5.0 Introduction
It is the only physical theory of universal content concerning which I am convinced that, within the framework of the applicability of its basic concepts, it will never be overthrown. – Albert Einstein
Thermodynamics is the study of Heat and Temperature and their interrelation. Thermodynamics is a branch of Physics that explains how thermal energy is changed to other forms of energy and the significance of thermal energy in matter. The behavior of heat, work, and temperature, along with their relations to energy and entropy are governed by the Four Laws of Thermodynamics.
What is Thermodynamics?
The term “thermodynamics” is made of two terms, “thermo” and “dynamics” where the term “thermo” refers to heat, and the term “dynamics” refers to a mechanical motion that requires “work.” So the field of physics that studies the relationship between heat and other types of energy is called thermodynamics.
Thermodynamics Definition
Thermodynamics is a branch of Physics that deals with the concept of energy, heat and temperature and their interrelation with radiation, energy and physical characteristics of matter.
To be specific, it explains how thermal energy is converted to or from other forms of energy and how matter is affected by this process. Thermal energy is the energy that comes from heat. This heat is generated by the movement of tiny particles within an object, and the faster these particles move, the more heat is generated.
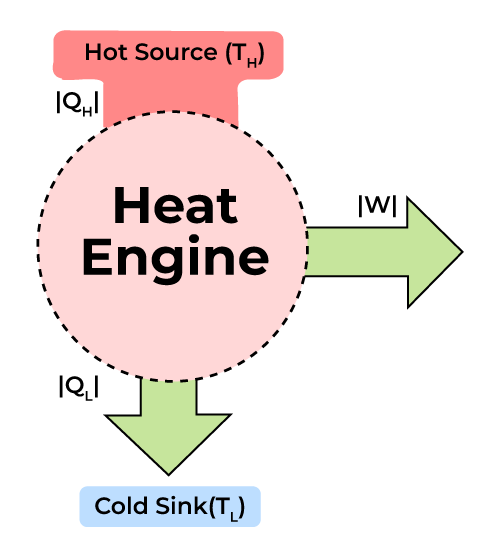
The laws of thermodynamics deal with energy changes of macroscopic systems involving a large number of molecules rather than microscopic systems containing a few molecules. Thermodynamics is not concerned about how and at what rate these energy transformations are carried out, but is based on the initial and final states of a system undergoing the change.
Laws of thermodynamics apply only when a system is in equilibrium or moves from one equilibrium state to another equilibrium state. Macroscopic properties like pressure and temperature do not change with time for a system in equilibrium state.
Distinction Between Mechanics and Thermodynamics
The distinction between mechanics and thermodynamics is worth noting. In mechanics, we solely concentrate on the motion of particles or bodies under the action of forces and torques. On the other hand, thermodynamics is not concerned with the motion of the system as a whole. It is only concerned with the internal macroscopic state of the body.
Different Branches of Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is classified into the following four branches:
- Classical Thermodynamics: In classical thermodynamics, the behaviour of matter is analysed with a macroscopic approach. Units such as temperature and pressure are taken into consideration, which helps the individuals calculate other properties and predict the characteristics of the matter undergoing the process.
- Statistical Thermodynamics: In statistical thermodynamics, every molecule is under the spotlight, i.e. the properties of every molecule and how they interact are taken into consideration to characterise the behaviour of a group of molecules.
- Chemical Thermodynamics: Chemical thermodynamics is the study of how work and heat relate to each other in chemical reactions and in changes of states.
- Equilibrium Thermodynamics: Equilibrium thermodynamics is the study of transformations of energy and matter as they approach the state of equilibrium.