Past Entrance Papers
Quiz Summary
0 of 45 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 45 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 45
1. Question
Which of the following is not a natural/traditional contraceptive method? [NEET 2024]
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) [NCERT pg 44]
Natural methods work on the principle of avoiding chances of ovum and sperms meeting. Periodic abstinence is one such method in which the couples avoid or abstain from coitus from day 10 to 17 of the menstrual cycle when ovulation could be expected. As chances of fertilisation are very high during this period, it is called the fertile period. Therefore, byabstaining from coitus during this period, conception could be prevented. Withdrawal or coitus interruptus is another method in which the male partner withdraws his penis from the vagina just before ejaculation so as to avoid insemination. Lactational amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) method is based on the fact that ovulation and therefore the cycle do not occur during the period of intense lactation following parturition. Therefore, as long as the mother breast-feeds the child fully, chances of conception are almost nil. However, this method has been reported to be effective only upto a maximum period of six months following parturition. As no medicines or devices are used in these methods, side effects are almost nil.
-
Question 2 of 45
2. Question
Match column I with column II, and choose the correct combination from the options given below.
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { a } & \text { Non-medicated IUD } & \text { 1 } & \text { Progestasert and LNG-20 } \\
\hline \text { b } & \text { Copper releasing IUD } & \text { 2 } & \text { Lippes loop } \\
\hline \text { c } & \text { Hormone releasing IUD } & \text { 3 } & \text { Cu-T, Cu-7 and Multiload-375 } \\
\hline \text { d } & \text { Barrier } & \text { 4 } & \text { Vaults } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) [NCERT pgno 44]
The correct option is \(\mathrm{C} a-2, b-3, c-1, d-4\)
Non-medicated IUD- Lippes loop Non-medicated IUDs work by immunomodulating the environment of the uterus. It initiates a sterile inflammatory response in the uterus which stimulates accumulation of macrophages. This results in the phagocytosis of the sperms. Examples include Lippes loop.Copper releasing IUD- Multiload 375 Copper releasing IUDs releases copper ions in the uterus which suppress the motility and fertilising ability of sperms and prevent fertilisation. Examples include CuT, Cu7, Multiload 375.
Hormone releasing IUD- LNG-20 Hormone-releasing IUDs release hormones such as progesterone in the uterus which make the cervix hostile by making the mucus thick and sticky due to which sperm are not able to reach the uterus. Besides, it makes the uterus unsuitable for allowing implantation. Examples include LNG-20 and progestasert.
Barrier contraceptive methods- Vaults Barrier contraceptive methods prevent the physical meeting of sperm and ovum. Examples include condoms, diaphragms, cervical caps etc. Vault is a barrier used by the females to cover their cervix during coitus to prevent fertilisation. -
Question 3 of 45
3. Question
Match List-I with List-II
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { List-I } & & \text { List-II } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & \text { Vaults } & \text { (i) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Entry of sperm through the } \\
\text { Cervix is blocked }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { (b) } & \text { IUDs } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Removal of Vas deferens } \\
\hline \text { (c) } & \text { Vasectomy } & \text { (iii) } & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Phagocytosis of sperms within } \\
\text { the Uterus }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { (d) } & \text { Tubectomy } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Removal of the fallopian tube } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: [NEET 2023]CorrectIncorrectHint
Answer (3)
(i) Vasectomy is a surgical method of contraception
(ii) Coitus interruptus is a natural method of contraception
(iii) Cervical cap is a barrier method of contraception
(iv) Saheli is an oral method of contraception which is a non-steroidal pill -
Question 4 of 45
4. Question
Lippe’s loop is a type of contraceptive used as: [NEET 2022]
CorrectIncorrectHint
Answer (3)
Sol. Option (3) is the correct answer because the intrauterine device (IUD) presently available as the nonmedicated IUDs, is Lippe’s loop.
Option (4) is incorrect as copper releasing IUDs are CuT, Cu7 and multiload 375.
Option (1) and (2) are incorrect as diaphragms, cervical caps and vaults are included in barrier method of contraception. -
Question 5 of 45
5. Question
\(
\text { Match List-I with List-II with respect to methods of Contraception and their respective actions. }
\)
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { List-I } & & \text { List-II } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & \text { Diaphragms } & \text { (i) } & \text { Inhibit ovulation and Implantation } \\
\hline \text { (b) } & \text { Contraceptive Pills } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Increase phagocytosis of sperm within Uterus } \\
\hline \text { (c) } & \text { Intra Uterine Devices } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Absence of Menstrual cycle and ovulation following parturition } \\
\hline \text { (d) } & \text { Lactational Amenorrhea } & \text { (iv) } & \text { They cover the cervix blocking the entry of sperms } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below [NEET 2022]CorrectIncorrectHint
Answer (2)
Sol. Option (2) is the correct answer because
Diaphragms are barrier methods of contraception. They cover the cervix and block the entry of sperms.
– Contraceptive pills are preparations containing either progestogens alone or combination of progestogen and oestrogen. They inhibit ovulation and implantation as well as alter the quality of cervical mucus to prevent entry of sperms.
– Intra uterine devices increase the phagocytosis of sperms within the uterus.
– Lactational amenorrhoea is a natural method of contraception and it is based on the fact that the ovulation and therefore menstrual cycle do not occur during the period of intense lactation following parturition. -
Question 6 of 45
6. Question
Match the following sexually transmitted diseases (column I) with their causative agent (column II) and select the correct option. [NEET 2017]
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|}
\hline & \text { Column I } & & \text { Column II } \\
\hline \text { (a) } & \text { Gonorrhea } & \text { (i) } & \text { HIV } \\
\hline \text { (b) } & \text { Syphilis } & \text { (ii) } & \text { Neisseria } \\
\hline \text { (c) } & \text { Genital Warts } & \text { (iii) } & \text { Treponema } \\
\hline \text { (d) } & \text { AIDS } & \text { (iv) } & \text { Human Papilloma virus } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)
\(
\begin{array}{lllll}
& \text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D } \\
\text { (a) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (iv) } & \text { (i) } & \text { (ii) } \\
\text { (b) } & \text { (iv) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (i) } \\
\text { (c) } & \text { (iv) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (i) } \\
\text { (d) } & \text { (ii) } & \text { (iii) } & \text { (iv) } & \text { (i) }
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(d)
-
Question 7 of 45
7. Question
The function of copper ions in copper releasing IUDs is (NEET 2017)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Copper releasing IUDs (i.e., CuT, LNG-20) are placed in the uterus of the females. They are an efficient birth control methods. Copper ions released by them suppress motility and fertilising capacity of the sperms.
-
Question 8 of 45
8. Question
In case of a couple where the male is having a very low sperm count, which technique will be suitable for fertilisation?
(NEET 2017)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b, c)
-
Question 9 of 45
9. Question
Which of the following is hormone-releasing IUD? (NEET-II 2016)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a): LNG-20 is the hormone releasing IUD, multiload 375 and \(\mathrm{Cu} 7\) are copper releasing IUDs and Lippes loop is a non-medicated IUD.
-
Question 10 of 45
10. Question
Which of the following is incorrect regarding vasectomy? (NEET-II 2016)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Vasectomy is a surgical contraception method performed in males. In vasectomy, a small part of the vas deferens is removed or tied up through a small cut on the scrotum. This prevents sperm transport. Vasectomy has a poor reversibility. There is no effect on libido and erectile functioning. Seminal vesicles are one pair of sac like structures which join vasa deferentia to form ejaculatory duct. They secrete seminal fluid which contains fructose, prostaglandins and clotting protein, but no sperms. In a male who has undergone vasectomy, the ejaculatory duct will receive seminal fluid but due to cut in vasa deferentia sperms will not be transported from epididymis hence the semen will lack sperms.
-
Question 11 of 45
11. Question
Which of the following approaches does not give the defined action of contraceptive? [NEET 2016]
\(
\begin{array}{|l|l|}
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { (a) Hormonal } \\
\text { contraceptives }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Prevent/retard entry of } \\
\text { sperms, prevent ovulation } \\
\text { and fertilisation }
\end{array} \\
\hline \text { (b) Vasectomy } & \text { Prevents spermatogenesis } \\
\hline \text { (c) Barrier methods } & \text { Prevent fertilisation } \\
\hline \begin{array}{l}
\text { (d) Intra uterine } \\
\text { devices }
\end{array} & \begin{array}{l}
\text { Increase phagocytosis of } \\
\text { sperms, suppress sperm } \\
\text { motility and fertilising } \\
\text { capacity of sperms }
\end{array} \\
\hline
\end{array}
\)CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Vasectomy is a sterilisation technique for the males in which a small part of the vas deferens is removed or tied up through a small cut on the scrotum to prevent passage of sperms. Spermatogenesis is the series of cell division in the testis that results in the production of spermatozoa or sperms.
-
Question 12 of 45
12. Question
Embryo with more than 16 blastomeres formed due to in vitro fertilisation is transferred into (NEET-II 2016)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Embryo with more than 16 blastomeres formed due to in vitro fertilisation is transferred into uterus (intra-uterine transfer, IUT).
-
Question 13 of 45
13. Question
In context of amniocentesis, which of the following statements is incorrect? (NEET-I 2016)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Amniocentesis is fetal sex determination and disorder test based on the chromosomal pattern in the amniotic fluid surrounding the developing embryo. It can be used to determine the sex of the infant, to identify some abnormalities in the number of chromosomes and to detect certain biochemicals and enzymatic abnormalities. It is usually done when woman is 14-16 weeks pregnant. Cleft palate can be detected by ultrasound.
-
Question 14 of 45
14. Question
A childless couple can be assisted to have a child through a technique called GIFT. The full form of this technique is (NEET 2015)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT) is an assisted reproductive technology in which both the sperm and unfertilised oocytes are transferred into the Fallopian tubes. Fertilisation takes place in vivo (inside the body of the female).
-
Question 15 of 45
15. Question
Which of the following is not a sexually transmitted disease? (NEET 2015)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b)
-
Question 16 of 45
16. Question
Which of the following viruses is not transferred through semen of an infected male? (NEET 2015)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Chikungunya virus is transmitted through an Aedes aegypti mosquito.
-
Question 17 of 45
17. Question
Tubectomy is a method of sterilization in which (NEET 2014)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Sterilization provides a permanent and sure birth control. In females, it is called tubectomy. Tubectomy involves the blocking of the Fallopian tubes. A small part of the Fallopian tube is removed or tied up through a small incision in the abdomen or through vagina.
-
Question 18 of 45
18. Question
Which of the following is a hormone releasing Intra Uterine Device (IUD)? (NEET 2014)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Intra uterine devices (IUDs) are plastic or metal objects which are inserted by doctors in the uterus through vagina. These are available as nonmedicated IUDs (i.e., Lippes loop), copper releasing IUDs (CuT, Cu7, Multiload 375) and hormone releasing IUDs (progestasert, LNG-20). Vault cap is hemispheric dome like rubber or plastic cap with a thick rim which is meant for fitting over the vaginal vault over the cervix.
-
Question 19 of 45
19. Question
Assisted reproductive technology, IVF involves transfer of (NEET 2014)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) include a number of special techniques which assist infertile couples to have children. An important technique of ART is test tube baby programme. The baby produced by conceiving in a culture dish and nursing in the uterus is called a test tube baby. This method involves in vitro fertilization (IVF), i.e., fertilization of male and female gamete outside the body in almost similar conditions as that in the body followed by embryo transfer (ET). Zygote or embryo upto 8 blastomeres is transferred into the Fallopian tube (ZIFT – Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer) and mature embryo with more than 8 blastomeres is transferred to uterus to complete its further development.
-
Question 20 of 45
20. Question
Artificial insemination means (NEET 2013)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : In artificial insemination technique, the semen of a healthy donor male is collected and is introduced artificially through a flexible polyethylene catheter into the vagina or into uterus called intrauterine insemination (IUI). Best results are obtained when the motile sperm count is more than 10 million. The fertilizing capacity of spermatozoa (sperms) is for 24 – 48 hours. The procedure may be repeated 2 3 times over a period of \(2-3\) days.
-
Question 21 of 45
21. Question
One of the legal methods of birth control is (NEET 2013)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Intentional or voluntary termination of pregnancy by taking an appropriate medicine before full term is called medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) or induced abortion. Nearly 45 to 50 million MTPs are performed in a year all over the world whichaccount to \(1 / 5\) th of the total number of conceived pregnancies in a year. MTP has a significant role in decreasing the population though it is not meant for that purpose. Government of India legalized MTP in 1971 with some strict conditions to avoid its misuse. Such restrictions are all the more important to check indiscriminate and illegal female foeticides.
-
Question 22 of 45
22. Question
The stage transferred into the uterus after induced fertilization of ovum in the laboratory is (Karnataka NEET 2013)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Cleavage divisions produce a solid ball of cells called morula. It has 8-16 cells, occasionally 32 cells. It is transferred into uterus (IUT-Intra-uterine transfer) for further development.
-
Question 23 of 45
23. Question
One of the following is not a method of contraception. Which one? (Karnataka NEET 2013)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Oxytocin is a birth hormone and vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone) reabsorbs water from the renal tubules to conserve water in the body. They have no role in contraception.
-
Question 24 of 45
24. Question
What is the figure given below showing in particular? (NEET 2012)
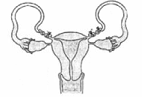 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c): Tubectomy involves blocking of the Fallopian tubes. The Fallopian tube are tied twice and cut between the knot. It prevents the sperms from reaching the ovum and thus prevents fertilization. It is a permanent method of sterilization.
-
Question 25 of 45
25. Question
The test-tube baby programme employs which one of the following techniques? (NEET 2012)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : In in vitro fertilization method, popularly known as test tube baby programme, ova from the wife/donor (female) and sperms from the husband/ donor (male) are collected and are induced to form zygote under simulated conditions in the laboratory. The zygote or early embryos (with upto 8 blastomeres) could then be transferred into the Fallopian tube (ZIFT-zygote intra Fallopian transfer) and embryos with more than 8 blastomeres, into the uterus (IUTintra uterine transfer), to complete its further development.
-
Question 26 of 45
26. Question
Which one of the following is the most widely accepted method of contraception in India at present? (NEET 2011)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : At present the most widely accepted method of contraception in India is IUDs. These Intra Uterine Devices (IUDs) are presently available as the nonmedicated IUDs (e.g., lippes loop), copper releasing IUDs (CuT, Cu7, Multiload 375) and the hormones releasing IUDs (Progestasert, LNG-20). IUDs increase phagocytosis of sperms within the uterus and the \(\mathrm{Cu}\)-ions released suppress sperm motility and the fertilizing capacity of sperms. The hormone releasing IUDs make the uterus unsuitable for implantation and cervix hostile to the sperms.
-
Question 27 of 45
27. Question
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) is considered safe up to how many weeks of pregnancy? (NEET 2011)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) or abortion is the termination of pregnancy before the foetus becomes viable. MTP is comparatively safe upto 12 weeks (the first trimester) of pregnancy. It becomes more risky after the first trimester period of pregnancy as the foetus becomes intimately associated with the maternal tissues.
-
Question 28 of 45
28. Question
The technique called Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT) is recommended for those females (NEET 2011)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT) is transfer of an ovum collected from a donor into the Fallopian tube of another female who cannot produce ova but can provide proper environment for fertilization and further development.
-
Question 29 of 45
29. Question
In vitro fertilisation is a technique that involves transfer of which one of the following into the Fallopian tube? (NEET 2010)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : Assisted reproductive technologies (ART) include a number of special techniques which assist infertile couples to have children. An important technique of ART is test tube baby programme. The baby produced by conceiving in a culture dish and nursing in the uterus is called a test tube baby. This method involves in vitro fertilization (IVF), i.e., fertilization of male and female gamete outside the body in almost similar conditions as that in the body followed by embryo transfer (ET). Zygote or embryo upto 8 blastomeres is transferred into the Fallopian tube (ZIFT – Zygote Intra Fallopian Transfer) and mature embryo with more than 8 blastomeres is transferred to uterus to complete its further development.
-
Question 30 of 45
30. Question
The permissible use of the technique amniocentesis is for (NEET 2010)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Amniocentesis is withdrawal of a sample of the fluid (amniotic fluid) surrounding a foetus in the uterus by piercing the amniotic sac through the abdominal wall, under direct ultrasound guidance. As the amniotic fluid contains cells from the foetus, cell cultures enable chromosome patterns to be studied so that prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities can be made. Certain metabolic errors and other abnormalities, such as spina bifida, can also be diagnosed prenatally from analysis of the cells or of the fluid.
As this technique also helps in detection of sex of the unborn foetus, it has been banned in order to legally check increasing female foeticides. -
Question 31 of 45
31. Question
\(\mathrm{Cu}\) ions released from copper-releasing intra uterine devices (IUDs) (NEET 2010)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) Copper releasing IUDs (i.e., CuT, LNG-20) are placed in the uterus of the females. They are an efficient birth control methods. Copper ions released by them suppress motility and fertilising capacity of the sperms.
-
Question 32 of 45
32. Question
Consider the statements given below regarding contraception and answer as directed there after
(1) medical termination of pregnancy (MTP) during first trimester is generally safe
(2) generally chances of conception are nil until mother breast-feeds the infant upto two years
(3) intrauterine devices like copper-T are effective contraceptives
(4) contraception pills may be taken upto one week after coitus to prevent conception.
Which two of the above statements are correct? (NEET 2008)CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Intrauterine devices like copper \(T\) are effective contraceptives for birth control. It suppresses sperm motility and the fertilising capacity of the sperm. Medical termination of pregnancy or induced abortion is voluntary or intentional termination of pregnancy before full term of foetus. It is comparatively safe upto 12 weeks (the first trimester) of pregnancy.
-
Question 33 of 45
33. Question
The formula for exponential population growth is (NEET 2006)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Nearly all populations will tend to grow exponentially as long as there are resources available. The formula for exponential population growth is \(d N /\) \(d t=r N\). In this equation \(d\) is the rate of change, \(N\) is the number of existing individuals, \(r\) is the intrinsicgrowth rate, \(t\) is time, and \(\mathrm{dN} / \mathrm{dt}\) is the rate of change in population size.
-
Question 34 of 45
34. Question
Test tube baby means a baby born when (NEET 2003)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c): By in vitro fertilization, the ovum is fertilized with sperm outside the body of a woman, providing the ovum with the same environmental conditions as it would have got inside the uterus. The zygote is grown inside a culture and when embryo is formed, it is then implanted into uterus where it develops into foetus and then into a child. This is called test tube baby.
Methodology involves the following steps :
– Removal of unfertilised ovum from reproductive tract of a female.
– Ovum is kept under aseptic conditions.
– Fusion of sperm and ovum in a culture medium, outside the female body to form the zygote.
– Zygote is stimulated to develop in vitro upto 32-celled stage.
– Developing embryo is implanted on the endometrium of the uterus at 32 -celled stage. So the pregnancy in the woman starts and further the development of the child continues in the womb till it is born. -
Question 35 of 45
35. Question
Two opposite forces operate in the growth and development of every population. One of them is related to the ability to reproduce at a given rate. The force opposite to it is called (NEET 2003, 1998)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b): The environmental factors which can check the growth of population size constitute the environmental resistance. These include predators, food, water, nesting sites, similar competitors, etc. All living things tend to reproduce until the point at which their environment becomes a limiting factor. No population, human or otherwise, can grow indefinitely; eventually, some biotic or abiotic variable will begin to limit population growth.
-
Question 36 of 45
36. Question
In a population, unrestricted reproductive capacity is called as (NEET 2002)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Biotic potential is defined as the physiological capacity of organisms to produce their offspring under natural conditions. It is also called reproductive potential. In nature, the biotic potential of organisms is enormous but all the organisms do not survive due to the lack of food and space. There are also a number of diseases and the predatory organisms, that feed upon other organisms. The carrying capacity is the maximum number of individuals which the environment can support or sustain.
-
Question 37 of 45
37. Question
What is the work of copper-T? (NEET 2002)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b, c) : Copper-T is an intrauterine device (IUD) used by women as a birth control. An IUD is a small device which is placed inside the uterus. The vertical and horizontal arms of the Copper – T contain copper which is slowly released into the uterine cavity. Copper stops sperm from making their way upthrough the uterus into the tubes, and it reduces the ability of sperm to fertilize the egg. It also prevents a fertilized egg (blastocyst) from successfully implanting in the lining of the uterus if fertilization has occurred.
-
Question 38 of 45
38. Question
What is the work of progesterone which is present in oral contraceptive pills? (NEET 2000)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : Pills also called contraceptive pills contain small doses of either progestogens or progestogenoestrogen combinations. They inhibit ovulation and implantation.
-
Question 39 of 45
39. Question
Tablets to prevent male contraception contain (AIPMT 1999)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(d) : Male contraceptives work by interfering with sperm production or delivery, that means they inhibit the spermatogenesis as well as the function of male sex hormone testosterone.
\(\mathrm{LH}\) and FSH (both called gonadotropic hormone are secreted from anterior pituitary) have specific functions in the testis. FSH stimulates male germ cells for spermatogenesis and \(\mathrm{LH}\) stimulates accessory cells, called Leydig cells to produce sex steroids, especially testosterone. Thus, these two hormones (FSH and \(\mathrm{LH}\) ) prevent male contraception. -
Question 40 of 45
40. Question
The most important component of the oral contraceptive pills is (AIPMT 1998)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : The most common type of pill is the so called “combined pill”. It contains a combination of synthetic progestins (acting like progesterone) and estrogen. Combined pills inhibit ovulation by inhibiting the normal release of FSH and LH from the pituitary. They mimic the hormones produced by the corpus luteum, causing the uterine walls to thicken, as during normal menstrual cycle, and suppressing the release of FSH and \(\mathrm{LH}\).
-
Question 41 of 45
41. Question
The present population of the world is about (AIPMT 1997)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) : As this question appeared in 1997 , so the population of world in mid 1997 was 5, 840, 324, 240 i.e., approximately 6 billion.
-
Question 42 of 45
42. Question
Foetal sex can be determined by examining cells from the amniotic fluid by looking for (AIPMT 1997)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(c) : Barr body is a structure consisting of a condensed \(\mathrm{X}\) chromosome that is found in nondividing nuclei of female mammals. Amniotic fluid contains foetal skin cells, that are stained to determine the presence of sex chromatin (barr body). The presence of barr body indicates that the developing foetus is female with two X-chromosome.
-
Question 43 of 45
43. Question
The test tube baby means (AIPMT 1996)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(b) :
-
Question 44 of 45
44. Question
In India, human population is heavily weighed towards the younger age groups as a result of (AIPMT 1995)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a) : A population having mostly younger age group means its birth rate is high. If death rate is increased then the proportion of old age group will be increased. But in this case death rate has increasing trend thence in a human population which is heavily weighted towards the younger age groups, there will be short life span and high birth rate.
-
Question 45 of 45
45. Question
Which of the following statements is correct with reference to a test tube baby? (AIPMT 1994)
CorrectIncorrectHint
(a):