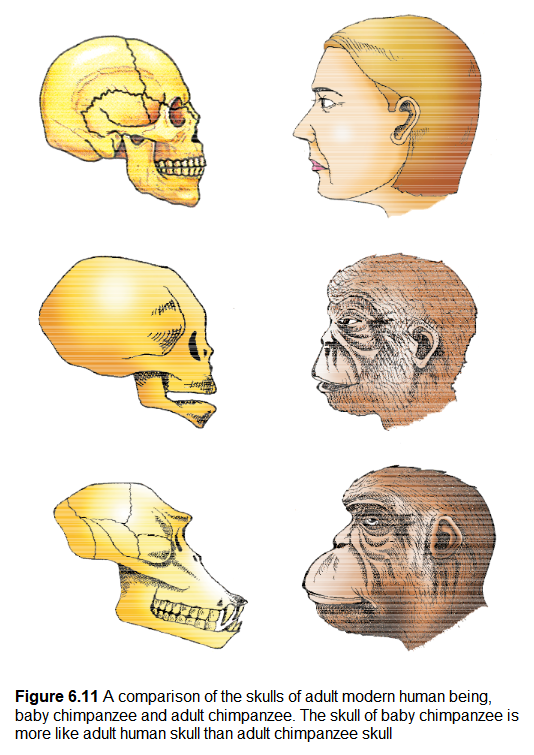
6.9 Origin and Evolution of Man
About 15 mya, primates called Dryopithecus and Ramapithecus were existing. They were hairy and walked like gorillas and chimpanzees. Ramapithecus was more man-like while Dryopithecus was more ape-like. Few fossils of man-like bones have been discovered in Ethiopia and Tanzania (Figure 6.11). These revealed hominid features leading to the belief that about 3-4 mya, man-like primates walked in eastern Africa. They were probably not taller than 4 feet but walked up right. Two mya, Australopithecines probably lived in East African grasslands. Evidence shows they hunted with stone weapons but essentially ate fruit. Some of the bones among the bones discovered were different. This creature was called the first human-like being the hominid and was called Homo habilis. The brain capacities were between 650-800cc. They probably did not eat meat. Fossils discovered in Java in 1891 revealed the next stage, i.e., Homo erectus about 1.5 mya. Homo erectus had a large brain around 900cc. Homo erectus probably ate meat. The Neanderthal man with a brain size of 1400 cc lived in near east and central Asia between 1,00,000-40,000 years back. They used hides to protect their body and buried their dead. Homo sapiens arose in Africa and moved across continents and developed into distinct races. During ice age between 75,000-10,000 years ago modern Homo sapiens arose. Pre-historic cave art developed about 18,000 years ago. One such cave paintings by Pre-historic humans can be seen at Bhimbetka rock shelter in Raisen district of Madhya Pradesh. Agriculture came around 10,000 years back and human settlements started. The rest of what happened is part of human history of growth and decline of civilisations.