected female mosquito malaria – Plasmodium vivax – bite of infected female Anopheles mosquito.
-
Question 32 of 93
32. Question
Common cold is not cured by antibiotics because it is (Mains 2011)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a): Common cold is caused by some 100 types of Rhino viruses. It is one of the most common infectious disease in human. Antibiotics are substances that destroy or inhibit the growth of microorganisms, particularly disease-producing bacteria and fungi. Antibiotics are obtained from microorganisms (especially moulds) or synthesized. Many antibiotics interfere with the pathogen protein synthesis. Some (e.g. Penicillin) prevent cross-linking of the glycan chains of peptidoglycan molecules in bacterial cell walls. Since the viruses do not possess cell wall and their own protein synthesising apparatus, they are not attacked by antibiotics.
-
Question 33 of 93
33. Question
Ringworm in humans is caused by (NEET 2010)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Ringworm (tinea) is a fungal infection of the skin, the scalp, or the nails. Ringworm is caused by the dermatophyte fungi-species of microsporum, trichophyton, and epidermophyton and also affects animals, a source of infection for humans. It can be spread by direct contact or via infected materials. The lesions of ringworm may form partial or complete rings and may cause intense itching. The disease is treated with antifungal agents taken by mouth or applied locally.
-
Question 34 of 93
34. Question
Widal test is used for the diagnosis of (NEET 2010)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d):
-
Question 35 of 93
35. Question
Which one of the following statements is correct with respect to AIDS? (NEET 2010)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : AIDS (acquired immuno deficiency syndrome) a syndrome, is caused by the retrovirus HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). The virusdestroys a subgroup of lymphocytes, the helper T-cells (or CD4 lymphocytes), resulting in suppression of the body’s immune response. HIV is transmitted in blood, semen and vaginal fluid; the major routes of infection are unprotected vaginal and anal intercourse, intravenous drug abuse, and the administration of contaminated blood and blood products. A combination of antiviral drugs can delay the development of full-blown AIDS for many years but cannot fully care the disease.
-
Question 36 of 93
36. Question
Infectious proteins are present in (NEET 2010)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Prions are named by Stanley Prusiner (got Nobel Prize in 1997). Prions are infectious agents which are made of proteins only (without nucleic acid). Prions are the causal agents of scrapie disease of sheep.
-
Question 37 of 93
37. Question
Select the correct statement from the ones given below. (NEET 2010)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Morphine is an potent opioid analgesic used mainly to relieve severe and persistent pain, particularly in terminally ill patients or who have undergone surgery. It also induces feelings of euphoria. It is administered by mouth, injection, or in suppositories. Common sideeffects are nausea and vomiting, constipation, and drowsiness. With regular use, tolerance develops and dependence may occur.
-
Question 38 of 93
38. Question
Which one of the following techniques is safest for the detection of cancers? (NEET 2010)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Histopathological study is the invasive technique. Radiography and CT involves X-rays which are harmful.
In MRI strong magnetic fields and non-ionising radiations are used to detect any physiological changes in the concerned tissue. Hence it is safe for detection of cancers. -
Question 39 of 93
39. Question
A person suffering from a disease caused by Plasmodium, experiences recurring chill and fever at the time when (Mains 2010)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Plasmodium is a tiny protozoan which is responsible for malaria in the human. In malaria the patient experiences high fever which periodically rises and also experiences recurring chills with fever. Such symptoms are seen because when the RBCs carrying Plasmodium (one of the stage in the life cycle of the parasite) ruptures it releases a toxic substance called haemozoin which is chiefly responsible for the chill and high fever recurring every three to four days.
-
Question 40 of 93
40. Question
Which one of the following statements is correct? (NEET 2009)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Tumour is of two types : benign and malign. Malign or malignant tumour exhibit metastasis. It is the phenomenon in which cancer cells spread to distant sites through body fluids to develop secondary tumour.
-
Question 41 of 93
41. Question
Which of the following is a pair of viral diseases? (NEET 2009)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Common cold is a viral disease. It is caused by Rhino viruses. It causes fever and pain all over the body and affects the nose, throat and air passages. AIDS (Acquired immuno deficiency syndrome) is a disorder of cell mediated immune system of the body. It is caused by HIV (Human immunodeficency virus). \(\mathrm{HIV}\) is a retrovirus that attacks helper T-cells.
-
Question 42 of 93
42. Question
Match the disease in column I with the appropriate items (pathogen/prevention/treatment) in column II. (2009)
\(
\begin{array}{|c|c|}
\hline \text { Column I } & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { (i) Amoebiasis } & \text { (a) Treponema pallidum } \\
\hline \text { (ii) Diphtheria } & \text { (b) Use only sterilized food and water } \\
\hline \text { (iii) Cholera } & \text { (c) DPT vaccine } \\
\hline \text { (iv) Syphilis } & \text { (d) Use oral rehydration therapy } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Amoebiasis is caused by Entamoeba histolytica. Prevention of infection is entirely a matter of hygiene, both personal as well as municipal. Their prevention include use of only sterilized food and water. Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae. The symptoms are fever, sore throat, severe damage to heart, nerve cell and adrenal glands. The vaccine DPT is used for diphtheria, pertusis and tetanus. Cholera is caused by Vibrio cholerae, a Gram negative bacterium. It spreads by faecal contamination. The dehydration and loss of mineral salts can cause death. It is treated by use of oral rehydration therapy. Syphilis is caused by Treponema pallidum, a spirochaete and it spread by sexual contact.
-
Question 43 of 93
43. Question
Which one of the following is the correct statement regarding the particular psychotropic drug specified? (NEET 2008)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Hashish or charas is a pure resin obtained from female flowers and leaves of selected varieties of Cannabis sativa. It is the most potent hemp product (cannabinoids), and is usualy smoked with tobacco. Its use may lead to euphoria, hallucination, drowsiness and continuous laughing. The hallucinogens act mainly on CNS and greatly alter one’s thought, feelings and perceptions.
-
Question 44 of 93
44. Question
Increased asthmatic attacks in certain seasons are related to (NEET 2007)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b): Increased asthmatic attacks in certain seasons are related to inhalation of seasonal pollen. Pollens are microscopic grains produced by plants in order to reproduce. Pollen allergy is a hypersensitive reaction to pollen. Pollen induced reactions include extrinsic asthma, rhinitis and bronchitis.
-
Question 45 of 93
45. Question
Lysozyme that is present in perspiration, saliva and tears, destroys (NEET 2007)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Lysozyme is an antibacterial enzyme with natural antibiotic properties. Normally excreted in the tears, nasal mucus, milk, and saliva in most animals, lysozyme is part of the body’s first natural defence against bacteria and viruses. Lysozyme is an enzyme that degrade the polysaccharide protective coating on the surface of many bacteria and viruses (glycoprotein covering) to allow other enzymes and antibodies to find their appropriate attachment sight. Most of the bacteria affected by lysozyme are not pathogenic. Lysozyme serves as a non-specific innate opsonin by binding to the bacterial surface, reducing the negative charge and facilitating phagocytosis of the bacterium before opsonins from the acquired immune system arrive at the scene. In other words, lysozyme makes it easier for phagocytic white blood cells to engulf bacteria.
-
Question 46 of 93
46. Question
The causative agent of mad-cow disease is a (NEET 2006)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Mad cow disease is the common term for Bovine spongiform encepholopathy (BSE), a progressive neurological disorder of cattle. It is caused by prions. Symptoms include an excitable or nervous temperament to external stimuli such as touch to the skin. A prion (short for proteinaceous infectious particle) is a unique type of infectious agent, as it is made only of protein. Prions are abnormally structured forms of a host protein, which are able to convert normal molecules of the protein into the abnormal structure.
-
Question 47 of 93
47. Question
The bacterium (Clostridium botulinum) that causes botulism is (NEET 2006)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Clostridium is a genus of gram-positive bacteria. They are obligate anaerobes capable of producing endospores. Individual cells are rodshaped.
Foodborne disease caused by \(C\). botulinum is referred to as botulism (a muscle-paralyzing disease). It is caused by the ingestion of a neurotoxin (botulin) produced by the microorganism in the food. Botulin blocks nerve function leading to respiratory and musculoskeletal paralysis. Symptoms of botulism include weakness, fatigue and dizziness, followed by blurred vision and progressive difficulty in speaking and swallowing. Weakening of the respiratory muscles is also observed and death may occur due to respiratory failure. -
Question 48 of 93
48. Question
HIV that causes AIDS, first starts destroying (NEET 2006)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a):
-
Question 49 of 93
49. Question
Antibodies in our body are complex (NEET 2006)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Antibody are members of a class of proteins known as immunoglobulins. Immunoglobulins are glycoproteins in the immunoglobulin superfamily. The terms antibody and immunoglobulin are often used interchangeably. They are found in the blood and tissue fluids, as well as many secretions. In structure, they are globulins (in the \(\gamma\)-region of protein electrophoresis). They are synthesized and secreted by plasma cells that are derived from the B cells of the immune system.
-
Question 50 of 93
50. Question
Which one of the following depresses brain activity and produces feelings of calmness, relaxation and drowsiness? (NEET 2005)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) :Valium is a benzodiazephine (sedative) that gives a feeling of relaxation, calmness or drowsiness in the body. Morphine is the main opium alkaloid that depresses respiratory centre and contributes to the fall in blood pressure. Amphetamines are synthetic drugs and are stimulant in nature. Hashish is a hallucinogen.
-
Question 51 of 93
51. Question
Damage to thymus in a child may lead to (NEET 2005)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : The thymus is the major gland of our immune system. The thymus is responsible for many immune system functions including the production of T-lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell responsible for cell mediated immunity. Cell mediated immunity is a type of immunity in which specialized cells carry out defensive activities. They protect the body against pathogens including the protists and fungi which have entered the host’s cells. T-cells and B-cells are the type of lymphocytes that develop from bone marrow cells. Those lymphocytes that migrate to the thymus and differentiate are called T-cells and those cells that continue to be in the bone marrow for differentiation are known as B-cells. T-cells are responsible for cell mediated immunity, however, B-cells produce antibodies and take part in antibody mediated immunity.
-
Question 52 of 93
52. Question
Which one of the following is not correctly matched? (NEET 2004)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : All the options given are diseases with their associated vector which transmit the respective diseases.
Leishmaniasis, also called kala azar is caused by Leishmania donovani. It is spread by sand fly (Phlebotomus) and characterised by enlarged spleen and liver with high fever.
Sleeping sickness is caused by a protozoan Trypanosoma gambiense. Filariasis is caused by worm Wuchereria bancrofti. Dengue fever is caused by arbo virus. -
Question 53 of 93
53. Question
Carcinoma refers to (NEET 2003)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Carcinoma is a cancer that arises in epithelium, the tissue that lines the skin and internal organs of the body. It may occur in any tissue containing epithelial cells. It includes cervical cancer, breast cancer, skin cancer, stomach cancer etc.
-
Question 54 of 93
54. Question
Short-lived immunity acquired from mother to foetus across placenta or through mother’s milk to the infant is categorised as (NEET 2003)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Short-lived immunity acquired from mothers to foetus across placenta or through mother’s milk to the infant is categorised as passive immunity. Passive immunity, an acquired immunity, is resistance based on antibodies performed in another host. In this case, the foetus is not directly responsible for its body immunity but it becomes immunised by mother’s milk across placenta.
-
Question 55 of 93
55. Question
Cancerous cells can easily be destroyed by radiations due to (NEET 2002)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Cancerous cells are the cells that undergo rapid cell division. These cells are destroyed by X-ray radiaton. During cell division, the DNA double helix opens up and undergo various other processes. Such processes are disrupted when exposed to radiation and the cancerous cells die selectively when radiated.
-
Question 56 of 93
56. Question
Which one of the following is correct match? (NEET 2001)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a): Tranquillisers are drugs that have good effect in all types of psychosis, especially in schizophrenia. In a psychotic patient, these drugs reduce aggressiveness, thoughts and behaviour are gradually normalized and anxiety is relieved, e.g., reserpine which is an alkaloid extracted from the roots of Rauwolfia serpentina. Higher doses of it can cause sedation and mental depression. Cocaine is a stimulant. Morphine is an opiate narcotic. Bhang is a hallucinogenic.
-
Question 57 of 93
57. Question
L.S.D. is (NEET 2001)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a): Hallucinogens are drugs that change thoughts, feelings and perceptions of individuals. They cause hallucinations. LSD (Lysergic acid diethylamide) is one such hallucinogen that causes horrible dreams, chronic psychosis and severe damage to the central nervous system. Sedatives give a feeling of calmness, relaxation or drowsiness in the body. Their high doses induce sleep. Tranquillisers lower tension and anxiety without inducing sleep. Stimulants are the drugs that stimulate the nervous system, make a person more wakeful, alert and active; and cause excitement.
-
Question 58 of 93
58. Question
Salmonella is related with (NEET 2001)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Typhoid is caused by Salmonella typhi. The organisms of the disease are present in the stool. They may be present in urine. They can, therefore, be carried by water and contaminated food. Their spread through water can give rise to severe epidemics.
Polio is caused by Enterovirus. TB is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tetanus is caused by Clostridium tetani. -
Question 59 of 93
59. Question
Which is the most infectious disease? (NEET 2001)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a): Hepatitis B (serum hepatitis) occurs at any age and mode of transmission is through contact or blood. Infection is severe, often fatal and is accompanied by loss of appetite, nausea, whitish stool (due to lack of bile) and jaundice. \(0.0002 \%\) of hepatitis B infected blood contact is enough to transmit hepatitis B.
-
Question 60 of 93
60. Question
Interferons are synthesized in response to (NEET 2001)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Interferons are proteins that increase the resistance of a cell to attack by viruses by unmasking genes that synthesize antiviral proteins. In humans, three groups of interferons have been discovered: \(\alpha\) interferons from white blood cells; \(\beta\)-interferons from connective tissue fibroblasts; and \(\gamma\)-interferons from lymphocytes.
-
Question 61 of 93
61. Question
Reason of lung cancer is (AIPMT 2001)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a): Lung cancer is a disease where tissue in the lung grows out of control. This may lead to metastasis, invasion of adjacent tissue and infiltration beyond the lungs. The vast majority of primary lung cancers are carcinomas of the lung, resulting from epithelial cells. One of the causes of lung cancer is exposure to coal dust. Exposure to coal dust can cause some coal mine workers to develop pneumoconiosis, or “black lung.” This occurs when inhaled coal dust becomes embedded in the lungs, causing them to harden and making breathing difficult.
-
Question 62 of 93
62. Question
Which is showing accurate pairing? (AIPMT 2000)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Syphilis is caused by a spirochete (spiral bacterium) Treponema pallidum. The symptoms of syphilis occur in three stages. The first stage usually consists of a painless lesion called a chancre at the organism’s site of entry. The second stage begins as the organism enters the blood. Symptoms such as fever, a flu like illness, a skin rash, hair loss, and swollen joints may come and go over a period of several years. In the third stage permanent brain damage, heart disease, and blindness often occurs.
AIDS is a viral disease caused by Human Immuno deficiency virus. Gonorrhoea is a sexual disease and its causative organism is Neisseria gonorrhoea. Typhoid is caused by bacillus bacteria Salmonella typhi. -
Question 63 of 93
63. Question
Which disease of man is similar with cattle’s, bovine spongiform encephalopathy? (AIPMT 2000)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : The common term for bovine spongiform encephalopathy is mad cow disease, which is a progressive neurological disorder of cattle. In humans it is called Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, after the two doctors who first described the symptoms of the disease. It is caused by prions (proteinaceous infectious particles). It is characterized by rapidly progressive dementia associated with myoclonic jerks. The brains of affected individuals show a characteristic cystic degenerations.
-
Question 64 of 93
64. Question
Saline solution is given to patients of cholera because (AIPMT 2000)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Cholera is an acute infection of the small intestine by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, which causes severe vomiting and diarrhoea (known as ricewater stools) leading to dehydration. The disease is contracted from food or drinking water contaminated by faeces from a patient. The resulting dehydration and the imbalance in the concentration of body fluids can cause death within 24 hours. Since, a large quantity of fluid and salts are rapidly lost through stools and vomit, therefore, the most important treatment is to replace the lost fluid and salts equally rapidly. Rapid replacement of fluid and elecrolytes is needed by oral rehydration-therapy. The electrolytes consists of \(\mathrm{Na}^{+}\)ions that prevents water loss from the body.
-
Question 65 of 93
65. Question
The antibodies are (AIPMT 1999)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a)
-
Question 66 of 93
66. Question
The term ‘active immunity’ means (AIPMT 1999)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Active immunity is the immune response generated in an individual due to contact with infectious pathogen or vaccination. In many cases, it is life long.
-
Question 67 of 93
67. Question
Human immuno deficiency virus (HIV) has a protein coat and a genetic material which is (AIPMT 1998)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : HIV is a retrovirus, which contains single stranded RNA, surrounded by protein coat (core shell) as genetic material. It causes AIDS. HIV is different in structure from other retroviruses. It is around \(120 \mathrm{~nm}\) in diameter (around 60 times smaller than a red blood cell) and roughly spherical.
-
Question 68 of 93
68. Question
Botulism caused by Clostridium botulinum affects the (AIPMT 1998)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) :
-
Question 69 of 93
69. Question
Typhoid fever is caused by (AIPMT 1998)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d):
-
Question 70 of 93
70. Question
Which of the following is an opiate narcotic? (AIPMT 1997)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) Opiates are derived from opium along with their synthetic relatives. Opiates have narcotic, analgesic, sedative and astringent effects. Narcotic is a drug that induces stupor and relieves pain. Morphine is the main opium alkaloid, which is a strong analgesic and also has sedative and calming effect. It depresses respiratory centre and contributes to the fall in blood pressure. It can cause release of \(\mathrm{ADH}\), reduction in urine output, constipation and mild hyperglycaemia etc. It causes addiction. Barbiturates are substituted derivatives of barbituric acid. They reduce anxiety and induce sleep. Amphetamines are synthetic drugs which are strong stimulants. LSD (Lysergic acid diethylamide) is the most powerful hallucinogens that causes severe damage to central nervous system.
-
Question 71 of 93
71. Question
Which of the following will be curable in next two decades? (AIPMT 1997)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Cancer may be curable in next two decades. The completion of the human genome is causing profound changes in thinking and direction of biomedical research. Cancer is caused by malfunctioning of genes, either through activation of cancer causing oncogens, or through inactivation of tumor suppressor genes. By comparing the active genes in the tumor to that of normal cells, the genes causing the cancer can be determined. Side by side there is a huge progress in the field of genetic engineering and biotechnology. All these aspects give us hope that cancer may be curable in next two decades. TB is curable by taking anti-tubercular drugs and polio may be on the verge of eradication if the pulse polio programme succeeds.
-
Question 72 of 93
72. Question
Diphtheria is caused by (AIPMT 1997)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Diphtheria is caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae (bacteria) usually affecting children upto five years of age. It may start as sore throat, chills with mild fever, sometimes vomiting and headache. Throat and/or tonsils show a grey membrane which may spread down and cause hoarseness and difficulty in breathing. Nose may be affected giving rise to a blood-tinged nasal discharge from one nostril. If the disease is not treated early and properly the toxin produced by the bacteria affects the heart and the nervous system, and proves fatal. The germs are present in the discharges from the nose and throat of patients and also of healthy people who act as the “carriers”. The patients and the carriers spread the disease through acts like kissing, talking, coughing and sneezing. Incubation period is of \(2-5\) days. The patient should be kept in a well-ventilated room if there is no isolation hospital in the town. The most important preventive measure-against this disease is that all babies should be immunised within the first six weeks of birth using DPT vaccine.
-
Question 73 of 93
73. Question
Which of the following diseases is now considered completely eradicated from India? (AIPMT 1997)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a): Small pox is an acute highly communicable disease. It is caused by virus named Variola virus. Now it is eradicated from world including India. It is highly infectious disease starting with high fever, chill, backache and headache, followed by appearance of rash on the third day of illness. The rash appears first on the face, then on the rest of the body. The rash starts as small reddish spots which change into papules. These in turn change into small vesicles containing clear fluid. Vesicles change into postules. Finally, a scab is formed and it falls off by the third week. These scabs leave deep pits or scars known as pock marks. The virus is present in the oral and nasal discharges of the patients and is ejected during the acts of coughing, sneezing, etc., and infects the healthy people.
-
Question 74 of 93
74. Question
Which of the following symptoms indicate red sickness? (AIPMT 1997)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : The symptoms of red sickness are ulcerated skin, nausea and loss of hair.
-
Question 75 of 93
75. Question
If a person shows production of interferons in his body, the chances are that he has got an infection of (AIPMT 1997)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Interferons are antiviral proteins that increase the resistance of a cell to attack by viruses. As measles is a viral disease, so body produces interferons. Measles is an acute infectious eruptive viral disease of childhood, caused by an RNA containing Rubeola virus/Polynosa morbillorum. Typhoid and tetanus are bacterial diseases caused by Salmonella typhi and Clostridium tetani respectively. Malaria is a protozoan disease caused by Plasmodium species.
-
Question 76 of 93
76. Question
Which of the following pair of diseases is caused by virus? (AIPMT 1996)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Mumps is an infectious disease causing fever, difficulty in opening the mouth and painful swelling of the parotid glands which lie just below the lobe of the ears. It is caused by a Paramyxovirus, which comes out in the saliva of the infected person. Rabies (Hydrophobia) is caused by a virus named as rabies virus. It is introduced in the body by the bite of rabid (mad) dogs usually. Fear of water is the most important characteristic symptom of this disease.Other symptoms are saliva from the mouth, severe headache, high fever, alternating periods, of excitement and depression, inability to swallow even fluids due to choked throat. The virus destroys the brain and spinal cord. Rabies is \(100 \%\) fatal.
Cholera and tuberculosis are bacterial diseases caused by Vibrio cholerae and Mycobacterium tuberculosis respectively. Typhoid and tetanus are bacterial diseases caused by Salmonella typhi and Clostridium tetani respectively. AIDS is caused by HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). Syphillis is caused by spirochaete Treponema pallidum. -
Question 77 of 93
77. Question
Antibodies are produced by (AIPMT 1996)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Lymphocytes secrete antibodies to destroy microbes and their toxins, reject grafts and kill tumor cells. Antibodies are protein in nature. Monocytes (type of WBC) is phagocytic in nature and engulf bacteria and cellular debris. Spleen is an organ that produces lymphocytes.
-
Question 78 of 93
78. Question
The interferons are (AIPMT 1996)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b):
-
Question 79 of 93
79. Question
Which of the following is the false statement about antibiotics? (AIPMT 1996)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Antibiotics are not capable of curing any disease. Antibiotics are those substances that destroy or inhibit the growth of micro-organisms, particularly disease producing bacteria and fungi. The term antibiotic was introduced by Waksman in 1942. Antibiotics are obtained form micro-organisms (especially moulds) or synthesized. Common antibiotics include penicillins, streptomycin and tetracyclines. They are used to treat various infections but tend to weaken the body’s natural defence mechanisms and can cause allergies. Overuse of antibiotic can lead to the development of resistant strains of micro-organism.
-
Question 80 of 93
80. Question
Nicotine acts as a stimulant, because it mimics the effect of (AIPMT 1995)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Nicotine is the major stimulatory component of tobacco products including cigarettes. Nicotine has a number of effects on the human body similar to acetylcholine. It stimulates passage of nerve impulses, causes muscles to relax and causes the release of adrenaline, increasing both blood pressure and heart beat rate.
-
Question 81 of 93
81. Question
The blood cancer is known as (AIPMT 1995)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c): The normal count of WBCs is 5000 to 10000 per cubic millimeter of blood. Leukaemia or blood cancer is characterized by abnormal increase of WBCs count, \(20000-1000000 / \mathrm{mm}^3\) due to their increased formation in the bone marrow. Haemolysis is breakdown of RBCs. Haemophilia is a disease in which blood clots slowly. Thrombosis is a clot formation inside the blood vessels.
-
Question 82 of 93
82. Question
Which one of the following pairs is not correctly matched? (AIPMT 1995)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Syphilis is caused by a spirochete (spiral bacterium) Treponema pallidum.Sleeping sickness is a disease of tropical Africa caused by the presence in the blood of the parasitic protozoan, Trypanosoma gambiense. Plague is an epidemic disease of rats which is transmitted to humans by rat fleas. Dengue is a disease transmitted to humans by mosquito, Aedes aegypti.
-
Question 83 of 93
83. Question
Which one of the following diseases is due to an allergic reaction? (AIPMT 1995)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Hay fever is a form of allergy due to the pollen of grasses, trees, and other plants, characterized by inflammation of the membrane lining the nose and sometimes of the conjunctiva. The symptoms of sneezing, running or blocked nose, and watering eyes are due to histamine released by the mast cells.
-
Question 84 of 93
84. Question
Which of the following causes plague? (AIPMT 1995)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Plague is an acute epidemic disease of rats and other wild rodents caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, which is transmitted to humans by rat fleas. Headache, fever, weakness, aching limbs, and delirium develop and are followed by acute painful swellings of the lymph nodes. Bleeding under the skin, producing black patches, can lead to ulcers, which may prove fatal. Treatment with tetracycline, streptomycin, and chloramphenicol is effective.
Trichinosis is caused by Trichinella spiralis which lives as an endoparasite in human intestine. Salmonella typhimurium causes enteric fevers. Leishmania donovani causes kala-azar. -
Question 85 of 93
85. Question
Antigens are present (AIPMT 1995)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : An antigen is any foreign substance like protein or polysaccaharide present on the external coating of pathogen, feathers, constituent of a vegetable, fruit, meat, drug, chemical, tissue or organ transplant which induces the immune system to produce antibodies.
-
Question 86 of 93
86. Question
A cell-coded protein that is formed in response to infection, with most animal viruses, is called (AIPMT 1994)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c):
-
Question 87 of 93
87. Question
Which one of the following does correctly match a sexually transmitted disease with its pathogen? (AIPMT 1994)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Syphilis is caused by a spirochete (spiral bacterium) Treponema pallidum. Gonorrhoea is caused by Neisseria gonorrhoea. Urethritis is inflammation of urethra.
-
Question 88 of 93
88. Question
A metastatic cancerous tumour is termed ‘sarcoma’ if the disorder is in (AIPMT 1994)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Fibroblasts are the cells present in connective tissue. Sarcomas are cancers that are located in connective and muscular tissues derived from mesoderm. Thus, they include the cancers of bones, cartilages, tendons, adipose tissue, lymphoid tissue and muscles.
-
Question 89 of 93
89. Question
The main reason why antibodies could not solve all the problems of bacteria mediated disease is (AIPMT 1994)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Bacteria develop mutant strains that become resistant to antibodies, so these antibodies become incapable of removing bacteria mediated diseases.
-
Question 90 of 93
90. Question
Opiate narcotic is (AIPMT 1993)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : The drugs derived from opium alongwith their synthetic relatives are called opioids or opiates. Opiates have narcotic, analgesic, astringent (that causes contraction of body parts), and sedative effect.
-
Question 91 of 93
91. Question
Give the correct matching of causative agent/ germ and disease. (AIPMT 1993)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d): Wuchereria bancrofti is a parasitic filarial nematode worm spread by a mosquito vector. It is one of the three parasites that cause lymphatic filariasis. Elephantiasis can result if the infection is left untreated. Limited treatment modalities exist and no vaccines have been developed. Malaria is caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium. Malaria parasites are transmitted by female Anopheles mosquitoes. Sleeping sickness or African trypanosomiasis is a parasitic disease in people and animals, caused by protozoa of genus Trypanosoma and transmitted by the tsetse fly. Kala-azar is caused by Leishmania (protozoan) and is transmitted by sand fly.
-
Question 92 of 93
92. Question
Analgesic drugs (AIPMT 1990)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : A substance that reduces pain without causing unconsciousness, either by reducing the pain threshold or by increasing pain tolerance. There are several categories of analgesic drugs, including morphine and its derivatives which produce analgesia by acting on the central nervous system; nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g. aspirin); and local anaesthetics.
-
Question 93 of 93
93. Question
Which one engulfs pathogens rapidly? (AIPMT 1989)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Neutrophils, are the most abundant type of white blood cells and form an integral part of the immune system. These phagocytes are normally found in the blood stream. However, during the acute phase of inflammation, particularly as a result of bacterial infection, neutrophils leave the vasculature and migrate toward the site of inflammation in a process called chemotaxis. They are the predominant cells in pus, accounting for its whitish/yellowish appearance. Neutrophils react within an hour of tissue injury and are the hallmark of acute inflammation. Monocytes are also phagocytes but take \(7-8\) hours to reach at the site of injury. Acidophils and basophils are not phagocytic in nature.