1.2 Pre-fertilisation: Structures and Events
Much before the actual flower is seen on a plant, the decision that the plant is going to flower has taken place. Several hormonal and structural changes are initiated which lead to the differentiation and further development of the floral primordium. Inflorescences are formed which bear the floral buds and then the flowers. In the flower the male and female reproductive structures, the androecium and the gynoecium differentiate and develop. You would recollect that the androecium consists of a whorl of stamens representing the male reproductive organ and the gynoecium represents the female reproductive organ.
Stamen, Microsporangium and Pollen Grain
Figure 1.2 a shows the two parts of a typical stamen – the long and slender stalk called the filament, and the terminal generally bilobed structure called the anther. The proximal end of the filament is attached to the thalamus or the petal of the flower. The number and length of stamens are variable in flowers of different species. If you were to collect a stamen each from ten flowers (each from different species) and arrange them on a slide, you would be able to appreciate the large variation in size seen in nature. Careful observation of each stamen under a dissecting microscope and making neat diagrams would elucidate the range in shape and attachment of anthers in different flowers.
A typical angiosperm anther is bilobed with each lobe having two theca, i.e., they are dithecous (Figure 1.2b). Often a longitudinal groove runs lengthwise separating the theca.
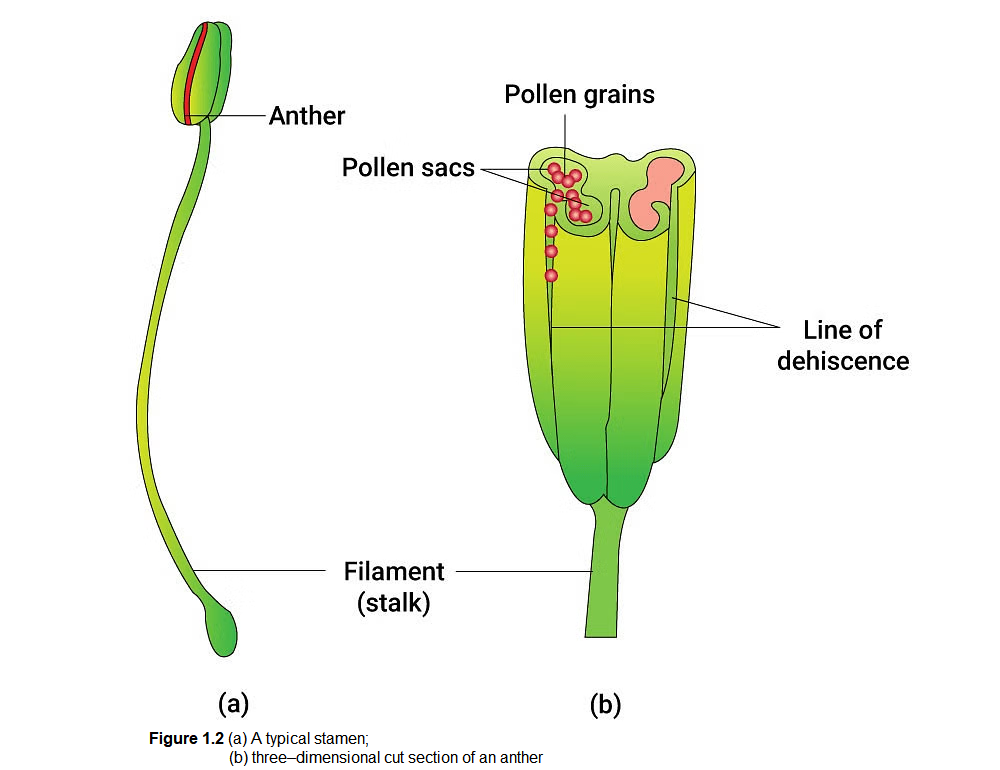
Let us understand the various types of tissues and their organisation in the transverse section of an anther (Figure 1.3a). The bilobed nature of an anther is very distinct in the transverse section of the anther. The anther is a four-sided (tetragonal) structure consisting of four microsporangia located at the corners, two in each lobe.
The microsporangia develop further and become pollen sacs. They extend longitudinally all through the length of an anther and are packed with pollen grains.
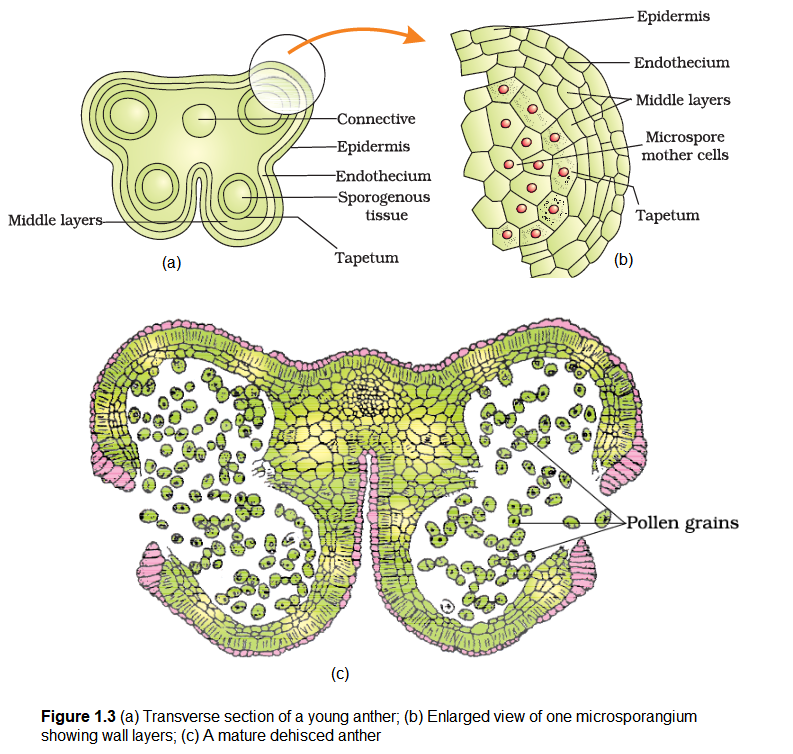
Structure of microsporangium: In a transverse section, a typical microsporangium appears near circular in outline. It is generally surrounded by four wall layers (Figure 1.3b)- the epidermis, endothecium, middle layers and the tapetum. The outer three wall layers perform the function of protection and help in dehiscence of anther to release the pollen. The innermost wall layer is the tapetum. It nourishes the developing pollen grains. Cells of the tapetum possess dense cytoplasm and generally have more than one nucleus. Can you think of how tapetal cells could become bi-nucleate?
When the anther is young, a group of compactly arranged homogenous cells called the sporogenous tissue occupies the centre of each microsporangium.
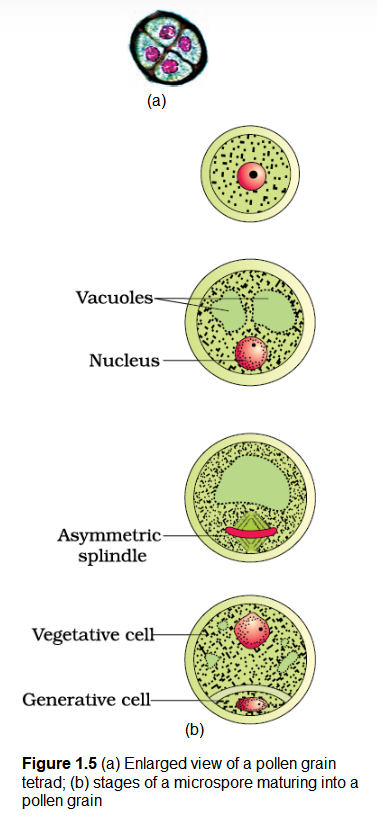
Microsporogenesis: As the anther develops, the cells of the sporogenous tissue undergo meiotic divisions to form microspore tetrads. What would be the ploidy of the cells of the tetrad?
As each cell of the sporogenous tissue is capable of giving rise to a microspore tetrad. Each one is a potential pollen or microspore mother cell. The process of formation of microspores from a pollen mother cell (PMC) through meiosis is called microsporogenesis. The microspores, as they are formed, are arranged in a cluster of four cells-the microspore tetrad (Figure 1.3a). As the anthers mature and dehydrate, the microspores dissociate from each other and develop into pollen grains (Figure 1.3 b). Inside each microsporangium several thousands of microspores or pollen grains are formed that are released with the dehiscence of anther (Figure 1.3c).
Pollen grain: The pollen grains represent the male gametophytes. If you touch the opened anthers of Hibiscus or any other flower you would find deposition of yellowish powdery pollen grains on your fingers. Sprinkle these grains on a drop of water taken on a glass slide and observe under a microscope. You will really be amazed at the variety of architecture sizes, shapes, colours, designs – seen on the pollen grains from different species (Figure 1.4).

Pollen grains are generally spherical measuring about 25-50 micrometers in diameter. It has a prominent two-layered wall. The hard outer layer called the exine is made up of sporopollenin which is one of the most resistant organic material known. It can withstand high temperatures and strong acids and alkali. No enzyme that degrades sporopollenin is so far known. Pollen grain exine has prominent apertures called germ pores where sporopollenin is absent. Pollen grains are well preserved as fossils because of the presence of sporopollenin. The exine exhibits a fascinating array of patterns and designs. Why do you think the exine should be hard? What is the function of germ pore? The inner wall of the pollen grain is called the intine. It is a thin and continuous layer made up of cellulose and pectin. The cytoplasm of pollen grain is surrounded by a plasma membrane. When the pollen grain is mature it contains two cells, the vegetative cell and generative cell (Figure 1.5b). The vegetative cell is bigger, has abundant food reserve and a large irregularly shaped nucleus. The generative cell is small and floats in the cytoplasm of the vegetative cell. It is spindle shaped with dense cytoplasm and a nucleus. In over 60 per cent of angiosperms, pollen grains are shed at this 2-celled stage. In the remaining species, the generative cell divides mitotically to give rise to the two male gametes before pollen grains are shed (3-celled stage).
Pollen grains of many species cause severe allergies and bronchial afflictions in some people often leading to chronic respiratory disorders- asthma, bronchitis, etc. It may be mentioned that Parthenium or carrot grass that came into India as a contaminant with imported wheat, has become ubiquitous in occurrence and causes pollen allergy.
Pollen grains are rich in nutrients. It has become a fashion in recent years to use pollen tablets as food supplements. In western countries, a large number of pollen products in the form of tablets and syrups are available in the market. Pollen consumption has been claimed to increase the performance of athletes and race horses (Figure 1.6).

When once they are shed, pollen grains have to land on the stigma before they lose viability if they have to bring about fertilisation. How long do you think the pollen grains retain viability? The period for which pollen grains remain viable is highly variable and to some extent depends on the prevailing temperature and humidity. In some cereals such as rice and wheat, pollen grains lose viability within 30 minutes of their release, and in some members of Rosaceae, Leguminoseae and Solanaceae, they maintain viability for months. You may have heard of storing semen/ sperms of many animals including humans for artificial insemination. It is possible to store pollen grains of a large number of species for years in liquid nitrogen \(\left(-196^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\right)\). Such stored pollen can be used as pollen banks, similar to seed banks, in crop breeding programmes.
The Pistil, Megasporangium (ovule) and Embryo sac
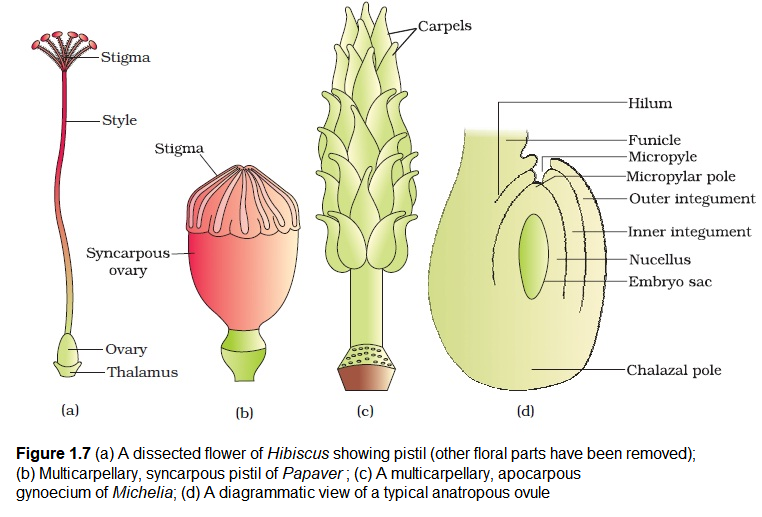
The gynoecium represents the female reproductive part of the flower. The gynoecium may consist of a single pistil (monocarpellary) or may have more than one pistil (multicarpellary). When there are more than one, the pistils may be fused together (syncarpous) (Figure 1.7b) or may be free (apocarpous) (Figure 1.7c). Each pistil has three parts (Figure 1.7a), the stigma, style and ovary. The stigma serves as a landing platform for pollen grains. The style is the elongated slender part beneath the stigma. The basal bulged part of the pistil is the ovary. Inside the ovary is the ovarian cavity (locule). The placenta is located inside the ovarian cavity. Recall the definition and types of placentation that you studied in Class XI. Arising from the placenta are the megasporangia, commonly called ovules. The number of ovules in an ovary may be one (wheat, paddy, mango) to many (papaya, water melon, orchids).
The Megasporangium (Ovule) : Let us familiarise ourselves with the structure of a typical angiosperm ovule (Figure 1.7 d ). The ovule is a small structure attached to the placenta by means of a stalk called funicle. The body of the ovule fuses with funicle in the region called hilum. Thus, hilum represents the junction between ovule and funicle. Each ovule has one or two protective envelopes called integuments. Integuments encircle the nucellus except at the tip where a small opening called the micropyle is organised. Opposite the micropylar end, is the chalaza, representing the basal part of the ovule.
Enclosed within the integuments is a mass of cells called the nucellus. Cells of the nucellus have abundant reserve food materials. Located in the nucellus is the embryo sac or female gametophyte. An ovule generally has a single embryo sac formed from a megaspore.
Megasporogenesis: The process of formation of megaspores from the megaspore mother cell is called megasporogenesis. Ovules generally differentiate a single megaspore mother cell (MMC) in the micropylar region of the nucellus. It is a large cell containing dense cytoplasm and a prominent nucleus. The MMC undergoes meiotic division. What is the importance of the MMC undergoing meiosis? Meiosis results in the production of four megaspores (Figure 1.8a).
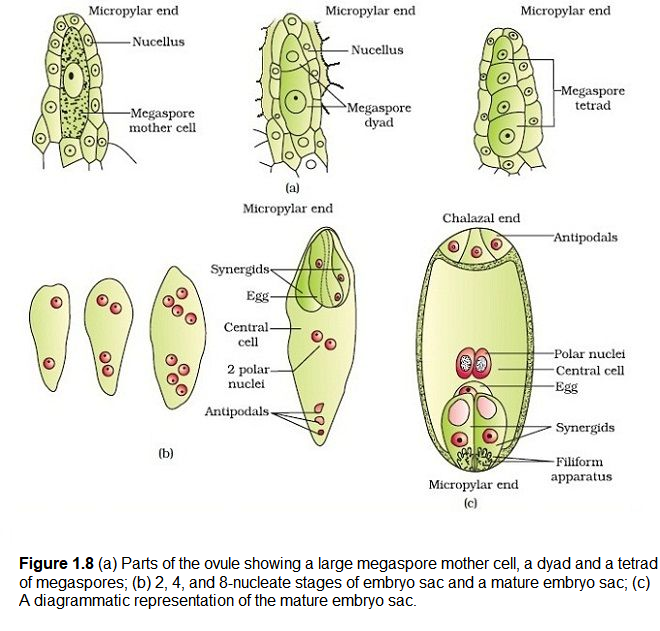
Female gametophyte : In a majority of flowering plants, one of the megaspores is functional while the other three degenerate. Only the functional megaspore develops into the female gametophyte (embryo sac). This method of embryo sac formation from a single megaspore is termed monosporic development. What will be the ploidy of the cells of the nucellus, MMC, the functional megaspore and female gametophyte?
Let us study about the formation of the embryo sac in detail. (Figure 1.8b). The nucleus of the functional megaspore divides mitotically to form two nuclei which move to the opposite poles, forming the \(\mathbf{2 -}\) nucleate embryo sac. Two more sequential mitotic nuclear divisions result in the formation of the 4 -nucleate and later the 8 -nucleate stages of the embryo sac. It is of interest to note that these mitotic divisions are strictly free nuclear, that is, nuclear divisions are not followed immediately by cell wall formation. After the 8-nucleate stage, cell walls are laid down leading to the organisation of the typical female gametophyte or embryo sac. Observe the distribution of cells inside the embryo sac (Figure \(1.8 \mathrm{~b}, \mathrm{c}\) ). Six of the eight nuclei are surrounded by cell walls and organised into cells; the remaining two nuclei, called polar nuclei are situated below the egg apparatus in the large central cell.
There is a characteristic distribution of the cells within the embryo sac. Three cells are grouped together at the micropylar end and constitute the egg apparatus. The egg apparatus, in turn, consists of two synergids and one egg cell. The synergids have special cellular thickenings at the micropylar tip called filiform apparatus, which play an important role in guiding the pollen tubes into the synergid. Three cells are at the chalazal end and are called the antipodals. The large central cell, as mentioned earlier, has two polar nuclei. Thus, a typical angiosperm embryo sac, at maturity, though 8-nucleate is 7-celled.
Pollination
In the preceding sections you have learnt that the male and female gametes in flowering plants are produced in the pollen grain and embryo sac, respectively. As both types of gametes are non-motile, they have to be brought together for fertilisation to occur. How is this achieved?
Pollination is the mechanism to achieve this objective. Transfer of pollen grains (shed from the anther) to the stigma of a pistil is termed pollination. Flowering plants have evolved an amazing array of adaptations to achieve pollination. They make use of external agents to achieve pollination. Can you list the possible external agents?
Kinds of Pollination : Depending on the source of pollen, pollination can be divided into three types.
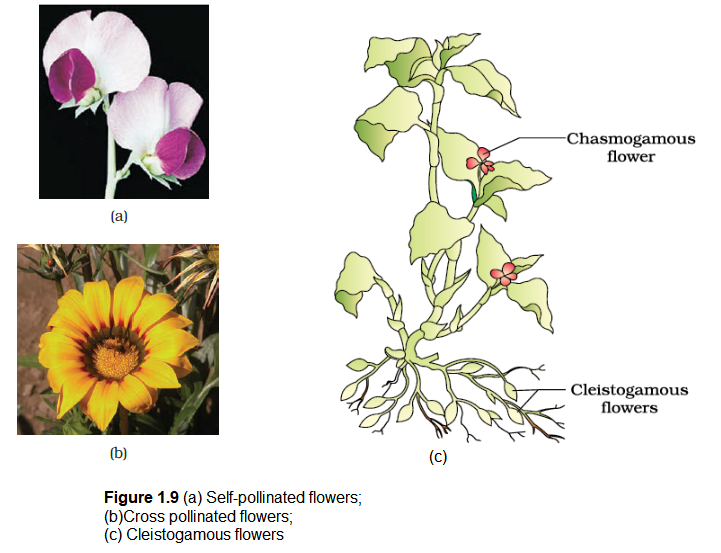
- (i) Autogamy : In this type, pollination is achieved within the same flower. Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of the same flower (Figure 1.9a). In a normal flower which opens and exposes the anthers and the stigma, complete autogamy is rather rare. Autogamy in such flowers requires synchrony in pollen release and stigma receptivity and also, the anthers and the stigma should lie close to each other so that self-pollination can occur. Some plants such as Viola (common pansy), Oxalis, and Commelina produce two types of flowers chasmogamous flowers which are similar to flowers of other species with exposed anthers and stigma, and cleistogamous flowers which do not open at all (Figure 1.9c). In such flowers, the anthers and stigma lie close to each other. When anthers dehisce in the flower buds, pollen grains come in contact with the stigma to effect pollination. Thus, cleistogamous flowers are invariably autogamous as there is no chance of cross-pollen landing on the stigma. Cleistogamous flowers produce assured seed-set even in the absence of pollinators. Do you think that cleistogamy is advantageous or disadvantageous to the plant? Why?
- (ii) Geitonogamy: Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of another flower of the same plant. Although geitonogamy is functionally cross-pollination involving a pollinating agent, genetically it is similar to autogamy since the pollen grains come from the same plant.
- (iii) Xenogamy: Transfer of pollen grains from anther to the stigma of a different plant (Figure 1.9 b). This is the only type of pollination which during pollination brings genetically different types of pollen grains to the stigma.
Agents of Pollination : Plants use two abiotic (wind and water) and one biotic (animals) agents to achieve pollination. Majority of plants use biotic agents for pollination. Only a small proportion of plants use abiotic agents. Pollen grains coming in contact with the stigma is a chance factor in both wind and water pollination. To compensate for this uncertainties and associated loss of pollen grains, the flowers produce enormous amount of pollen when compared to the number of ovules available for pollination.
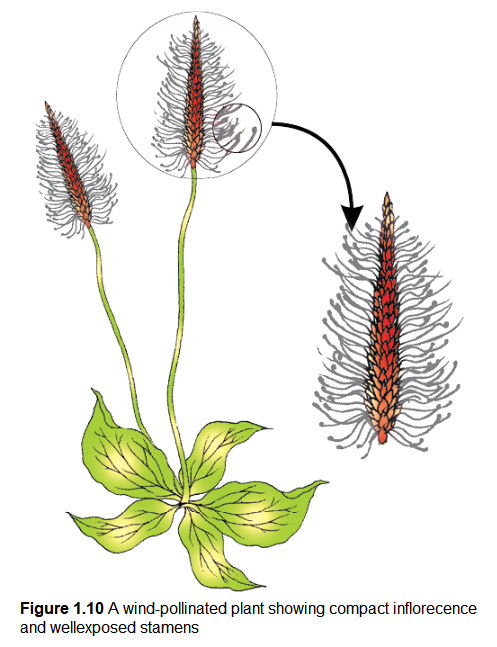
Pollination by wind is more common amongst abiotic pollinations. Wind pollination also requires that the pollen grains are light and non-sticky so that they can be transported in wind currents. They often possess well-exposed stamens (so that the pollens are easily dispersed into wind currents, Figure 1.10) and large often-feathery stigma to easily trap air-borne pollen grains. Wind-pollinated flowers often have a single ovule in each ovary and numerous flowers packed into an inflorescence; a familiar example is the corn cob – the tassels you see are nothing but the stigma and style which wave in the wind to trap pollen grains. Wind-pollination is quite common in grasses.
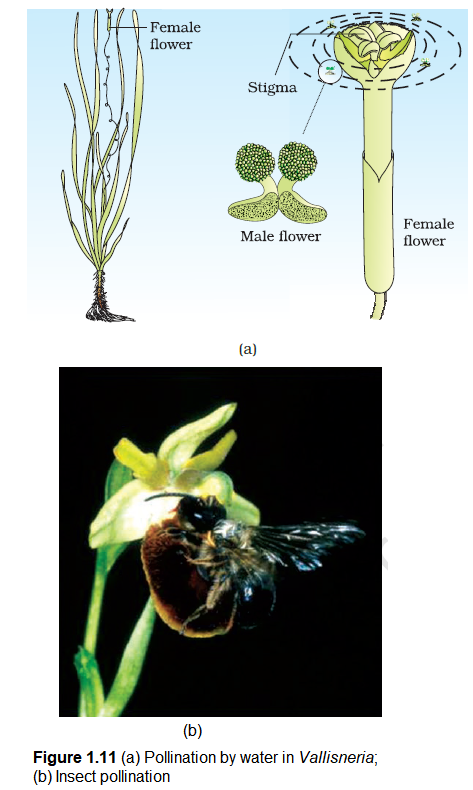
Pollination by water is quite rare in flowering plants and is limited to about 30 genera, mostly monocotyledons. As against this, you would recall that water is a regular mode of transport for the male gametes among the lower plant groups such as algae, bryophytes and pteridophytes. It is believed, particularly for some bryophytes and pteridophytes, that their distribution is limited because of the need for water for the transport of male gametes and fertilisation. Some examples of water pollinated plants are Vallisneria and Hydrilla which grow in fresh water and several marine sea-grasses such as Zostera. Not all aquatic plants use water for pollination. In a majority of aquatic plants such as water hyacinth and water lily, the flowers emerge above the level of water and are pollinated by insects or wind as in most of the land plants. In Vallisneria, the female flower reach the surface of water by the long stalk and the male flowers or pollen grains are released on to the surface of water. They are carried passively by water currents (Figure 1.11a); some of them eventually reach the female flowers and the stigma. In another group of water pollinated plants such as seagrasses, female flowers remain submerged in water and the pollen grains are released inside the water. Pollen grains in many such species are long, ribbon like and they are carried passively inside the water; some of them reach the stigma and achieve pollination. In most of the water-pollinated species, pollen grains are protected from wetting by a mucilaginous covering.
Both wind and water pollinated flowers are not very colourful and do not produce nectar. What would be the reason for this?
Majority of flowering plants use a range of animals as pollinating agents. Bees, butterflies, flies, beetles, wasps, ants, moths, birds (sunbirds and humming birds) and bats are the common pollinating agents. (Figure 1.11b). Among the animals, insects, particularly bees are the dominant biotic pollinating agents. Even larger animals such as some primates (lemurs), arboreal (tree-dwelling) rodents, or even reptiles (gecko lizard and garden lizard) have also been reported as pollinators in some species.
Often flowers of animal-pollinated plants are specifically adapted for a particular species of animal.
Majority of insect-pollinated flowers are large, colourful, fragrant and rich in nectar. When the flowers are small, a number of flowers are clustered into an inflorescence to make them conspicuous. Animals are attracted to flowers by colour and/or fragrance. The flowers pollinated by flies and beetles secrete foul odours to attract these animals. To sustain animal visits, the flowers have to provide rewards to the animals. Nectar and pollen grains are the usual floral rewards. For harvesting the reward(s) from the flower the animal visitor comes in contact with the anthers and the stigma. The body of the animal gets a coating of pollen grains, which are generally sticky in animal pollinated flowers. When the animal carrying pollen on its body comes in contact with the stigma, it brings about pollination.
In some species floral rewards are in providing safe places to lay eggs; an example is that of the tallest flower of Amorphophallus (the flower itself is about 6 feet in height). A similar relationship exists between a species of moth and the plant Yucca where both species – moth and the plant – cannot complete their life cycles without each other. The moth deposits its eggs in the locule of the ovary and the flower, in turn, gets pollinated by the moth. The larvae of the moth come out of the eggs as the seeds start developing.
Why don’t you observe some flowers of the following plants (or any others available to you): Cucumber, Mango, Peepal, Coriander, Papaya, Onion, Lobia, Cotton, Tobacco, Rose, Lemon, Eucalyptus, Banana? Try to find out which animals visit them and whether they could be pollinators. You’ll have to patiently observe the flowers over a few days and at different times of the day. You could also try to see whether there is any correlation in the characteristics of a flower to the animal that visits it. Carefully observe if any of the visitors come in contact with the anthers and the stigma as only such visitors can bring about pollination. Many insects may consume pollen or the nectar without bringing about pollination. Such floral visitors are referred to as pollen/nectar robbers. You may or may not be able to identify the pollinators, but you will surely enjoy your efforts!
Outbreeding Devices: Majority of flowering plants produce hermaphrodite flowers and pollen grains are likely to come in contact with the stigma of the same flower. Continued self-pollination result in inbreeding depression. Flowering plants have developed many devices to discourage selfpollination and to encourage cross-pollination. In some species, pollen release and stigma receptivity are not synchronised. Either the pollen is released before the stigma becomes receptive or stigma becomes receptive much before the release of pollen. In some other species, the anther and stigma are placed at different positions so that the pollen cannot come in contact with the stigma of the same flower. Both these devices prevent autogamy. The third device to prevent inbreeding is self-incompatibility. This is a genetic mechanism and prevents self-pollen (from the same flower or other flowers of the same plant) from fertilising the ovules by inhibiting pollen germination or pollen tube growth in the pistil. Another device to prevent self-pollination is the production of unisexual flowers. If both male and female flowers are present on the same plant such as castor and maize (monoecious), it prevents autogamy but not geitonogamy. In several species such as papaya, male and female flowers are present on different plants, that is each plant is either male or female (dioecy). This condition prevents both autogamy and geitonogamy.
Pollen-pistil Interaction : Pollination does not guarantee the transfer of the right type of pollen (compatible pollen of the same species as the stigma). Often, pollen of the wrong type, either from other species or from the same plant (if it is self-incompatible), also land on the stigma. The pistil has the ability to recognise the pollen, whether it is of the right type (compatible) or of the wrong type (incompatible). If it is of the right type, the pistil accepts the pollen and promotes post-pollination events that leads to fertilisation. If the pollen is of the wrong type, the pistil rejects the pollen by preventing pollen germination on the stigma or the pollen tube growth in the style. The ability of the pistil to recognise the pollen followed by its acceptance or rejection is the result of a continuous dialogue between pollen grain and the pistil. This dialogue is mediated by chemical components of the pollen interacting with those of the pistil. It is only in recent years that botanists have been able to identify some of the pollen and pistil components and the interactions leading to the recognition, followed by acceptance or rejection.
As mentioned earlier, following compatible pollination, the pollen grain germinates on the stigma to produce a pollen tube through one of the germ pores (Figure 1.12a). The contents of the pollen grain move into the pollen tube. Pollen tube grows through the tissues of the stigma and style and reaches the ovary (Figure 1.12b, c). You would recall that in some plants, pollen grains are shed at two-celled condition (a vegetative cell and a generative cell). In such plants, the generative cell divides and forms the two male gametes during the growth of pollen tube in the stigma. In plants which shed pollen in the three-celled condition, pollen tubes carry the two male gametes from the beginning. Pollen tube, after reaching the ovary, enters the ovule through the micropyle and then enters one of the synergids through the filiform apparatus (Figure 1.12d, e). Many recent studies have shown that filiform apparatus present at the micropylar part of the synergids guides the entry of pollen tube. All these events-from pollen deposition on the stigma until pollen tubes enter the ovule-are together referred to as pollen-pistil interaction. As pointed out earlier, pollen-pistil interaction is a dynamic process involving pollen recognition followed by promotion or inhibition of the pollen. The knowledge gained in this area would help the plant breeder in manipulating pollen-pistil interaction, even in incompatible pollinations, to get desired hybrids.
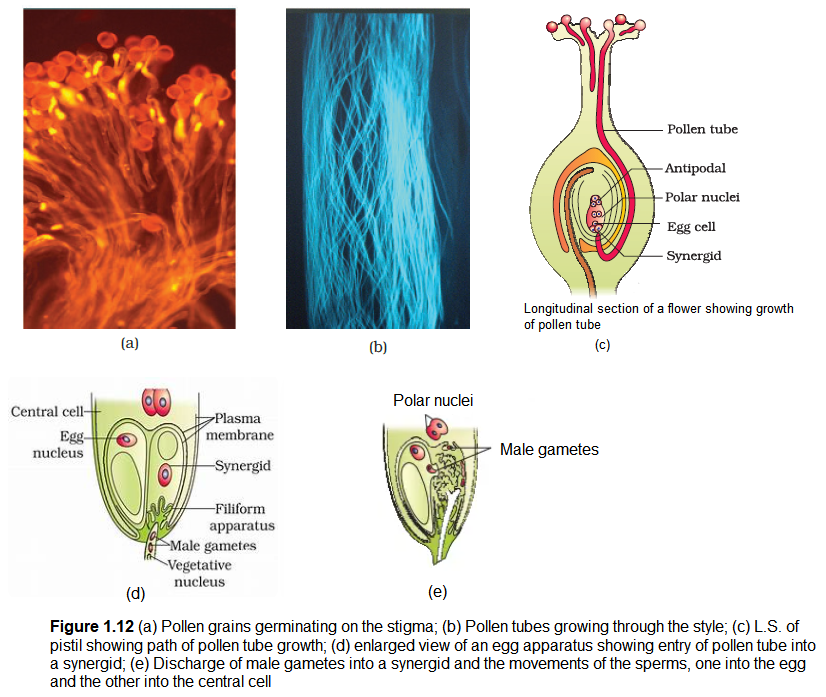
You can easily study pollen germination by dusting some pollen from flowers such as pea, chickpea, Crotalaria, balsam and Vinca on a glass slide containing a drop of sugar solution (about 10 per cent). After about 15-30 minutes, observe the slide under the low power lens of the microscope. You are likely to see pollen tubes coming out of the pollen grains.
A breeder is interested in crossing different species and often genera to combine desirable characters to produce commercially ‘superior’ varieties. Artificial hybridisation is one of the major approaches of crop improvement programme. In such crossing experiments it is important to make sure that only the desired pollen grains are used for pollination and the stigma is protected from contamination (from unwanted pollen). This is achieved by emasculation and bagging techniques.
If the female parent bears bisexual flowers, removal of anthers from the flower bud before the anther dehisces using a pair of forceps is necessary. This step is referred to as emasculation. Emasculated flowers have to be covered with a bag of suitable size, generally made up of butter paper, to prevent contamination of its stigma with unwanted pollen. This process is called bagging. When the stigma of bagged flower attains receptivity, mature pollen grains collected from anthers of the male parent are dusted on the stigma, and the flowers are rebagged, and the fruits allowed to develop.
If the female parent produces unisexual flowers, there is no need for emasculation. The female flower buds are bagged before the flowers open. When the stigma becomes receptive, pollination is carried out using the desired pollen and the flower rebagged.